Abstract
Background. The fusion protein encoded by the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene may differ in size, but the great majority of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients have a e13a2 (b2a2) or a e14a2 (b3a2) junction. In CML patients treated frontline with imatinib, the e14a2 transcript has been recently associated to faster and deeper molecular responses; in some studies a better outcome has been also reported. Very limited information on the prognostic impact of the BCR-ABL1 transcript type in CML patients treated frontline with second generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) is still available: a study from MDACC reported lower molecular response rates and a trend for inferior event-free survival in e13a2 patients.
Aim. To evaluate if the BCR-ABL1 transcript type (e14a2 vs e13a2) affect the response and the clinical outcome in newly diagnosed adult CML patients treated frontline with nilotinib (NIL).
Methods. An analysis of 345 CML patients in early chronic phase (ECP) enrolled within 3 multicentric prospective studies of the GIMEMA CML Working Party (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00481052, NCT00769327, NCT01535391) was performed. The initial treatment was NIL 300 mg BID or NIL 400 mg BID. Definitions: major molecular response (MMR), BCR-ABL1IS ratio < 0.1%; deep molecular response (MR4.0), BCR-ABL1IS ratio < 0.01% with > 10,000 ABL1 copies; progression, transformation to advanced phases; death, at any time and for any reason. Cumulative incidences of response were estimated under consideration of competing risks (progression, death) and compared by Gray test. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by log-rank test.
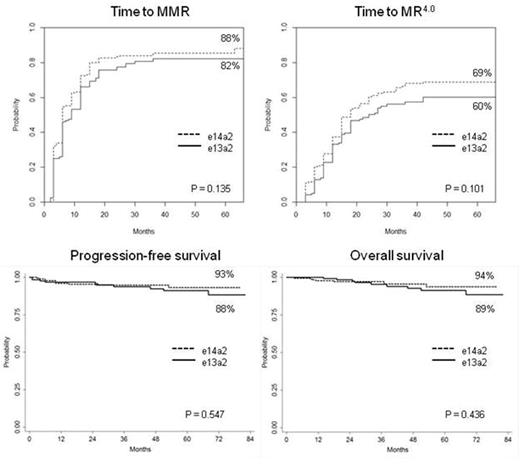
Results. Seven patients expressing rare transcripts (e1a2 or e19a2) and 10 patients with unknown transcript type were excluded: 328 out of 345 patients were evaluable, 124 (38%) with e13a2 transcript, 174 (53%) with e14a2 transcript and 30 (9%) expressing both transcripts. The baseline characteristics of patients with e13a2 or e14a2 transcripts were comparable: no significant differences in age, gender, Sokal or EUTOS long-term survival score distribution, presence of clonal chromosomal abnormalities in Ph+ cells, NIL dose were observed; the only difference was a higher platelet count in patients with e14a2 transcript (median 374 vs 313 x 103/µl, p=0.006). The median follow-up was 60 months in both groups (range 24-82 months). The response rates and the survival probabilities were uniformly lower in patients with e13a2 transcript (N=124) compared to patients with e14a2 transcript (N=174), but the differences were not significant: MMR by 12 months, 66% vs 72%, p=0.244; MR4.0 by 36 months, 56% vs 66%, p=0.067; estimated cumulative incidence of MMR, 82% vs 88%, p=0.135; estimated cumulative incidence of MR4.0, 60% vs 69%, p=0.101; estimated PFS, 88% vs 93%, p=0.547; estimated OS, 89% vs 94%, p=0.436 (Figure 1). The responses and the survival probabilities of patients co-expressing the e13a2 and the e14a2 transcripts (N=30) were similar to or even better than the ones of e14a2 patients. Grouping together the patients with e14a2 transcript alone and the patients with co-expression of both transcripts (N=174+30=204), and comparing them to patients with e13a2 transcript alone (N=124), the response differences became significant (cumulative incidence of MMR and MR4.0, p=0.050 and p=0.036, respectively), but no outcome differences emerged (PFS and OS, p=0.340 and p=0.276, respectively).
Conclusions. Despite a trend for lower response rates and inferior outcome in patients with e13a2 transcript, the observed differences were small and mostly not significant. Further studies in larger patient cohorts are required to clarify whether nilotinib and other second generation TKIs are able to overcome the adverse prognostic impact of transcript type, potentially affecting the speed and the depth of molecular response, the probability of achieving a treatment-free remission and the patient outcome.
Castagnetti:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; ARIAD Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Gugliotta:Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Breccia:Ariad: Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Carella:Millenium: Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Speakers Bureau. Tiribelli:Ariad Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Bocchia:Janssen: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria. Soverini:Ariad: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Cavo:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Millennium: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen-Cilag: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria. Martinelli:ARIAD: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; MSD: Consultancy; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; BMS: Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; ARIAD: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; MSD: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy. Rosti:Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.