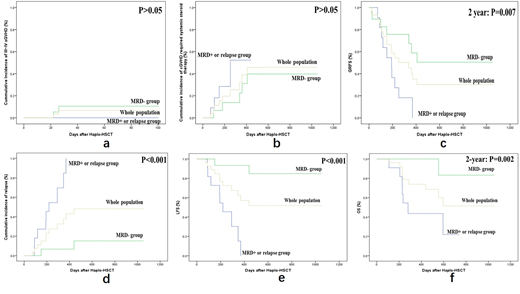
Patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R ALL) usually have a very poor prognosis and an expected survival of less than 6 months.The complete remission (CR) rates in the setting of the first salvage chemotherapy are about 30% to 46% and these rates drop sharply to 18% to 25% after the second salvage chemotherapy. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T) can induce high CR rates of 70-95% (MRD negative CR rates of 60-90%) among patients with R/R ALL. Howeve, relapse after CAR-T treatment is supposed a main obstacle for long-term outcome. Some reports have described relapse rates of 20-70% when the follow-up was long enough. It remains controversial whether these patients should receive allo-HSCT after CAR-T treatment or not. We designed a multi-center retrospective study to assess the efficacy and safety profiles of CAR-T therapy followed by haplo-HSCT. A total of 31 patients treated with CAR-T therapy followed by haplo-HSCT were included. Eleven patients who progressed to MRD positive or relapse subsequently underwent haplo-HSCT (MRD positive or relapse group) and the rest 20 patients with MRD negativity received haplo-HSCT (MRD negative group). The median time from CAR-T infusion to haplo-HSCT was 83 (range 62-114) days. After a median follow-up period of 288 (range 189-554) days post-transplantation, the 100-day cumulative incidence (CI) of grade III~IV aGVHD was 0% and 10.5% in the MRD positive or relapse group and MRD negative group, respectively (P>0.05)(Figure 1a). One and 2-year CIs of cGVHD requiring systemic steroid therapy were 52.3% and 31.1% (P>0.05), 52.3% and 39.7% (P>0.05) in the MRD positive or relapse group and MRD negative group, respectively(Figure 1b).The 1-year cumulative incidence of CMV viremia was 90.9%, 68.4% and 77.8% in the MRD positive or relapse group, MRD negative group and the whole population respectively (P>0.05). The 2-year cumulative incidence of CMV viremia was 90.9%, 78.9% and 85.2% in the MRD positive or relapse group, MRD negative group and the whole population respectively (P>0.05). The 1-year cumulative incidence of EBV viremia was 90.9%, 79.6% and 84.2% in the MRD positive or relapse group, MRD negative group and the whole population, respectively (P>0.05). And the 2-year cumulative incidence of EBV viremia was 90.9%, 89.8% and 89.5% in the MRD negative or relapse group, MRD negative group and the whole population, respectively (P>0.05). Onset of CMV and EBV viremia occurred in 33.5 (26.3-50.0) days and 44.0 (28.5-57.0) days after transplantation in 24 and 25 patients, respectively. Median peak CMV DNA and EBV DNA load were 1.5X104 (2.6X103-3.4X104) copies/ml and 2.2X104 (1.1X104, 4.1X104) copies/ml, respectively. One and 2-year CIs of relapse were 84.8% and 6.7% (p<0.001), 100% and 15.2% (p<0.01%) in the MRD positive or relapse group and MRD negative group, respectively (Figure 1d). One-year GVHD and relapse free survival (GRFS), leukemia free survival (LFS) and overall survival (OS) in the MRD positive or relapse group and MRD negative group were 18.2% and 58.9% (P=0.024), 15.2% and 93.3% (P<0.001), 43.6% and 100% (P=0.002), respectively (Figure 1f). Two-year GRFS, LFS and OS in the MRD positive or relapse group and MRD negative group were 0% and 50.5% (P=0.007), 0% and 84.8% (P<0.001), 14.5% and 83.3% (P<0.001), respectively (Figure 1c,e,f). No patient died of therapy-associated complications. Relapse or MRD positivity at the time of haplo-HSCT is the only independent factor associated with poor LFS [hazard ratio (HR): 23.6, 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.78-201.63, P=0.004] and OS [HR: 10.4, 95% CI: 1.12-94.45, P= 0.037]. In conclusion, our trial provided data to illustrate the safety and efficacy profiles of a novel combining therapeutic strategy against R/R ALL by using the combination of CAR-T cells for re-induction followed by haplo-HSCT for consolidation. We confirmed that achieving pre-transplant MRD negativity after CAR-T treatment is a suitable basis for haplo-HSCT. Our study results imply that CAR-T therapy followed by haplo-HSCT could further improve LFS and OS without increasing risks of treatment-related toxicity in such a previously heavily treated population. Further evaluation is needed from larger scale studies with a more homogeneous patient population and longer follow-ups.
Blaise:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Molmed: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pierre Fabre medicaments: Honoraria. Mohty:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.