Abstract
Abstract 3255
The platelet αIIbβ3 integrin receptor plays a central role in hemostasis and thrombosis. Small molecule inhibitors of αIIbβ3 based on the RGD cell recognition sequence block ligand binding by interacting with αIIb D224 via their positively-charged (R-like) group and coordinating the Mg2+ ion in the metal ion adhesion site (MIDAS) via their carboxyl (D-like) group. We recently reported a novel inhibitor of αIIbβ3 (RUC-1) that binds exclusively to αIIb and we now report the structure-based design and synthesis of RUC-2 [2-amino-N-(3-(5-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-5H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidin-2-yl)phenyl)acetamide; MW 385], a RUC-1 derivative with ∼100-fold higher affinity and an IC50= ∼90 nM for ADP-induced platelet aggregation. RUC-2, like RUC-1 shows specificity for αIIbβ3 compared to αVβ3 and produces much less exposure of the β3 LIBS1 epitope than does eptifibatide (eptifibatide=100%, untreated platelets=22±3 %; RUC-2=21±3%). RUC-2 also produces less of a global conformational change in αIIbβ3 compared to eptifibatide as measured by dynamic light scattering, gel permeation chromatography, and electron microscopic imaging of αIIbβ3 in nanodiscs. X-ray crystallography of RUC-2 soaked into the αIIbβ3 headpiece in 1 mM Ca2+ and 5 mM Mg2+ at 2.6 Å revealed that RUC-2 binds to αIIb much the way RUC-1 does, but in addition it binds to one of the sidechain carboxyl oxygens of the β3 MIDAS residue Glu-220, thus displacing Mg2+ from the MIDAS. When RUC-2 was soaked into the crystal in the presence of 20 mM Mg2+, however, the Mg2+ was identified in the MIDAS and RUC-2 was absent from the pocket. Molecular dynamics simulations were in accord with the X-ray crystallographic data. Support for competition between RUC-2 and Mg2+ for binding to the MIDAS came from studies showing that increasing the Mg2+ concentration significantly decreased RUC-2's ability to inhibit PAC-1 binding to CHO cells expressing αIIbβ3, platelet adhesion to fibrinogen, and thrombin receptor activating peptide-induced platelet aggregation. We conclude that RUC-2 inhibits ligand binding with high affinity and specificity by a novel mechanism in which it competes with Mg2+ for Glu-220, and as such may offer advantages as a therapeutic agent.
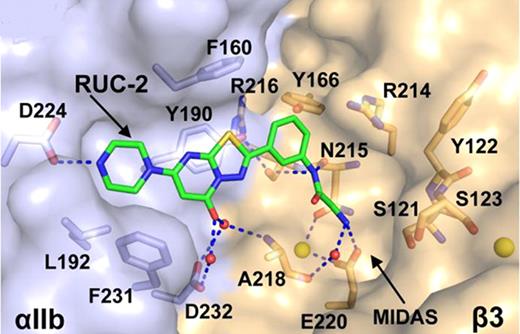
The binding pocket of RUC-2 in the closed αIIbβ3 headpiece crystal structure. αIIb and β3 are shown as solvent accessible surfaces. Ca2+ ions of SyMBS or ADMIDAS (yellow) are shown as spheres. RUC-2 and selected αIIbβ3 sidechain and backbone atoms are shown as sticks with green (RUC-2), light blue (αIIb), or wheat carbons (β3), red oxygens, blue nitrogens, and yellow sulphurs. Water molecules are small red spheres. Hydrogen and metal coordination bonds are shown as dashed blue lines.
Coller:Centocor/Accumetrics/Rockefeller University: Royalty interests in abciximab/VerifyNow assays/RUC-1 and RUC-2.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal