Abstract
Background The outcome of lower-risk MDS patients with red blood cell transfusions (RBCT) dependency is inferior to that of RBCT independent patients, but whether the intensity of RBCT is important for prognosis is unknown. The EUMDS Registry is a non-interventional, observational longitudinal study enrolling patients with lower-risk MDS from 142 sites in 17 countries as described elsewhere (1). The EUMDS registry has accrued 1,902 patients as of July 21, 2015. We hypothesized that RBCT intensity is an independent prognostic factor for survival.
Methods We first assessed the impact of RBCT intensity in the first year post-diagnosis (1yrPD) on progression-free survival among the 1034 patients who survived at least 1yrPD and had potential for a further year of follow-up. Secondly, we developed a longitudinal model of platelet counts throughout follow-up for 1660 patients in the registry with potential for at least one year follow-up.
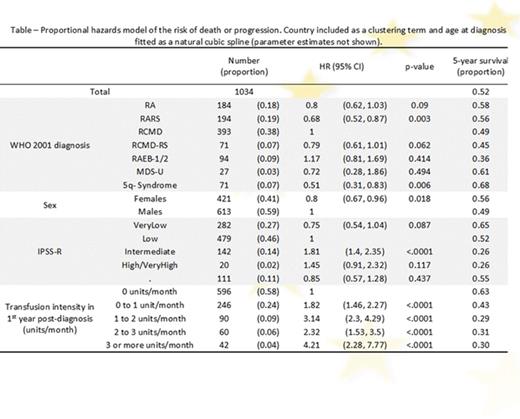
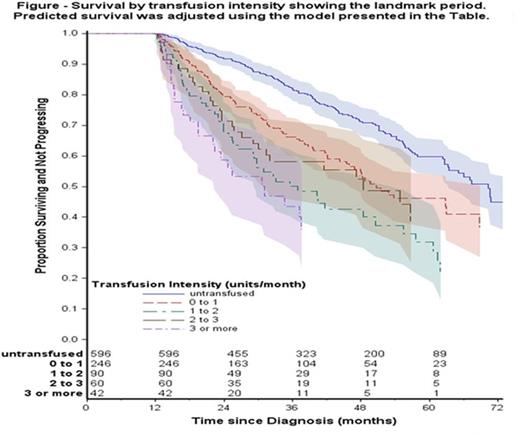
Results Among the 1034 patients, 323 patients had died: 67 after progression to higher-risk MDS/AML and 256 without progression. A further 41 surviving patients had progressed to AML. The overall 5-year survival was 52%. In a proportional hazards regression model (Table), the risk of death or progression increased in a non-linear fashion with age at diagnosis (p<0.001). The risk of death was increased in the intermediate IPSS-R risk group compared to low risk. Patients with RARS and 5q- syndrome had a better outcome compared to RCMD. Increased RBCT intensity in 1yrPD (Table, Figure) was strongly associated with an increased risk of death (p<0.001).
In the 1660 patients no significant decline in platelet counts was observed (0.16x109 platelets/l average monthly decline, p=0.16) among patients who were not RBC transfused at any time during follow-up. However platelet counts of patients receiving RBCT declined more quickly (p<0.0001) at an average rate of 1.14x109 platelets/l/month. Among the 920 RBCT dependent patients, lower platelet counts were associated with receiving more RBCT units in the preceding six months. 185 Patients had at least 2 observations both before and after becoming RBCT dependent, defined as 1st RBCT. 50% of these patients had a decreasing trend of platelets prior to their 1st RBCT and 67% had a decreasing slope of platelets after their 1st RBCT. In the control group of RBC untransfused patients, decreasing slopes of platelets occurred in around 50% of the patients throughout the whole observation period of 4 visits. Logistic regression of the risk of having a post-1st RBCT decreasing trend in platelets showed that transfused patients were at a greater risk (OR=1.7, 95% CI: 1.1-2.7) of having a post-1st RBCT decreasing trend in platelets than untransfused patients.
Conclusion These multivariate regression models including age, sex, country, IPSS and WHO classification showed that more intensive RBCT treatment is associated with poor prognosis and a more rapid decline of platelets. This indicates that the intensity of RBCT should be incorporated in the regular prognostic scoring systems and the choice of therapeutic interventions.
(1): De Swart L et al. Br J Haematol 2015; 170: 372-83.
Fenaux:NOVARTIS: Honoraria, Research Funding; CELGENE: Honoraria, Research Funding; JANSSEN: Honoraria, Research Funding; AMGEN: Honoraria, Research Funding. Hellström-Lindberg:Celgene Corporation: Research Funding. Sanz:JANSSEN CILAG: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Mittelman:Roche: Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Research Funding; Johnson & Johnson: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Research Funding. Almeida:Bristol Meyer Squibb: Speakers Bureau; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Park:Hospira: Research Funding; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Itzykson:Oncoethix: Research Funding. de Witte:Novartis: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.