Abstract
Background: Platelet-activating anti-PF4 antibodies that cause thrombocytopenia and thrombosis are implicated in Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and, more recently, in a newly recognized entity, vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT). Current frontline PF4-Polyanion ELISAs utilize simple techniques but are highly non-specific. Functional gold-standard assays such as the serotonin-release assay (SRA) and PF4-dependent P-selectin expression assay (PEA) have limited availability due to technical complexity and the requirement for freshly-drawn normal donor platelets which results in significant delays in diagnosis. Thus, there is an unmet need for near-patient, functional assays for HIT/VITT diagnosis.
Aim: To develop a highly sensitive and specific functional assay to detect platelet-activating antibodies associated with HIT and VITT using long-term stored platelets. The assay should be technically simple, avoiding current functional HIT testing endpoints such as aggregometry, radioactivity measurement or flow cytometry.
Methods: Platelets were subjected to controlled-rate freezing in a trehalose-based buffer. Cryopreserved platelets were then thawed after variable storage periods, incubated with platelet factor 4 (PF4), and sera from HIT or VITT suspected patients. Thrombospondin-1 (TSP1), a protein highly expressed in platelet α-granules, was quantified from activated platelet supernatants in an ELISA-based assay as a measure of platelet activation.
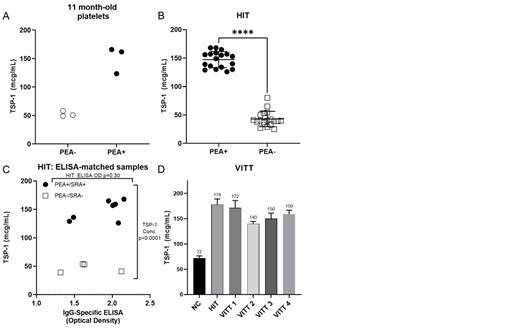
Results: In initial studies, p-selectin expression was induced by platelet-activating HIT antibodies using cryopreserved platelets and the TSP1-release assay (TRA) detected HIT antibody-mediated PF4-dependent cryopreserved platelet activation across 20 different platelet lots (data not shown). A representative study using platelets stored for 11 months is shown in Figure 1A. A cohort of thirty-six HIT-suspected patient sera, half with PF4-dependent platelet-activating antibodies (PEA+) and without (PEA-), were used to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the TRA (Figure 1B). All 18 PEA+ samples activated platelets strongly with a mean TSP1 concentration of 147 µg/mL measured in the supernatant compared to a mean of 43 µg/mL obtained with non-activating samples. TSP1 release in a subgroup of 7 PEA+/SRA+/ELISA+ and 4 PEA-/SRA-/ELISA+ samples that were matched for ELISA Optical Density was examined (Figure 1C). Results demonstrated that even strong ELISA+ samples that were non-activating (PEA-/SRA-) did not induce platelet activation in the TRA, confirming high specificity of the assay. The TRA was tested for its ability to detect platelet-activating antibodies in four patients who developed VITT after the Janssen vaccine (Ad26.COV2.S). All samples induced high levels of TSP1 release from cryopreserved platelets (Figure 1D).
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that cryopreserved platelets stored for several months are viable and capable of degranulation upon activation. Further, we demonstrate that measurement of TSP-1 released from cryopreserved, PF4-treated platelets is highly accurate for detecting platelet-activating HIT and VITT anti-PF4 antibodies. Specificity and sensitivity were both 100% even with samples that were strongly false-positive in the HIT ELISA. Coupling cryopreserved platelet activation to a simple ELISA endpoint, as demonstrated here, precludes the need for fresh platelets and complex testing techniques. Thus, the TRA has the potential to transform the diagnostic testing paradigm in HIT and VITT by making near-patient in-hospital functional testing available for rapid and accurate diagnosis.
Figure Legend:
Figure 1. TSP-1 quantification of (A) 3 HIT patient samples (closed circles) relative to 3 normal control samples (open circles) after 11-months of frozen platelet storage. (B) Thirty-six HIT-suspected patient samples: 18 PEA+ samples (closed circles), and 18 PEA- samples (open squares). Data are compared using two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test. **** P<0.0001. (C) Eleven high optical density matched HIT ELISA patient sera: 7 PEA+/SRA+ samples (closed circles) and 4 PEA-/SRA- samples (open squares). (D) TSP-1 quantification of VITT patient sera. NC-normal control.
Pruthi: Instrumentation Laboratory: Honoraria; HEMA Biologics: Honoraria; Bayer Healthcare AG: Honoraria; Genentech: Honoraria; CSL Behring: Honoraria; Merck: Honoraria. Padmanabhan: Veralox Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.