Abstract
Introduction: Relapse of CD19+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) post-hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) portends a dismal prognosis and opportunities to intensify the anti-tumor potency of HCT are limited by regimen related toxicities. While pre-transplant CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy can increase the numbers of patients who achieve minimal residual disease negative remissions, there remains an unmet need to further reduce the incidence of early post-HCT relapses through the use of adoptive immunotherapy. However, the use of CAR T cell therapies in this setting is severely limited as patients are on immunosuppressive therapy (IST) to prevent graft versus host disease (GVHD). Here, we report on a multiplexed engineering strategy to generate donor-derived CD19CAR T cells that are resistant to combinations of cyclosporine (CSA)/Tacrolimus (FK506) and/or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), and devoid of GVHD reactivity for this patient population.
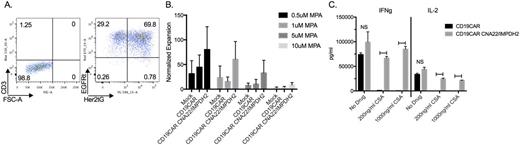
Methods and Results: We developed CNA22 or CNA12-P2A-IMPDH2Δ-T2A-Her2tG vectors using the CNA22, CNA12 [Brewin M, et al, Blood 2009] and IMPDH2Δ [Jonnalagadda J, et al, PLoS One 2013] mutants conferring CSA, FK506 and MMF resistance, respectively. Her2tG is a truncated HER2 extracellular protein developed in our lab and used for selection and transduction efficiency determination using Herceptin. The drug resistant lentivirus packaged vector was used to co-transduce human T cells with our CD19CAR vector which includes a 4-1BB co-stimulatory domain and truncated EGFR protein (EGFRt) for cell selection, transduction efficiency and in vivo suicide using Erbitux [Wang, X, et al, Blood 2011]. We coupled dual transduction with mRNA TALEN transfection technology using a TALEN pair targeting the first exon of the TcRα constant region to transfect T cells for efficient knockout of the endogenous T cell receptor (TcR) thus eliminating the risk of causing GVHD. Our multiplexed technologies yield CD3/TcR knockouts rates greater than 80% with successful dual transduction of both vectors demonstrated by EGFRt and Her2tG expression (Figure A). Cells demonstrated MMF resistance in vitro as evidenced by increased Her2tG expression for culture purification following mycophenolic acid (MPA, active metabolite of MMF) exposure. In addition, prolonged MPA drug exposure at multiple drug concentrations (0-10uM) demonstrated improved culture expansion and viability for cultures containing cells transduced to express IMPDH2Δ over a 21 day culture period (Figure B). CD19CAR expressing cells demonstrated CD19 antigen targeted cell lysis as evaluated by chromium release assay. Furthermore, cytokine evaluations of cells following co-culturing with target cells at multiple CSA concentrations (0-1000ng/ml) yielded sustained IL-2, IFNg and TNFa secretion by CNA22 expressing cells following CD19CAR activation (Figure C). In vivo experiments are in progress to assess the functional attributes of these multiplexed engineered CAR T cells in relevant murine model systems.
Conclusions: We successfully used multiplexed engineering strategies to generate CD3/TcR- CD19CAR+EGFRt+ CNA22-IMPDH2Δ-HER2tG+ T cells. Cells expressing CNA22 and IMPDH2Δ mutants exhibited activation and expansion in vitro in the presence of immunosuppressive agents CSA and MPA with targeted CD19CAR activity. These studies suggest the ability to generate modified T cells that remain functional in vivo even in the presence of IST and without induction of GVHD, allowing for this approach in the post-transplant setting to prevent/treat disease relapse.
A) Cells underwent successful dual transduction followed by mRNA TALEN transfection for development of CD3/TcR- CD19CAR+EGFRt+ CNA22-IMPDH2Δ-HER2tG+ T cells. B) Transduced T cells underwent selection for their respective markers, were stimulated and cultured for 21 days at varying MPA concentrations. Cells transduced to express IMPDH2Δ exhibited improved expansion as compared to CD19CAR and mock control cells. Data was normalized to the cell group's no drug control expansion. C) Following co-culture with K562-CD19 antigen cells with CSA concentrations of 0-1000ng/ml CD19CAR cells transduced with the drug resistant vector secreted significantly increased IFNg and IL-2 levels compared to CD19CAR only cells. NS = not significant; Horizontal bars indicate statistical significance defined as p-value <0.05.
A) Cells underwent successful dual transduction followed by mRNA TALEN transfection for development of CD3/TcR- CD19CAR+EGFRt+ CNA22-IMPDH2Δ-HER2tG+ T cells. B) Transduced T cells underwent selection for their respective markers, were stimulated and cultured for 21 days at varying MPA concentrations. Cells transduced to express IMPDH2Δ exhibited improved expansion as compared to CD19CAR and mock control cells. Data was normalized to the cell group's no drug control expansion. C) Following co-culture with K562-CD19 antigen cells with CSA concentrations of 0-1000ng/ml CD19CAR cells transduced with the drug resistant vector secreted significantly increased IFNg and IL-2 levels compared to CD19CAR only cells. NS = not significant; Horizontal bars indicate statistical significance defined as p-value <0.05.
Jensen:Juno Therapeutics, Inc: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal