Abstract
Introduction:
Mutations in IDH1 and IDH2 genes are found in 15% to 20% of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Mutated IDH enzymes produce in excess the D stereoisomer 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) in leukemic cells, which can act as a biomarker predictive of the presence of IDH1 and IDH2 mutations. Total serum 2-HG (D and L stereoisomers) >2µM and ratio D/L 2-HG >2.5 are strong predictors of the presence of IDH1/2 mutations at diagnosis (Janin et al; JCO 2014). We measured 2-HG levels in serial samples of 47 patients with IDH1/2 mutations during induction or first salvage therapy to determine whether 2HG can serve as a surrogate marker of treatment efficacy.
Methods:
Between 2007 and 2015, 47 AML patients with IDH1 or IDH2 mutation received intensive chemotherapy as induction therapy (n=42) or as first salvage regimen (n=5) in our center (Table 1). Genomic DNA was extracted from BM samples using conventional procedures. IDH1-(codon R132) and IDH2- targeted (codons R140 and R172) regions were amplified by PCR with primers containing Ion Torrent adapters and unique barcodes to generate libraries. Pooled amplicons libraries were clonally amplified on Ion Spheres using the Ion Xpress Template 200 Kit. All available serum samples (n=394) prior and during induction/salvage chemotherapy were analyzed for total 2-HG, D-2-HG and L-2-HG by reverse-phase liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry.
We studied the serum 2-HG values (D-2-HG and ratio D/L 2-HG) evolution during IC according to complete remission (CR) evaluated at the end of IC. When a patient had a missing value for 2-HG, the missing value was replaced by the last available observation (up to 7 days before the missing value). At each day we tested the difference between the dosage values of the responders and the non-responders with non-parametric Wilcoxon 2-sided tests. The analyses were done with SAS software (version 9.3; SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Patients and treatment characteristics:
| AML at diagnosis / RR AML (N) . | 42 / 5 . |
|---|---|
| Median age (years) | 58.2 (23.1 - 75.7) |
| Sex ratio (M/F) | 23/24 |
| Conventional cytogenetic: - Normal karyotype - Trisomy 8 - Monosomy 7 | 39 (83%) 3 (6%) 2 (4%) |
| Associated gene mutations: - NPM1 - FLT3-ITD - FLT3-TKD | 24 (51%) 10 (21%) 5 (11%) |
| IDH mutation: - IDH1 R132 (N) - IDH2 R140 (N) - IDH2 R172 (N) | 8 (17%) 32 (65%) 7 (15%) |
| Intensive treatment: - "3+7" regimen - Intensified induction chemotherapy - High-dose cytarabine based chemotherapy | 24 (51%) 19 (40%) 4 (8%) |
| AML at diagnosis / RR AML (N) . | 42 / 5 . |
|---|---|
| Median age (years) | 58.2 (23.1 - 75.7) |
| Sex ratio (M/F) | 23/24 |
| Conventional cytogenetic: - Normal karyotype - Trisomy 8 - Monosomy 7 | 39 (83%) 3 (6%) 2 (4%) |
| Associated gene mutations: - NPM1 - FLT3-ITD - FLT3-TKD | 24 (51%) 10 (21%) 5 (11%) |
| IDH mutation: - IDH1 R132 (N) - IDH2 R140 (N) - IDH2 R172 (N) | 8 (17%) 32 (65%) 7 (15%) |
| Intensive treatment: - "3+7" regimen - Intensified induction chemotherapy - High-dose cytarabine based chemotherapy | 24 (51%) 19 (40%) 4 (8%) |
Results:
Complete remission (CR) 1 was obtained in 35/42 patients (83%) and CR2 in 3/5 (60%) after IC. All (8/8) IDH1 -R132 mutated patients achieved CR1, 25/28 (89%) IDH2 -R140 mutated patients and 3/4 achieved CR1 and CR2 respectively; 2/6 (33%) IDH2 -R172 mutated patients and 0/1 achieved CR1 and CR2, respectively.
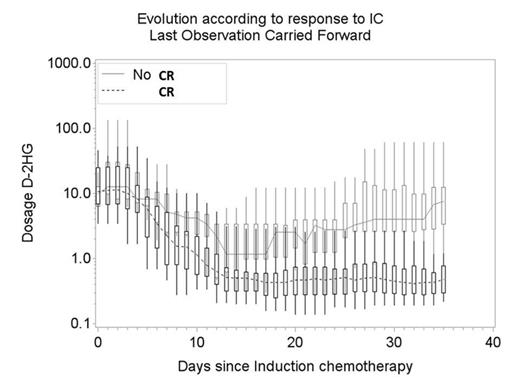
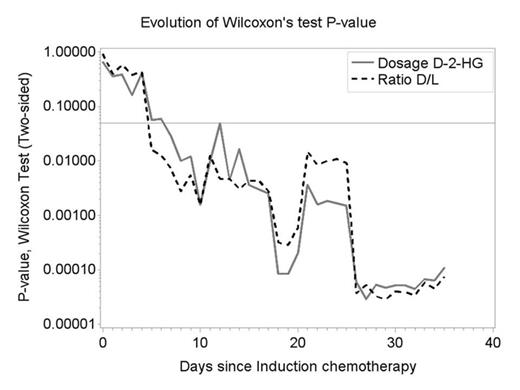
Median serum 2-HG values before IC were as follow: total 2-HG 10.9 µM (range: 2.1-135.5); D-2-HG 10.7 µM (range: 1.7-132.6) and ratio D/L 36.9 (range: 3.9-131.2). Median number of serum 2-HG values per patient was 7 (range: 5-10). Serum D-2-HG and ratio D/L 2-HG evolution according to CR status after IC began to differ significantly at day 5 after IC (Wilcoxon test P=0.02, Figure 1). The difference between responders and non-responders increased overtime (Wilcoxon test P<10-3 at day 21). At day 21, a ratio D/L 2-HG ≥2.5 and D-2-HG ≥2µM were correlated with the absence of CR (Fisher's exact P = 0.02 for each). Despite the very limited statistical power of the comparisons due to a limited number of patients in the no response group (n=9), the comparisons achieved a very high statistical significance.
Conclusion:
The oncometabolite 2-HG can act as a biomarker to monitor early response to conventional IC in AML patients with IDH1/2 mutations. D-2-HG and ratio D/L 2-HG measurements are rapid, robust, non-invasive and can predict IC failure in these patients, allowing selection of patients who could potentially benefit from early salvage treatment or IDH inhibitors.
D-2-HG and ratio D/L 2-HG evolution according to response to IC (CR) and p-value Wilcoxon tests.
D-2-HG and ratio D/L 2-HG evolution according to response to IC (CR) and p-value Wilcoxon tests.
Ribrag:Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Esai: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmamar: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. De Botton:Agios pharmaceuticals: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal