Abstract
There is a need to determine whether culture conditions may exist for ex vivo expansion of hematopoeitic stem cells (HSC), which favor solely proliferative self-renewal of HSC as opposed to proliferation with differentiation. Using single cells, we studied the effects of individual and combinations of cytokines in serum-free medium on the kinetics of the first cell doubling and the resulting phenotype of each of individual daughter cell. CD34+Thy-1+lin−cells were plated 1 cell per well in Terasaki plates in serum-free medium containing cytokines. Each well containing a single cell was monitored daily over 7 days for maintenance, division, or death. When division occurred in an individual well, the phenotype of the daughter cells was determined by staining with anti-CD34 fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)- and phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated lineage specific antibodies. The cumulative percent of wells with an undivided single cell, wells in which the cell had divided, and wells in which the cell had died were scored. The number of doublets with conserved phenotype (CD34+lin−) was compared to those wells with one or more differentiated daughter cells (CD34+lin+). Over 7 days, cells cultured in single factors showed that between 13% (interleukin-6 [IL-6]) and 29% (thrombopoietin [TPO]) of the cells were undivided, between 13% (IL-1) and 35% (TPO) of the cells doubled, and between 35% (TPO) and greater than 60% (IL-11, IL-1, or hepatocyte growth factor [HGF]) died. When combinations of cytokines were used over 7 days, between 5% (FLT-3 ligand [FLT-3L], stem cell factor [SCF], IL-3, IL-6, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor [G-CSF], β nerve growth factor [βNGF]) and 22% (FLT-3L + HGF) of the cells remained undivided, between 15% (HGF, IL-1, IL-11, G-CSF) and 68% (SCF + TPO) of the cells had doubled and between 27% (FLT-3L + TPO) and 70% (HGF, IL-1, IL-11, G-CSF) died. The combination of FLT-3L + TPO induced the highest total percent (64.6%) of cells with conserved phenotype (percent conserved doublets + percent with 1 cell conserved), followed by SCF + TPO, (50%) and the combination of FLT-3L, SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, βNGF (53%). These combinations also produced the highest yield of cells with conserved phenotype after one division (FLT-3L + TPO − 81 cells/100 initial cells, SCF + TPO − 68 cells/100 initial cells) (P = .01). Observation of the time of the initial cell division and phenotype of the daughter cells allowed us to identify candidate combinations of cytokines that promote maintenance of lin− cells (TPO), or recruit the primitive cells to divide and undergo phenotypic self-renewal (FLT-3L + TPO, SCF + TPO).
THE INCREASED clinical indications for bone marrow transplantation (BMT) and progress in gene therapy have led to a critical need to expand hematopoietic stem cells in vitro. Recent improvements in the ability to enrich stem cells from human BM, peripheral blood (PB), or umbilical cord blood (CB) do not increase the number of stem cells available. Progress toward extending the usefulness of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has been limited by lack of sufficient understanding of what is required to induce stem cell self-renewal or even to maintain stem cells in a “noncommitted” state in vitro. Studies of human stem cells, in particular, have been limited by lack of definitive (exclusive) phenotypic characterization, or assays that can be feasibly applied and agree with other assays. Stem cells in vivo are maintained as a very minor population of the whole BM and are not amplified except after severe depletion. This situation in vivo is very different from the goal of efforts to expand stem cells in vitro, which is to amplify stem cells while preventing differentiation and then possibly to direct differentiation to a chosen lineage.
Although the precise cell-surface phenotype of the human hematopoietic stem cell remains a subject of debate, it is generally agreed that stem cells are among the CD34+lin− fraction of cells from BM, PB, or CB. Culture of CD34+lin− cells in combinations of recombinant cytokines has resulted in a significant increase in cell numbers without loss of the ability to reconstitute myeloablated hosts.1-3 However, the extent of expansion of true stem cell numbers in these large pools of expanded cells remains to be determined. The need to expand and maintain human stem cells in vitro has led to development of methods for greatly enriching primitive cells, identification of recombinant cytokines that influence their behavior, and several assays for primitive cells.
Past interest has been on identifying which growth factors are able to stimulate proliferation and differentiation, whereas current focus is on what cytokines allow primitive and progenitor cells to remain viable. In particular, FLT-3 ligand (FLT-3L) has been shown to have a direct effect on primitive hematopoietic cells from both mice and humans,4-14 is synergistic with other growth factors, and the yield of primitive cells can be increased with use of FLT-3L in cultures. Studies by Haylock et al10showed that FLT-3L recruited more CD34+CD38− cells into division, and that transduction of these cells was enhanced by FLT-3L. Stem cell factor (SCF) has been shown to be effective in promoting viability of progenitor cells in culture,11,15-17 but to varying degrees. Borge et al18 showed that thrombopoietin (TPO) was more efficient in promoting viability of primitive cells than SCF, and that it was effective in suppressing apoptosis. Other recent studies19-22 support the fact that TPO plays role in supporting the survival of primitive cells, in addition to its effects on megakaryocyte development.23 When TPO is used in combination with other early acting growth factors, such as SCF or FLT-3L, the effect is more prolonged, in vitro, maintenance and expansion of primitive populations of cells from mice4,24,25 and humans.26-32Piacibello et al9 showed that with the combination of FLT-3L and TPO, CB CD34+ cells could be expanded and continue to produce committed progenitors for more than 6 months. Using the combination of FLT-3L, TPO, and SCF, Solar et al33reported an increase in total cells over 8 weeks in culture and that 28% of these cells were CD34+CD38−. With the addition of interleukin-6 (IL-6) to TPO, SCF, and flk2/flt3 ligand, Murray et al34 reported less expansion of BM CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells over 6 days than without IL-6, but a higher percent of cells retaining Thy-1. In a recent study by Luens et al,35 it was shown that the combination of TPO, flk2/flt3 ligand (FL), and c-kit ligand (KL) stimulated the majority of the CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells in their cultures to divide with little loss of CD34 or Thy-1 expression.
Although these questions are provocative, the question remains as to whether the numbers of true stem cells can be expanded significantly in vitro. A key to answering this question is the ability to detect stem cell self-renewal in vitro. Because daughter cells from the first doubling can produce other cytokines with negative regulatory capacity and can, therefore, limit stem cell self-renewal, we have studied the fate of single human umbilical CB CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells in serum-free medium containing different combinations of recombinant cytokines. We investigated how selected cytokines affect the kinetics of proliferation of single CD34+Thy 1+lin− cells and the ability of these cells to self-renew in vitro. In this study we show that TPO as a single factor can support the survival of CD34+lin− cells, and that it can interact with FLT-3L and SCF to promote doubling and phenotypic self-renewal of primitive cells. Our data provide evidence of phenotypic self-renewal or differentiation that can be detected as early as the first cell division. Significant variation in the frequencies of phenotypic self-renewal of single cells is obtained depending on the cytokine combination used. These studies provide basic information on both the heterogeneity of human cord blood CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells after one division and support use of single cell culture methods for identifying conditions that support/induce the self-renewal of a subset of these cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Hematopoietic Growth Factors
Recombinant human hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) was generously supplied by Dr G.K. Michalopoulos (University of Pittsburgh). All other recombinant growth factors were purchased from PeproTech, Inc (Rocky Hill, NJ). Unless indicated otherwise, growth factors were used at the following concentrations: FLT-3L 50 ng/mL; TPO, 10 U/mL; IL-1, 10 ng/mL; SCF, 50 and 100 ng/mL; HGF, 1 ng/mL; IL-6, 20 ng/mL; IL-11, 10 ng/mL when used singly. When multifactor combinations were used the concentrations were as follows: the combination of FLT-3L 100 ng/mL, SCF 100 ng/mL, IL-3 20 ng/mL, IL-6 20 ng/mL, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) 20 ng/mL, β nerve growth factor (βNGF) 5 ng/mL; the combination of SCF 100 ng/mL, IL-3 100 ng/mL, IL-6 10 ng/mL, G-CSF 30 ng/mL, granulocyte-macrophage (GM)-CSF 20 ng/mL; the combination of HGF 1 ng/mL, IL-1 10 ng/mL, IL-6 or IL-11 10 ng/mL, G-CSF 20 ng/mL; FLT-3L 50 ng/mL + TPO 10 U/mL; FLT-3L 50 ng/mL + HGF 1 ng/mL; SCF 50 ng/mL + TPO 10 U/mL.
CD34+ Cell Isolation
Human umbilical CB samples were obtained immediately after delivery in accordance with institutional guidelines, and placed in 50-mL tubes containing ACD-A (Cytosol Labs, Braintree, MA). Low-density mononuclear cells were isolated by Ficoll-Paque (1.077 g/mL) density gradient centrifugation (Pharmacia Biochem, Piscataway, NJ). CD34+progenitor cells were isolated by immunomagnetic selection techniques, as previously described.36 Briefly, cells were incubated with blocking reagent and anti-CD34 antibody at 4°C, then washed in phosphate-buffered saline/anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution-A (PBS/ACD-A) followed by incubation with a secondary antibody-magnetic microbead conjugate at 4°C. The unlabeled fraction of CD34− cells were separated from the labeled CD34+ fraction on a high gradient magnetic separation column (Miltenyi Biotec, Sunnyvale, CA). The percentage of CD34+ cells was determined by flow cytometric analysis.
Enrichment of CD34+Thy-1+lin− Cells
CD34+ cells initially isolated by immunomagnetic selection were labeled with a mixture of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-CD34 (HPCA-2) (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA), Thy-1(anti-CDw90) (Pharmingen, San Diego, CA), and phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated antilineage markers, including the following: anti-CD3, CD11b, CD19, CD33, CD38, CD56, and HLA-DR (Becton Dickinson); and anti–glycophorin A antibodies (Dako Corp, Carpenteria, CA). FITC and PE isotype-matched mouse IgG1 and IgG2a were used as controls. Labeled cells were washed and resuspended in PBS + 2% fetal calf serum (FCS) for sorting. Cells were sorted using a Becton Dickinson FACStar Plus flow cytometer. Viability of the CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells after sorting as determined by Trypan blue dye exclusion was greater than 95%.
Single-Cell Culture and Growth Kinetics
CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells were plated at a density of 1 cell/well in Terasaki plates in 15 μL serum-free medium. Iscove’s medium was supplemented with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA), 10 μg/mL insulin, 200 μg/mL transferrin (Stem Cell Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada), 10−4 mol/L 2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma, St Louis, MO), 40 μg/mL low-density lipoproteins (Bayer Corp, Kankakee, IL), 2 mmol/L glutamine, 50 μg/mL streptomycin, 50 U/mL penicillin (GIBCO, Gaithersburg, MD), and selected recombinant growth factors as described above. The initial number of cells, in each well, in all plates was verified by light microscopy, and only those wells that contained one viable cell were included. Each well containing a single cell was observed daily for up to 7 days for evidence of maintenance (cell is viable, but undivided), cell doubling, or cell death. Characteristic morphology using phase contrast microscopy was used for identification of viable cells on days 1-7. CD34+ cells were plated in parallel, monitored daily, and stained for phenotype as were the lin− cells; these cells served as a positive control for fluorescence detection (data not shown). Cells that remained undivided over the 7 days were tested for viability using Trypan blue dye exclusion.
Phenotypic Analysis of Individual Daughter Cells
The wells in which a single cell had divided were stained with FITC–anti-CD34 and PE antilineage antibodies for phenotype assessment of the daughter cells. The media were removed from each well containing a cell doublet and replaced with 7 μL of the FITC/PE antibody cocktail. The antibodies were used at a predetermined optimal concentration for each individual antibody (range of protein concentration, 0.2 μg/mL to 1 μg/mL). After incubation for 15 to 20 minutes at 4°C, each well was washed three times with 13 μL of PBS + 2% FCS. The phenotype of each individual daughter cell of the cell doublet was scored, by the same observer each day, based on detection (by eye) using epifluorescence microscopy immediately after staining. Each of four different phenotypes possible for each cell in the doublet was observed: 1, FITC+(34+lin−); 2, PE+(34−lin+); 3, FITC+/PE+ (34+lin+); 4, FITC−/PE−(34−lin−). The frequency of each phenotype (conserved doublet, both daughter cells CD34+lin− [phenotypic self-renewal] or differentiated, one or two differentiated cells) was determined.
Statistics
Statistical significance was determined using the Student’st-test or Exact Confidence Limits for binomial distributions.
RESULTS
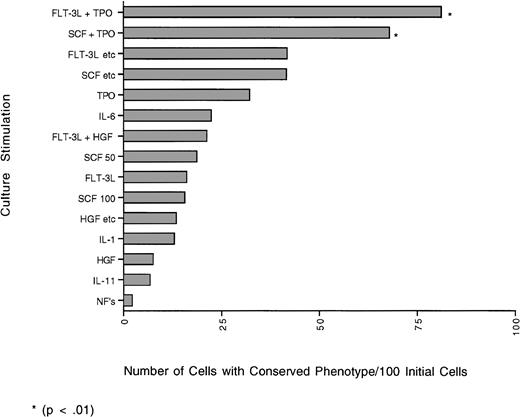
To study the influence of growth factors on the doubling kinetics and immunophenotype of individual daughter cells resulting from the first division of single cells, CB CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells were cultured in the presence of single and various combinations of recombinant human cytokines. Single CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells were plated at a density of 1 cell/well in Terasaki plates in serum-free medium containing cytokines. Each well containing a single cell was observed daily for 7 days for evidence of maintenance (cell remains viable, but undivided), cell death, or cell division. The wells in which division was observed (Fig 1) were then stained with anti-CD34 and antilineage antibodies to determine the phenotype of the daughter cells. The growth kinetics (percent of wells with maintenance, division, death) for each day (days 1-7) in culture, for each of the single and combinations of factors used, are shown in Tables 1 through15, and the cumulative percent over 7 days and the phenotype data are shown in Table 16. Figures 2 and 3show the number (yield) of cells with conserved (Fig 2) or differentiated (Fig 3) phenotype resulting from the first cell division of 100 initial CD34+Thy-1+lin− cells.
Phase contrast images of a single CD34+Thy-1+lin− cell undergoing its first cell division. The time elapsed from when the beginning of division was observed (upper left) until division was complete (lower right) was approximately 25 minutes. When a doublet was observed in a well, the daughter cells were stained for phenotype assessment by fluorescence microscopy.
Phase contrast images of a single CD34+Thy-1+lin− cell undergoing its first cell division. The time elapsed from when the beginning of division was observed (upper left) until division was complete (lower right) was approximately 25 minutes. When a doublet was observed in a well, the daughter cells were stained for phenotype assessment by fluorescence microscopy.
The graph represents the yield of cells (number) with the CD34+lin− phenotype obtained from 100 initial individual cells that have undergone one cell division based on the percent of cells that doubled and the percent of daughter cells that retained the CD34+lin− phenotype (phenotypic self-renewal). Although the yields obtained with the combination of FLT-3L + TPO and SCF + TPO were not significantly different from each other, they were significantly different (P≤ .01) from all other cytokine combinations tested.
The graph represents the yield of cells (number) with the CD34+lin− phenotype obtained from 100 initial individual cells that have undergone one cell division based on the percent of cells that doubled and the percent of daughter cells that retained the CD34+lin− phenotype (phenotypic self-renewal). Although the yields obtained with the combination of FLT-3L + TPO and SCF + TPO were not significantly different from each other, they were significantly different (P≤ .01) from all other cytokine combinations tested.
The graph represent the yield of cells (number) with differentiated phenotype (CD34+lin+) obtained from 100 initial individual cells that have undergone one cell division based on the percent of cells that doubled and the percent of daughter cells that expressed lineage markers (did not phenotypically self-renew). The yields obtained with the combination of SCF + TPO were significantly different (P ≤ .01) from all other cytokine combinations tested.
The graph represent the yield of cells (number) with differentiated phenotype (CD34+lin+) obtained from 100 initial individual cells that have undergone one cell division based on the percent of cells that doubled and the percent of daughter cells that expressed lineage markers (did not phenotypically self-renew). The yields obtained with the combination of SCF + TPO were significantly different (P ≤ .01) from all other cytokine combinations tested.
Effects of Single Cytokine Stimulation on the First Doubling Kinetics of Single CD34+Thy-1+lin− Cells
TPO promotes viability of 34+lin− cells.
Individual 34+lin− cells were cultured in the presence of single growth factor stimulation or no added factors, and the kinetics of cell growth over 7 days in TPO, FLT-3L, SCF (50 and 100 ng/mL), IL-6, IL-11, IL-1, and HGF was examined (Tables 1 through9). Cultures supplemented with TPO, SCF (50 ng/mL), and FLT-3L had the most single cells that remained undivided and viable (maintained) cumulatively over 7 days, with 29.4%, 26%, and 22.1% of the wells, respectively, with one live cell (Table 16) (P ≤ .05). The least number of single cells maintained undivided and viable cumulatively over 7 days were in cultures with IL-6 and IL-11, where only 13.1% and 13.6% of the wells, respectively, had 1 live cell. Tables 1 through 9 show the growth kinetics for each individual day in culture, for days 1-7. On day 7, with FLT-3L (Table 3), no added factors (Table 4), SCF 100 ng/mL (Table 5), IL-6 (Table 6), IL-11 (Table 7), IL-1 (Table 8), and HGF (Table 9), less than 24% of the starting number of wells had one undivided cell. In contrast, on day 7 with TPO (Table 1), 30.9% and with SCF (50 ng/mL) 27.7% of the starting number of wells had one undivided cell. Of all the single factors tested, the largest total percent of viable cells (cells that remained undivided + cells that had doubled), 64.7% were in cultures supplemented with TPO. These cultures had 15.7% more viable cells cumulatively over 7 days than did cultures supplemented with SCF (50 ng/mL) and 18% more than with FLT-3L.
The highest cumulative percent of wells in which the single cell doubled over 7 days were seen in cultures stimulated with TPO, FLT-3L, and SCF (50 ng/mL) with 35.3%, 24.6%, and 23%, respectively (Table16). The cumulative percent of wells in which the single cell doubled over 7 days ranged from a low of 13.0% (IL-1) to a high of 35.3% for TPO (P ≤ .05). When no factors were added, doubling occurred in only 2.2% of wells cumulatively over 7 days. The responses with SCF (100 ng/mL) and HGF were similar to each other, with 21.0% and 20.5% of the wells doubling, as were responses with IL-6 and IL-11 stimulation, both with 18.2%.
Single cells underwent their first division beginning on day 2, and most of the doubling occurred by day 4 (Tables 3, and 5 through 9) in all single-factor–stimulated cultures, except those with TPO (Table 1) and SCF (50 ng/mL) (Table 2), where initial doubling began on day 3 and most of the doubling occurred by day 5. Doubling only occurred on days 4 and 5 when no factors were added (Table 4). In cultures supplemented with TPO (Table 1), SCF (50 ng/mL) (Table 2), FLT-3L (Table 3), and SCF (100 ng/mL) (Table 5), there were still wells in which the single cell doubled on day 7. We did observe wells that contained a single cell, which proliferated to more than 2 cells (either 3 or 4 cells) in the interval between observations. Although these wells were assessed for phenotype as were the wells containing only 2 cells, the results are not included in this study. Cells were also observed to divide during daily observation. In other experiments with TPO, SCF, FLT-3L, and FLT-3L + TPO, some of the cells that remained undivided and viable at 7 days were maintained as long as 35 days without dividing. In some cultures, up to 50% (range, 27% to 50%) of the cells that were undivided at 7 days were still undivided at 30 days.
With all single-factor stimulation or with no added factors, there were wells in which the single cell died without dividing on days 1-7 (Tables 1 through 9). The majority of the cell death occurred during the first 4 days in cultures with SCF (50 and 100 ng/mL) and FLT-3L, IL-6, and IL-1. In contrast, the majority of cell death in cultures supplemented with TPO was seen on days 5-7 and on days 4-7 in cultures supplemented with HGF or IL-11. The IL-6, IL-11, HGF, and IL-1 cultures had the highest cumulative percent of wells in which the cell died over 7 days with 68.7%, 68.2%, 64.1%, and 66.3%, respectively (Table16). In contrast, the cumulative percent of wells in which the cell died over 7 days in the presence of TPO was only 35.3%.
Effects of Combinations of Multiple Cytokines on the First Doubling Kinetics of Single CD34+Thy-1+lin− Cells
FLT-3L + TPO and SCF + TPO promote viability of 34+lin− cells.
Individual 34+lin− cells were cultured in the presence of multiple growth factors and the kinetics of cell growth over 7 days in FLT-3L + TPO; SCF + TPO; FLT-3L + HGF; the combination of FLT-3L, SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, βNGF; the combination of SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, GM-CSF; and the combination of HGF, IL-1, IL-6 or IL-11 1, G-CSF was examined. The results are presented in Tables 10 through 15. Cumulatively over 7 days there were fewer wells in which the cell was maintained undivided than with single factors alone. With combinations of growth factors, the majority of the cells either doubled or died, depending on the culture stimulation (Table16).
The percent of wells in which the cell was still undivided on day 7 ranged from 1.2% for SCF 50 ng/mL + TPO to 13.5% for the combination of HGF, IL-1, IL-6, or IL-11 G-CSF. The largest total percent of wells with viable cells (cells that remained undivided + cells that had doubled) were in cultures supplemented with FLT-3L + TPO, with 73%. These cultures had 4% more viable cells cumulatively over 7 days than did cultures supplemented with SCF (50 ng/mL) + TPO (69.1%) and 23% more than with FLT-3L + HGF with 50%.
Cells doubled on days 3-6, with most doubling occurring by day 4 for all combinations tested, and only the combination of HGF, IL-1, IL-6, G-CSF still had doubling that occurred on day 7. The highest cumulative percent (67.9%) of wells in which the cell doubled over 7 days was in cultures with SCF + TPO. With FLT-3L + TPO culture stimulation, the cumulative percent of wells in which the cell doubled over 7 days was less, 64%, but in these cultures more cells remained undivided (10%v 1.2%) and fewer died over the 7 days. For all but the FLT-3L + TPO combination, cells died without dividing on days 3-7 (Tables 11through 16). With FLT-3L + TPO, cell death was observed on days 2-7 (Table 10). In all cultures, most death was seen between days 3 and 5. The cumulative percent, over 7 days, of wells in which the a cell died without dividing ranged from 27% for FLT-3L + TPO to 70.3% for the combination of HGF, IL-1, IL-6 or IL-11 G-CSF (Table 16). A larger total percent of viable cells (cells that remained undivided + cells that had doubled) were observed with the combinations of FLT-3L + TPO and SCF + TPO than with the best single factor, TPO.
Phenotype of Daughter Cells After the Initial Cell Division. FLT-3L + TPO Promotes Phenotypic Self-Renewal
To determine whether cells undergo a change in phenotype after only one cell division and whether the influence of cytokines could affect the frequency of phenotypic self-renewal after the first cell doubling of CD34+Thy-1+ lin− cells in vitro, wells containing single cells were monitored daily for evidence of division. The wells in which a single cell had divided (Fig 1) were stained with FITC–anti-CD34 and PE antilineage antibodies for phenotype assessment of the daughter cells. The phenotype of each individual daughter cell of the cell doublet was scored using fluorescence microscopy and the percent of cells undergoing a conserved doubling (phenotypic self-renewal) to two like daughter cells (CD34+lin−) or the percent of doublets with one or two differentiated cells were determined. Each of four different phenotypes possible for each cell in the doublet was observed: 1, FITC+ (34+lin−); 2, PE+ (34−lin+); 3, FITC+/PE+ (34+lin+); 4, FITC−/PE−(34−lin). The frequency of each phenotype outcome was determined and results are shown in Table 16, and the yield (number) of cells obtained with conserved or differentiated phenotype/100 initial cells is shown in Figs 2 and 3 for each combination of growth factors. A population of CD34+ cells were plated in parallel, monitored, and stained as the lin− population; these served as a positive control for the staining (data not shown). Conserved doublets were defined as CD34+lin− in both daughter cells and differentiated doublets as those where both cells were lin+.
There were no doublets with conserved phenotype (both daughter cells CD34+lin−) detected in cultures supplemented with IL-11, HGF, or no added factors. Doublets with conserved phenotype were detected with all other cytokines used. With the combination of FLT-3L + TPO, 57% of the doublets were of conserved phenotype (CD34+lin−), the highest percent of phenotypic self-renewal of all the combinations tested. SCF + TPO; the combination of FLT-3L, SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, βNGF; and IL-6 used alone had the next highest percent of doublets with conserved phenotype, with 39%, 39%, and 38%, respectively. There was no correlation between when the cell divided and the phenotype of the daughter cells.
When looking at the total percent of cells with conserved phenotype (percent conserved doublets + percent with 1 cell conserved), FLT-3L + TPO was still best overall, with 64%. Although in cultures with IL-1, IL-6, no added factors; the combination of HGF, IL-1, IL-6, G-CSF; or the combination of SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, GM-CSF there were more doublets with one daughter cell conserved, over the 7 days, as much as 55% more cells died than doubled or than remained undivided. Therefore, the number of cells with the 34+lin− phenotype was less. Other combinations in which the total percent of cells with conserved phenotype was high were FLT-3L, SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, βNGF; the combination of SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, GM-CSF; and SCF + TPO with 53%, 53%, and 43%, respectively. The yield (number) of cells with conserved phenotype after the first division of 100 initial cells was determined for each cytokine combination (Fig 2). The combinations of FLT-3L + TPO and SCF + TPO produced the highest yield of cells with 34+lin− phenotype after one division (FLT-3L + TPO 81 cells/100 initial cells and SCF + TPO 68 cells/100 initial cells). Although the yields are not significantly different from each other, they are significantly (P ≤ .01) different from all the other cytokines tested. Cultures with no added factors and IL-11 had the lowest yield of cells with conserved phenotype (2 cells/100 initial cells, and 7 cells/100 initial cells, respectively). Although cultures with IL-1, IL-6, no added factors; the combination of HGF, IL-1, IL-6, G-CSF; or the combination of SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, GM-CSF had more doublets with one daughter cell conserved, over the 7 days, more cells died than doubled or were maintained. Therefore, the actual yield of cells with the 34+lin−phenotype was significantly (P ≤ .01) less than with FLT-3L + TPO; SCF + TPO; or FLT-3L, SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, βNGF.
The highest percent of doublets with both daughter cells having a differentiated phenotype (CD34+lin+, CD34−lin+) were seen in cultures with IL-11 and HGF with 63% each, and the lowest percent when single cells were cultured in the absence of added growth factors (Table 16). The combination of SCF + TPO produced the highest (P ≤ .01) yield (number) of cells with CD34+lin+ differentiated phenotype after one division (68 cells/100 initial cells) (Fig 3). With SCF + TPO the yield of conserved cells was equal to the yield of differentiated cells. The combinations of FLT-3L + TPO and SCF + TPO allowed the most single cells to undergo a conserved doubling, due to the fact that more cells divided than died in these cultures, combined with the total percent of cells that were still the CD34+lin− phenotype.
DISCUSSION
In this study we have investigated the phenotype of cells resulting from the first division of single CD34+Thy 1+lin− cells, whether changes in phenotype occurred with the first cell division, and the influence of growth factors on the survival and doubling kinetics of individual cells. We report that cells self-renew or differentiate with respect to phenotype after the first division, and this is influenced by different growth factors. The question of what cytokines are able to maintain most viable cells and selectively enhance maintenance rather than proliferation or death is still unanswered, although recent studies illustrate the ability of SCF, TPO, and FLT-3L to stimulate growth and survival of primitive hematopoietic cells from CB and BM.
Cultures supplemented with TPO, SCF, and FLT-3L had the most single cells that remained undivided and viable (maintained) cumulatively over 7 days (P ≤ .05). Of all the single factors tested, the largest total percent of viable cells (cells that remained undivided + cells that had doubled) were in cultures supplemented with TPO. These cultures had more viable cells cumulatively over 7 days than did cultures supplemented with SCF alone or with FLT-3L alone. The combination of FLT-3L + TPO produced the highest total percent of wells with viable cells (cells that divided + percent of cells viable and undivided) of all the cytokines evaluated. These cultures had more viable cells cumulatively over 7 days than did cultures supplemented with SCF + TPO or FLT-3L + HGF, both of which were better that TPO alone. In some cultures, 27% to 50% of the cells that remained undivided on day 7 were still undivided and viable on day 30. With combinations of growth factors, the majority of the cells either doubled or died depending on the culture stimulation. As expected, all cytokines studied induced some division and death. In some cultures, more cells remained viable (cells that were maintained + cells that divided) cumulatively over 7 days than died.
There was less doubling with single factors, and this was consistent with the fact that for proliferation of more primitive cells multifactor stimulation is required. SCF + TPO and FLT-3L + TPO induced more doubling than death, whereas the percent of cells that doubled in cultures supplemented with single factors was only slightly higher than the percent than remained undivided. The cumulative percent of wells in which the single cell doubled over 7 days varied with the culture stimulation.
Culture wells with the lowest percentage of single cell death over 7 days were those with FLT-3L + TPO and SCF + TPO, consistent with the fact that with these combinations induced more than 60% of the cells to divide and, therefore, had a larger total percent of viable cells (cells that remained undivided + cells that had doubled) than those with the best single factor, TPO. These observations are in agreement with other studies showing TPO is more effective with the addition of other early acting cytokines, such as SCF and FLT-3L.
Phenotypic self-renewal of both daughter cells (both CD34+lin−) was not observed in cultures supplemented with IL-11, HGF, or no added factors. Doublets with conserved phenotype were detected with all other cytokines used. The combination of FLT-3L + TPO induced the highest percent of phenotypic self-renewal and yield (P ≤ .01) of all the combinations tested. Cultures with SCF + TPO, the combination of FLT-3L, SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, βNGF, were also effective. FLT-3L + TPO was still best overall when looking at the total percent of cells with conserved phenotype (percent conserved doublets + percent with one cell conserved). Although in cultures with IL-1, IL-6, no added factors; the combination of HGF, IL-1, IL-6, G-CSF; or the combination of SCF, IL-3, IL-6, G-CSF, GM-CSF had more doublets with one daughter cell conserved over the 7 days, more cells died than doubled or than remained undivided. Therefore, the number of cells with the 34+lin− phenotype was less than with FLT-3L + TPO, which may be important for obtaining expanded populations of cells with primitive phenotype. In addition, approximately 50% of the cells that remained undivided after 30 days in culture still retained the CD34+lin−phenotype. The present studies do not address which particular lineage marker is being expressed. The daughter cells that are lineage positive could be expressing any one of the markers present in the cocktail. As the feasibility of determining this on individual cells increases, future studies will look at which specific markers are being expressed as soon as the first division and which others are picked up or lost with subsequent divisions.
Analysis of individual wells shows heterogeneity among individual CB samples in the rate of doubling, maintenance, and death, and daughter cell phenotype. A study by Gothot et al37 showed that the position of cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle could account for the functional differences (heterogeneity) in CD34+cells.
Other single cell studies have relied on allowing the single cells to grow to large numbers over time (looking at total fold expansion) and analyzing phenotype on large populations of cells. We have used this single-cell system to look at the concept of possible proliferation without differentiation and to track this occurrence after the initial cell division of primitive population containing stem cells. These observations are in agreement with other studies using with FLT-3L, TPO, and SCF, and follow what has been observed by examining larger numbers of cells or single cells that proliferate to large numbers and phenotype assessment by FACS. TPO as a single factor can support the survival of 34+lin− cells and acts with FLT-3L and SCF to induce doubling and viability. Although stem cell phenotype does not necessarily correlate with function, our studies use phenotype as a starting point, because long-term culture–initiating cells and in vivo repopulating cells are in the population with conserved phenotype. Retention of phenotype after division does not mean certain loss of function, but there is certain loss of stem cell function if there is not retention of phenotype. Recent studies35 using 104CD34+Thy-1+lin−cells/well cultured with TPO, FL, and KL show similar retention of primitive phenotype and that engraftment potential was retained.
These present data show, on a single-cell basis, that early acting cytokines which recruit cells to divide stimulate phenotypic self-renewal, and that cell fate decisions (self-renew or differentiate) are seen as soon as the initial cell division of CD34+Thy 1+lin− cells, and that this can be influenced by culture conditions. These results may have implications for targeting primitive cells for gene therapy, by knowing which day cells are most likely to divide and which cytokines stimulate phenotypic conserved or differentiated division, and the yield of cells retaining the CD34+lin− phenotype that could be obtained within a population. These data may allow the study of the factors that control quiescence and self-renewal of expanded homogeneous populations of primitive cells. Although others have looked at the effects of these cytokines on single-cell proliferation and assessment of phenotype on large numbers of the progeny of those single cells, this is the first study to show the effects of cytokines on the potential of single primitive cells to retain or change phenotype after one cell division.
Our data clearly show the effects of the synergy between FLT-3L +TPO and SCF + TPO in affecting proliferation and maintenance of stem cell phenotype and the ability of these factors to induce division with less differentiation to increase the numbers of primitive cells that have undergone phenotypic self-renewal, and that cell fate/phenotype decisions are made as early as the first division.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors express appreciation to Christine Contis of Magee Womens Research Institute for her efforts in the collection of cord blood samples, and to Bob Lakomy and Alex Styche of the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute Flow Cytometry Facility for the cell sorting. We also thank Dr Sallie Boggs for her helpful discussions.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
REFERENCES
Author notes
Address reprint requests to Joel S. Greenberger, MD, Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Pittsburgh, 200 Lothrop St, Pittsburgh, PA 15213.