Abstract
Introduction: The recently proposed Myelofibrosis Secondary to PV and ET-Prognostic Model (MYSEC-PM) (Passamonti, Leukemia 2017) refines overall survival in patients with post-polycythemia vera and post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis (PPV, PET-MF) molecularly annotated for JAK2, CALR, and MPL mutations.
Objective: We aimed to validate the prognostic utility of MYSEC-PM for MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) PET/PPV-MF patients at the time of diagnosis, and at the time of referral.
Methods: We have retrospectively reviewed medical charts of PPV/PET-MF patients, as defined by IWG-MRT (Barosi, Leukemia 2008), referred to MDACC between years 1984-2015. We applied MYSEC-PM to PPV/PET-MF patients with available JAK2, MPL, or CALR molecular status: 178 newly diagnosed patients, and 244 patients at the time of referral to MDACC. Categorical and continuous variable were analyzed using the Fisher's exact, Kruskal-Wallis or Mann-Whitney U tests, as appropriate. Survival analysis (censored for stem cell transplantation, n=12) was carried out using Kaplan-Meier analysis with the log-rank test. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from the time of diagnosis (n=178, newly diagnosed patients), and from the time of referral (n=244, all patients).
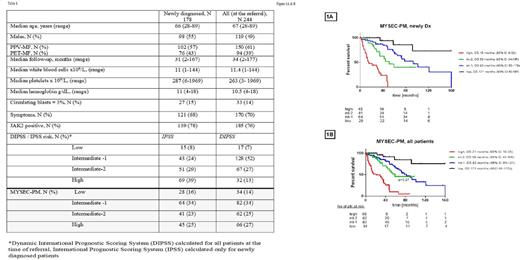
Results: Table 1 summarizes basic clinical characteristics and demographics of all patients. Patients were reclassified using MYSEC-PM composing of: patient's age (according to MYSEC-PM nomogram), hemoglobin <11 g/dl (2 points), platelets <150×109/l (1 point), circulating blasts ≥3% (2 points), presence of constitutional symptoms (1 point) and CALR-unmutated genotype (2 points). We have identified 4 groups among newly diagnosed patients: low (n=28), intermediate-1 (int-1, n=64), intermediate-2 (int-2, n=41), high risk (n=45) with distinctive OS of 15, 59, 93, and 171 months, respectively (p<0.0001, Graph 1A).
To compare MYSEC-PM prognostic utility to IPSS risk model, we analyzed OS by IPSS, and found OS for low (n=15), int-1 (n=43), int-2 (n=51), and high (n=69): not reached, 171, 61, and 44 months (p=0.007, graph not shown). Patients with int-1 and low, as well as int-2 and high risk IPSS had similar OS. MYSEC-PM model better classified patients within intermediate risk IPSS (int-1 and int-2): among 110 patients, 44 (40%) patients were up-staged to better risk category according to MYSEC-PM, and 18 (16%) patients were down-staged, creating 4 subgroups with distinct OS among intermediate risk IPSS patients : 15, 42, 72, and 171 months for low (n=14), int-1 (n=20), int-2 (n=42) and high (n=18) MYSEC-PM, respectively (p<0.0001).
Among all patients evaluated at the time of referral (median time to presentation to MDACC from the diagnosis of 18 months, range, 4-378), we have identified 4 groups according to MYSEC-PM model: low (n=34), int-1, (n=82), int-2 (n=62), high risk (n=66) with OS of 21, 59, 82, and 171 months, respectively (p<0.0001, Graph 1B). Patients in int-1 and int-2 risk groups have similar OS (p=0.27).
Overall survival stratified by DIPSS for low (n=17), intermediate-1 (n=128), intermediate-2 (n=67), and high (n=32) risk were not reached, 65, 44, and 36 months, respectively (p=0.01). Patients with int-1 and int-2, as well as int-2 and high risk DIPSS have similar OS. The MYSEC-PM model better distinguished different OS between patients in high and int-2 DIPSS risks, but not between patients in int-1 and int-2 DIPSS risks. Among 195 patients with int-1 and int-2 DIPSS, 39 (20%) patients were up-staged to a better risk category according to MYSEC-PM, and 71 (36%) patients were down-staged, which were exactly the opposite results as for IPSS stratification of newly diagnosed patients. The MYSEC-PM model revealed 4 groups within intermediate risk DIPSS - low (n=43), int-1 (n=46), int-2 (n=65) and high (n=20) with OS of 15, 51, 78, and 171 months (p<0.0001), similar between int-1 and int-2 patients (p=0.31).
Conclusions: Our results validated MYSEC-PM's prognostic value at the time of diagnosis, but not during the course of disease. We could demonstrate a clear distinction of overall survival by the MYSEC-PM model in newly diagnosed patients, with results comparable to those reported in the original report. However, we were not able to confirm the ability of the MYSEC-PM to clearly distinguish between patients with intermediate risk DIPSS during the course of the disease, where other factors not accounted for in the model may play a significant role.
Pemmaraju: novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria; abbvie: Research Funding; LFB: Consultancy, Honoraria; cellectis: Research Funding; roche diagnostics: Consultancy, Honoraria; stemline: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; affymetrix: Research Funding. Daver: Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding; Pfizer Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Consultancy, Research Funding. Cortes: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sun Pharma: Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding. Kantarjian: Novartis: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding. Verstovsek: Astrazeneca: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Galena BioPharma: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Galena BioPharma: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Lilly Oncology: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Lilly Oncology: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.