Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Progression from precursor states, MGUS and smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM), to multiple myeloma (MM) is dependent upon adaptive and innate immune contexture shaped by cross-talk between malignant plasma cells and bone marrow (BM) milieu. The complexity and heterogeneity of interactions between the immune system and plasma cells in BM triggers alterations in peripheral blood (PB) immune cell subsets. The advantage of using PB as a surrogate is that dynamic changes in the immune cells can be measured at various time points during disease progression or therapeutic intervention. Here, we performed a comprehensive analysis of immune repertoire to identify immune signatures in PB and BM associated with MM or its precursor states. We also performed T cell receptor (TCR) clonotyping to quantify clonal expansion specific to each immunotype.
METHODS: Paired PB and BM specimens were collected from patients with MGUS/SMM (n=12) and MM (n=16) through an IRB-approved biospecimen protocol. PB mononuclear cells and BM mononuclear cells were isolated for immune profiling. A total of 59 immune variables were analyzed by flow cytometry surveying 6 cell lineages' [NK, NK-T, Th, CTL, Treg and ɣδ T cells] distribution and functional status [activation, differentiation and anergy]. In addition, ArcherDx Immunoverse TCR αδ-βɣ CDR3 targeted NGS assay was performed to study clonal distributions of Vα24Jα18 NK-T, βα and ɣδ T cell. Univariate analyses (ANOVA) were performed using p<0.15 cutoff. Each set of variables (PB or BM) was then validated by multivariate analyses (Wilk's lambda) and used for unsupervised hierarchical analysis by WPGMA methods. Innate (NK-T, ɣδ T) and adaptive (βα T) mobilization for each cluster were finally confirmed by calculating Shannon's TCR clonal diversity index (SI).
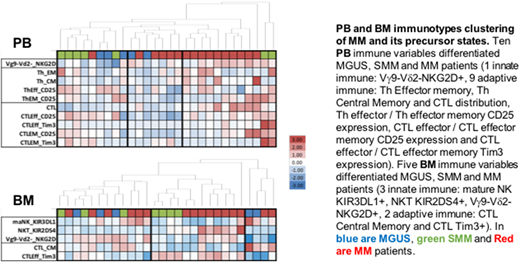
RESULTS: PB immunotyping identified 1 marker of innate inflammation and 9 markers of adaptive T mobilization that differentiated precursor states and MM (p=0.005). This model generated 3 PB immune clusters (Figure): cluster #1 [8 precursor states, 1 MM] showed a lack of innate inflammation and low Th/CTL mobilization, cluster #2 [2MGUS, 5MM] showed low innate inflammation and, cluster #3 [2SMM, 10MM] showed strong innate inflammation (Vɣ9-Vδ2-NKG2D+), Th terminal differentiation (central memory phenotype) and CTL anergy (Tim3+). TCR clonotyping confirmed increased innate inflammation (TCRδ SI 3.99±0.3 vs 4.75±0.15, p<0.05) and T cell mobilization (TCRα SI 7.12±0.3 vs. 8.20± 0.2, p<0.05) in PB cluster #3 compared with PB cluster #1.
BM immunotyping identified 3 markers of innate inflammation and 2 markers of adaptive T mobilization (p=0.0274) distinguishing precursor states from MM. This model generated 3 BM immune clusters: cluster #1 [6 precursor states, 6 MM] showed innate inflammation (ɣδ T) and CTL terminal differentiation (central memory phenotype); cluster #2 [4 SMM, 8 MM] showed innate inflammation (NK-T, ɣδ T) and CTL effector anergy; and cluster #3 [2 MGUS, 2 MM] showed low NK cell cytotoxicity (KIR3DL1+) and CTL terminal differentiation. TCR clonotyping confirmed qualitative differences in innate inflammation between BM cluster #1 and #2 with higher NK-T (%Vα24Jα18 p<0.01) but lower ɣδ T (TCRδ SI 3.36±0.2 vs 4.57±0.2, p<0.05). In addition, CTL mobilization whether resulting in terminal differentiation or anergy in BM cluster #1 and #2, respectively was associated with similar clonal expansion of T cells (TCRα SI 7.21±0.26 vs. 7.87± 0.4, ns).
Comparisons showed associations between PB and BM ɣδ T cell involvement in 13/13 patients. High PB Th/CTL mobilization (terminal differentiation) was associated with high T cell anergy in BM in 9/12 patients; conversely low PB Th/CTL mobilization was associated with low BM T cell involvement in 6/7 patients.
CONCLUSION: This pilot study shows immune clustering of MGUS, SMM and MM patients based on BM and PB immunotypes. This is the first study to demonstrate two very distinct MM immunotypes based on low vs. high inflammatory states. We also show a high correlation between innate immune inflammation status in both PB and BM, specifically pertaining to ɣδ T cell, conventional T cell mobilization or lack thereof. Additional studies including a larger cohort for validation and longer follow up to establish correlation with clinical outcomes are currently underway.
Foureau:Teneobio Inc.: Research Funding. Berlin:ArcherDx: Employment. Johnson:ArcherDx: Employment. Williams:ArcherDx: Employment. Voorhees:Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: served on an IRC; Amgen Inc.: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: served on an IRC; Oncopeptides: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: served on an IRC; TeneoBio: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Usmani:Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Janssen, Merck, Pharmacyclics,Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Takeda: Research Funding; Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Genmab, Merck, MundiPharma, Janssen, Seattle Genetics: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.