Abstract
Expression profiling has shown 2 main and clinically distinct subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs): germinal-center B cell–like (GCB) and activated B cell–like (ABC) DLBCLs. Further work has shown that these subtypes are partially characterized by distinct genetic alterations and different survival. Here, we show with the use of an assay that measures DNA methylation levels of 50 000 CpG motifs distributed among more than 14 000 promoters that these 2 DLBCL subtypes are also characterized by distinct epigenetic profiles. DNA methylation and gene expression profiling were performed on a cohort of 69 patients with DLBCL. After assigning ABC or GCB labels with a Bayesian expression classifier trained on an independent dataset, a supervised analysis identified 311 differentially methylated probe sets (263 unique genes) between ABC and GCB DLBCLs. Integrated analysis of methylation and gene expression showed a core tumor necrosis factor-α signaling pathway as the principal differentially perturbed gene network. Sixteen genes overlapped between the core ABC/GCB methylation and expression signatures and encoded important proteins such as IKZF1. This reduced gene set was an accurate predictor of ABC and GCB subtypes. Collectively, the data suggest that epigenetic patterning contributes to the ABC and GCB DLBCL phenotypes and could serve as useful biomarker.
Introduction
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common B-cell malignancy and is highly heterogeneous from both clinical and molecular standpoints.1 Gene expression profiling of primary DLBCL cases identified biologically distinct subtypes of DLBCL.2,3 One such approach classified DLBCL into germinal center B cell–like (GCB) and activated B cell–like (ABC) DLBCL subtypes, based on similarities of the respective gene signatures to normal germinal center B cells and activated peripheral B cells, respectively.2 This subclassification is clinically significant and predicts overall and progression-free survival in patients treated with cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin hydrochloride, vincristine, and prednisone and rituximab with cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin hydrochloride, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP).2,4,5
Several years after the discovery of these subtypes, the mechanisms controlling gene expression in ABC and GCB DLBCLs are still only partially understood. For example, ABC DLBCLs feature aberrant activity of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling, in part because of mutations in upstream components of this pathway.6,7 Chromosomal translocations, including 3q27 or t(14;18), often do not correlate with the affected protein expression and do not alone define lymphoma phenotypes.8-10 Lenz et al11 used genomewide copy number analysis to describe 30 recurrent but relatively infrequent chromosomal aberrations with DLBCL subtype-specific frequencies. ABC DLBCLs were characterized by deletion of SPIB, deletion of INK4a/ARF, and trisomy 3. GCB DLBCLs showed preferential deletion of PTEN and amplification of the locus encoding the mir17-92 microRNA.11 In another study, Compagno et al6 showed that greater than 50% of ABC DLBCLs carry somatic mutations in multiple effectors of NF-κB, which is required for survival of ABC DLBCLs. Despite all of these findings, the biologic differences between 2 subtypes of DLBCLs are not fully understood.
Gene expression patterning is also affected by epigenetic modifications such as methylation of CpG dinucleotides. In normal development and homeostasis, cytosine methylation mediates gene imprinting, X chromosome inactivation, tissue-specific gene expression, and silencing of parasitic DNA elements.12 Aberrant distribution of cytosine methylation is a hallmark of tumors and involves aberrant hypermethylation and hypomethylation of promoters, as well as redistribution of intergenic DNA methylation.13 Aberrant DNA methylation of specific gene loci has been reported in DLBCL. For example, the MGMT promoter is hypermethylated in 39% of DLBCLs and is associated with favorable prognosis.14 On a more global level, Rahmatpanah et al15 studied gene methylation patterns in 43 small B-cell lymphomas with the use of differential methylation hybridization and showed that 256 genes are differentially methylated between small lymphocytic lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma.15 Martin-Subero et al16 examined a set of 1505 CpGs across 807 genes with the use of the Illumina GoldenGate Methylation Cancer panel in a set of 83 mature aggressive B-cell lymphomas and identified, with the use of supervised analysis, a group of 56 hypermethylated genes in lymphoma. They subsequently showed that these genes are enriched in target genes of Polycomb (PcG) complex in stem cells, thus suggesting interplay between these 2 types of epigenetic repressive mechanisms in lymphoma cells. Importantly for the present study, the investigators did not detect any difference in DNA methylation pattern between ABCs and GCB cell-of-origin subtypes of DLBCL. In a more recent study, Pike et al17 was able to identify 15 differentially methylated genes (eg, FLJ21062, GNMT, ONECUT2, CYP27B1, DRD1, KL, MINT2, and NEUROG1) between ABC and GCB DLBCLs with the use of a CpG island microarray with 4395 probes in 27 cases.17 Because these studies were limited in both sample size and scope, we wondered whether a more comprehensive DNA methylation platform might still distinguish more extensive aberrant epigenetic patterning associated with the ABC and GCB DLBCL subtypes. Using the HpaII tiny fragment enrichment by ligation-mediated PCR (polymerase chain reaction) (HELP) assay, we examined the status of 50 000 CpGs distributed among 14 000 promoters in a cohort of patients with DLBCL who were uniformly treated with R-CHOP and integrated these data with gene expression profiles obtained from the same samples. We find that ABC and GCB DLBCLs do indeed display distinctive epigenetic profiles, involving biologic pathways of probable significance and that there is a partial overlap between ABC and GCB DNA methylation and gene expression signatures. Collectively, these data suggest that aberrant epigenetic patterning contributes to the phenotype of these 2 main DLBCL subtypes.
Methods
DLBCL samples
Specimens were obtained at diagnosis from 69 patients with de novo DLBCL in Vancouver at the British Columbia Cancer Agency. Cases were selected on the basis of the presence of at least 80% of the neoplastic cells within the tumor section. The use of human tissue was approved by the research ethics board of the Vancouver Cancer Center/University of British Columbia and the Weill Cornell Medical Center. Patients were selected according to the availability of tissue and independent of the outcome. All patients were treated with R-CHOP (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). The primary endpoints of the study were the overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS).
High-molecular-weight DNA extraction
Frozen tissue (100 mg or 3 mm3) was cut into small pieces and submerged in liquid nitrogen, followed by pestle pulverization. Liquid nitrogen was allowed to evaporate, and the powder was quickly collected and transferred to the Eppendorf tube on ice. DNA purification was done with the QIAGEN Puregene Gentra cell kit. DNA was diluted in water or 10mM Tris (tris[hydroxymethyl]aminomethane)–HCl, pH 8.0, and the quality was assessed in 1% agarose gel.
Array-based methylation analysis with the use of HELP
The HELP assay was performed as previously published.18,19 One microgram of high-molecular-weight DNA was digested overnight with isoschizomer enzymes HpaII and MspI, respectively (New England Biolabs). DNA fragments were purified with phenol/chloroform, resuspended in 10mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, and used immediately to set up the ligation reaction with MspI/HpaII-compatible adapters and T4 DNA ligase. Ligation-mediated PCR was performed with enrichment for the 200 to 2000 base pair (bp) products and was submitted for hybridization to Roche NimbleGen Inc. We used the HG_17 human promoter custom array covering 25 626 HpaII amplifiable fragments within the promoters of the genes. Data quality control and analysis were performed as described previously,20 using R software and Bioconductor package (http://www.bioconductor.org/). Probe sets with intensity less than 2.5 mean absolute deviation of the random probe sets on the array were marked as missing values. After quality control processing, a median normalization was performed on each array by subtracting the median log-ratio (HpaII/MspI) of that array (resulting in median log-ratio of 0 for each array). Differentially methylated probe sets between the ABC and GCB DLBCLs were determined by the t test. The significance threshold was set to P less than .001, and concurrently false discovery rate was determined with the Benjamini-Hochberg method. In addition, we required that to be considered differentially methylated, the methylation difference for each gene between the means of ABC and GCB groups had to be greater than 20% (ie, ratio of the mean methylation in the 2 groups > 1.5 from HELP, which corresponds to 20% difference by MASSArray EpiTYPING; see supplemental Figure 2). GEO number GSE23967.
Single locus quantitative DNA methylation assays
EpiTYPER assays (Sequenom Inc) were performed on bisulfite-converted DNA, as previously described.21 EpiTYPER primers were designed to cover the flanking HpaII sites of selected HpaII amplifiable fragments, as well as any other HpaII sites found up to 2000 bp upstream of the downstream site and up to 2000 bp downstream of the upstream site, to cover all possible alternative sites of digestion. For the biologic validation of the 16 gene overlap signature, primers were designed to cover CpG dense areas of interest associated with the respective HpaII amplifiable fragments. The primers were designed with the use of the Sequenom EpiDesigner beta software (http://www.epidesigner.com/). The primer sequences are available in supplemental Table 2.
Quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA was extracted from 107 cells with the use of the RNeasy mini kit from QIAGEN and eluted in RNAse-free water. cDNA synthesis was done with the Superscript III First Strand Kit from Invitrogen. All primer sequences are available in supplemental Table 3.
Gene expression profiling and data processing
Total RNA was extracted from 69 fresh frozen tissue with the use of the All Prep kit (QIAGEN), was reverse transcribed, and hybridized to Affymetrix HG U133 plus 2.0 arrays according to the manufacturer's protocol (Affymetrix). CEL files were processed with Microarray Suite Version 5.0 with the use of Affymetrix default analysis settings and global scaling as normalization method. The trimmed mean target intensity of each array was set to 500. GEO number GSE23501.
Expression-based classification of ABC and GCB subtypes
To assign gene expression-based ABC and GCB labels to our 69 DLBCLs, we used the gene expression microarray data of 203 DLBCLs (GEO accession no. GSE11318) with known ABC and GCB labels as the training data,11 and the 185 Affymetrix probe sets as the ABC and GCB gene expression signature11 in a Bayesian predictor.22 We normalized the gene expression data of our 69 DLBCL cases with the 203 training DLBCL cases11 with the use of BRB-ArrayTools with the median array as a reference array (http://linus.nci.nih.gov/BRB-ArrayTools.html). Among 203 DLBCLs, there were 74 ABC DLBCLs, 72 GCB DLBCLs, 31 primary mediastinal B-cell lymphomas, and 26 unclassified DLBCLs (supplemental Figure 1). We only used ABC and GCB DLBCLs to train the Bayesian predictor. We replicated the procedure of Bayesian predictor as described in Wright et al22 for ABC/GCB classification of DLBCLs. A tumor is classified as ABC or GCB subtype if the probability that it belongs to the ABC or GCB subgroup is greater than 0.9; otherwise it is unclassifiable (supplemental Table 4). Differentially expressed probe sets between our ABC and GCB DLBCLs were determined by the t test with P less than .001.
Pathway analysis
We explored the association of gene sets with Gene Ontology terms, canonical pathways (KEGG and BioCarta), and lymphoid-specific gene expression signatures curated by the laboratory of Dr Staudt (Metabolism Branch, NIH; supplemental Tables 5-6).23 Fisher exact test was used to calculate enrichment P values, and the Benjamini-Hochberg method was used for the multitest adjustment and false discovery rate control. We also used the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software (Ingenuity Systems Inc, www.ingenuity.com) to identify deregulated gene networks. We first integrated the most differentially expressed and methylated genes in ABC versus GCBs present on both arrays: of 263 differentially methylated genes 239 were present on both platforms, and of 622 differentially expressed genes, 411 were present on both platforms (for the lists, see supplemental information).
Motif analysis
Finding Informative Regulatory Elements software24 was used to find consensus motifs among the differentially methylated probes in the 311 methylation signature.
Results
ABC and GCB DLBCLs have distinct epigenetic signatures
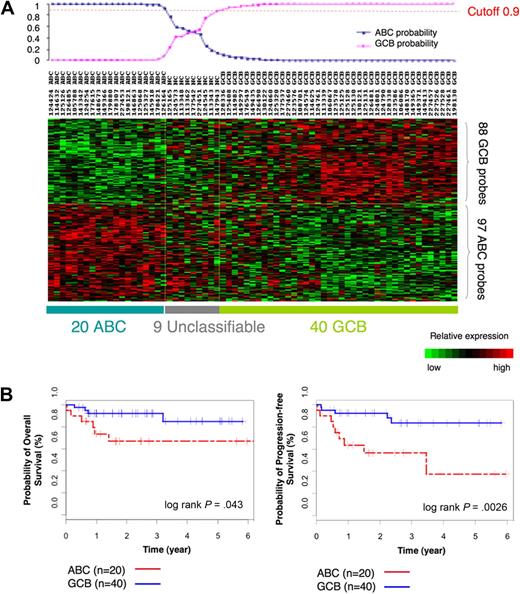
To determine whether GCB and ABC DLBCLs feature unique DNA methylation signatures, we selected a cohort of 69 cases of primary DLBCL uniformly treated with R-CHOP and with available high-quality tissue samples for microarray analysis (for patient characteristics, see supplemental Table 1). Before determining whether GCB and ABC DLBCLs had distinct DNA methylation signatures, it was necessary to identify each case as belonging to the ABC or GCB subtype on the basis of their gene expression signature. Gene expression profiles were obtained with Affymetrix HG U133 plus 2.0 microarrays. We used a Bayesian predictor22 and the published 185-gene expression signature from Lenz et al4 to assign ABC or GCB labels to our DLBCL cases. The Bayesian predictor was trained on a publicly available gene expression dataset that consisted of 203 DLBCL cases with known ABC and GCB labels11 (supplemental Figure 1). The predictor was then used to divide our patients into 20 ABC and 40 GCB DLBCLs with a probability greater than 0.9 (Figure 1A; supplemental Table 4). Nine cases were unclassifiable at this threshold. Kaplan-Meier estimates in these patients showed an overall 5-year survival of 85% for GCB and 67% for ABC cases (log-rank P = .043) and 5-year PFS of 83% for GCB and 37% for ABC (log-rank P < .003; Figure 1B), consistent with findings by other groups.4,5,25
ABC/GCB labels of our 69 DLBCLs on the basis of the gene expression signature. (A) Heatmap shows assignment of labels to our 69 cases of DLBCLs on the basis of the gene expression signature with the use of Bayesian predictor with cutoff value of 0.9. (B) Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival and PFS according to case labels assigned on the basis of the gene expression signature show that patients with GCB DLBCL have higher probability of OS (left) and PFS (right) than patients with ABC DLBCL.
ABC/GCB labels of our 69 DLBCLs on the basis of the gene expression signature. (A) Heatmap shows assignment of labels to our 69 cases of DLBCLs on the basis of the gene expression signature with the use of Bayesian predictor with cutoff value of 0.9. (B) Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival and PFS according to case labels assigned on the basis of the gene expression signature show that patients with GCB DLBCL have higher probability of OS (left) and PFS (right) than patients with ABC DLBCL.
DNA methylation profiles were determined on the same 69 patients with the use of the HELP assay and a NimbleGen microarray representing more than 50 000 CpGs contained within the promoters of 14 000 genes.19 After data processing and normalization to establish the relative methylation level of each probe set, we performed a series of technical validations to confirm the reliability of HELP in determining the percentage of methylation of CpGs. Five randomly selected high-variance genes (p53AiP1, S100A9, B2M, CSF2, TREML2) in 4 randomly selected DLBCL cases were assessed by a direct quantitative DNA methylation sequencing method, MassARRAY EpiTYPING. MassARRAY and HELP displayed high correlation (R = 0.91; supplemental Figure 2), indicating that HELP values accurately reflect the CpG methylation status of the various genes.
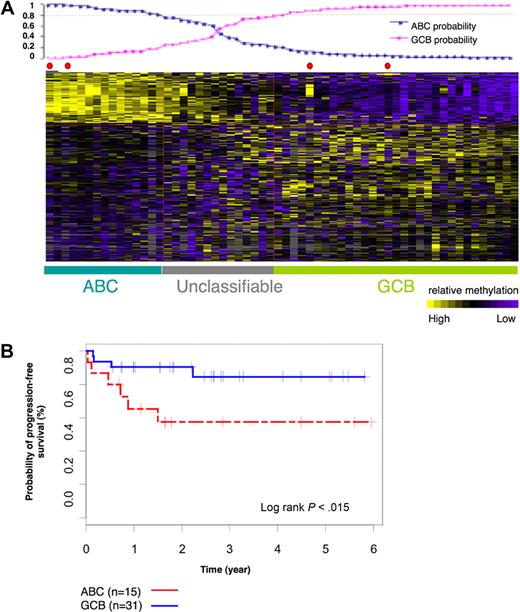
We next performed a supervised analysis on the methylation profiles of the 60 DLBCLs labeled as ABC or GCB on the basis of gene expression profiling to determine whether any genes were differentially methylated between the 2 subtypes. We identified 311 differentially methylated probe sets that corresponded to 263 unique genes with the use of the t test with P less than .001 (which corresponds to false discovery rate < 0.064 after multitest adjustment) and a methylation difference greater than 20% (ie, ratio of the mean methylation in the 2 groups > 1.5 from HELP, which corresponds to 20% difference by MASSArray EpiTYPING according to the curve in supplemental Figure 2) between ABC and GCB DLBCLs (Figure 2A). This 311-probe set methylation signature assigned ABC and GCB labels to DLBCL cases with the predictive accuracy of 91%, when using the Bayesian predictor, and a probability greater than 0.8. This is comparable to the performance of the gene expression signature. When considering ABC and GCB labels assigned according to methylation profiles, the 5-year PFS of GCB cases was 83% and ABC cases was 57% (log-rank P = .015; Figure 2B). Collectively, these data show that ABC and GCB DLBCLs feature specific and distinct DNA methylation profiles, suggesting that aberrant DNA methylation contributes to the biology of these disease subtypes.
ABC and GCB subgroups of DLBCLs have distinct methylation signatures. (A) Sixty-nine cases of DLBCLs were studied with the use of HG_17 human promoter array from Roche NimbleGen. The heatmap shows methylation values of 311 probe sets in 69 cases. With the use of the leave one out cross validation method we demonstrated that the 311 probe signature is able to correctly assign ABC and GCB labels to the DLBCL cases with the use of Bayesian predictor with probability cutoff of 0.8 (plot above the heatmap) and predictive accuracy of 91%. (B) Kaplan-Meier estimates of PFS in ABC and GCB subgroups, classified on the basis of 311 methylation signature, show that patients with GCB DLBCL had a higher probability of PFS than patients with ABC DLBCL.
ABC and GCB subgroups of DLBCLs have distinct methylation signatures. (A) Sixty-nine cases of DLBCLs were studied with the use of HG_17 human promoter array from Roche NimbleGen. The heatmap shows methylation values of 311 probe sets in 69 cases. With the use of the leave one out cross validation method we demonstrated that the 311 probe signature is able to correctly assign ABC and GCB labels to the DLBCL cases with the use of Bayesian predictor with probability cutoff of 0.8 (plot above the heatmap) and predictive accuracy of 91%. (B) Kaplan-Meier estimates of PFS in ABC and GCB subgroups, classified on the basis of 311 methylation signature, show that patients with GCB DLBCL had a higher probability of PFS than patients with ABC DLBCL.
Differentially methylated genes between ABC and GCB DLBCLs involve specific biologic pathways
We next determined whether these differentially methylated genes were associated with specific biologic functions. The most enriched Gene Ontology terms included regulation of protein metabolic processes, adaptive immune response, and metallopeptidase activity (supplemental Table 5). The top scoring KEGG pathway was antigen processing and presentation (supplemental Table 6). Significantly enriched BioCarta pathways were cytokine and inflammatory signaling, which remained statistically significant after correction for multiple testing (supplemental Table 6).
As a more functional approach we examined enrichment within publicly available gene sets defined by manipulating specific transcription factors with the use of RNAi technology, dominant-negative inhibition, or drug treatments and published gene profiling studies5,23,26 (supplemental Table 6). The most significantly enriched pathways included NFκB pathway as defined after treatment with an IκBα kinase inhibitor in the K1106 primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma cell line27 and GCB genes differentially expressed between ABC and GCB DLBCLs measured by LymphoChip.28 Although enrichment of some of these pathways was not significant when corrected for multiple testing, their representation among methylated genes is suggestive of their potential biologic effect. This analysis also confirmed involvement of pathways previously defined by gene expression analysis as differentially regulated in ABC and GCB lymphomas, underscoring the probable relevance of DNA methylation in gene regulation in these DLBCL subtypes.
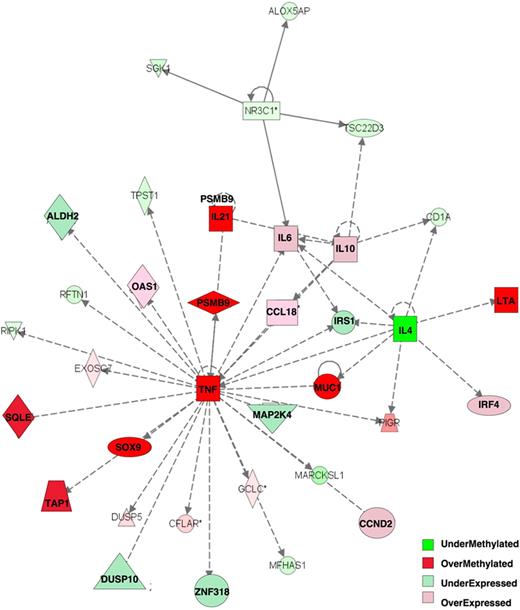
Integration of DNA methylation with gene expression profiling was shown to be more informative than either platform alone in capturing differentially involved gene networks between tumor subtypes.29 The 263 differentially methylated genes at P less than .001 with greater than 20% methylation difference were analyzed together with the 622 genes differentially expressed between the ABC and GCB subtypes at P less than .001 (t test). All of the genes were categorized on the basis of whether their relative methylation and expression levels were greater in ABC DLBCLs than in GCB DLBCLs. With the use of Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software with this combined set of differentially methylated or expressed genes, we identified the heavy involvement of one particular gene network centered on TNFα, which was hypermethylated in ABC DLBCLs, along with the TAP1, SOX9, PSMB9, IL21, SQLE, LTA, and MUC1 genes (Figure 3). Downstream of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) several other genes were also relatively repressed in ABCs (including MAP2K4, IRS1, ALDH2, ZNF318, DUSP10), whereas the subsequent more peripheral genes were more highly expressed (IRF4, IL10, IL6, CCND2, CCL18, OAS1). These data are consistent with the KEGG and BioCarta pathway analysis in being enriched for inflammatory and cytokine pathways and collectively implicate these cytokine networks in playing central and distinct roles in GCB and ABC DLBCLs.
Tumor necrosis factor α network is key epigenetically dysregulated network between ABC and GCB DLBCLs. Integration of 263 differentially methylated genes with 622 differentially expressed genes allowed identification of one main differentially regulated network with the use of Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software: Tumor Necrosis Factor α Pathway. Relative expression and methylation is represented by the ratio of ABC to GCB: overmethylated genes have greater methylation in ABC than in GCB DLBCLs, and overexpressed genes have greater expression in ABC than in GCB DLBCLs.
Tumor necrosis factor α network is key epigenetically dysregulated network between ABC and GCB DLBCLs. Integration of 263 differentially methylated genes with 622 differentially expressed genes allowed identification of one main differentially regulated network with the use of Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software: Tumor Necrosis Factor α Pathway. Relative expression and methylation is represented by the ratio of ABC to GCB: overmethylated genes have greater methylation in ABC than in GCB DLBCLs, and overexpressed genes have greater expression in ABC than in GCB DLBCLs.
To determine whether differentially methylated genes shared any specific DNA motifs we used the Finding Informative Regulatory Elements program24 to study sequences up to 1 kilobase upstream of the reported transcription start sites. This analysis identified that a motif resembling the Sp1 transcription factor binding site is significantly enriched in the genes that were relatively highly methylated in ABC compared with GCB and the control genes (all the rest of the genes). Sp1 was detected in 67% of the methylated sequences in ABC, whereas it was found in 40% of the methylated sequences in GCB and 31% of the control sequences (supplemental Figure 3).
Sixteen genes overlap and are inversely correlated between methylation and gene expression signatures
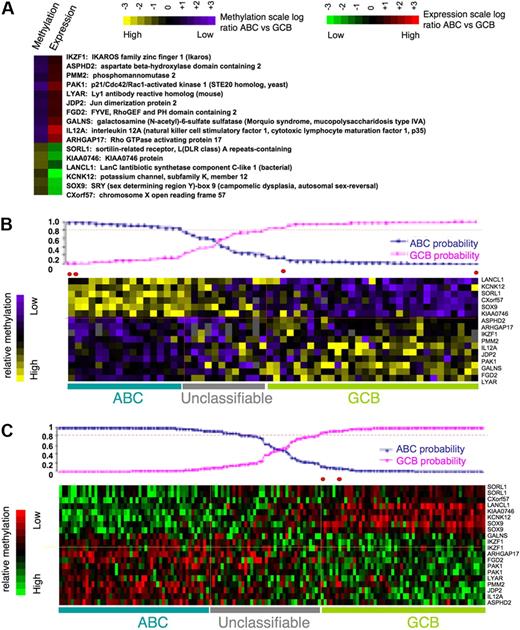
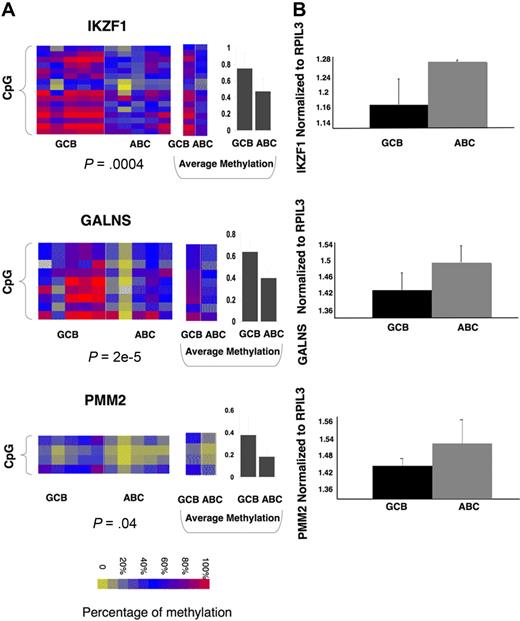
To identify a core set of functionally relevant differentially methylated genes we explored the overlap of the differentially regulated gene sets captured by gene expression (411 genes) and DNA methylation (239 genes) and represented on both arrays. A set of 16 genes was present in both signatures. Although this number is relatively low, it is still much greater than expected by chance (P = .005 by Fisher exact test; Figure 4A) given the number of genes present in both platforms. All of these genes displayed inverse correlation between DNA methylation and gene expression, suggesting that their DNA methylation is functionally significant. The 16 differentially methylated genes predicted GCB versus ABC labels with 92% accuracy with the use of Bayesian predictor with probability greater than 0.8 (as expected, because the gene set was derived from the same patients; Figure 4B). Moreover expression of the same 16 genes also had 98% accuracy in predicting ABC and GCB labels in an independent cohort of 203 DLBCLs from Lenz et al11 (Figure 4C). Included among these 16 genes were IKZF1, which is a tumor suppressor in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia,30 and also IL12, JDP2, PAK1, and PMM2. To further confirm differential methylation of these genes we performed single locus quantitative methylation sequencing assays (MassARRAY EpiTYPER) in a set of 5 patients randomly selected with GCB and 5 patients with ABC DLBCLs. These assays covered most CpGs at each locus up to 3 kilobase upstream of the transcriptional start site, providing a more inclusive and extensive coverage than HELP (Figure 5A; supplemental Figure 4). In 13 of the 16 genes, Epityping confirmed significant differences in methylation between ABC and GCB DLBCLs observed in HELP (P < .005 for most genes except for one with P < .1). For 3 genes (JDP2, SORL1, ARHGAP17) we failed to detect marked difference in overall promoter methylation (supplemental Figure 4C). Further comparison of the methylation profiles showed that all 3 genes have more focal differences (only selected CpGs, P < .01) in methylation between ABC and GCB groups. We also validated differential expression of a subset of the 16 genes (IKZF1, GALNS, and PMM2) in 5 randomly selected cases of ABC and 5 GCB primary DLBCLs with the use of quantitative PCR (Q-PCR; patients for EpiTYPING validation and Q-PCR validation were not matched because of the lack of corresponding sample material). The Q-PCR showed a similar trend of differential expression in ABC and GCB to that predicted by the expression arrays but not statistically significant probably because of the limited sample size (Figure 5B). This core methylation signature between ABC and GCB DLBCLs thus contains genes potentially contributing to biologic differences between 2 subtypes of lymphoma and which may serve as potential biomarkers.
Methylation or expression level or both of 16 genes can accurately differentiate between ABC and GCB DLBCLs. (A) Sixteen genes represent an overlap between differentially methylated (P < .001) and most differentially expressed (P < .001) genes between ABC and GCB DLBCLs. This set of genes represents genes potentially regulated by methylation with inverse methylation and expression levels (the inverse correlation is not random with P < .005 in Fisher exact test). (B-C) The mean log-ratio levels in ABC vs GCB DLBCLs of methylation and expression values of the 16 signature genes are depicted according to color scale in the heatmaps. The prediction probability graphs (on top of heatmaps) show that 16-gene methylation level can assign ABC and GCB labels with 92% accuracy with the use of Bayesian predictor at probability cutoff of 0.8 (B), whereas gene expression level can assign ABC and GCB labels with 98% accuracy with the use of Bayesian predictor at probability cutoff of 0.8 with an independent set of 203 DLBCL cases from Lenz et al11 (C).
Methylation or expression level or both of 16 genes can accurately differentiate between ABC and GCB DLBCLs. (A) Sixteen genes represent an overlap between differentially methylated (P < .001) and most differentially expressed (P < .001) genes between ABC and GCB DLBCLs. This set of genes represents genes potentially regulated by methylation with inverse methylation and expression levels (the inverse correlation is not random with P < .005 in Fisher exact test). (B-C) The mean log-ratio levels in ABC vs GCB DLBCLs of methylation and expression values of the 16 signature genes are depicted according to color scale in the heatmaps. The prediction probability graphs (on top of heatmaps) show that 16-gene methylation level can assign ABC and GCB labels with 92% accuracy with the use of Bayesian predictor at probability cutoff of 0.8 (B), whereas gene expression level can assign ABC and GCB labels with 98% accuracy with the use of Bayesian predictor at probability cutoff of 0.8 with an independent set of 203 DLBCL cases from Lenz et al11 (C).
Single genes of 16-gene methylation signature can differentiate between ABC and GCB subtypes of primary DLBCLs across platforms. (A) Heatmaps represent EpiTYPER results for 3 of the 16 genes: IKZF1, GALNS, and PMM2 (for the rest of the 16 genes, see supplemental Figure 4), performed in 5 randomly selected ABC and 5 GCB primary DLBCL cases. Rows of the heatmap represent individual CpGs in the promoter regions with color reflecting methylation value; whereas columns represent individual cases with class label on the bottom. A t test with methylation values from all tested CpGs was performed between ABC and GCB subtypes, with P value represented below each heatmap. Panels in the middle show the methylation levels for each CpG averaged in ABC and GCB cases. Panels on the right show the average methylation level of all CpGs in ABC and GCB cases with error bar for standard deviation. (B) Q-PCR was performed in 5 ABC and 5 GCB DLBCLs with primers specific for IKZF1, GALNS, and PMM2. The amount of transcript was calculated by normalizing to internal control gene RPIL3 and is shown as an average within the subtype. It shows the trend for greater expression in ABC than GCB DLBCLs, which is inversely correlated with greater DNA methylation of the corresponding promoters.
Single genes of 16-gene methylation signature can differentiate between ABC and GCB subtypes of primary DLBCLs across platforms. (A) Heatmaps represent EpiTYPER results for 3 of the 16 genes: IKZF1, GALNS, and PMM2 (for the rest of the 16 genes, see supplemental Figure 4), performed in 5 randomly selected ABC and 5 GCB primary DLBCL cases. Rows of the heatmap represent individual CpGs in the promoter regions with color reflecting methylation value; whereas columns represent individual cases with class label on the bottom. A t test with methylation values from all tested CpGs was performed between ABC and GCB subtypes, with P value represented below each heatmap. Panels in the middle show the methylation levels for each CpG averaged in ABC and GCB cases. Panels on the right show the average methylation level of all CpGs in ABC and GCB cases with error bar for standard deviation. (B) Q-PCR was performed in 5 ABC and 5 GCB DLBCLs with primers specific for IKZF1, GALNS, and PMM2. The amount of transcript was calculated by normalizing to internal control gene RPIL3 and is shown as an average within the subtype. It shows the trend for greater expression in ABC than GCB DLBCLs, which is inversely correlated with greater DNA methylation of the corresponding promoters.
Discussion
It is increasingly clear that aberrant epigenetic regulation of gene expression is a hallmark of cancer. As such, we reasoned that examination of DNA methylation profiles could help to understand the unique biologic properties of ABC and GCB DLBCLs. Because genetic lesions do not fully explain the differences between these DLBCL subtypes, it is reasonable to postulate that epigenetic programming might also contribute to the phenotype of these tumors. Accordingly, by analyzing the DNA methylation status of more than 50 000 CpGs distributed among 14 000 gene promoters we identified 263 genes (311 probe sets) that are differentially methylated among ABC and GCB DLBCLs. Previous studies of DNA methylation in DLBCL either failed to find differentially methylated genes between ABC and GCB DLBCLs or identified only a small set of genes.16,17 The most probable reason for this was the methylation platforms interrogating smaller numbers of genes and CpGs. In our study the main gene pathways affected by differential methylation between GCB and ABC DLBCLs were cytokine signaling, germinal center (GC) B cell, and NFκB-regulated genes, which in fact are consistent with the known biologic differences between the GCB and ABC DLBCLs.5,27 ABC DLBCLs are known to harbor mutations in genes within the NFκB pathway and to display prominent signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling.7,31 These data confirm the relevance of these signaling pathways to DLBCL pathophysiology and show that DNA methylation may contribute together with genetic lesions to their deregulation in ABC versus GCB lymphomas.
Although the GCB lymphomas are often thought of as arising from GC B cells and the ABC lymphomas from B cells of late GC cells or plasmablasts, the cells of origin of these tumors have not been strictly defined functionally.5,32 Emerging data suggest that at least some of the gene expression differences of these tumors could have a root in the distinct biology of the respective normal cell of origin, which might reflect the differential ability of genetic or epigenetic alterations to contribute to lymphomagenesis. We hypothesize that both genetic and epigenetic factors contribute to establishing ABC and GCB signatures. It is increasingly clear that DNA methylation patterns vary among tissues and with differentiation, and in other studies we have found that naive B cells display differences in DNA methylation compared with GC centroblasts.33 As future studies more clearly delineate the cell of origin for these DLBCLs, it will be interesting to evaluate whether the stage-specific DNA methylation distribution of B-cell precursors contributes to the epigenetic differences between ABC and GCB DLBCLs.
An alternative hypothesis explaining aberrant DNA methylation in DLBCLs is based on the observation reported by Martin-Subero et al,16 suggesting that de novo methylated genes in lymphomas are enriched for PcG targets and reflect acquisition of “stemness” during lymphomagenesis, which may represent the early event in neoplastic transformation of B cells. The same group demonstrated that different forms of non-Hodgkin lymphomas have distinct epigenetic profiles.34 Along these lines, it is possible that alterations of certain transcriptional or epigenetic regulatory proteins might induce specific epigenetic patterns in lymphoma. For example, Morin et al35 discovered frequent point mutations in the PcG protein and histone methyltransferase EZH2, more frequently occurring in GCB type DLBCLs. Given that the interplay between DNA methylation and histone modifications is possible, such lesions could induce specific alternations in DNA methylation.
Another possible mechanistic clue can be derived from our finding that an Sp1 motif is enriched in differentially hypermethylated genes in ABC DLBCLs. It is possible that levels of Sp1 determine the occupancy of the binding motifs and thus the degree to which those are protected from methylation. Because Sp1 binding may be affected by methylation status of the cytosines in its binding motif (5′-GGGCGG),36,37 aberrant methylation of Sp1 sites in ABC DLBCLs may lead to dysregulation in Sp1 binding and affected transcriptional regulation of its downstream targets. Alternatively, lower levels of Sp1 binding in ABC precursor cells might facilitate aberrant methylation of these sites.
We find that integration of the differentially expressed and differentially methylated gene signatures between patients with ABC and GCB captured a specific gene network centered on TNFα, suggesting that this network could play a significant role in explaining the biologic difference between these tumors. The genes involved include TNFα, SOX9, MUC1, IL21, IL4, IL10, LTA, and so forth and reflect a possible functional attenuation of TNFα pathway in ABC compared with GCB DLBCLs. Although the DNA methylation status of these genes was inversely correlated with gene expression, they did not reach our cutoff for statistical significance and so were not captured as part of the 16 gene overlap signature. Nonetheless, it is reasonable to propose that this gene network be further explored because gain or loss of function of components of this pathway have been linked to lymphomagenesis.38 TNFα has autocrine and paracrine effects39 and can mediate activation of NF-κB pathway with antiapoptotic effects,40 activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway with proliferation and differentiation effects,41 and induction of death signaling with activation of caspase-8 and induced apoptosis.42 Stimulation of TNFα occurs during inflammatory disease, and a link between infection, chronic antigenic stimulation, and lymphomagenesis has been reported as relevant to DLBCL pathogenesis. De Vita et al38 reported expression of TNFα in premalignant lymphoproliferative lesions in the setting of Sjögren disease and during progression to B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.38 Elevated secretion of TNFα in combination with Helicobacter pylori–specific T helper 1 (TH-1) response predisposes to a more adverse outcome of gastritis, including peptic ulcer and higher risk of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue–derived lymphomas.43 The InterLymph consortium reported that polymorphisms of TNFα, LTA, and IL10 are associated with a higher risk of developing DLBCL.44,45 Elevated serum levels of TNFα and interleukin-10 (IL-10) were also associated with inferior survival in patients with DLBCL, although no distinction was made about whether these were ABC or GCB tumors.46,47 However, a link between treatment with TNFα-suppressing drugs used for chronic inflammatory diseases and lymphomagenesis has been reported. More detailed mechanistic studies of this pathway are clearly warranted, specifically in the context of GCB versus ABC DLBCLs. However, one potential therapeutic implication of the involvement of this network relates to use of steroids, which are included in most DLBCL regimens, and which function in part through a TNFα-related pathway. Perturbation of this network might influence the therapeutic actions of steroids.
Using stringent criteria we identified a minimal set of 16 genes that were significantly differentially methylated and inversely correlated with expression between ABC and GCB DLBCLs and which readily distinguished ABC from GCB cases. This set of genes includes known tumor suppressor (such as IKZF148 ) or pro-oncogenic (such as SOX9 and PAK1) functions.49,50 Further functional study of these genes is warranted to define whether they contribute to lymphomagenesis. This gene set might also serve as a potential clinically useful biomarker, as suggested by the fact that expression of these genes was 98% accurate in distinguishing patients with ABC and GCB in an independent cohort. Given the stability of DNA methylation in clinical specimens and the relatively technical ease with which DNA methylation abundance can be determined, it is possible that methylation biomarkers such as these could eventually be used either alone or in combination with other methods to distinguish ABC from GCB cases in the clinical setting. Prospective validation studies will help to define the utility of this approach.
The online version of the article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NCI (K08 CA127353; R.S.), LLS SCOR (grant 7017-09; A.M.), the National Cancer Institute of Canada (NCIC; R.D.G.), the Terry Fox Foundation Program Project (grant 019001; R.D.G.), the Terry Fox Foundation (grant 019005; N.A.J.), the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research (ST-PDF-01793; N.A.J.), and the Canadian Institute of Health Research (STP-53912; N.A.J.). A.M. is a Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Scholar.
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: R.S. performed HELP profiling, analyzed methylation data and Q-PCR data, and wrote the manuscript; H.G. performed gene expression analysis, statistical and integrative analysis, and wrote the manuscript; L.T. performed Q-PCR and DNA extraction; L.C. performed gene expression analysis and revised manuscript; N.A.J. collected patient samples and performed gene expression analysis; and R.D.G., O.E., J.M.G., and A.M. designed and supervised the research.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Randy D. Gascoyne, Center for Lymphoid Cancers, BC Cancer Agency & BC Cancer Research Center, 675 W 10th Ave, Vancouver, BC V5Z 1L3; e-mail: rgascoyn@bccancer.bcca; or Olivier Elemento, Weill Cornell Medical College, Institute for Computational Medicine, Department of Physiology and Biophysics, 1305 York Ave, New York, NY 10021; e-mail: ole2001@med.cornell.edu; or Ari Melnick, Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, 1300 York Ave, New York, NY 10065; e-mail: amm2014@med.cornell.edu.
References
Author notes
R.S. and H.G. contributed equally to this study.