Abstract
Abstract 4794
The diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and the monitoring during therapy requires identification and quantification of the BCR-ABL1 transcripts. Molecular monitoring has become a requirement as therapy has become more efficient in inducing cytogenetic and molecular remissions. Unfortunately, there is great variability in the methodologies used for molecular monitoring, with various levels of expertise, great variability of the results between different laboratories, and frequently limited access. A simple method for rapid detection and quantification of BCR-ABL1 transcripts would benefit patients and improve outcomes. The GeneXpert DX System rapidly detects and quantifies BCR-ABL1 mRNA transcripts (type e13a2/b2a2 or e14a2/b3a2) in patients diagnosed with CML via an automated, quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Results are available within 2 hours and adjusted to the international scale. We assessed the correlation between the GeneXpert system with the results from the Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory (MDL) at MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Peripheral blood specimens were collected from 55 patients with CML, acute lymphoblastic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia and used for assay development, analytical validation and precision studies that compared the GeneXpert BCR-ABL1 Monitor Assay versus the standard MD Anderson MDL real-time PCR protocol. CML Ph positive was assessed as belonging to categories based on the BCR-ABL1 mRNA transcript level (Category I, >1%; Category 2, >0.1–1%; Category 3, >0.01%–0.1%; Category 4, ≤0.01%). Patients who had tyrosine kinase therapy resulting in stable disease were in categories 3 or 4, whereas newly diagnosed patients or those with acute disease were in categories 1 and 2. Ph-negative patients with ALL (n=2) and AML (n=4) were the negative controls.
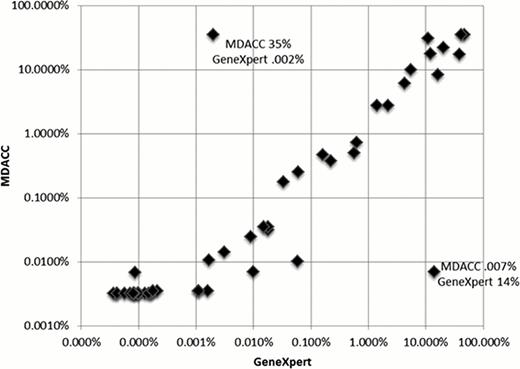
Of the 55 patients whose blood was tested by the GeneXpert monitoring assay, 49 patients with CML fell into categories 1–4 (3, 7,4,35 respectively). The remaining 6 patients had a diagnosis of ALL or AML and acted as negative control. These patients had undetectable transcript levels by the GeneXpert system. The median time to obtaining results with the GeneXpert system was 1 hour and 30 min (range 1:29:51 to 1:31:16). There was a strong correlation between the results achieved with the GeneXpert system and those obtained at the MDACC MDL (R=0.7597; P=< 0.0001). Only two samples showed clearly discordant values and these likely represent swapping of the samples which were run at the same time. Excluding these samples the correlation is even tighter (R=0.8937; P= < 0.0001).
Results from GeneXpert system BCR-ABL1 are rapid and reliable and can be obtained with little training required. These results suggest that this methodology can be used to expand access and reproducibility to molecular monitoring in CML.
Cortes:Cepheid: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal