Abstract
To investigate whether bone marrow (BM) stem cell compartment and/or BM microenvironment are affected by the immune insult in autoimmune cytopenias (AICs), BM stem cell reserve and function and BM stromal function were studied in 15 AIC patients. Stem cells were evaluated by means of flow cytometry, clonogenic progenitor cell assays, long-term BM cultures (LTBMCs), and limiting dilution assay for quantification of long-term–culture initiating cells (LTC-ICs). Stromal cell function was assessed with the use of preformed irradiated LTBMCs from patients and normal controls, recharged with normal CD34+ cells. AIC patients exhibited a high number of CD34+, CD34+/CD38+, and CD34+/CD38− cells; high frequency of granulocyte-macrophage colony forming units in the BM mononuclear cell fraction; high colony recovery in LTBMCs; and normal LTC-IC frequency. Patient BM stromal layers displayed normal hematopoietic-supporting capacity and increased production of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor. Data from this study support the concept that AIC patients with severe, resistant disease might be appropriate candidates for autologous stem cell transplantation.
Introduction
Autoimmune cytopenias (AICs) are well-defined hematologic disorders characterized by a reduced number of circulating mature blood elements due to increased peripheral cell destruction and/or decreased cell production in the bone marrow (BM) by humoral or cellular cytotoxic mechanisms. They may present as isolated cytopenias affecting red blood cells (autoimmune hemolytic anemia, pure red cell aplasia), neutrophils (autoimmune neutropenia), or platelets (autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura) or as a combination involving 2 (eg, Evans syndrome) or 3 lineages (autoimmune pancytopenia).1
Although immune-mediated destruction of mature blood elements has long been recognized, mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of AIC were better defined following the introduction of in vitro clonogenic assays.1 With the use of culture studies, it was shown that immune inhibition of hematopoietic cell production may be as important as increased peripheral cell destruction in AIC2-8 and that humoral or cellular immune mechanisms affecting not only the progenitor cells but even BM stromal cells may be involved in their pathogenesis.9 However, stem cells per se and BM microenvironment in these patients have not been extensively studied.
Because there has been much interest during the last decade in exploring the use of high-dose immunotherapy followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with severe, resistant autoimmune diseases including AIC,10 it seems crucial to answer the question of whether stem cell compartment and/or BM microenvironment is already affected by the immune insult in these patients. The aim of the present study was to evaluate hematopoietic stem cell reserve and function and BM stromal function in terms of its capacity to support hematopoiesis in patients with AIC.
Study design
BM samples and immunophenotyping
BM mononuclear cells (BMMCs) were obtained from 15 AIC patients (Table 1) and 20 normal controls as previously described.11 CD34+ cells were isolated from BMMCs by indirect magnetic labeling by means of a MACS isolation kit (Mitenyi Biotec, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions. BMMCs or CD34+ cells were labeled with anti-CD34 (HPCA-2; Becton Dickinson, United Kingdom) and anti-CD38 (HIT-2; Becton Dickinson) fluorescent monoclonal antibodies and were analyzed on a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). Data on a minimum of 50 000 events were acquired and processed by means of CellQuest software.
Clonogenic progenitor cell assays
BMMCs or CD34+ cells were cultured in methylcellulose culture medium (StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada) for granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM) and erythroid-burst colony formation (BFU-E) as previously described.12 BMMCs and CD34+ cells were also assessed for megakaryocytic colony formation (CFU-Meg) by means of a commercially available kit (MegaCult-C, StemCell Technologies) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Long-term BM cultures and cytokine measurement in culture supernatants
Long-term BM cultures (LTBMCs) from 107BMMCs were grown according to a standard technique.11-14At weekly intervals, nonadherent cells were counted and assayed for colony formation, and results were expressed as total numbers of colony forming cells (CFCs) (CFU-GM + BFU-E). At week 3, cell-free supernatants were harvested and stored at −70°C for granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) quantification by means of commercially available ELISA kits (R&D Systems, Oxon, United Kingdom).
Limiting dilution assay for quantification of long-term culture initiating cells
Seven dilutions of a single suspension of CD34+cells were overlaid on preformed murine MS-5 stromal layers15 at concentrations ranging from 10 to 1000 cells per well in 96-well culture plates. Cultures were fed weekly by demi-depopulation and, after 5 weeks, were overlaid with methylcellulose culture medium for 2 additional weeks. The frequency of long-term culture initiating cells (LTC-ICs) was calculated by determining, by means of a Fig. P Biosoft PC program, the CD34+ cell dilution that resulted in 37% wells or fewer being negative for colonies.16 17
Assessment of BM stromal cell function
Irradiated confluent stromal layers from patients and normal controls grown in standard LTBMCs were recharged with 5 × 104 normal allogeneic CD34+ BM cells as previously described.14 At weekly intervals, supernatants were monitored by determining the number of nonadherent cells and CFC frequency.
Data were analyzed by means of the nonparametric Wilcoxon rank test, standard 2-way variance analysis test, and 2-tailed Studentt test.
Results and discussion
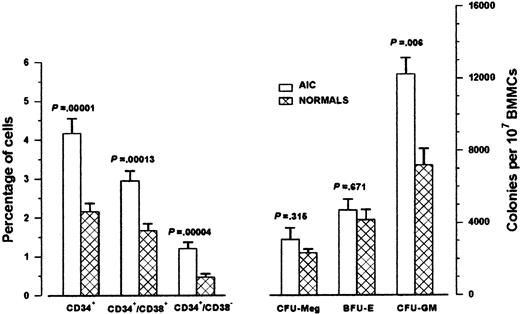
AIC patients had significantly higher proportions of CD34+ cells compared with controls owing to the higher proportion of both the committed CD34+/CD38+cells and the more primitive CD34+/CD38− cells (Figure 1). Furthermore, CFU-GM colony formation by 107 BMMCs was significantly higher in AIC patients than in the normal controls. The frequency of BFU-E/107 BMMCs and the frequency of CFU-Meg/107 BMMCs did not differ statistically between patients and normal controls (Figure1). To investigate whether the high CFU-GM colony formation in AIC patients was due to an intrinsic increased clonogenic potential of patient stem cells or was the consequence of an extrinsic effect, we tested the frequency of CFU-GM obtained by immunomagnetically sorted highly purified CD34+ BM cells. The number of colonies obtained was similar in patients (mean, 307 per 104 CD34+ cells; range, 174-537) and normal controls (mean, 262 per 104 CD34+ cells; range, 93-540; P = .429), suggesting that accessory cells may influence the colony growth in patient unfractionated samples. An alternative explanation is that the increased colony number obtained by patient BMMCs simply reflects the increased proportion of CD34+ cells in AIC BM. Similarly, no significant difference was observed between patients and normal controls in the mean number of BFU-E and CFU-Meg obtained from CD34+ cells (P = .189 and P = .591, respectively).
Bone marrow CD34+ cells and clonogenic progenitor cells in AIC patients.
The left bars represent the mean percentages (± SEM) of CD34+ cells in 15 AIC patients and 20 normal controls obtained in 2-color flow cytometric analysis of BMMCs. The right bars represent the mean colony values (± SEM) obtained from BMMCs in the clonogenic progenitor cell assays. We cultured 105BMMCs from AIC patients (n = 13) and normal controls (n = 16) in 1 mL methylcellulose 0.9% in Iscove modified Dulbecco medium supplemented with 30% fetal calf serum (PAA Laboratories GmbH, Linz, Austria), 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA; Sigma, St Louis, MO), 10−4 mol/L mercaptoethanol (Sigma), 0.075% sodium bicarbonate (GibcoBRL; Life Technologies), and 2 mmol/L L-glutamine (Sigma), in the presence of 5 ng GM-CSF, 50 ng interleukin (IL)-3 and 2 IU erythropoietin for CFU-GM and BFU-E colony formation. Colonies were enumerated on day 14. We cultured 106 BMMCs from AIC patients (n = 12) and normal controls (n = 10) in MegaCult-C medium for CFU-Meg colony growth. Colonies were scored after 10 to 12 days of incubation after fixation and staining by alkaline phosphatase antialkaline phosphatase technique with the use of anti-CD41 monoclonal antibody. Comparison between patients and normal controls was performed by means of the 2-tailed Student t test.
Bone marrow CD34+ cells and clonogenic progenitor cells in AIC patients.
The left bars represent the mean percentages (± SEM) of CD34+ cells in 15 AIC patients and 20 normal controls obtained in 2-color flow cytometric analysis of BMMCs. The right bars represent the mean colony values (± SEM) obtained from BMMCs in the clonogenic progenitor cell assays. We cultured 105BMMCs from AIC patients (n = 13) and normal controls (n = 16) in 1 mL methylcellulose 0.9% in Iscove modified Dulbecco medium supplemented with 30% fetal calf serum (PAA Laboratories GmbH, Linz, Austria), 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA; Sigma, St Louis, MO), 10−4 mol/L mercaptoethanol (Sigma), 0.075% sodium bicarbonate (GibcoBRL; Life Technologies), and 2 mmol/L L-glutamine (Sigma), in the presence of 5 ng GM-CSF, 50 ng interleukin (IL)-3 and 2 IU erythropoietin for CFU-GM and BFU-E colony formation. Colonies were enumerated on day 14. We cultured 106 BMMCs from AIC patients (n = 12) and normal controls (n = 10) in MegaCult-C medium for CFU-Meg colony growth. Colonies were scored after 10 to 12 days of incubation after fixation and staining by alkaline phosphatase antialkaline phosphatase technique with the use of anti-CD41 monoclonal antibody. Comparison between patients and normal controls was performed by means of the 2-tailed Student t test.
The average nonadherent cell recovery, over a period of 8 weeks, was similar in patient and normal LTBMCs (F = 1.343 < F1188 at 5%) but the CFC frequency was significantly higher in patients than in normal controls (F = 6.464 > F1188 at 1‰), supporting the concept that the stem cell compartment is increased in our patients. However, the frequency of LTC-ICs, which represent the best available approximation of primitive stem cells,18 19 did not differ significantly between patients (mean, 12.29 per 5 × 103 CD34+ cells; range, 5.3-22.42) and normal controls (mean, 12.99 per 5 × 103CD34+ cells; median, 11.94; range, 7.4-20; P = .753).
Patient stromal function, assessed by its ability to support hematopoietic progenitor cell growth, was comparable to the normal controls as indicated by the number of nonadherent cells (F = 2.497 < F1105 at 5%) and the CFC frequency (F = .029 < F1105 at 5%) over a period of 5 weeks. In keeping with the fact that BM stromal cell function was normal in AIC patients were the increased G-CSF concentrations in patient supernatants (mean, 642.39 pg/mL; range, 30.5-1913; n = 10) compared with the normal supernatants (mean, 154.32 pg/mL; range, 26.85-409; n = 10; P = .0156), suggestive of a compensatory G-CSF production by patient stromal cells in response to the peripheral cytopenia.20-22 In contrast, GM-CSF levels did not differ statistically between AIC patient and normal control supernatants (P = .089).
In conclusion, our findings suggest that AIC patients exhibit normal stem cell function and high frequency of committed progenitors as indicated by the significant increase in the proportions of CD34+ cells in flow cytometric analysis, the increased numbers of CFU-GM in BMMCs, and the increased committed progenitor cell recovery in LTBMCs. Our data also suggest that AIC patients display normal BM stromal function in terms of its ability to support normal hematopoiesis. This study encourages further the concept that patients with severe, resistant AIC might be appropriate candidates for autologous stem cell transplantation following intensive immunosuppression.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd and Janssen-Ciliag Ltd for their gifts of cytokines and the hematology clinical staff of St George's Hospital for aspirating bone marrow samples.
Supported by a European Molecular Biology Organization grant.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Helen A. Papadaki, Department of Hematology of the University Hospital of Heraklion, PO Box 1352, Heraklion, Crete, Greece; e-mail: epapadak@med.uoc.gr.