Abstract
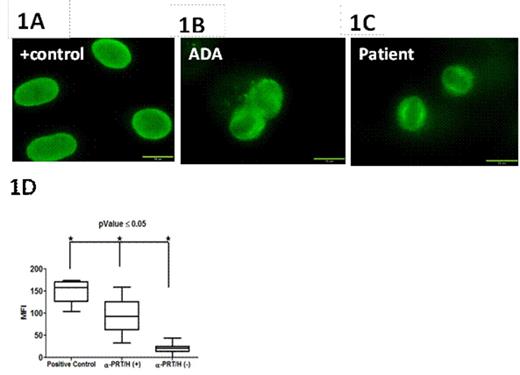
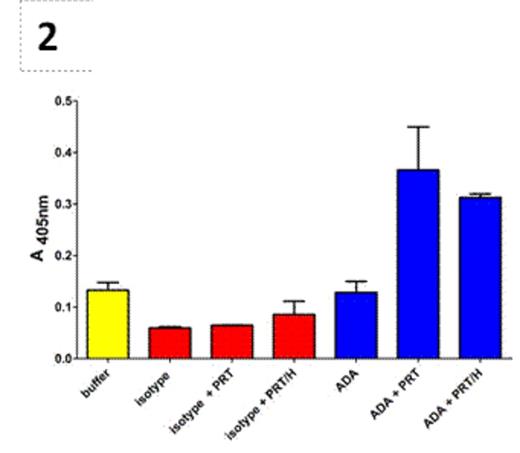
Protamine/heparin (PRT/H) antibodies (Abs) are a newly described class of heparin-dependent antibodies found in ~25% of patients exposed to protamine and heparin during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery (CPB). Although recent studies show that PRT/H Abs have several serologic properties similar to platelet factor 4 (PF4)/heparin Abs, the clinical significance of PRT/H Abs is unknown. To understand their clinical significance, we undertook studies to characterize the biologic effects of PRT/H Abs in vitro. Using a previously described murine monoclonal antibody to PRT/H complexes (IgG3 isotype, ADA) and patient-derived PRT/H Abs, we examined antibody cross-reactivity with histones and nuclear proteins as well as functional effects of PRT/H Abs on neutrophil activation. Using a commercial ANA immunofluorescence assay (ImmuGlow Hep-2 Cells Anti-nuclear Antibody IFA kit), we first examined cross-reactivity of anti-PRT/H on nuclear proteins. As seen in Figure 1, both ADA and patient-derived PRT/H Abs (depicted as α-PRT/H (+) in Figure 1D) showed significant binding to Hep-2 cells. In contrast, no reactivity was seen when Hep-2 cells were incubated with plasma from CPB patients who were seronegative for PRT/H antibodies (depicted as α-PRT/H (-) in Figure 1D) or with IgG3 isotype (data not shown). To confirm that PRT/H Abs were binding to nuclear antigens, we examined the cross-reactivity of monoclonal and polyclonal anti-PRT/H on individual nuclear binding proteins, including Single Stranded Binding Protein, RO-52, JO-1, (Sigma; St. Louis, MO, USA) and nucleosomes (New England Biolabs; UK) by ELISA. As shown in Table 1, ADA showed significantly higher binding to all nuclear antigens as compared to isotype control. Polyclonal PRT/H Abs from CPB patients also showed increased binding to nuclear antigens relative to control plasma, but did not achieve statistical significance. To determine if PRT/H Abs activate neutrophils, we isolated neutrophils by gradient centrifugation and incubated cells with 100 ug/mL of ADA or isotype in the presence or absence of antigen (PRT 31 ug/mL + H4 U/mL) and measured release of myeloperoxidase (MPO). As shown in Figure 2, ADA alone or isotype control showed minimal MPO release. In the presence of PRT or PRT/H, ADA, but not isotype control, showed significant MPO release. Taken together, these studies demonstrate that PRT/H Abs cross-react with nuclear antigens and can trigger neutrophil activation. These findings suggest that PRT/H Abs cross-react with a closely related class of antigens (histones) and enhance inflammation through cross-reactivity with nuclear antigens and/or through functional effects on neutrophil activation.
| Antibody . | SSBP . | RO52 . | JO-1 . | nucleosomes . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADA v. Isotype | 1.36 ± 0.06 v. 0.13 ± 0.01 | 1.76 ± 0.06 v. 0.08 ± 0.01 | 1.64 ± 0.03 v. 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.73 ± 0.03 v. 0.07 ± 0.01 |
| Polyclonal PRT/H Abs v. control plasma | 1.01 ± 0.23 v. 0.54 ± 0.05 | 1.15 ± 0.21 v. 0.72 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.16 v. 0.49 ± 0.04 | 0.81 ± 0.14 v. 0.75 ± 0.3 |
| Antibody . | SSBP . | RO52 . | JO-1 . | nucleosomes . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADA v. Isotype | 1.36 ± 0.06 v. 0.13 ± 0.01 | 1.76 ± 0.06 v. 0.08 ± 0.01 | 1.64 ± 0.03 v. 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.73 ± 0.03 v. 0.07 ± 0.01 |
| Polyclonal PRT/H Abs v. control plasma | 1.01 ± 0.23 v. 0.54 ± 0.05 | 1.15 ± 0.21 v. 0.72 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.16 v. 0.49 ± 0.04 | 0.81 ± 0.14 v. 0.75 ± 0.3 |
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal