Abstract
The role of telomeres in human health and disease is yet to be fully understood. The limitations of mouse models for the study of human telomere biology and difficulties in accurately measuring the length of telomere repeats in chromosomes and cells have diverted attention from many important and relevant observations. The goal of this perspective is to summarize some of these observations and to discuss the antagonistic role of telomere loss in aging and cancer in the context of developmental biology, cell turnover, and evolution. It is proposed that both damage to DNA and replicative loss of telomeric DNA contribute to aging in humans, with the differences in leukocyte telomere length between humans being linked to the risk of developing specific diseases. These ideas are captured in the Telomere Erosion in Disposable Soma theory of aging proposed herein.
Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution.
—Theodosius Dobzhansky (1973)
Introduction
The evolutionary biologist August Weismann proposed several brilliant ideas in about 1890. He proposed that cells of the soma and germline are distinct, and he formulated the theory that inheritance is transmitted solely through the germline via the nuclei of egg and sperm. He also advanced a theory of senescence suggesting that aging could involve, next to senescence, which he compared with mechanical wear, a “death mechanism” involving a limitation in the number of times cells can divide (reviewed by Kirkwood and Cremer1). George Williams, famous for proposing “antagonistic pleiotropy,” which is the idea that alleles that provide a fitness advantage early in life often have pleiotropic deleterious effects late in life, formulated several objections against Weismann’s ideas in 1957.2 He pointed to “the fallacy of identifying senescence with mechanical wear” and to “the failure of several decades of gerontological research to uncover any death-mechanism.”2 (page 398) Subsequent research has invalidated both arguments: damage to DNA is now recognized as a primary cause of aging3 and loss of telomeric DNA can act as a mitotic clock to limit the number of times cells can divide.4 In 1977, Thomas Kirkwood combined Weismann’s ideas that germline and soma are distinct and that senescence results from mechanical wear, in the disposable soma (DS) theory of aging.5 The essence of the DS theory is that the amount of energy an organism allocates for somatic maintenance and repair is less than would be required for the soma to last indefinitely. The DS theory predicts that unrepaired somatic damage accumulates throughout life causing aging, and ultimately, death. Strong support for the DS theory has come from recent sequence data showing that somatic cells accumulate mutations at a rate that is at least 10-fold higher than cells of the germline.6 Specifically, ∼60 de novo mutations have been observed between human generations, mostly originating in the male germline7 at a rate of 1 to 2 mutations per year.6,8 In contrast, human cortical neurons, smooth muscle cells, colon epithelial cells, and nucleated blood cells acquire 10 to 40 mutations per cell per year.6 The steady accumulation of mutations in somatic cells is likely to compromise the function of an increasing number of cells and contribute to aging. The DS theory of aging does not include a limit to the number of times cells can divide, as was proposed by Weismann. Such a limit is not present in all species, and its purpose or advantage is not obvious. One possibility is that limiting telomerase levels in somatic cells increases lifespan by acting as a tumor suppressor mechanism. Although it is advantageous early in life in suppressing the malignant progression of cells, telomere erosion contributes to aging late in life by compromising cell renewal.9,10 Differences in average telomere length between humans and cell types help explain differences in the risk of developing cancer and other age-related diseases. These ideas are captured in the Telomere Erosion in Disposable Soma (TEDS) theory of aging proposed herein. To build a case for the TEDS theory, key aspects of telomere biology, telomere length measurements, and telomere disorders are briefly reviewed, followed by a discussion of cell turnover and telomere erosion in relation to various forms of DNA damage, aging, and cancer.
Telomere structure, function, and maintenance
In all mammals, the natural ends of chromosomes, called telomeres, are characterized by a variable number of TTAGGG repeats and associated proteins.11 A central question in the telomere field is and has been: how do the natural ends of a chromosome avoid being recognized as double strand breaks? In most cells the protection of chromosome ends requires between a few dozen and a few hundred telomere repeats.12 A minimum number of repeats is needed to recruit sufficient telomere-specific proteins to form a structure that effectively protects the ends of chromosomes from being recognized as a broken end.13,14 The protective function of telomeres eventually fails in cells that do not fully compensate telomere loss. Telomere repeats are lost with each cycle of DNA replication.15,16 The primary mechanism by which telomere erosion is countered is by expression of telomerase, the reverse transcriptase that adds TTAGGG repeats to the 3′ ends of chromosomes.17,18 However, recombination can also elongate telomeres during embryogenesis19 and in some tumor cells.20
Telomerase in embryonic cells
The telomerase ribonucleoprotein enzyme complex is minimally composed of the telomerase reverse transcriptase, telomerase RNA, and dyskerin.21 However, many additional proteins associate with the enzyme and participate in its recruitment to chromosome ends and the interaction with telomeric DNA.18 Embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells are “immortal” for most practical purposes, in that the loss of telomere repeats is fully compensated. Before the onset of embryonic differentiation, all chromosomes must be “capped” by an adequate number of telomere repeats, to prevent premature loss of cells. The mechanisms of telomere protection change during embryonic development,22,23 and both telomerase24 and recombination pathways19 are implicated in adjusting the length of telomere repeats in chromosome ends before the onset of embryonic differentiation. Further studies are needed to clarify how the length of telomeres in cells is established in early embryogenesis. Such studies should also elucidate why individual chromosome arms differ in telomere length, exemplified by the relative short track of telomere repeats on the p arm of human Chr17.25,26
Measuring telomere length
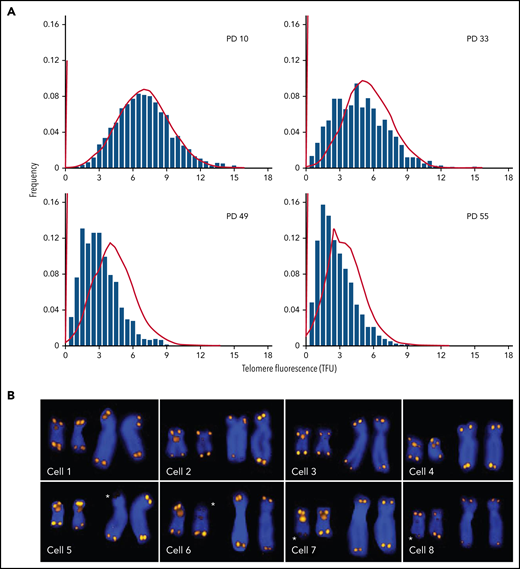
Every normal human diploid cell has 46 chromosomes and 92 telomeres before it enters the cell cycle. All techniques that are used to measure the length of telomere repeats have limitations and shortcomings. Ideally, the length of all telomeres should be measured, because the shortest telomeres are biologically the most relevant.12,27 The important distinction between the average length and the telomere length distribution in cells is illustrated in Figure 1. With increasing population doublings, the distribution of telomere length values is increasingly skewed toward short telomeres (Figure 1A). Sporadic loss of telomeric DNA (Figure 1B; asterisks) most likely contributes to this skewing,28 and damage to telomeric DNA resulting from various forms of stress contributes to telomere erosion. Current methods typically only estimate the average length of telomere repeats in DNA or cells with variable degree of accuracy. New methods that measure the length of telomere repeats in single DNA molecules29,30 hold promise for generating data on the distribution as well as the average telomere length in cells. The application of such measurements and the development of consensus measurement standards are needed to advance the field.
Q-FISH measurements of metaphase chromosomes from human fibroblasts at different population doublings (PDs). The telomere length values are increasingly skewed toward short telomeres as the cultured cells approach senescence. (A) Actual data (bars; adapted from Martens et al, with permission28) correspond to predictions based on a mathematical model (lines; adapted from Rodriguez-Brenes and Peskin with permission99) but show more pronounced skewing. (B) Snapshots of Q-FISH images of chromosomes X and 17 (also hybridized with a Chr17-specific probe) from individual metaphase cells of different diploid fibroblasts clones. For details see Martens et al,28 Asterisks indicate sporadic loss of telomere repeats on specific chromosome arms. Q-FISH, quantitative fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Q-FISH measurements of metaphase chromosomes from human fibroblasts at different population doublings (PDs). The telomere length values are increasingly skewed toward short telomeres as the cultured cells approach senescence. (A) Actual data (bars; adapted from Martens et al, with permission28) correspond to predictions based on a mathematical model (lines; adapted from Rodriguez-Brenes and Peskin with permission99) but show more pronounced skewing. (B) Snapshots of Q-FISH images of chromosomes X and 17 (also hybridized with a Chr17-specific probe) from individual metaphase cells of different diploid fibroblasts clones. For details see Martens et al,28 Asterisks indicate sporadic loss of telomere repeats on specific chromosome arms. Q-FISH, quantitative fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Limitations of mouse models
The initial study of mice without telomerase suggested that telomerase is not essential for survival.31 The first generation of such mice appeared to be healthy, fertile, and without a clear phenotype. However, with each generation ∼5 kb of telomere repeats was lost, and a distinct phenotype, including infertility and characteristic chromosome fusions, was observed after 4 to 6 generations.31 Together, these findings support that telomerase is essential for maintaining telomeres, that telomere length is not linked to aging in the mouse, and that telomerase pathology is driven by loss of telomere repeats and not by other functions of telomerase. The same conclusion was reached in studies of Tert knockout mice.32 The long telomeres in most laboratory mice and the delayed phenotype in the absence of telomerase have greatly complicated the extrapolation of findings in the murine model to human telomere biology.33
Telomerase expression in human somatic cells
Whereas telomerase expression maintains the length of telomeres to support unlimited proliferation of embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent cells, telomerase levels in most human somatic cells are downregulated upon differentiation by mechanisms that include transcriptional silencing34 and alternative splicing24 of the telomerase reverse transcriptase gene TERT. By limiting telomerase levels, most human somatic cells show progressive telomere shortening, first described more than 30 years ago and described in several reviews.10,33,35TERT was cloned and expressed in human fibroblasts.4 This prevented telomere shortening, as well as replicative senescence, providing an important mechanistic link between telomere loss and replicative senescence. Whereas telomerase activity is difficult to detect in human fibroblasts, purified “candidate” hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and lymphocytes express low telomerase levels.36,37 The role of this telomerase activity was puzzling, given the observed loss of telomeric DNA in these cells.38,39
Loss of telomere repeats in human leukocytes
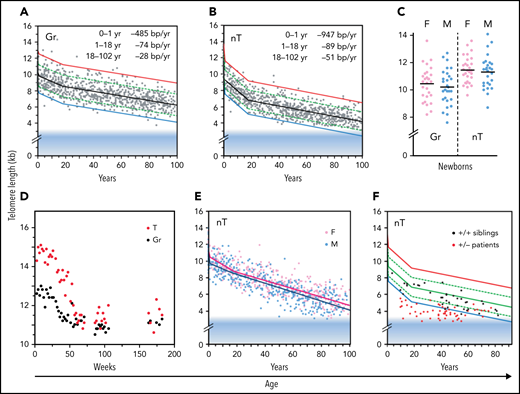
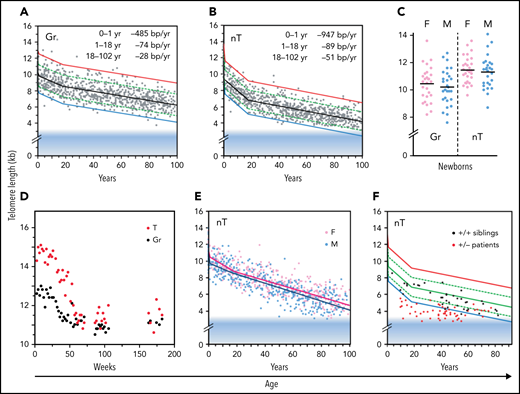
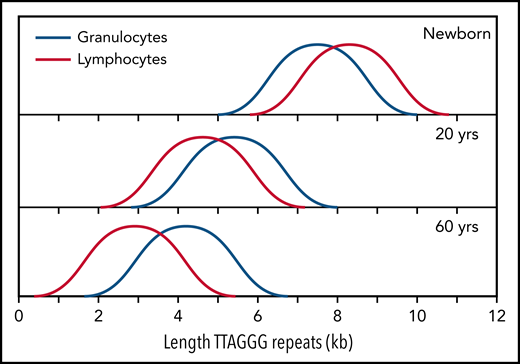
The median telomere length in granulocytes, lymphocytes, and some lymphocyte subsets can be measured using fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometry (flow FISH).40 With this method, it was found that the age-related decline in the telomere length in leukocytes from humans and baboons is not linear in time and is markedly different between cell types.41,42 Key findings are shown in Figure 2 and are summarized in Figure 3. When the telomere length in granulocytes is used as an indirect reporter of the telomere length in HSC (assuming a relative constant number of cell divisions between HSCs and granulocytes), cell division in HSCs appears in rapid succession only in the first year(s) of life (Figure 2A-D).41,42 This is most clearly shown in leukocyte telomere length data collected biweekly from a newborn baboon (Figure 2D). In both humans and baboons, the telomere length at birth was longer in T cells than in granulocytes (Figures 2A-D and 3). However, this difference is reversed by the second year of life, presumably because, by then, T cells have accumulated more cell divisions than HSCs. After puberty, telomeres shorten in granulocytes at a rate of only 28 bp per year. At any given age there is a large variation in the average telomere length between individuals (Figures 2A-B and 3) with females having, on average, longer telomeres than males, both at birth (Figure 2C) and throughout life (Figure 2E).42,43 Of all leukocytes, memory T cells and NK cells show the most pronounced decline in telomere length with age, whereas telomeric DNA is lost in most but not all B cells at a rate that is similar to loss in granulocytes.40,42
Loss of telomere repeats with age in leukocytes. Adapted, with permission, from Baerlocher et al41 and Aubert et al.42 (A-B) Telomeric DNA in human granulocytes (Gr, n = 808) and naive T cells (nT, n = 832) from normal human donors is lost most rapidly in the first year of life, slows down after puberty, and is more pronounced in T cells than in granulocytes. The range in distribution of telomere length at a given age is expressed as a percentile based on best fit regression lines: 99th (red), 90th (green), 50th (black), 10th (green) and 1st (blue). The shaded blue area reflects ∼3 kb of subtelomeric DNA included in calculated values to allow comparisons with telomere length estimates by terminal restriction fragment (TRF) analysis. (C) The median telomere length in human granulocytes and naive T cells in female (pink; n = 29) vs male (blue; n = 29) cord blood samples. (D) The decline in telomere length in nucleated blood cells from a baboon was nonlinear and showed a pronounced drop after 1 year. (E) In humans, naive T cells from females (n = 414) have, on average, longer telomeres compared with those in males (n = 418). (F) Patients heterozygous for a mutation in either TERT or TERC (n = 58) have very short telomeres compared with siblings (n = 37) without the mutation.
Loss of telomere repeats with age in leukocytes. Adapted, with permission, from Baerlocher et al41 and Aubert et al.42 (A-B) Telomeric DNA in human granulocytes (Gr, n = 808) and naive T cells (nT, n = 832) from normal human donors is lost most rapidly in the first year of life, slows down after puberty, and is more pronounced in T cells than in granulocytes. The range in distribution of telomere length at a given age is expressed as a percentile based on best fit regression lines: 99th (red), 90th (green), 50th (black), 10th (green) and 1st (blue). The shaded blue area reflects ∼3 kb of subtelomeric DNA included in calculated values to allow comparisons with telomere length estimates by terminal restriction fragment (TRF) analysis. (C) The median telomere length in human granulocytes and naive T cells in female (pink; n = 29) vs male (blue; n = 29) cord blood samples. (D) The decline in telomere length in nucleated blood cells from a baboon was nonlinear and showed a pronounced drop after 1 year. (E) In humans, naive T cells from females (n = 414) have, on average, longer telomeres compared with those in males (n = 418). (F) Patients heterozygous for a mutation in either TERT or TERC (n = 58) have very short telomeres compared with siblings (n = 37) without the mutation.
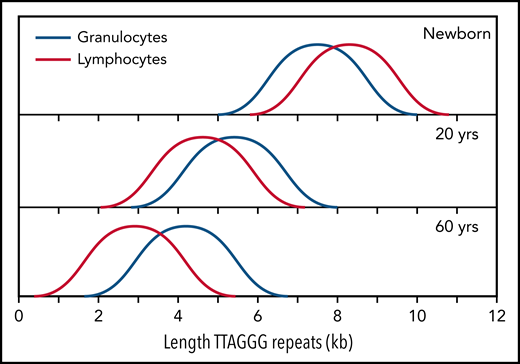
Normalized telomere length distribution in lymphocytes and granulocytes from normal, healthy individuals at the indicated ages. Data for schematic distributions are shown in Figure 2. Calculated length of telomere repeats rather than data compatible with terminal restriction fragment (TRF) results are shown by subtraction of 3 kb of subtelomeric DNA (included in TRF values and data shown in Figure 2). Note that the age-related decline in telomere length is not linear over time and is more pronounced in lymphocytes than in granulocytes.
Normalized telomere length distribution in lymphocytes and granulocytes from normal, healthy individuals at the indicated ages. Data for schematic distributions are shown in Figure 2. Calculated length of telomere repeats rather than data compatible with terminal restriction fragment (TRF) results are shown by subtraction of 3 kb of subtelomeric DNA (included in TRF values and data shown in Figure 2). Note that the age-related decline in telomere length is not linear over time and is more pronounced in lymphocytes than in granulocytes.
The role of telomerase in bone marrow cells and lymphocytes
Clinical studies have shown that haploinsufficiency for either the telomerase RNA template gene (TERC) or TERT can result in bone marrow failure,44 pulmonary fibrosis45 and other disease manifestations in a clinically and genetically diverse spectrum of telomere biology disorders (reviewed by Niewisch and Savage46). The finding that a modest twofold reduction in telomerase levels can cause bone marrow failure in humans was a surprise, in view of the findings in the telomerase knockout mouse. Apparently, telomerase levels in human HSCs, although insufficient to prevent the loss of telomere repeats with replication and with age, are nevertheless crucial in limiting the rate of telomere attrition in HSCs and in preventing premature loss of HSCs. These effects are illustrated by comparing the leukocyte telomere length from patients with heterozygous mutations in either TERC or TERT with those of their unaffected siblings (Figure 2F). One possibility is that both TERC and TERT must be expressed from both alleles to produce sufficient telomerase to repair a limited number of short telomeres in HSCs. Failure of telomere repair could trigger apoptosis in HSCs, initiating a feed-forward loop of compensatory cell divisions in the remaining HSCs, shorter telomeres (Figure 2F), and more telomere failure, among other effects that end in loss of all HSCs. Whereas bone marrow failure is the most prominent phenotype in young patients, the most common clinical manifestation of telomerase haploinsufficiency in patients past puberty is pulmonary fibrosis.45 Whether the lung pathology in older patients reflects loss of lung epithelial cells or other cell types remains to be clarified.
Cell division in HSCs
The number of times stem cells in self-renewing tissues divide over a lifetime is not known. Erwin Schrödinger predicted in 1944, “We infer by an easy computation that on average as few as 50-60 successive divisions suffice to produce the number of cells in a grown man (very roughly a hundred or a thousand × 1012) or say, ten times that number, taking into account the exchange of cells during a lifetime. Thus, a body cell of mine is, on average, only the 50th or 60th ‘descendant’ of the egg that I was.”47,(p22) This conservative estimate is in sharp contrast to recent publications suggesting that stem cells divide many more times.48,49 It is possible, perhaps even likely, that all somatic stem cells are organized in an economical, hierarchical manner, not only to conserve energy but also to limit the risk of malignant transformation, as will be discussed later. Fetal human fibroblasts can divide a maximum of 40 to 60 times in vitro (the “Hayflick limit”)50 and the replicative potential of HSCs could be in the same range. With each round of replication, human fibroblasts lose 50 to 150 bp of telomeric DNA.28 At this rate, adult HSCs are expected to divide only once every few years, given that telomeric DNA in granulocytes is only lost at a rate of only 28 bp per year42 (Figure 2A). Very infrequent cell divisions in HSCs and their immediate progeny is compatible with the daily production of hundreds of billions of specialized blood cells by assuming a deep hierarchy of progressively more numerous and more rapidly dividing cells.51 The production of CD34+ cells in tissue culture declines rapidly during development52 and coincides with a decline in telomere length.39 The number of HSCs actively making white blood cells in an adult was recently estimated to be in the range of 50 000 to 200 000.53 Further studies are needed to elucidate how cell divisions in HSCs are regulated and distributed over a lifetime. Such studies are complicated by the very low frequency and proliferation rate of HSC in adult bone marrow. Whether all stem cells, including those in the digestive system and testis, are organized in an economical hierarchy is subject to debate.54,55
DNA damage and aging
Support for a central role of DNA damage in aging was recently summarized.3 Both endogenous and exogenous compounds can damage DNA. Reactive oxygen species and other compounds generated by metabolism and respiration cause damage to many biological molecules, including DNA.56 Oxygen radicals are also implicated in loss of telomeric DNA.57,58 Lowering the oxygen tension in tissue culture decreases the rate of telomere loss in fibroblast and increases their replication potential,59 possibly by reducing the sporadic loss of telomere repeats (Figure 1B). In addition to endogenous damage, DNA can be damaged by exogenous sources illustrated by the increased mutation burden in bronchial epithelial cells from smokers.60 Even error-free repair of DNA lesions can alter gene expression in cells by changing the chromatin environment or the “epigenome” around DNA repair events.61 The role of such “epimutations” next to actual DNA mutations in the deregulation of gene expression,62 and the increased transposon activity63 in cells from “old” tissues is currently not clear. Future studies should look at the role of all genomic rearrangements that may accumulate in cells over time, including repeat instability, transposition events and other structural genomic rearrangements including translocations, deletions, duplications, insertions, and inversions. Ideally, all such events should be studied at the level of single cells in thousands of cells from various tissues over a lifespan.
DNA mutations and aging
Most human somatic tissue cells acquire 10 to 40 point mutations per year.6 To consider the role of such mutations in aging, a distinction should be made between neutral, loss-of-function, and gain-of-function mutations, as well as their consequences for dividing vs nondividing cells. Most mutations are expected to have no or minimal functional consequence as most genomic DNA is noncoding. Biallelic gene expression typically ensures that a loss-of-function mutation in a nondividing cell will have only mild or no functional effect. Gain-of-function mutations in nondividing cells are also not expected to affect overall tissue function, because most human tissues are composed of billions of cells. In contrast, a single loss- or gain-of-function mutation in a stem cell can provide a growth advantage to a cell. The risk of a second mutation providing a further growth advantage in such a cell increases rapidly, given enough time, even when the number of cell divisions is limited. For example, assuming 1 cell division and 20 mutations per cell per year in a stem cell with an initial mutation that provides a growth advantage, only 10 “self-renewal” cell divisions over 10 years will result in 20 × 103 mutations divided over 1000 cells, and 20 cell divisions in 20 years will result in 20 × 106 mutations distributed over a million cells. More rapid and more numerous cell divisions could make malignant progression very likely, especially when errors during DNA replication, which can give rise to large genomic rearrangements with major functional consequences, are also considered. Of course, not all cell divisions in stem cells are exponential self-renewal divisions. However, the argument also holds for the more numerous and more rapidly dividing progeny of stem cells, especially when the original mutation shortens the cell cycle or impedes differentiation. Based on these considerations, I propose that without increasing the efficiency of DNA repair to reduce the mutation rate, lifespan could only increase by imposing a limit to the number of times stem cells are allowed to divide. This proposition agrees with long-held views that telomere loss acts to suppress tumor growth, as reviewed in several publications,35,64-66 and the reported correlations between lifespan and telomerase suppression in rodents67 and larger mammals.68
Telomere loss: an imperfect tumor suppressor mechanism
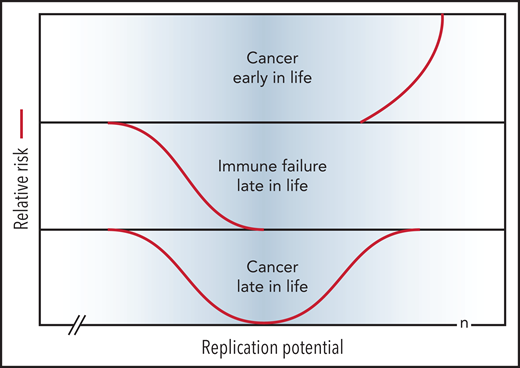
A review of the extensive literature on the role of telomeres and telomerase in cancer is beyond the scope of this perspective and the reader is referred to several excellent reviews.35,64-66 Telomere repeats are lost in most primary human cells with replication in vitro69 and with age in vivo (reviewed in Demanelis et al70), illustrated for human leukocytes in Figures 2 and 3. Limiting telomerase levels in somatic cells results in loss of telomeric DNA with each cell division, which acts as an important, albeit clearly imperfect, tumor suppressor mechanism. Both long and short telomeres increase the risk of cancer via distinct, but partially overlapping, mechanisms as discussed below. The proposed relationship between replication potential, telomere length, and relative cancer risk is shown in Figure 4.
Short telomeres reduce the risk of cancer early in life at the expense of impaired regeneration late in life. Genetic variation in telomere length between humans is shown in blue. The TEDS theory of aging proposes that telomere erosion allowed lifespan to increase by suppressing the growth of malignant tumors before reproduction. Telomere loss has pleiotropic detrimental effects late in life by limiting cell renewal in the immune system and other tissues. Long and short telomeres increase the risk of cancer late in life via distinct, but partially overlapping, mechanisms (see text for details). Note that the rate of telomere loss depends, not only on cell divisions, but also on damage to telomeric DNA and variable levels of telomerase. The replication potential or maximum number of cell divisions (n) in stem cells is not known but is predicted to be less than 100 by TEDS: 50 to 60 divisions predicted by Schrödinger47 plus 0 to 40 additional cell divisions to account for stem cell renewal over a lifetime.
Short telomeres reduce the risk of cancer early in life at the expense of impaired regeneration late in life. Genetic variation in telomere length between humans is shown in blue. The TEDS theory of aging proposes that telomere erosion allowed lifespan to increase by suppressing the growth of malignant tumors before reproduction. Telomere loss has pleiotropic detrimental effects late in life by limiting cell renewal in the immune system and other tissues. Long and short telomeres increase the risk of cancer late in life via distinct, but partially overlapping, mechanisms (see text for details). Note that the rate of telomere loss depends, not only on cell divisions, but also on damage to telomeric DNA and variable levels of telomerase. The replication potential or maximum number of cell divisions (n) in stem cells is not known but is predicted to be less than 100 by TEDS: 50 to 60 divisions predicted by Schrödinger47 plus 0 to 40 additional cell divisions to account for stem cell renewal over a lifetime.
Long telomeres increase cancer risk
Long telomeres predispose to various cancers, including melanoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia in cancer-prone families.71,72 Several genome-wide association studies have linked both rare and common single-nucleotide variants to long telomeres and increased cancer risk (reviewed by McNally et al71 and Haycock et al73). Longer telomeres in leukocytes were found to be a significant risk factor for the development of myeloproliferative neoplasms.74 Collectively, these findings support that longer telomeres enable more cell divisions in stem cells before telomere erosion limits further proliferation. With each additional cell division, the probability of additional mutations driving tumor progression can increase exponentially.
Short telomeres also increase cancer risk
Starting life with shorter-than-average telomeres also increases the risk of developing cancer the “telomere paradox.”75 Patients with mild telomerase deficiency or other forms of telomere biology disorders have very short telomeres and an increased risk of developing myelodysplastic syndrome, acute myeloid leukemia, and various other malignancies (reviewed by Niewisch and Savage46). Most likely, tumor formation in such patients and individuals with shorter than average telomeres results from (1) strong selection for abnormal stem cells after loss of normal stem cells and (2) eventual failure of tumor suppression by progressive telomere erosion. Further studies are needed to map the signals and pathways that stimulate the proliferation of stem cells in response to a decrease in the number of stem cells. More is known about the pathways by which tumor cells evade tumor suppression by progressive telomere erosion, as reviewed in several publicaions.35,64-66 Telomerase activity is upregulated in >70% of human cancers by TERT point mutations, rearrangements, DNA amplifications, and transcript fusions.76,77 Mutations in the promotor of TERT are among the most frequent noncoding mutations in cancer.78,79 Such mutations increase TERT expression and increase the replicative potential of cells.34 Limits to cell proliferation imposed by progressive telomere erosion are avoided altogether in cells with corrupted DNA damage responses (eg, by loss of p53).9,10,33 Once p53 is lost, tumor progression typically accelerates, as chromosomes without telomeres are highly unstable, facilitating genetic rearrangements (reviewed by Shay and Wright10 and Maciejowski and deLange35). Loss of p53 typically occurs late in tumor development, and the telomere length in tumor cells correlates with disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and possibly other tumors.80,81
Telomere length and clonal hematopoiesis
Clonal hematopoiesis (CH), with and without candidate driver mutations, is very common in the elderly.82,83 Between 10% and 20% of persons older than 70 years harbor a clone of appreciable size in nucleated blood cells and clones of variable size are seen in many tissues in association with aging.84 The germline risk of CH is associated with long74,85,86 and short86 telomeres. Unexplained anemia is common in the older population, and its prevalence rises rapidly with advancing age.87 The possibility that anemia and CH in normal individuals with short telomeres is comparable to the loss of HSCs in patients with mild telomerase deficiency warrants further study.
Telomere length and immune function
The progressive loss of telomere repeats in lymphocytes with age (Figures 2 and 3) is likely to compromise innate and adaptive immune responses in the elderly.88 Leukocyte telomere length has been reported to be a heritable biomarker of genomic aging,89 and short telomeres in leukocytes are associated with adverse COVID-19 outcomes, independent of several major risk factors for COVID-19, including age.90 The precise role of telomeres in immune senescence and aging remains to be clarified. Studies in this area are complicated by the limitations of current telomere length measurements as well as the challenge of defining the phenotype and function of various immune cells. A further complication is that cells of interest may be lost for study because DNA damage signals from short telomeres could trigger apoptosis rather than senescence. The role of NK cells and T cells in suppressing tumor growth is increasingly appreciated.91,92 The loss of lymphocytes could synergize with accumulated mutations to increase cancer risk with age (Figure 4). Short telomeres and senescence in endothelial cells93 could also synergize with loss of immune cells, perhaps explaining the association between short telomeres and cardiovascular disease.94-96
Conclusions
Aging is characterized by a progressive loss of physiological integrity, leading to impaired function and increased vulnerability to death.97 DNA damage resulting from endogenous and exogenous sources can cause cell death or result in mutations that compromise cell and tissue function.3 Given enough time and enough cell divisions, random mutations in stem and progenitor cells can also cause cancer. The TEDS hypothesis of aging proposes that genetic variants that decreased telomerase activity in somatic cells provided a selective advantage that allowed lifespan to increase by decreasing the risk of malignant transformation. Limited renewal of cells, imposed by progressive telomere loss, has pleiotropic deleterious effects late in life, including impaired immune responses and the accumulation of senescent cells, which are known to contribute to aging.98 Both DNA damage and telomere erosion can cause loss of cells and cell senescence. Future studies should clarify the relative role of each of these mechanisms in the aging of various human tissues.
Since the time of Weismann’s prescient ideas about the role of the germline and soma in reproduction and the role of mechanical wear and the counting of cell divisions in ageing, great strides have been made in all areas of biology. In the process of understanding more about telomere biology, the picture has also become more complicated, with differences in telomerase expression between cells and tissues, not only during development but also between humans and between species. The idea that loss of telomeric DNA in human cells, first described more than 30 years ago, represents a tumor suppressor mechanism has been proposed many times. However, the idea has not stuck, in part because telomere loss is not obvious in model organisms used in aging research such as worms and mice. Prevalent notions about the nature of stem cells and the number of times stem cells divide over a lifetime represent additional obstacles to the idea that telomere loss plays a major role in human aging. By measuring the telomere length and the number of mutations in different cells from different species over their lifespan, it should be possible to resolve current uncertainties in the near future.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Geraldine Aubert, Olga Lansdorp, and anonymous reviewers for critically reading the manuscript and helpful suggestions. The author apologizes to all researchers whose work was not mentioned or discussed. Every topic in the paper would have to be expanded enormously to provide a more complete overview of all relevant work. Unfortunately, such an extension would have greatly complicated the communication of the major points that the author wanted to make. Readers are referred to the references that are included to obtain a deeper understanding of topics.
Work in the author’s laboratory is funded by a Program Project Grant (#1074) from the Terry Fox Research Institute, a Project Grant (#PJT-159787) from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and a grant (#40044) from the Canadian Foundation for Innovation and the Government of British Columbia.
Authorship
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author is a founding shareholder of Repeat Diagnostics Inc, a company specializing in clinical telomere length measurements since 2006.
Correspondence: Peter M. Lansdorp, BC Cancer Research Institute, 675 W. 10th Ave, Vancouver, BC V5Z1L3, Canada; e-mail: plansdor@bccrc.ca.