Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
Telomeres, aging, and cancer: the big picture
Lansdorp contributes a personal perspective that reviews the literature around telomeres and aging and proposes a model that synthesizes data from mice and humans in conjunction with evolutionary theory. Differences in average telomere length between humans and between cell types help explain differences in the risk of developing cancer and other age-related diseases. These ideas are captured in the “telomere erosion in disposable soma” theory of aging proposed here.
REVIEW ARTICLE
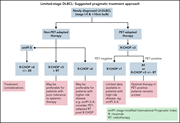
Limited-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Approximately one-fourth of all patients diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) have localized (or limited-stage) disease. Hawkes et al provide a comprehensive review of biological characteristics and treatment options for these patients, including those being managed in resource-constrained areas where access to positron emission scanning is not possible.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
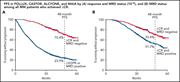
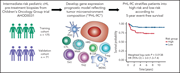
Prognostic value of minimal residual disease negativity in myeloma: combined analysis of POLLUX, CASTOR, ALCYONE, and MAIA
Clinical Trials & Observations
Cavo et al confirmed the prognostic value of uniformly conducted prospective minimal residual disease (MRD) assessments with next-generation sequencing in multiple myeloma (MM) through a robust analysis of pooled data of 2510 patients from 4 recent phase 3 registrational studies. This report is timely, as MRD negativity using highly sensitive assays is being explored as a potential surrogate endpoint in clinical trials to accelerate drug approval and to guide future treatment strategies for MM.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
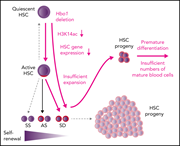
The histone lysine acetyltransferase HBO1 (KAT7) regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and self-renewal
Histone acetylation acts to unfold chromatin to facilitate DNA access for replication or transcription. By analyzing two mouse models, Yang and colleagues revealed the importance of HBO1, an enzyme that establishes acetylation of histone 3 lysine 14, to maintenance of the blood system. They established that HBO1 promotes hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) quiescence and self-renewal, thereby protecting against HSC exhaustion. This study provides data that could inspire the development of new epigenetic modulators for therapeutic purposes.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
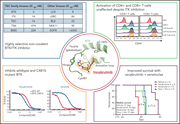
Evaluation of vecabrutinib as a model for noncovalent BTK/ITK inhibition for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
A gene expression–based model predicts outcome in children with intermediate-risk classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Johnston et al demonstrate differences in gene expression between pediatric and adult classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL), finding that eosinophil, B-cell, and mast cell signatures were enriched in children while macrophage and stromal cell signatures were more prominent in adults. They also developed and validated a gene expression profile–based model reflective of the tumor microenvironment biology, but independent of clinical features, that predicts event-free survival in pediatric patients. This model may be applicable for use in future clinical trials.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
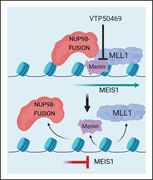
The menin-MLL1 interaction is a molecular dependency in NUP98-rearranged AML
Effective therapy for AML with RUNX1 mutation by cotreatment with inhibitors of protein translation and BCL2
Mutant RUNX1 (mtRUNX1), either somatic or germline, is associated with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Mill and colleagues used cell line and murine models to document that mtRUNX1 AMLs exhibit impaired ribosomal biogenesis and increased sensitivity to protein translation inhibitors, such as omacetaxine. Omacetaxine represses c-MYC, MCL1, and BCL-xL and is additive when combined either with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax or with BET inhibitors, suggesting a strategy for future clinical evaluation.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
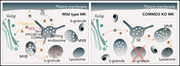
Syntaxin 12 and COMMD3 are new factors that function with VPS33B in the biogenesis of platelet α-granules
Platelet α-granules are lysosome-related organelles loaded with hundreds of proteins that are either synthesized by megakaryocytes or internalized via endocytosis. Ambrosio et al identified 3 proteins and complexes that contribute to platelet α-granule biogenesis. Their work greatly advances knowledge into how cargos are packaged and how megakaryocytes repurpose the ubiquitous endosome retrieval and recycling machinery for trafficking of α-granule proteins.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
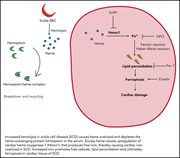
Excess heme upregulates heme oxygenase 1 and promotes cardiac ferroptosis in mice with sickle cell disease
Brief Report
Using a murine model of sickle cell disease (SCD), Menon et al show that excess circulating free heme upregulates cardiac heme oxygenase 1, resulting in increased cardiac nonheme iron and lipid peroxidation leading to ferroptosis and impaired cardiac function. These findings reveal an important mechanism underlying cardiac complications in SCD and provide the potential for novel interventional approaches for cardioprotection in patients with SCD.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Anti-CD38 therapy impairs SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response against alpha and delta variants in patients with multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Redefining nonmeasurable multiple myeloma using mass spectrometry
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Bone marrow failure in mice lacking the histone acetyltransferase HBO1. This is due not to cell death, but rather to loss of stem cell quiescence and premature differentiation leading to depletion of the stem and progenitor cell pools. See the article by Yang et al on page 845.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





MRD end point in myeloma: ready for prime time?
Clinical Trials & Observations