Introduction
Blocking Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) with ibrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients (pts). However, resistance to therapy is common. Preclinical data suggest selinexor (oral selective inhibitor of nuclear export) downregulates BTK (Hing 2015). We hypothesized that dual BTK blockade by combining ibrutinib and selinexor would be tolerable and efficacious in CLL/NHL pts. Herein, we report the phase I combination study with expansion cohorts.
Methods
Pts with histologically confirmed CLL/NHL were enrolled (n=33). Eligible pts were age ≥18 years (yrs), had ≥1 prior therapy and ECOG performance status of 0-1. CLL pts met iwCLL 2008 criteria for therapy. Pts received selinexor orally 1-2 times weekly (3 weeks of 4-week cycle) and daily oral ibrutinib (420mg) starting Cycle 1 Day 8. Treatment cycles were repeated until disease progression, intolerance, death or discontinuation of trial participation. Primary endpoint was determination of maximum tolerated dose (MTD). Dose-finding proceeded using a modified continual reassessment method targeting a probability of dose limiting toxicity (DLT)<0.30. Response was assessed by iwCLL 2008 (CLL) or IWG 2007 Response Criteria (NHL) by CT scan at Cycle 2 and 4, then Q 3 months (mos) during Yr 1 and then Q 6 mos. Complete responses (CR) were confirmed with bone marrow (BM) aspirate if BM was initially involved. Progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) estimates were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results
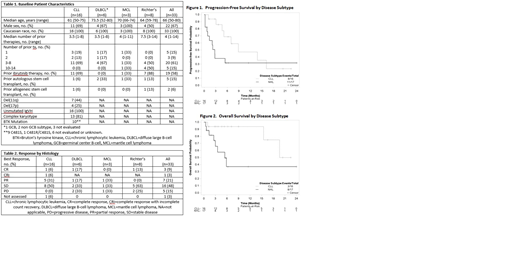
Median age was 66 yrs (50-80). Included pts had CLL (n=16), Richter's transformation (RT=8), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL, n=6), and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL=3). Median number of prior therapies was 4 (1-14) and 58% had received ibrutinib. Baseline characteristics are detailed in Table 1. The combination was tolerated. MTD was 40mg of selinexor (D1, 8, 15) and 420mg daily ibrutinib [dose level 1 (DL1)]. Two pts were treated with selinexor 30mg twice weekly and 420mg of daily ibrutinib (DL2) and both experienced significant fatigue and discontinued therapy. These adverse events (AE) were considered DLTs. The remainder of pts received DL1. Grade ≥3 hematologic AEs were rare with 3 (9%) and 1 (3%) pt experiencing neutropenia and anemia, respectively. Most common non-hematologic AEs of any grade were nausea (39%) diarrhea (33%), fatigue (33%), and anorexia (27%). Grade ≥3 non-hematologic AEs were uncommon with 2 pts (6%) experiencing hypertension and 1 pt each (3%) experiencing diarrhea, nausea, elevated alkaline phosphatase, cataract, weight gain, upper respiratory tract infection, pancreatitis, pneumonitis, and multi-system organ failure. Other AEs of interest were weight loss, bleeding, and tachycardia, experienced by 5 (15%), 4 (12%), and 3 (9%) pts, respectively. There were 5 pt deaths while on study; 3 related to disease progression and 2 related to infection.
In total, 81% achieved disease control with 33% achieving CR or PR (partial response) and 48% achieving stable disease (SD; Table 2). All CLL pts who received prior ibrutinib or had complex karyotype achieved at least SD, and all who did not receive prior ibrutinib had CR or PR. Two CLL pts with known BTK mutation had response to therapy and 7 had SD. One CLL pt who received 1 prior therapy achieved CR with no detectable residual disease. One of the 8 RT pts achieved CR and 5 achieved SD. In the 11 pts who achieved at least PR, the median duration of response was not reached (NR). In the 15 pts with SD and >2 mos of follow-up, 20% (3/15) maintained SD for >6 mos. Median PFS for pts with CLL and NHL was 8.9 (95%CI:4.6-NR) and 2.7 (95%CI:0.7-NR) mos, respectively (Figure 1). For CLL pts who received and did not receive prior ibrutinib, 64% (7/11) and 20% (1/5) progressed, respectively. For CLL pts who received 1-2 and ≥3 prior therapies 20% (1/5) and 64% (7/11) progressed, respectively. With median follow-up of 5.3 (range:1.2-22.5) and 5.5 (range:0.7-33.1) mos, median OS for CLL and NHL pts was NR (95%CI:15.4-NR) and 5.4 (95%CI:2.6-NR) mos, respectively (Figure 2).
Conclusions
Ibrutinib (420mg daily) and selinexor (40mg weekly) was tolerable and demonstrated efficacy in this heavily pretreated, high-risk population of CLL/NHL pts. Efficacy may be greater in earlier lines of therapy. Further investigation is needed to optimize response rates and durability.
Stephens:Karyopharm: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding. Rogers:Janssen: Research Funding; Acerta: Consultancy; Abbvie: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Bhat:Janssen: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. William:Guidepoint Global: Consultancy; Defined Health: Consultancy; Techspert: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy; Kyowa Kirin, Inc.: Consultancy. Jaglowski:Kite: Consultancy, Other: advisory board, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: advisory board, Research Funding; Juno: Consultancy, Other: advisory board; Unum Therapeutics Inc.: Research Funding. Glenn:BMS: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Byrd:Genentech: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; TG Therapeutics: Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Ohio State University: Patents & Royalties: OSU-2S; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Ohio State University: Patents & Royalties: OSU-2S; Acerta: Research Funding; Novartis: Other: Travel Expenses, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Other: Travel Expenses, Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Research Funding; Gilead: Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Woyach:Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Loxo: Research Funding; Morphosys: Research Funding; Verastem: Research Funding.
Selinexor is an oral inhibitor of nuclear export. This presentation will describe the combination of ibrutinib and selinexor, which is an off-label use for the drug.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.