Abstract
Abstract 984
Poster Board I-6
The Ph chromosome is the most common cytogenetic abnormality in adult patients with ALL and is associated with a higher risk of relapse and death. With the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI; imatinib, dasatinib), the treatment of patients with Ph+ ALL has evolved. Regimens combining conventional chemotherapy with TKI have lead to significant improvements in the outcome of these patients. However, there is still a high incidence of relapse, and the determination of prognostic factors in these patients might lead to the development of risk-adapted therapy. CD20 is a cell surface marker expressed in 40% of adult patients with ALL, and it is associated with worse survival (Thomas D et al, Blood 2009; 113: 6330-6337). CD25 is the a-chain of the IL-2 receptor and has been reported to be associated with adverse outcomes in Ph+ ALL (Paietta E et al, Blood 2008; 112:Abstract 1500).
To determine the prognostic impact of CD20 and CD25 expression in patients with Ph+ ALL.
We retrospectively reviewed data of patients with Ph+ ALL treated at our institution with conventional chemotherapeutic protocols (Hyper-CVAD) alone or combined with TKI (Hyper-CVAD + imatinib and Hyper-CVAD + dasatinib). None of the patients received therapy with Rituximab. CD20 and CD25 expression were assessed by flow cytometry, and the cut-off for positivity was 20%. Survival was estimated by Kaplan-Meier method and compared by log-rank test.
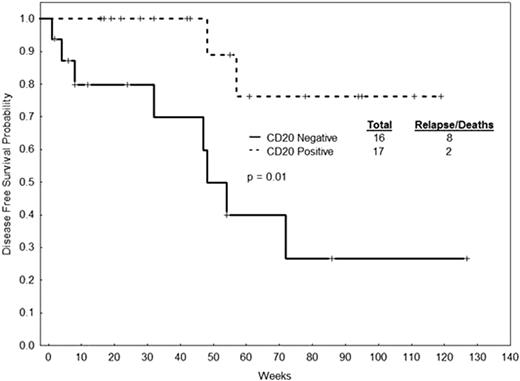
We analyzed 126 patients with Ph+-ALL treated at our institution from November, 1992, until February, 2009. Patients received Hyper-CVAD alone (N=44), Hyper-CVAD + Imatinib (N=47) and Hyper-CVAD + Dasatinib (N=35). Median age of the whole cohort was 49 years (range 16-84). CD20 was positive in 69 of 124 (57%) evaluable patients. CD25 was positive in 63 of 112 (56%) evaluable patients. Patients that were CD20-positive had a higher incidence of peripheral lymphadenopathy (21% vs. 7%, p=0.04). Patients that were CD25-positive had lower lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels (median 1006 IU/L vs. 1433 IU/L; p=0.01), lower percentage of bone marrow blasts (median 86% vs. 90%, p=0.02), higher platelet counts (median 50×109/L vs. 32×109/L, p=0.01) and a higher incidence of CNS disease at diagnosis (21% vs. 4%, p=0.01). The complete response rate of the whole cohort was 91%. There was no impact of CD20 or CD25 positivity on disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) of patients treated with Hyper-CVAD alone. In patients treated with Hyper-CVAD + dasatinib, CD20 positivity was associated with improved DFS (Figure 1) (median – not reached [NR] vs. 48 weeks [wks], p=0.01) and OS (median NR vs. 65 wks, p=0.06). Patients treated with Hyper-CVAD + imatinib who were CD20-positive had better DFS (median 91 vs. 57 wks, p=0.77) and OS (median 118 vs. 73 wks, p=0.98), but this did not reach statistical significance. There was a trend for worse survival in patients treated with Hyper-CVAD + dasatinib that were CD25 positive, but without a statistically significant difference (median DFS 55 wks vs. NR, p=0.10; median OS 85 wks vs. NR, p=0.11). We repeated the analysis combining Hyper-CVAD + dasatinib and Hyper-CVAD + imatinib (Hyper-CVAD + TKI). There was no significant difference in DFS and OS by CD20 expression (median DFS 130 wks vs. 53 wks, p=0.11; median OS 124 wks vs. 74 wks, p=0.11) or CD25 expression (median DFS 63 wks vs. 86 wks, p=0.33; median OS 100 wks vs. 117 wks, p=0.39).
In patients with Ph+-ALL treated with regimens combining conventional chemotherapy and TKI, expression of CD20 may be associated with better survival outcomes. CD25 did not influence survival in our patients. More studies are needed to better determine the prognostic value of these markers and implement risk-adapted strategies treatment.
DFS by CD20 expression in patients with Ph+-ALL treated with Hyper-CVAD + dasatinib
DFS by CD20 expression in patients with Ph+-ALL treated with Hyper-CVAD + dasatinib
Off Label Use: Off label use of imatinib and dasatinib in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapy. Cortes:Novartis: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Kantarjian:Novartis: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal