Abstract
The ability to assess anti-leukemic activity of drugs on patient samples is a powerful tool in determining potential drug targets and may enhance selection of therapeutic agents with a biologic and functional rationale for individual patients. We have previously optimized small-molecule screens performed on freshly isolated leukemia cells for this purpose. Here we describe a novel method we have recently developed that produces reliable functional testing results from previously frozen specimens. This method was established to take advantage of bio-repositories containing archival primary leukemia specimens and to aid in the validation of potential drug target analysis and pathway activation.
Three different culture media comprising various cocktails of cytokines were tested for their ability to maintain cell viability after thawing and to produce inhibitor results similar to those obtained using freshly isolated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. We identified a method of thawing cells by first culturing for 24-48 hours in cytokine-enriched medium (RPMI-1640, 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and low concentrations of GM-CSF, G-CSF, SCF, and IL-3) prior to plating in RPMI-1640 and 10% FBS (R10). This method maintained high cell viability and produced inhibitor results comparable to those of freshly isolated cells plated in R10. Half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) analysis was used to determine the relative success of the thaw process and reliability of results. Comparison of data produced from frozen cells initially cultured in cytokine-enriched medium to data obtained from freshly isolated cells showed few differences in effective drug hits.
To examine the effects of freeze-thawing and cytokines on cell subpopulations, we performed FACS analysis on 8 markers to examine the level of cell differentiation under each condition. FACS sorting revealed increases in expression of myeloid differentiation markers (CD11b and CD14) after thaw in all media tested compared to fresh cells in cultured in R10. Thawed cells grown in cytokine-enriched medium remained closest to fresh controls as measured by antigen expression, including CD11b and CD14.
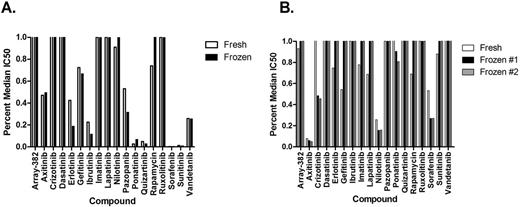
Cell viability post-thaw was a strong indicator of samples that would fail to produce reliable inhibitor results. We observed that post-thaw viability <80% served as a strong indicator of unreliable inhibitor data, even if dead cells were removed prior to plating. Cells cultured in cytokine-enriched medium for 24-48 hours resulted in 11-33% higher viability prior to plating in R10. Percent median IC50 for specific inhibitors assayed on fresh and frozen samples showed similar trends in effective drugs (Fig. 1A). Discrepancies observed in fresh and frozen sample data may be due to inconsistent fresh sample data as we demonstrated that frozen samples were highly consistent compared to other frozen samples (Fig. 1B). Lower R2 values could be attributed to variability observed with non-effective drugs. Taken together, our data indicate that thawing leukemia specimens in cytokine-enriched media can allow for the generation of informative small-molecule inhibitor screening data and provide a novel method for making use of archived primary human leukemia specimens for further downstream functional analyses.
Median IC50 Comparison. Median IC50 values are calculated from >3000 samples IC50 values. Percent median is the percent a particular sample IC50 compares to the median of all samples of that disease character. Mean values are shown for inhibitors with replicates. R2 from raw IC50. (A) Comparison of effective drug hits on fresh and frozen primary peripheral blood AML samples (R2 = 0.8151). (B) Comparison of effective drug hits obtained on a freshly isolated AML bone marrow sample versus 2 matched frozen/thawed samples from peripheral blood. Fresh vs. frozen (R2 = 0.45); frozen vs. frozen drug (R2 =0.9999).
Median IC50 Comparison. Median IC50 values are calculated from >3000 samples IC50 values. Percent median is the percent a particular sample IC50 compares to the median of all samples of that disease character. Mean values are shown for inhibitors with replicates. R2 from raw IC50. (A) Comparison of effective drug hits on fresh and frozen primary peripheral blood AML samples (R2 = 0.8151). (B) Comparison of effective drug hits obtained on a freshly isolated AML bone marrow sample versus 2 matched frozen/thawed samples from peripheral blood. Fresh vs. frozen (R2 = 0.45); frozen vs. frozen drug (R2 =0.9999).
Agarwal:CTI BioPharma: Research Funding. Druker:Oregon Health & Science University: Patents & Royalties; MolecularMD: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Sage Bionetworks: Research Funding; Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncotide Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; CTI Biosciences: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Roche TCRC, Inc.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Henry Stewart Talks: Patents & Royalties; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millipore: Patents & Royalties; McGraw Hill: Patents & Royalties; Leukemia & Lymphoma Society: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Aptose Therapeutics, Inc (formerly Lorus): Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Cylene Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal