Key Points
The commonest lesions in anaplastic large cell lymphomas are losses at 17p13 and at 6q21, concomitant in up to one-quarter of the cases.
PRDM1 (BLIMP1) gene (6q21) is inactivated by multiple mechanisms and acts as a tumor suppressor gene in anaplastic large B-cell lymphoma.
Abstract
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a mature T-cell lymphoma that can present as a systemic or primary cutaneous disease. Systemic ALCL represents 2% to 5% of adult lymphoma but up to 30% of all pediatric cases. Two subtypes of systemic ALCL are currently recognized on the basis of the presence of a translocation involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase ALK gene. Despite considerable progress, several questions remain open regarding the pathogenesis of both ALCL subtypes. To investigate the molecular pathogenesis and to assess the relationship between the ALK+ and ALK− ALCL subtypes, we performed a genome-wide DNA profiling using high-density, single nucleotide polymorphism arrays on a series of 64 cases and 7 cell lines. The commonest lesions were losses at 17p13 and at 6q21, encompassing the TP53 and PRDM1 genes, respectively. The latter gene, coding for BLIMP1, was inactivated by multiple mechanisms, more frequently, but not exclusively, in ALK−ALCL. In vitro and in vivo experiments showed that that PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in ALCL models, likely acting as an antiapoptotic agent. Losses of TP53 and/or PRDM1 were present in 52% of ALK−ALCL, and in 29% of all ALCL cases with a clinical implication.
Introduction
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a mature T-cell lymphoma with either a systemic or primary cutaneous disease (cALCL) presentation.1,2 Systemic ALCL represents a small subset of adult lymphomas (2%-5%), but up to 30% of pediatric cases. Systemic ALCLs are currently stratified on the presence or absence of a translocation involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase ALK gene.1 ALK+ALCL most frequently occur among children or young adults, while ALK−ALCL cases are more often observed among elderly people.3 Although several studies have shown that ALK+ALCL has a significantly better outcome than ALK−ALCL, when ALCL patients are stratified according to the clinical parameters (mostly age and/or stage), both subsets display similar failure-free and overall survival (OS) rates.3
The ALK+ALCL subset most frequently carries the t(2;5)(p23;q35) fusing ALK to the nucleophosmin (NPM) gene.4,5 All ALK fusions have a constitutive activation of the catalytic domain of the ALK tyrosine kinase, leading to the phosphorylation and activation of several downstream pathways favoring in lymphoma survival, growth, and/or regulating the proliferation and cell-cycle control.4 Besides 2 translocations, more frequent among cALCL than systemic ALK−ALCL,6-9 the molecular events responsible for the pathogenesis of ALK−ALCL cases are still largely unknown. Because ALCL is a relatively rare disease, only few studies regarding the genomic analysis of ALCL are available,5,10-13 often composed by few samples and analyzed with low-resolution techniques. Nevertheless, genomic lesions have been observed in the 2 ALCL subsets: ALK+ALCL can carry chromosomal imbalances including loss of 4q13-q28, 6q13-q22, 11q14-q23, and 13q and gains of 7p11-pter and chromosome 17.6,8-11 Conversely, ALK−ALCL generally presents a more complex genomic profiling respect to ALK+ALCL, and shows gains of 1q41-qter, 5q, 6p, 7p, 8q, 12q, and 17q and losses of 6q21-q22 and 13q.6,8-11
To disclose the molecular pathogenesis and to assess the relationship between ALK+ and ALK− ALCL subtypes, we performed genome-wide DNA profiling using high-density, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays on a relative large series of primary ALCL samples and ALK+ALCL cell lines.
Material and methods
Tumor panel
Clinical specimens were derived from involved sites and obtained in the course of routine diagnostic procedures, before therapy. Diagnoses were made following the recommended criteria.1 Cases were selected on the availability of frozen material with a fraction of neoplastic cells in the specimen representing >70% of overall cellularity as determined by morphologic and/or immunophenotypic studies. Informed consent was obtained in accordance to the Helsinki Declaration following the procedures approved by the local ethical committees and institutional review boards of each participating institution. The study was approved by the Bellinzona ethical committee.
Genome-wide DNA profiling
Mutational analysis
Whole-genome amplification (WGA) was performed as described,16 and all PRDM1 coding exons and TP53 exons 4 to 8 were polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplified (primers in supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood Web site), and sequenced as described.16 Mutations were confirmed by independent PCR from non-WGA DNA, and germline polymorphisms (obtained from the NCBI SNP database or present in available matched normal DNA) were discarded. The presence of a copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at the PRDM1 gene locus was assessed using dChipSNP (www.dchip.org).17
Methylation analysis
The methylation status of the PRDM1 gene promoter was investigated by bisulfite sequencing PCR method. DNA samples (500 ng) underwent bisulphite modification using the EZ DNA Methylation kit (Zymo Research). PCR was performed with primers specific for converted bisulfite converted DNA (supplemental Table 1) designed with MethPrimer,18 and the amplicons were visualized on agarose gels. PCR products were purified using the QIAquick PCR Purification kit (Qiagen), and paired-end sequenced (Mycrosynth).
Immunohistochemistry
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections of 38 ALCL cases from the University of Turin Department of Pathology were stained on a semiautomated immunostainer (Bond-Max; Leica Microsystems). Briefly, paraffin-embedded sections were first dewaxed, and epitope retrieval was performed in 0.01M citrate buffer, pH 6.0. Antibodies used were anti–PRDM-1 (1:20, mouse monoclonal ROS195G,19 kindly provided by Dr Giovanna Roncador, Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Oncológicas, Madrid, Spain). Slides were analyzed by light microscopy and reviewed by 2 independent operators.
FISH
Cell lines
Established human cell lines SUDHL1, SupM2, SupM2-TS, JB6, L82, Karpas 299 (ALK+ALCL), FE-PD (ALK−ALCL), MAC-1 (cALCL) were cultured with RPMI media supplemented with fetal bovine serum (10%) and penicillin-streptomycin-neomycin (Sigma-Aldrich).
Lentiviral infection
Packaging cells were transfected with PRDM1 cloned in pWPI lentiviral vector (kindly provided by Dr Laura Pasqualucci) in combination with third-generation helper plasmids. The viral supernatant was collected after 48 hours, filtered, and SupM2-TS, SUDHL1, and JB6 ALCL cells were infected. One cycle of infection was performed. Cells were collected at different days after infection; RNA and proteins were extracted and then processed, respectively, for real-time PCR and western blotting analysis.
Evaluation of infection efficiency
Cells infected with pWPI-HA-BLIMP1 or the control cells (cells infected with empty vector and cells not transfected) were harvested and washed once in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and analyzed using a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). The analysis of the percentage of green fluorescent protein (GFP)–positive cells was performed using CellQuest Pro software (Becton Dickinson).
Cell proliferation
Cells infected with pWPI-HA-BLIMP1 and the control cells (cells infected with empty vector and cells not transfected) were recovered and an equal number of cells were plated in triplicates. Cells were collected and counted daily up to 10 days after the recovery.
Evaluation of cell death and cell-cycle analysis
Cells infected with pWPI-HA-BLIMP1 and the control cells were harvested and washed once in PBS and then stained with propidium iodide (PI) (1 μg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich) in PBS and analyzed using a FACScan flow cytometer. The analysis of the percentage of cell death was performed using CellQuest Pro software.
Cells infected with pWPI-HA-BLIMP1 and the control cells were harvested at different time points, washed once in PBS. and then fixed in 70% ethanol at 4°C for at least 1 hour. Cells were stained with PI (50 μg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich) in PBS containing RNAse-A (75 kU/mL; Sigma-Aldrich) and analyzed for DNA content using the FACScan flow cytometer. The analysis of cell cycle was performed using the FlowJo software (TreeStar).
Western blotting analysis
Cells were solubilized in hot sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) lysis buffer and sonicated for 15 seconds. The protein content was determined using the BCA protein assay (Pierce Chemical Co). Lysates were fractionated by 8% SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Membranes were incubated with anti-PRDM1 (6D3, SC-47732; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) anti-α–glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (MAB374; Millipore), anti-Actin (MAB1501R; Millipore) or anti-GFP (2555; Cell Signaling Technology) overnight, followed by the appropriate horseradish peroxidase–conjugated anti-mouse or anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (Amersham Life Science) for 1 hour. Enhanced chemiluminescence detection was then done following the manufacturer’s instructions (Amersham Life Science). Equal loading of samples was confirmed by probing for GAPDH or Actin.
Real-time PCR
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and purified using the RNeasy total RNA Isolation kit (Qiagen). The concentration of total RNA was determined spectrophotometrically at 260 nm using NanoDrop (NanoDrop Technologies). One microgram of total RNA was reverse-transcribed using the Superscript First-Strand Synthesis System for the RT-PCR kit (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Real-time PCR amplification was performed using Fast SYBR Green Master Mix on a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems), with primers (supplemental Table 1) designed using Primer3.22 All samples were analyzed in triplicates. The messenger RNA (mRNA) relative quantities for each sample were calculated based on mean cycle threshold (Ct) values using the Δ-Δ Ct correcting for experimental variations by GAPDH normalization.
Gene expression profiling
Gene expression profiling (GEP) was performed on 3 biologic replicates for each condition of Supm2-TS cells using the HumanHT-12v4 Expression BeadChip (Illumina), as described.23 Data were first extracted with the Illumina GenomeStudio software and then imported in GenomicsSuite 6.4 (Partek) and quantile normalized. Differentially expressed transcripts were identified by analysis of variance (ANOVA) (fold change, >1.5; false discovery rate, <0.2).
Mice and in vivo experiments
Male NSG (NOD/Shi-scid/IL-2Rγnull) mice, chosen for the rate of engraftments they manifest,24 were injected subcutaneously with 1 × 106 SupM2-TS cells infected with empty vector or with vector for PRDM1 reexpression in both flanks. Tumor growth was measured over time. At day 20, tumors were explanted and analyzed. Mice were treated properly and ethically in accordance with European Community guidelines.
Analysis of clinical data
OS was calculated from the time of diagnosis to the last follow-up or death of any cause. The log-rank test was used to investigate the impact on OS of categorical variables. The cumulative probability of OS was plotted as a curve according to the Kaplan-Meier method. Statistical analyses were performed with Stata/SE version 12.1 (StataCorp).
Results
Genomic profiling of ALCL
Genome-wide DNA profiling was performed on clinical specimens of 64 ALCL cases (31 ALK−ALCL and 33 ALK+ALCL) and 7 ALCL cell lines (5 derived from ALK+, 1 ALK−ALCL, and 1 cALCL) (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 1). Supplemental Table 2 reports the main clinical and pathological characteristics of patients.
Genomic aberrations in ALCL samples. (A) Frequency of DNA gains (up) and losses (down) observed in 64 systemic ALCL (top panel), 31 ALK−ALCL (middle panel), and 33 ALK+ALCL samples (bottom panel). Red represents gains and blue represents losses. X-axis represents chromosome localization and physical mapping; y-axis, proportion of cases showing the aberrations. (B-C) Representation of focal aberrations in ALCL samples. Analysis via GISTIC of copy number gains (left) and losses (right) for the 64 ALCL samples and only for the 31 ALK−ALCL samples. False-discovery rate q values are plotted along the x-axis with chromosomal position along the y-axis. Altered regions with significant levels exceeding the vertical green line (significance threshold) were deemed significant. Chromosomal positions are shown for each significant region on the right side of the plots.
Genomic aberrations in ALCL samples. (A) Frequency of DNA gains (up) and losses (down) observed in 64 systemic ALCL (top panel), 31 ALK−ALCL (middle panel), and 33 ALK+ALCL samples (bottom panel). Red represents gains and blue represents losses. X-axis represents chromosome localization and physical mapping; y-axis, proportion of cases showing the aberrations. (B-C) Representation of focal aberrations in ALCL samples. Analysis via GISTIC of copy number gains (left) and losses (right) for the 64 ALCL samples and only for the 31 ALK−ALCL samples. False-discovery rate q values are plotted along the x-axis with chromosomal position along the y-axis. Altered regions with significant levels exceeding the vertical green line (significance threshold) were deemed significant. Chromosomal positions are shown for each significant region on the right side of the plots.
ALK+ and the ALK− ALCL clearly differed in terms of genomic profiles (Figure 1A). The minimal common regions (MCRs), which should encompass the loci likely containing the pathogenetic genes, were calculated for the whole series of 64 clinical ALCL specimens (Table 1). The most common losses affected 17p13.3-p12 (25%), in which TP53 gene is located, and 6q21 (17%), the region that encompassed PRDM1 and ATG5. Other common losses were identified at 13q32.3-q33.3 and 16q23.2 (16%). More than 20% of ALCL samples presented gains of different regions of the long arm of chromosome 1, while 8q24.22 was gained in 16% of cases.
Most frequent recurrently affected regions detected in 64 ALCL samples
| Lesion/Cytoband . | Start* . | Size, kb* . | RefSeq genes† . | ALCL % . | ALK−ALCL % . | ALK+ALCL % . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Losses | |||||||
| 17p13.3-p12 | 526 | 11 747.22 | >20 (TP53) | 25 | 42 | 9 | .002 |
| 6q21 | 105 944 900 | 951.75 | ATG5, PRDM1 | 19 | 56 | 6 | <.001 |
| 13q32.3-q33.3 | 99 090 837 | 9349.42 | >20 | 16 | 23 | 9 | ns |
| 16q23.2 | 78 371 498 | 11 642 | MAF, WWOX | 16 | 29 | 3 | .004 |
| Gains | |||||||
| 1q | 121 344 093 | 127 880.29 | >20 | 23 | 32 | 15 | ns |
| 8q24.22 | 133 799 280 | 919.4 | NDRG1, PHF20L1, SLA, ST3GAL1, TG, WISP1 | 17 | 23 | 12 | ns |
| Lesion/Cytoband . | Start* . | Size, kb* . | RefSeq genes† . | ALCL % . | ALK−ALCL % . | ALK+ALCL % . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Losses | |||||||
| 17p13.3-p12 | 526 | 11 747.22 | >20 (TP53) | 25 | 42 | 9 | .002 |
| 6q21 | 105 944 900 | 951.75 | ATG5, PRDM1 | 19 | 56 | 6 | <.001 |
| 13q32.3-q33.3 | 99 090 837 | 9349.42 | >20 | 16 | 23 | 9 | ns |
| 16q23.2 | 78 371 498 | 11 642 | MAF, WWOX | 16 | 29 | 3 | .004 |
| Gains | |||||||
| 1q | 121 344 093 | 127 880.29 | >20 | 23 | 32 | 15 | ns |
| 8q24.22 | 133 799 280 | 919.4 | NDRG1, PHF20L1, SLA, ST3GAL1, TG, WISP1 | 17 | 23 | 12 | ns |
P values were calculated between ALK+ALCL and ALK−ALCL frequencies.
ns, not significant.
Numbering according to Genome Reference Consortium Human Build 37 (GRCh37) (hg19).
According to the NCBI RefSeq database.
ALK−ALCL displayed recurrent lesions at a higher frequency than ALK+ALCL. Losses of 17p13.3-p12 and 6q21 were observed in 42% and 35%, respectively, and losses of distal regions of chromosome 13, 12q, and 10 were identified in >20% of the cases. Gains at 1q were observed in almost 30% of ALK−ALCL. ALK+ALCL presented less lesions or at a lower frequency than ALK−ALCL: only gains of 1q, 7q32.3, and 7p22.3-p21.3 were observed in >15% of samples.
To further define regions containing genes with putative tumorigenic potential, we applied the Genomic Identification of Significant Targets in Cancer (GISTIC) 2.0 algorithm,25 which identifies aberrations occurring at a frequency higher than expected by chance, giving particular relevance to loci targeted by DNA amplifications or homozygous deletions.25 GISTIC identified a limited series of regions of gains and of losses (Figure 1B-C; supplemental Tables 3-4). The most significant aberrations were the losses at 17p13.1 (TP53) and at 6q21 (PRDM1 and ATG5), both among all ALCL samples and within the ALK−ALCL cases. GISTIC highlighted the loss at 14q11.2, region in which the T-cell receptor α (TCRα) locus is located. Because this deletion is likely due to the physiological rearrangements taking place in T cells, we discarded it from further analyses. The most significant gain in ALCL was at the 9p24.1 region (JAK2, CD274, PDCD1LG2, UHRF, KMD4C), while gains at 20q11.2 (ASIP, AHYC, ITCH, MIR644), at 11p13 (APIP, PDHX, CD44) and at 13q31.3 (MIR17HG) were identified in both ALK+ and ALK− ALCL, being more significant in the latter entity.
PRDM1 gene is often inactivated in ALCL
Both MCR analysis and GISTIC pointed to 6q21 loss as one of the most significantly recurrent lesion. The minimally affected region encompassed 1120 kb including 2 genes: PRDM1 and ATG5 (Figure 2A). We observed losses at 6q21 in 11 of 31 (35%) ALK− samples, in 4 of 5 (80%) ALK+ cell lines, and in 1 of 33 (3%) ALK+ cases. A PRDM1 homozygous loss was detected in a single ALK+ case. Deletion at level of 6q21 locus has been validated with FISH analysis on all ALCL cell lines and in 3 of the clinical specimens bearing PRDM1 loss (supplemental Figure 2).
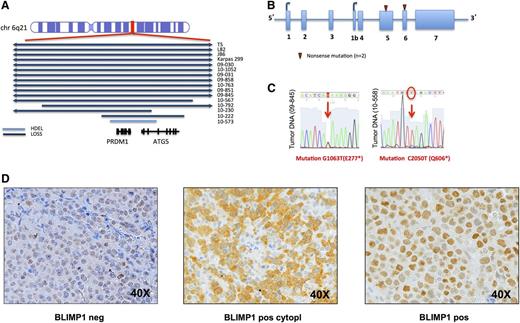
PRDM1 gene is inactivated in ALCL samples. (A) Representation of the aberrations, and their size, affecting the PRDM1 locus (6q21). Blue bars represent loss; light blue bars represent homozygous deletion (hdel). (B) Results of sequencing and mutational analysis of PRDM1 coding exons in 46 ALCL samples (31 ALK− and 15 ALK+ samples) and in 7 ALCL cell lines (5 ALK+ and 1 ALK− cell line and 1 cALCL). Red triangles are new mutations in 2 different ALK− samples. (C) View of the single nucleotide changes in different sequences. (D) Immunohistochemistry results for BLIMP1 staining: BLIMP1 staining was evaluated on TMA obtained from an independent series of ALCL samples. TMA samples were considered negative or positive for BLIMP1 depending on the intensity of the staining. A representative case for each condition, BLIMP1 negative (left panel), BLIMP1 positive only at cytoplasmic level (middle panel), BLIMP1 positive only at a nuclear level (right panel), is reported (magnification, ×40). TMA, tissue microarray.
PRDM1 gene is inactivated in ALCL samples. (A) Representation of the aberrations, and their size, affecting the PRDM1 locus (6q21). Blue bars represent loss; light blue bars represent homozygous deletion (hdel). (B) Results of sequencing and mutational analysis of PRDM1 coding exons in 46 ALCL samples (31 ALK− and 15 ALK+ samples) and in 7 ALCL cell lines (5 ALK+ and 1 ALK− cell line and 1 cALCL). Red triangles are new mutations in 2 different ALK− samples. (C) View of the single nucleotide changes in different sequences. (D) Immunohistochemistry results for BLIMP1 staining: BLIMP1 staining was evaluated on TMA obtained from an independent series of ALCL samples. TMA samples were considered negative or positive for BLIMP1 depending on the intensity of the staining. A representative case for each condition, BLIMP1 negative (left panel), BLIMP1 positive only at cytoplasmic level (middle panel), BLIMP1 positive only at a nuclear level (right panel), is reported (magnification, ×40). TMA, tissue microarray.
To evaluate whether this gene could also be inactivated by somatic mutations, we sequenced all coding exons of the PRDM1 gene. To evaluate whether the gene could also be inactivated by somatic mutations, we sequenced PRDM1 gene coding exons in all ALK−ALCL, all cell lines, and in 15 of 33 ALK+ALCL. Two mutations were detected in ALK− tumors, generating a stop codon (Figure 2B-C). One of these cases showed a copy-neutral LOH, while the other displayed the loss of the wild-type allele, suggesting a complete inactivation of the protein. We also analyzed the methylation profile of the PRDM1 gene promoter region in 40 of 69 ALCL samples, but no clear methylation was detected.
PRDM1 was inactivated, by deletion or by somatic mutations, in 12 of 31 (39%) and in 1 of 33 (3%) of the clinical specimens derived from ALK− and ALK+ ALCL, respectively, and in 4 of 5 (80%) ALK+ cell lines.
We then evaluated (by immunohistochemistry) the expression of PRDM1 protein on a series of 38 clinical specimens of ALCL, including 4 samples analyzed by DNA profiling. The protein was expressed at nuclear level in at least 10% of the neoplastic cells in 13 of 21 (62%) of ALK+ and 8 of 15 (53%) of ALK−ALCL. Two ALK−ALCL samples presented an exclusively cytoplasmic staining of PRDM1 (Figure 2D): 1 had a 6q21 loss and a PRDM1 stop codon mutation, possibly determining the aberrant protein localization.
PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in an in vitro model of ALCL
To understand the role of PRDM1 loss in ALCL, we studied the consequences of the reexpression of the gene, using lentiviral vectors, in the SupM2-TS cell line, an ALK+ALCL cell line with the same 6q21 loss observed in clinical specimens. Cells transduced with the pWPI-HA-BLIMP1 vector reexpressed PRDM1 at both the mRNA and the protein level (Figure 3A). The percentage of GFP-positive cells infected with empty vector increased over time with a concomitant decrease in the fraction of GFP-positive cells after PRDM1 reexpression (Figure 3B), suggesting that the enforced PRDM1 expression in an ALK+ALCL cell line, bearing PRDM1 loss, exerted a negative selective pressure.
PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in an in vitro model of ALCL. (A) PRDM1/BLIMP1 mRNA and protein level after infection with empty vector (pWPI) or vector for BLIMP1 reexpression (pWPI-HA-BLIMP1). (B) Percentage of GFP-positive cells after infection at 72 hours and 96 hours. (C) Percentage of growing cells after infection at 72 hours. *P = .017. (D) Growth curve after infection, cells counted at days 3, 5, and 7 after infection. (E) Percentage of dead cells after infection at 72 hours and 96 hours. (F) Cell-cycle profile after infection.
PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in an in vitro model of ALCL. (A) PRDM1/BLIMP1 mRNA and protein level after infection with empty vector (pWPI) or vector for BLIMP1 reexpression (pWPI-HA-BLIMP1). (B) Percentage of GFP-positive cells after infection at 72 hours and 96 hours. (C) Percentage of growing cells after infection at 72 hours. *P = .017. (D) Growth curve after infection, cells counted at days 3, 5, and 7 after infection. (E) Percentage of dead cells after infection at 72 hours and 96 hours. (F) Cell-cycle profile after infection.
We then evaluated whether the reexpression of PRDM1 gene could have an effect in terms of proliferation and apoptosis. Differently from control SupM2-TS cells (transduced with the empty vector), PRDM1 reconstituted cells underwent growth arrest, which was more marked starting from the third day after infection (Figure 3C-D). Concomitant to the proliferation arrest, we also observed a moderate increase in the percentage of apoptotic cells after PRDM1 transfection (23% vs 29% at 72 hours and 12% vs 17% at 96 hours) with an increase of the sub-G1 phase (8% vs 15%; P < .001). We observed also cell-cycle arrest comparing cells after infection with empty vector or with vector for PRDM1 reconstitution (G1: 49% vs 25%, P < .0001; S: 19% vs 13%, P < .001; and G2-M: 21% vs 31%, P < .05) (Figure 3E-F). Results were confirmed on 2 additional ALK+ALCL cell lines, SUDHL1 and JB6 (supplemental Figure 3).
PRDM1 exerts a prosurvival effect
To understand the transcriptional role of PRDM1 in ALCL, we carried out GEP in the SupM2-TS cells, infected with lentivirus pWPI or pWPI-HA-BLIMP1. Supervised analysis identified a limited number of genes modulated by PRDM1 reexpression (Figure 4), >70% of them upregulated after PRDM1 reconstitution. Among the differentially expressed transcripts, there were IRF4 and MIR155HG (downregulated), important for normal T-cell physiology and known to be deregulated in ALCL.8,9,26-31 The top upregulated genes also included transcripts involved in growth and cell proliferation inhibition (SERPINA3, KHDRBS3), apoptosis (S100A9, PMAIP1), and cell-cycle arrest (RASSF2). Because MIR155HG is a direct repressor of the proapoptotic factor SHIP1,32-35 we analyzed SHIP1 levels after BLIMP1 reexpression: SHIP1 mRNA levels were upregulated after BLIMP1 reconstitution.
Hierarchical clustering of samples analyzed with GEP. GEP analysis was performed in untreated Supm2-TS cells (n = 3), Supm2-TS cells 72 hours after infection with empty vector (pWPI; n = 3) and Supm2-TS cells after infection with lentivirus for BLIMP1 reconstitution (pWPI-HA-BLIMP1; n = 3).
Hierarchical clustering of samples analyzed with GEP. GEP analysis was performed in untreated Supm2-TS cells (n = 3), Supm2-TS cells 72 hours after infection with empty vector (pWPI; n = 3) and Supm2-TS cells after infection with lentivirus for BLIMP1 reconstitution (pWPI-HA-BLIMP1; n = 3).
PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in an in vivo model of ALCL
To further validate the in vitro data, we prepared pWPI-HA-BLIMP1 lentivirus for PRDM1 reexpression and pWPI empty vector for control for in vivo experiments using the SupM2 cell line, obtaining ∼50% of GFP-positive cells as read out of the efficiency of transfection. We then injected the cells in mice as follows: 3 mice infected with lentivirus for PRDM1 and 3 mice infected with empty vector. Tumors were explanted at day 20 after inoculum and reanalyzed by flow cytometry. Figure 5A shows that the percentage of GFP-positive cells in mice injected with PRDM1-positive cells was dramatically reduced with respect to the percentage of GFP-positive cells of control mice, suggesting that PRDM1-positive cells had growth impairment in vivo. These results were confirmed at protein level (Figure 5B). Xenograft growth curves of control and PRDM1-transduced SupM2 cells in NSG mice indicated that the latter cells grew less than controls, supporting the in vitro experiments (Figure 5C).
PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in vivo. (A) Percentage of GFP-positive cells in tumors explanted from mice infected with empty vector (pWPI) or with vector for BLIMP1 reexpression (pWPI-HA-BLIMP1). (B) Protein levels of BLIMP1 and GFP in tumors explanted from mice at day 20. A vertical line has been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. (C) Xenograft growth curves of infected cells in NSG mice.
PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in vivo. (A) Percentage of GFP-positive cells in tumors explanted from mice infected with empty vector (pWPI) or with vector for BLIMP1 reexpression (pWPI-HA-BLIMP1). (B) Protein levels of BLIMP1 and GFP in tumors explanted from mice at day 20. A vertical line has been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. (C) Xenograft growth curves of infected cells in NSG mice.
PRDM1 inactivation is associated with 17p losses and affects the clinical outcome
Figure 6A shows a heatmap of all the 64 ALCL cases, ranked as the most common recurrent lesions. Losses at 6q21, encompassing the PRDM1 gene locus, and losses at 17p often co-occurred with (P < .001). We investigated whether TP53, the tumor suppressor gene mapped at 17p13, was also inactivated by somatic mutations in cases without genomic loss. We analyzed the mutational status of coding exons from 4 to 8, the most common affected by mutations in other lymphomas,36 in 11 ALK− cases, 6 with PRDM1 loss and no 17p loss and 6 with both genes apparently nonaffected. In accordance with published articles,37,38 no TP53 gene mutations were identified in any of the clinical specimens, while we confirmed the presence of the TP53 mutations in cell lines39,40 (Karpas-299, in exon8; SU-DHL-1, in exon 8; L82, in exon 7).
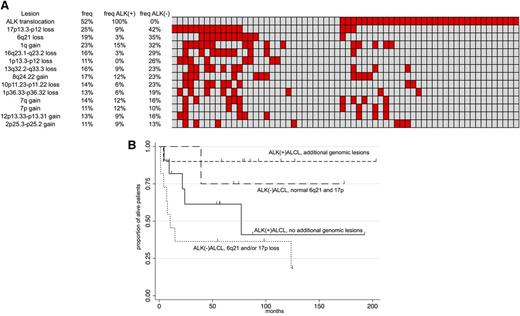
Distribution of main genomic aberration in ALK+ and ALK-ALCL and their impact on outcome. Heatmap with the relative distribution of the most common lesions detected in ALCL samples (A) and Kaplan-Meier graph showing OS in systemic ALCL according to ALK status and to the presence of PRDM1 inactivation and/or TP53 loss (B). In panel A: red, presence; gray, absence. In panel B: x-axis, months; y-axis, percentage of alive patients.
Distribution of main genomic aberration in ALK+ and ALK-ALCL and their impact on outcome. Heatmap with the relative distribution of the most common lesions detected in ALCL samples (A) and Kaplan-Meier graph showing OS in systemic ALCL according to ALK status and to the presence of PRDM1 inactivation and/or TP53 loss (B). In panel A: red, presence; gray, absence. In panel B: x-axis, months; y-axis, percentage of alive patients.
Based on the heatmap, 4 groups of ALCL could be identified: ALK−ALCL with PRDM1 inactivation and/or 17p loss (16 of 31 ALK−ALCL, 52%); ALK−ALCL bearing nor PRDM1 inactivation nor 17p loss (15 of 31 ALK−ALCL, 48%); ALK+ALCL with genomic aberrations (15 of 33 ALK+ALCL, 45%); and ALK+ALCL without additional aberrations (18 of 33 ALK+ALCL, 55%). Of clinical relevance, the group of patients with ALK−ALCL and bearing PRDM1 and/or 17p loss presented an inferior OS (Figure 6B), which was particularly evident when this group of cases was compared against all the remaining systemic ALCL cases (P = .007) (supplemental Figure 4). Because of the limited size of the our cohort we could not speculate whether the inferior OS observed in the ALK−ALCL group could be attributable mostly or entirely to TP53 deletion rather than PRDM1 loss. However, a recent case presenting wild-type TP53 and c-MYC genes, but PRDM1 gene loss, showed a very aggressive and fatal clinical course (Giorgio Inghirami, personal oral communication, July 2013). Also, due to the sample size, we could not investigate in detail the observed differences of ALK+ALCL with or without lesions different from 17p loss or 6q21 loss.
Discussion
Our results, obtained on a large series of ALCL samples studied by SNP array, showed that (1) the commonest lesions are losses at 17p13 and at 6q21, encompassing the TP53 and PRDM1 genes; (2) PRDM1 (BLIMP1) gene is inactivated by multiple mechanisms, more frequently, but not exclusively, in ALK−ALCL; (3) PRDM1 is a tumor suppressor gene in ALCL, as shown by both in vitro and in vivo experiments, likely acting as an antiapoptotic agent; and (4) the inactivation of both TP53 and PRDM1 genes is often concomitant and present in almost one-quarter of cases, possibly affecting the clinical outcome.
As expected,5,10-13 ALK+ALCL presented less genomic aberrations than ALK−ALCL, highlighting the extensive transforming activity owned by ALK fusion proteins.4 However, ALK+ and ALK− subsets also shared different genomic aberrations, indicating that the 2 subsets might undergo similar transforming events.41 Our results could confirm the presence of some but not all of the lesions previously reported in ALCL5,10-13 : discrepancies could be due to the different techniques that have been used, to the usual limited sizes of the series, and to the adopted diagnostic criteria, especially to define ALK−ALCL.
We observed a 6q21 loss in both ALK+ and ALK− specimens, with much higher frequency in the latter subtype. PRDM1, mapped in the 6q21 minimal common region, was inactivated by DNA losses, copy-neutral LOH and somatic mutations, as in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)42,43 and natural killer (NK) T-cell lymphoma.44,45 The inactivation was usually monoallelic, suggesting a haploinsufficiency effect, similar to that mainly seen in NK T-cell lymphoma,44,45 in which, however, it might be associated with promoter methylation,45 not detected in our series.
In vitro functional studies and in vivo experiments provided evidence that PRDM1 is a bona fide tumor suppressor gene in ALCL. The reintroduction of a functional PRDM1 in an ALCL cell line presenting the same loss observed in patients demonstrated the capacity of this gene to lead to cell proliferation impairment, cell-cycle block, and apoptosis. The high rate of PRDM1 deletion observed in ALK+ cell lines, severalfold higher than ALK+ALCL cases and even exceeding the frequency in ALK−ALCL clinical specimens, further suggests that PRDM1 inactivation might improve the chances of survival of the neoplastic cells. GEP following PRDM1 reexpression indicated that PRDM1 inactivation might exert its function regulating 2 main factors, MIR155HG and IRF4, which are central to a complex regulatory loop. We have observed that the loss of BLIMP1 might sustain the constitutive high expression of MIR155HG (miR-155) and IRF4 while negatively regulate PMAIP1 (NOXA) and INPP5D (SHIP1) expression. MIR155HG is often overexpressed in lymphomas,28 including ALCL, among which ALK− cases have higher levels than ALK+ cases.29,31 IRF4 is deregulated in cALCL,8,9 and its expression is necessary for the survival of the activated B-cell DLBCL and multiple myeloma cells.46,47 Moreover, INPP5D, a negative regulator of cell proliferation, could be suppressed by both MIR155HG and IRF4,32-35 and IRF4 positively regulates MIR155HG32 while suppressing PMAIP1,48 which can increase MIR155HG levels.
The role of PRDM1 in normal and neoplastic T cells is not clear contrary to its established role in normal and/or neoplastic B cells. The fundamental role of PRDM1 toward the plasma cell differentiation is reflected in the expression pattern observed in the 2 main subtypes of DLBCL, germinal center B-cell–like (GCB) DLBCL and activated B-cell–like (ABC) DLBCL, and in its inactivation limited to the DLBCL subgroup.42,43 Here, we have observed inactivation of the PRDM1 gene in approximately one-quarter of ALCLs, particularly in ALK−ALCL, while the protein was expressed in half of the ALCL cases, irrespective of the ALK status, similar to what was reported in another previous series of cases.19 Although we could speculate that the frequently observed PRDM1 loss (in a heterozygous way) in the ALK−ALCL subset did not affect protein expression detected in the immunohistochemistry assay, due to the low overlap between the series analyzed by genomic profiling or by immunohistochemistry, and also due to the still limited knowledge on ALCL in general, further studies will be necessary to clarify the relationship between protein expression and genetic lesions. Of interest, 1 ALK−ALCL case presented 6q21 loss on 1 allele, a stop codon mutation on the second allele, and it expressed aberrant cytoplasmic PRDM1 protein expression.
In our series, 6q21 losses were significantly associated with 17p deletions. The TP53 gene (17p13) or other transcripts mapped on chromosome 17 might act as tumor suppressor gene(s) and cooperate with PRDM1 loss in the ALCL pathogenesis. ALCL cases with deletion affecting 6q21 and/or 17p had a poorer outcome. Due to the relatively limited series of evaluable cases and due to the heterogeneous type of given treatments, this observation requires validation on an independent series of homogenously treated patients.
Finally, genomic profiling identified lesions, such as amplifications of 9p24.1 (JAK2) and 13q31.3 (MIR17HG), which suggest possible therapeutic targets. Both transcripts are involved in the regulation of the MYC gene,49 which was also recurrently gained, and MIR17HG is associated with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway activation.50 Thus, our data provide the rationale for the evaluation of new targeted therapies such as Janus kinase 2 inhibitors, MYC/Bromodomain inhibitors, and AKT/mTOR inhibitors in ALCL patients.
In conclusion, our data provide evidence from genomic studies, functional analysis, and in vivo experiments that PRDM1 is a bona fide tumor suppressor gene in ALCL. Genomic profiling identified ALCL subgroups with potential clinical and therapeutic significance.
Raw data reported in this article are available at the Gene Expression Omnibus database (accession number GSE50252).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Oncosuisse grant KLS-02403-02-2009, Anna Lisa Stiftung, Nelia et Amadeo Barletta Foundation, AIRC 5x1000 (Genetics-Driven Targeted Management of Lymphoid Malignancies Italy), F.E.S. R.2007-13 (Immonc), Converging Technologies (Modeling Oncogenic Pathways: From Bioinformatics to Diagnosis and Therapy, BIO_THER), Fonds Tom Debackere, Stefanie’s Rozen Fonds.
M.B. is enrolled in the Program in Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Geneva (Geneva, Switzerland).
Authorship
Contribution: M.B. interpreted data, performed validation and functional experiments, and cowrote the manuscript; A. Rinaldi performed genomic profiling; I.K. performed statistical analysis and interpreted data; P.B. helped in performing functional experiments; M.T. and F.T. performed in vivo experiments; R.P. and E.Z. provided advice; P.M.V.R. performed statistical analysis; A.M., B.T., T.T., S.M.R.-P., M.A.P., S.B., E.C., G.B., S.H.S., A. Rosenwald, M.P., K.H.Y., P.P.P., R.D., and S.P. collected and characterized tumor samples; G.I. designed research, collected and characterized tumor samples, provided advice, and cowrote the manuscript; F.B. designed research, performed statistical analysis, interpreted data, and cowrote the manuscript; and all authors have approved the final manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for G.I. is the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College/New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY.
Correspondence: Francesco Bertoni, Lymphoma and Genomics Research Program, IOR Institute of Oncology Research, Lymphoma Unit, IOSI Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland, via Vincenzo Vela 6, CH-6500 Bellinzona, Switzerland; e-mail: frbertoni@mac.com; and Giorgio Inghirami, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College/New York Presbyterian Hospital, 525 East 68th St, New York, NY 10065; e-mail: inghig01@gmail.com.