Introduction: Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has improved survival outcomes in patients with relapsed/refractory (r/r) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL). However, many patients experience systemic toxicities such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) and about 60% relapse. Recent studies indicate that the gut microbiome can modulate tumor response and also influence toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. However, the influence of gut microbiome has not been well-studied in patients receiving CAR T-cell therapy. Here, we analyzed the association between gut microbiome composition and diversity metrics with survival outcomes and toxicities in r/r LBCL patients treated with anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy.
Methods: Baseline stool samples were collected from r/r LBCL patients within 3 days of CAR T-cell infusion (days -3 to +3). Taxonomic profiling was performed on all samples using targeted ribosomal 16S RNA gene sequencing of the V4 region. The anti-tumor response was assessed as per Lugano 2014 criteria. Bacterial community alpha diversity was calculated using the inverse Simpson Index (ISI). Results were correlated with toxicity outcomes, including CRS and ICANS, as well as efficacy outcomes, including response, progression-free (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
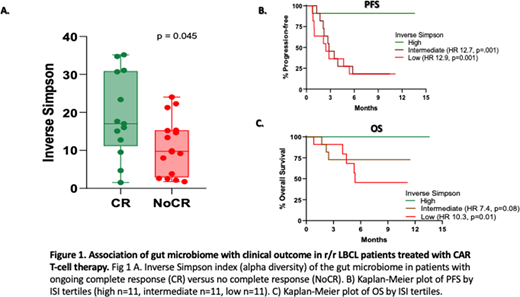
Results: We analyzed baseline stool samples from 33 r/r LBCL patients (24 DLBCL, 7 transformed follicular lymphoma, and 2 double-hit lymphomas) treated with standard of care axicabtagene ciloleucel (n =30) or tisagenlecleucel (n=3). The median age of the cohort (23 males, 10 females) was 54 (range 28 - 84) years. The number of patients with ECOG performance status (PS) 0-1, Ann-Arbor stage ≥3, and International Prognostic Index (IPI) of ≥3 at the time of apheresis were 29 (88%), 33 (100%), and 15 (46%), respectively. The median number of prior lines of therapy was 3 (range 2-6). The median follow-up from CAR-T infusion was 7.3 (range 0.8 -13.6) months. The best overall and complete response (CR) rates were 82% (27/33) and 58% (19/33), respectively. All patients were evaluable for toxicity assessment and 29 were evaluable for response assessment at 3 months (3 patients died of toxicity before 3 months and 1 was lost to follow-up). Since ongoing response at 3 months was previously shown to be associated with long-term durability (Locke et al, Lancet Oncol 2019), we analyzed differences in baseline gut microbiome markers in patients with or without ongoing CR at 3 months post-CAR-T infusion. ISI was significantly higher in patients with ongoing CR at 3 months (N=13) compared to those without ongoing CR (NoCR) group (N=16) (Fig.1A, p=0.045). However, beta diversity using weighted UniFrac distances by principal coordinate analysis was not significantly different. ISI did not correlate with age, sex, IPI score, ECOG PS, serum LDH, number of lines of therapy or disease status (primary refractory vs. relapsed). We found an increased relative abundance of several bacterial families in patients with ongoing CR vs. NoCR group. We also analyzed the impact of gut microbial diversity on PFS and OS by stratifying the patients according to the tertile of ISI. The PFS of patients in the highest tertile of ISI values (n=11, median PFS not reached) was significantly higher compared to those with intermediate (n=11, median PFS = 2.82 months, HR 12.7, 95% CI 3.61 to 44.77, log-rank, p=0.001) or low (n=11, median PFS = 2.43 months, HR 12.9, 95% CI 3.68 to 45.75, log-rank, p=0.001) ISI values (Fig. 1B). High ISI values also correlated positively and significantly with OS (Fig. 1C). We did not observe any significant association between microbial diversity, either alpha or beta, and toxicities including CRS [(grade 0-1 (N=22) vs ≥2 (N=11)] and ICANS [(grade 0-2 (N=23) vs ≥3 (N=10)]. Additional details including impact of microbial composition will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that the baseline gut bacterial diversity may serve as a predictive biomarker for efficacy of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in r/r LBCL patients, with high diversity favoring improved outcomes. If confirmed in larger studies, future investigations should explore if the microbiome could be a modulator of CAR T-cell response in order to determine whether developing therapeutic interventional strategies to favorably alter the microbiome are warranted.
Nastoupil:TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gamida Cell: Honoraria; Gilead/KITE: Honoraria; Bayer: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding; LAM Therapeutics: Research Funding; Karus Therapeutics: Research Funding. Westin:Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy, Research Funding; Curis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; 47: Research Funding; Morphosys: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding. Lee:Guidepoint Blogal: Consultancy; Celgene: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Oncternal Therapeutics: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Aptitude Health: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Research Funding. Kebriaei:Kite: Other: Served on advisory board; Novartis: Other: Served on advisory board; Ziopharm: Other: Research Support; Amgen: Other: Research Support; Pfizer: Other: Served on advisory board; Jazz: Consultancy. Shpall:Takeda: Other: Licensing Agreement; Adaptimmune: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Zelluna: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Magenta: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Jain:Cellectis: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Precision Bioscienes: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Verastem: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BeiGene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Fate Therapeutics: Research Funding; Aprea Therapeutics: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Green:KDAc Therapeutics: Current equity holder in private company. Flowers:Kite: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics/Janssen: Consultancy; Spectrum: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Leukemia and Lymphoma Society: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Acerta: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy; V Foundation: Research Funding; National Cancer Institute: Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy; Denovo Biopharma: Consultancy; Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas: Research Funding; Millennium/Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; BeiGene: Consultancy; OptumRx: Consultancy; Genentech, Inc./F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Research Funding; Burroughs Wellcome Fund: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding. Champlin:Genzyme: Speakers Bureau; DKMS America: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cytonus: Consultancy; Omeros: Consultancy; Johnson and Johnson: Consultancy; Actinium: Consultancy; Takeda: Patents & Royalties. Wargo:Imedex, Dava Oncology, Omniprex, Illumina, gilead, PeerView, PET, MedImmune and Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Merck: Consultancy; Microbiome DX: Consultancy; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Consultancy; Biothera Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Neelapu:Celgene: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Other: personal fees; Allogene Therapeutics: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Cell Medica/Kuur: Other: personal fees; Novartis: Other: personal fees; N/A: Other; Precision Biosciences: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Incyte: Other: personal fees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceuticals: Patents & Royalties; Poseida: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Karus Therapeutics: Research Funding; Calibr: Other; Legend Biotech: Other; Adicet Bio: Other; Merck: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Unum Therapeutics: Other, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.