Abstract
Background: Hydroxyurea is the primary disease modifying therapy for patients with sickle cell anemia (SCA). The clinical and laboratory benefits of hydroxyurea are the greatest when escalated to the maximum tolerated dose (MTD). The process of dose escalation to MTD requires expertise and can be tedious, often taking 6-12 months to titrate to the optimal dose. In addition, due in part to inter-patient variability in hydroxyurea pharmacokinetics (PK), the MTD varies among patients with a range of 15-35 mg/kg/day. We utilized a population PK model in combination with Bayesian estimation and a sparse sampling strategy, to individualize dosing of children starting hydroxyurea treatment.
Methods: The Therapeutic Response Evaluation and Adherence Trial (TREAT, ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02286154) is a prospective study of hydroxyurea for children with SCA. The primary objective is to develop and evaluate a population PK-based model to predict hydroxyurea MTD through an individualized dosing strategy. A sparse sampling approach was developed to allow practical sampling from young children with SCA. The sampling strategy includes administering a single oral 20 mg/kg dose followed by collection of small quantities of blood (~100uL) at three post-dosing time points (15-20 minutes, 50-60 minutes, and ~3 hours). Baseline labs (including liver and renal function) are typically collected by venipuncture, while the other two samples are drawn by fingerstick or heelstick. Plasma hydroxyurea concentrations are measured using HPLC using an internal standard of methylurea. Using the population PK model with Bayesian estimation and hydroxyurea concentrations measured at the three specified time points, hydroxyurea exposure is estimated using specialized therapeutic drug monitoring software (MWPharm, Mediware, Prague, Czech Republic). Using the area under the curve (AUC0-inf) estimated by the model, we calculate a starting dose that is predicted to achieve an AUC of 115 ug*h/mL, which was the mean AUC value at MTD for a large cohort of children from a previous study (Dong M et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2016). The primary objective is to select a starting dose that is close to actual MTD, to reduce the time to maximum therapeutic effect and need for dose modifications before achieving MTD.
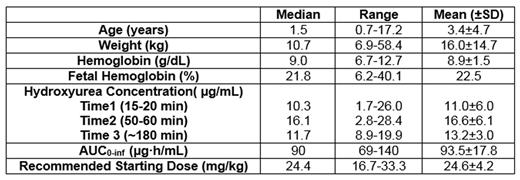
Results: From December 2014 through June 2016, 20 children taking taking hydroxyurea for the first time were enrolled in TREAT. Seventeen of the 20 participants had all 3 post-treatment PK samples collected and processed to allow calculation of an individualized PK-based dose, while 3 had difficulties in sampling or processing that prevented a safe PK-guided dose recommendation. These 3 participants were started at the standard hydroxyurea dose of 20 mg/kg/day. The Table summarizes baseline characteristics for the initial study population, notable for a very young starting age with 13/20 (65%) less than two years of age.
Twelve children with PK-based initial dosing have been treated with hydroxyurea for at least six months. Despite the young starting age, after six months of hydroxyurea, children have documented increases in total Hb (1.4+/-1.9 g/dL), HbF (11.3+/-6.4%), and MCV (15+/-8 fL) and decreases in absolute reticulocyte count (-217+/-128 x 109/L) and absolute neutrophil count (-1.0+/-1.9 x 109/L). In 9 of 12 participants, the PK-guided initial dose remained the best clinical dose at six months without significant dose changes except for minor adjustments for weight. Two patients required a single dose escalation due to inadequate marrow suppression, while one required a dose hold and decrease due to neutropenia during and following a viral infection.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate that a sparse sampling approach, requiring only 3 blood samples over 3 hours, is able to accurately estimate hydroxyurea exposure in children with SCA. Hydroxyurea exposure, as defined by AUC, was similar with this sparse sampling approach as previous studies that relied upon a more standard and prolonged PK sampling approach. This population PK model is then able to predict a safe starting dose of hydroxyurea that approximates the actual MTD, with clinically significant improvements in laboratory parameters following six months of therapy. This individualized PK-guided dosing regimen should simplify hydroxyurea dosing and reduce the time interval to reach MTD and maximal clinical benefits.
Kalfa:Baxter/Baxalta/Shire: Research Funding. Quinn:Silver Lake Research Corporation: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Research Funding. Ware:Nova Laboratories: Consultancy; Addmedica: Research Funding; Global Blood Therapeutics: Consultancy; Bayer Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Biomedomics: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.