Abstract
Abstract 3927
CLL B-cells interact with their microenvironment in a variety of ways that influence leukemia cell survival. Contact mediated interactions are the most widely studied. More recently, bidirectional cytokine mediated interactions have been found to modulate spontaneous and drug induced CLL B-cell death. Specifically, upregulation of CCL2, CCL3, and CCL4 are found when CLL B-cells are co-cultured with various accessory cells. We set out to more comprehensively profile the effect of CLL-stromal cell co-culture on immune cytokine regulation and to evaluate the effect of novel therapeutic agents in clinical testing for patients with CLL on these interactions.
Freshly isolated CLL B-cells (n=24) were cultured in AIM V media for 24 hours alone or in direct contact with HS-5 stromal cells. HS-5 cells were cultured alone in AIM V to determine basal level of immune cytokine secretion. Immune cytokine levels in the media under these 3 conditions (CLL alone; HS5 alone; co-culture) were assessed using multiplex cytokine arrays (Invitrogen). The protective effects of the 6 most highly upregulated cytokines on spontaneous apoptosis of CLL B-cells after 7 day culture were then examined by culturing leukemic cells with and without recombinant cytokines. The effect of sub-lethal doses of the PI3K inhibitor CAL-101, the AKT inhibitor MK2206 and the Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 were examined. To compare the effect of these drugs to a more conventional chemotherapeutic agent, we evaluated fludarabine (F-Ara-A) under the same conditions. To explore the ability of these novel agents to overcome stromal rescue, CLL B-cells pre-exposed to bendamustine (BEN) were cultured in media alone, or in direct contact with stroma with and without sub-lethal doses of CAL-101, MK2206, or PCI-32756. Leukemic cell viability was assessed by flow cytometry using annexin/PI staining.
Six cytokines increased ≥4 fold (e.g. >400%, all p<0.0001) on coculture relative to the expected additive value of individual cultures. Consistent with previous reports, (Schulz 2011; Burger 2009) CCL3 and CCL4 were found to have the greatest upregulation (both >20 fold the additive value). The other highly upregulated cytokines detected have not been previously reported to be influenced by coculture: IL12 (15 fold additive value), IL1β (11 fold additive value), TNF-α (11 fold additive value), and IL-1RA (4 fold additive value). Although transwell experiments (n=6) suggested upregulation of these cytokines was largely contact dependent, substantial upregulation of several cytokines still occurred without direct contact. Each of the 6 most upregulated cytokines reduced spontaneous apoptosis when CLL B-cells were cultured for 7 days in media plus recombinant cytokine.
When CLL B-cells and HS-5 cells were co-cultured with CAL-101, MK-2206, or PCI-32765, the effects on cytokine secreted upregulation were cytokine and drug specific (e.g. one drug affected individual cytokines differently; different drugs affected different cytokines). For example, PCI-3276 and CAL-101 had similar affects on the upregulation of CCL3 and CCL4 on co-culture but opposite effects on TNF-α and IL-1β. In contrast, F-Ara-A had minimal effect on upregulation of any of these 6 cytokines.
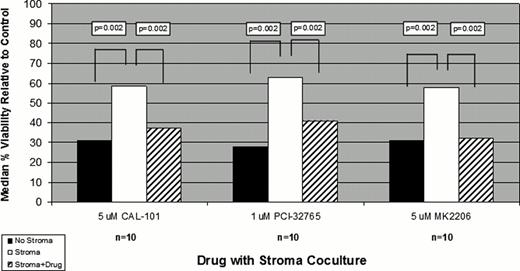
Finally, we evaluated the ability of these novel agents to overcome stromal rescue of CLL B-cells treated with conventional chemotherapeutic agents. At sublethal doses CAL-101, MK2206, PCI-32765 each significantly overcame stromal rescue of BEN exposed CLL B-cells. (Fig.1)
Direct physical interaction of CLL B-cells with bone marrow stromal cells resulted in profound upregulation of multiple immune cytokines. The 6 most upregulated cytokines identified in these experiments all reduced spontaneous apoptosis of CLL B-cells on extended culture. Sublethal doses of the PI3K inhibitor CAL-101, the AKT inhibitor MK2206, and the Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 had distinct effects on stromal cell mediated cytokine upregulation. Importantly, each of these 3 drugs also overcame stromal mediated rescue of BEN exposed CLL B-cells. These in vitro findings support the ongoing clinical trials of BEN in combination with CAL-101 (ASH 2011), PCI-32765 (ASCO 2012) or MK2206 (Ding et. al., unpublished observation).
Stromal Rescue after exposure to Bendamustine
Kay:Celgene: Research Funding. Shanafelt:Celgene: Research Funding; Hospira: Research Funding; Cephalon: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Glaxo-Smith-Kline: Research Funding; Polyphenon E International: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal