Continuous treatment with lenalidomide (R) and dexamethasone (d) is a standard of care for multiple myeloma (MM) patients (pts) not candidates for autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). As previously reported, the addition of Clarithromycin (C) to Rd has proven to be safe and effective, and case-control analyses suggested a significant additive value with the combination. C optimizes the therapeutic effect of glucocorticoids by increasing the area under the curve, has immunomodulatory effects and may have direct antineoplastic properties. However, there are not randomized phase III trials confirming these results.
GEM-Claridex in an open, randomized, phase III trial for untreated newly diagnosed MM pts ineligible for ASCT. Enrolled pts were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive 28-day cycles of R (25mg po qd days 1-21), d (40mg po [20mg in pts >75 years], days 1, 8, 15 and 22) plus or minus C (500mg po bid) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS). Secondary endpoints included overall response rate (ORR), overall survival (OS) and minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity rate and safety. MRD was evaluated in 99 pts using Euroflow NGF (limit of detection, 2x10-6). As expected, most pts in CR were tested for MRD whereas the majority of pts with missing MRD data achieved VGPR or less and were thus considered as MRD-positive for intent to treat analyses.
Two hundred and eighty-eight pts were included (144 to C-Rd and 144 to Rd). Median age was 76 (range: 65-93), 36.8% of pts had ISS 3 and 15.6% presented with high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities. Key baseline characteristics were well balanced between the two arms.
The addition of C to Rd resulted in deeper responses with a ≥ complete response (CR) rate of 20.1% in the C-Rd arm compared to 11.2% in the Rd arm (p = 0.037). Also, the ≥ very good partial response (VGPR) rate was 52.8% in the C-Rd arm as compared to the 37.1% in the Rd arm (p = 0.007). MRD analysis was performed at suspected CR and yearly afterwards. On intent-to-treat, 5/144 (3,5%) and 9/143 (6,2%) of pts achieved undetectable MRD with C-Rd and Rd, respectively (p = 0,7).
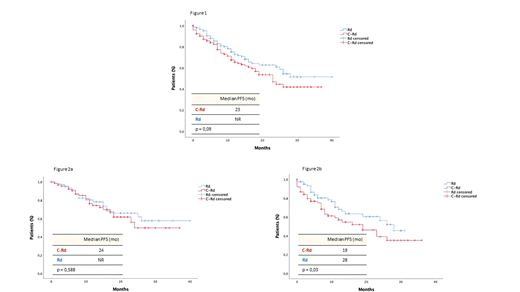
With a median follow-up of 16 months (range, 1-47), no significant differences were observed in PFS: in the C-Rd arm the median was 23 months and has not been reached in the Rd arm (p = 0.09); furthermore, although disease progression and/or death rate was comparable in both arms (C-Rd: 57/144 [39.6%] vs Rd: 45/144 [31.2%]), a trend towards shorter PFS was observed in the C-Rd group (Figure 1). This effect was less evident in younger (<75) pts (median PFS, C-Rd: 24 months vs Rd NR, p = 0,588) but, in older pts (≥ 75), the addition of C to Rd resulted into a significant deleterious effect on PFS (median PFS, C-Rd: 19 vs Rd 28 months, p = 0.03) (Figure 2a and 2b). Irrespectively of treatment arm, pts with MRD negative had significantly longer PFS (NR vs 26 months, p = 0,03). Concerning OS, no differences have been identified (p = 0.41), although median has not been reached yet in any arm. Out of the 33 and 28 deaths documented in the C-Rd and Rd arms respectively, the percentage of pts dying w/o documented PD was significantly higher in the C-Rd group (27/33 [82%] vs 13/27 [48%], p = 0.004). Furthermore, in the C-Rd arm, the most frequent causes of death were severe infections (14/27 [52%] and cardiovascular events 6/27 [22%]) the majority of them occurring in older (≥75) pts (20/27, 74%).
The most common G3-4 adverse events (AE) in the C-Rd and Rd arms were hematologic (neutropenia: 10,4% vs 16,7% [p = ns] and anemia: 2,1% vs 6,9% [p = 0,04], respectively). G3-4 infections occurred in 16% of cases in both arms and were the most frequent non-hematological AE. 7% of pts in both arms developed G3-4 GI toxicity and there were no differences between the two arms in G3-4 skin-related AEs (2,8% vs 3,5%). Only one case of invasive SPM (colon cancer) in the C-Rd arm was reported.
In conclusion, the addition of C to Rd in transplant ineligible newly diagnosed MM pts significantly increases the rate and depth of responses but it is not associated with an improved PFS and OS due to a higher proportion of deaths in the C-Rd arm, mostly infectious, in pts > 75 years and being early deaths. Overexposure to steroids due to the delayed clearance induced by C in this elderly population could explain our results.
Puig:The Binding Site: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Rosinol Dachs:Janssen, Celgene, Amgen and Takeda: Honoraria. De Arriba:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria. Oriol:Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. De La Rubia:AbbVie: Consultancy; AMGEN: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy. Amor:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Martín Sánchez:GILEAD SCIENCES: Research Funding. Rossi:BMS: Research Funding; Janssen, Celgene, Amgen: Consultancy. Coleman:Merck: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Speakers Bureau; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Equity Ownership; Gilead, Bayer, Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Paiva:Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi; unrestricted grants from Celgene, EngMab, Sanofi, and Takeda; and consultancy for Celgene, Janssen, and Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. San-Miguel:Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria. Bladé:Jansen, Celgene, Takeda, Amgen and Oncopeptides: Honoraria. Niesvizky:Takeda, Amgen, BMS, Janssen, Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding. Mateos:EDO: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmamar: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract