Key Points
In Cebpb−/− mice, the number of Ly6C− monocytes was specifically decreased in a cell-intrinsic manner due to their accelerated death.
C/EBPβ supports the survival of Ly6C− monocytes, at least in part through direct upregulation of Csf1r.
Abstract
The transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ) is highly expressed in monocytes/macrophages. However, its roles in monopoiesis are largely unknown. Here, we investigated the roles of C/EBPβ in monopoiesis. Further subdivision of monocytes revealed that Cebpb messenger RNA was highly upregulated in Ly6C− monocytes in bone marrow. Accordingly, the number of Ly6C− monocytes was significantly reduced in Cebpb−/− mice. Bone marrow chimera experiments and Mx1-Cre–mediated deletion of Cebpb revealed a cell-intrinsic and monocyte-specific requirement for C/EBPβ in monopoiesis. In Cebpb−/− mice, turnover of Ly6C− monocytes was highly accelerated and apoptosis of Ly6C− monocytes was increased. Expression of Csf1r, which encodes a receptor for macrophage colony-stimulating factor, was significantly reduced in Ly6C− monocytes of Cebpb−/− mice. C/EBPβ bound to positive regulatory elements of Csf1r and promoted its transcription. Collectively, these results indicate that C/EBPβ is a critical factor for Ly6C− monocyte survival, at least in part through upregulation of Csf1r.
Introduction
Monocytes are mononuclear phagocytic cells that are involved in host defense and maintenance of tissue homeostasis.1 The half-life of monocytes is short; therefore, they must be continuously replenished by proliferation and differentiation of monocyte precursors, a process called monopoiesis. Common myeloid progenitors, granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, macrophage dendritic cell precursors (MDPs), and common monocyte progenitors (cMoPs) are intermediates during the differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) into mature monocytes, although it is disputed whether MDPs are clonal common precursors of monocytes and dendritic cells.2-5 Recently, functionally and phenotypically distinct subsets of mature monocytes have been identified in mice and humans.6-9 In mice, CD11b+ CD115+ monocytes are subdivided into 2 subsets based on the expression of Ly6C.6 Ly6C+ monocytes (also called inflammatory or classical monocytes) are rapidly recruited to tissues during inflammation and exhibit antimicrobial activity,10 whereas Ly6C− monocytes (also called nonclassical, resident, or patrolling monocytes) are often found attached to or crawling on the luminal wall of the endothelium.11,12 Recent data show the involvement of nonclassical monocytes in a variety of pathophysiological conditions,9,13-16 although their precise significance is not fully understood. Developmentally, Ly6C− monocytes are considered to be downstream of Ly6C+ monocytes or direct progeny of MDPs or cMoPs under some circumstances.17-20 The molecular mechanisms that regulate the development of these monocyte subsets remain largely unknown.
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ) is a member of the C/EBP leucine zipper transcription factor family.21 In hematopoiesis, we previously reported that C/EBPβ is required for granulopoiesis under stressed conditions.22-24 At steady state, C/EBPβ is an important regulator of the differentiation and function of macrophages.25-28 Despite the well-characterized importance of C/EBPβ in macrophages, its precise roles in monopoiesis have remained largely elusive. Recently, we found that the level of monocytes in peripheral blood (PB) is severely reduced in Cebpb−/− mice.29 In this study, we further investigated monopoiesis in Cebpb−/− mice and found that C/EBPβ plays critical roles in the survival of Ly6C− nonclassical monocytes.
Methods
Mice
C57BL/6 mice (7-12 weeks old) were purchased from CLEA Japan (Tokyo, Japan). CD45.1+ mice were a kind gift from Shigekazu Nagata (Kyoto University). Cebpb−/− mice were bred and maintained under specific pathogen–free conditions at Kyoto University. Cebpbf/f mice (Cebpb is flanked with loxP) crossed with Mx1-Cre transgenic mice were kindly provided by Esta Sterneck (US National Cancer Institute). Littermates were used as controls in all experiments, except for the 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) pulsing experiments shown in Figure 3 and supplemental Figure 5 (available on the Blood Web site). The animal protocols were approved by the Committee on Animal Research of the Kyoto University Faculty of Medicine.
Cell lines
EML cells, a kind gift from Schickwann Tsai (University of Utah), were maintained in Iscove modified Dulbecco medium supplemented with 20% heat-inactivated horse serum and 10% BHK/MKL cell-conditioned medium as a source of stem cell factor.30 Cos-7 cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum.
Vectors
The Csf1r-EGFP-long Fms-intronic regulatory element (FIRE) vector was a kind gift from Clare Pridans and David A. Hume (The Roslin Institute, University of Edinburgh).31 To avoid long terminal repeats in the vector interfering with reporter expression, the Csf1r promoter-green fluorescent protein (GFP)-FIRE expression cassette was excised and cloned into the BamHI/ApaI sites of pBluescript SKII. Next, the GFP sequence in the vector was replaced with a sequence encoding luciferase obtained from the pGL4.20 vector (Promega, Fitchburg, WI). A KOD-Plus-Mutagenesis Kit (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan) was used to mutate the consensus binding sites for C/EBPβ in the promoter and FIRE regions. The mutations in the promoter changed the sequence from ATATTTCCAAA to GGTACCATAAA, and those in the FIRE changed the sequence from TTCCCTAAGA to TTCCCTTTGA. A mouse Cebpb expression vector was generated by cloning polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-amplified Cebpb complementary DNA (cDNA) obtained from mouse bone marrow (BM) cells into the pCDNA3.1 vector. The entire PCR-amplified region in the vector was verified by sequencing. pBABEPuro and pBABEPuroC/EBPβER, which express estrogen receptor (ER) or C/EBPβ fused to ER, respectively, were described previously.32
Flow cytometric analysis and cell sorting
PB samples were obtained from the tail vein or caudal vena cava, and blood cell counts were analyzed using an SE-9000 instrument (Sysmex, Kobe, Japan). BM cells and PB cells were stained with fluorescently conjugated antibodies and analyzed using a FACSCantoII, FACSAria, or FACSAria II instrument (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). Antibodies used to detect monocytes were fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)–conjugated anti-Ly6C (AL-21), allophycocyanin (APC) –conjugated anti-CD115 (AFS98), phycoerythrin (PE)-Cy7–conjugated anti-CD11b (M1/70), PE-conjugated anti-Ly6G (1A8), PE-conjugated anti-NK1.1 (PK136), PE-conjugated anti-CD4 (GK1.5), PE-conjugated anti-CD8 (53-6.7), and PE-conjugated anti-B220 (RA3-6B2). The following reagents were used to detect MDPs: APC-conjugated anti-CD115, PE-conjugated anti-CD135 (A2F10.1), and PE-Cy7-conjugated anti–c-kit (ACK2) antibodies; PerCP-Cy5.5–conjugated antibodies specific for lineage markers (CD11b [M1/70], CD3 [17A2], Ter119 [TER-119], and CD19 [eBio1D3]); biotin-conjugated antibodies specific for lineage markers (interleukin-7-Rα [B12-1], CD11c [HL3], NK1.1 [PK136], and Gr-1 [RB6-8C5]); and streptavidin-PerCP-Cy5.5. MDPs were regarded as CD135+ CD115+ c-kit+ lineage marker–negative BM cells. For experiments utilizing Mx1-Cre Cebpbf/f mice, APC-conjugated anti-CD115, PE-conjugated anti–c-kit (2B8), V450-conjugated anti-Ly6C (AL-21), and biotin-conjugated anti-CD135 (A2F10) antibodies; PerCP-Cy5.5–conjugated antibodies specific for lineage markers (CD3, CD19, NK1.1 [PK136], and Ly6G [1A8]); and streptavidin-PE-Cy7 were used to identify MDPs and monocytes. In this case, monocytes were regarded as CD115+ c-kit− CD135− lineage marker–negative BM cells. For HSCs and myeloid progenitors, APC-conjugated anti–c-kit (2B8), PE-Cy7–conjugated anti–Sca-1 (D7), PE-conjugated anti-CD16/32 (93), and FITC-conjugated anti-CD34 (RAM34) antibodies and PerCP-Cy5.5–conjugated antibodies specific for lineage markers, including CD11b, CD4 (RM4-5), CD8 (53-6.7), CD19, B220 (RA3-6B2), and Ter119, were used. V450-conjugated anti-CD45.1 (A20) and APC-Cy7–conjugated anti-CD45.2 (104) antibodies were used to distinguish donor type cells from recipient type cells for the experiments involving BM transplantation. To exclude dead cells, samples were stained with propidium iodide unless otherwise specified. All antibodies were purchased from BD Biosciences, eBioscience (San Diego, CA), or BioLegend (San Diego, CA). Data were analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree Star, Ashland, OR).
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
Total RNA was extracted using an RNeasy Micro Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) and converted to cDNA using random primers. The cDNA was amplified using a Step One Plus thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA). The following parameters were used: 95°C for 20 s, followed by 45 to 50 cycles at 95°C for 1 s and 60°C for 20 s. Primers and probes from the Universal Probe Library (Roche Applied Science, Mannheim, Germany) were used. The sequences of the primers and probes are listed in supplemental Table 1. Results were normalized against the level of Gapdh messenger RNA (mRNA).
Giemsa staining
Smears of mouse PB and cytospin slides of sorted cells were stained using a Diff-Quik Kit (Sysmex), which is a modified Wright Giemsa staining system. Images were obtained using an Olympus BX43 microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at original magnification ×400.
BM transplantation
To evaluate the cell-intrinsic requirement for C/EBPβ, 5 × 105 BM cells from wild-type (WT; Cebpb+/+), Cebpb−/− (CD45.2+), or Mx1-Cre Cebpbf/f mice (CD45.2+) were transplanted into lethally irradiated (8 Gy) CD45.1+ recipient mice. Mice were analyzed 6 to 8 weeks after BM transplantation.
BrdU pulsing
For BrdU pulsing, mice were intraperitoneally injected with 2 mg BrdU (BD Biosciences) 3 times 3 hours apart, as previously described.19 BM or PB cells were harvested and stained with fluorescently conjugated antibodies. The antibodies used to label monocytes were FITC-conjugated anti-Ly6C, APC-conjugated anti-CD115, PerCP-Cy5.5–conjugated anti-CD11b, PE-conjugated anti-Ly6G, PE-conjugated anti-NK1.1, PE-conjugated anti-CD4, PE-conjugated anti-CD8, and PE-conjugated anti-B220. APC-conjugated anti-CD115, PE-conjugated anti-CD135, and FITC-conjugated anti-c-kit (2B8) antibodies, PerCP-Cy5.5-conjugated antibodies specific for lineage markers (CD11b, CD3, Ter119, and CD19), and biotin-conjugated antibodies specific for lineage markers (IL7-Rα, CD11c, NK1.1, and Gr-1) were used to label MDPs. Biotinylated antibodies were labeled by subsequent staining with streptavidin-PerCP-Cy5.5. Labeled BM cells and PB cells were fixed, permeabilized, and treated with DNase to expose incorporated BrdU using a BrdU Flow Kit (BD Biosciences). Cells were then stained with a V450-labeled anti-BrdU (3D4) antibody and analyzed using a FACSCantoII instrument.
Annexin V staining
Annexin V and 7-amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD; BD Biosciences) were used to identify apoptotic and dead cell populations by flow cytometry. Following staining of surface markers, BM and PB cells were stained with V450-Annexin V (BD Biosciences) and 7-AAD according to the manufacturers’ protocols. The antibodies used to stain surface markers were FITC-conjugated anti-Ly6C and APC-conjugated anti-CD115. Forward scatterlow-int side scatterlow CD115+ cells were defined as monocytes in this analysis.
Reporter assay
Cos-7 cells (1 × 104) were seeded in 24-well plates 24 hours before transfection. Cells were transfected with 950 ng of Csf1r reporter vectors and 0, 1, 5, or 10 ng mouse Cebpb expression vector together with 2 ng pRL-null vector (Promega) using FuGENE6 reagent (Promega). Luciferase assays were performed 24 hours after transfection using the dual luciferase reporter assay system (Promega). Firefly luciferase activity was normalized against renilla activity to control for variation in the transfection efficiency.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) PCR assay
EML cells were retrovirally transduced with the pBABEPuro or pBABEPuroC/EBPβER vector, and transduced cells were selected using puromycin.33 Once established, nuclear translocation of ER or C/EBPβ-ER in the transduced cells was induced by addition of 1 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen to the medium. These cells were subjected to ChIP-PCR as previously described.34 In brief, cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde for 5 min at room temperature. Soluble chromatin-containing DNA 200 to 500 bp in length was immunoprecipitated using 2 μg anti-C/EBPβ antibody (sc-150X; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX) or 2 μg normal rabbit immunoglobulin G (sc2027X; Santa Cruz) overnight at 4°C. Purified ChIP and input DNA was measured by real-time quantitative PCR. The levels of ChIP DNA were normalized to those of input DNA. In each experiment, samples were analyzed in duplicate. The following oligonucleotide primers were used for amplification: Csf1r promoter, 5′-TTGAGCCTGGCCCCAGAT-3′ (forward), 5′-GGTTGCCTGAAAGGGAACTAC-3′ (reverse); FIRE, 5′-GCCCTCAGAGGCTGTGAATC-3′ (forward), 5′-CTCAAACCCCCTGTCAGGTC-3′ (reverse); negative region-1, 5′-GCTGGGAAGTAGGACTCGTG-3′ (forward), 5′-GCCCTGATCCCTCCATGTTC-3′ (reverse); negative region-2, 5′-GCTAGCGGACTCTCCTAGTG-3′ (forward), 5′-GTCCCATCATTCTCCCACCC-3′ (reverse).
Statistical analysis
Statistical differences were determined using the Student t test. Values of P < .05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Requirement of C/EBPβ for development of monocyte subsets
To determine the precise developmental stages at which monopoiesis is impaired in Cebpb−/− mice, we first measured Cebpb mRNA in purified cellular intermediates involved in the differentiation of HSCs into mature monocytes isolated from WT mice (Figure 1A). Cebpb mRNA expression remained relatively low during differentiation from HSCs to cMoPs, was induced in Ly6C+ monocytes, and was further upregulated in Ly6C− monocytes in the BM. In PB, Cebpb mRNA levels remained high in both Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes.
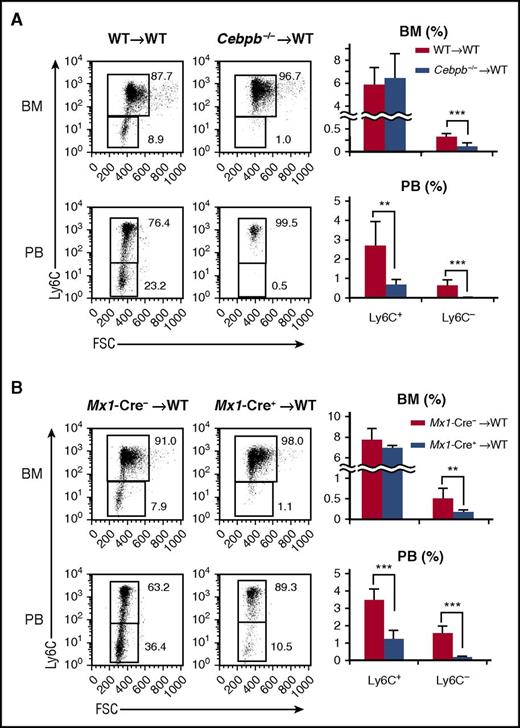
Cebpb−/− mice lack Ly6C−monocytes. (A) Cebpb mRNA expression in purified hematopoietic populations (n = 3). (B) Expression of CD115 and CD135 in BM cells among c-kit+ lineage marker (CD11b, Gr-1, CD11c, Ter119, IL-7R, CD3, CD19, and NK1.1)− cells. The frequencies of MDPs (CD115+ CD135+) and cMoPs (CD115+ CD135−) among lineage− BM cells are shown in the right panel (n = 5). Data were pooled from 4 independent experiments. (C,E) Gating strategy to define Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM (C) and PB (E). Lineage marker (Ly6G, B220, CD4, CD8, and NK1.1) − CD11b+ CD115+ monocytes were subdivided on the basis of Ly6C expression. (D,F) Frequencies of Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM (D) and PB (F) of WT or Cebpb−/− mice (n = 10 for BM and n = 19 for PB). Data were pooled from 7 independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). **P < .01, ***P < .001. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the adjacent boxed area. FSC, forward scatter; Lin, lineage.
Cebpb−/− mice lack Ly6C−monocytes. (A) Cebpb mRNA expression in purified hematopoietic populations (n = 3). (B) Expression of CD115 and CD135 in BM cells among c-kit+ lineage marker (CD11b, Gr-1, CD11c, Ter119, IL-7R, CD3, CD19, and NK1.1)− cells. The frequencies of MDPs (CD115+ CD135+) and cMoPs (CD115+ CD135−) among lineage− BM cells are shown in the right panel (n = 5). Data were pooled from 4 independent experiments. (C,E) Gating strategy to define Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM (C) and PB (E). Lineage marker (Ly6G, B220, CD4, CD8, and NK1.1) − CD11b+ CD115+ monocytes were subdivided on the basis of Ly6C expression. (D,F) Frequencies of Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM (D) and PB (F) of WT or Cebpb−/− mice (n = 10 for BM and n = 19 for PB). Data were pooled from 7 independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). **P < .01, ***P < .001. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the adjacent boxed area. FSC, forward scatter; Lin, lineage.
Next, BM and PB were closely compared between Cebpb−/− and WT mice (Figure 1B-F; supplemental Figure 1). The frequencies of MDPs and cMoPs (Figure 1B), as well as HSCs, common myeloid progenitors, and granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, in Cebpb−/− mice were comparable to those in WT mice (supplemental Figure 1A). Consistent with our previous report,29 Cebpb−/− and WT mice had a comparable number of total monocytes in the BM, whereas the frequency of monocytes in the PB was decreased in Cebpb−/− mice (Figure 1C,E, middle panels). We analyzed Ly6C+ and Ly6C− subsets of monocytes (Figure 1C-F). While there was no difference in the frequency of BM Ly6C+ monocytes, the frequency of Ly6C− monocytes in the BM was significantly lower in Cebpb−/− mice than in WT mice (0.22% ± 0.071% in WT mice vs 0.12% ± 0.073% in Cebpb−/− mice, P < .01; Figure 1C-D). The difference was more evident in the PB (Figure 1E-F). Subdivision of monocytes revealed a significant decrease in Ly6C+ monocytes and the almost complete absence of Ly6C− monocytes in the PB of Cebpb−/− mice (0.86% ± 0.67% in WT mice vs 0.029% ± 0.030% in Cebpb−/− mice, P < .001; Figure 1E-F). The difference was observed not only in frequencies but also in the absolute number of cells (supplemental Figure 1B). Similar differences were observed in the levels of monocytes in the spleen of Cebpb−/− mice (supplemental Figure 1C-E). These results clearly suggest that C/EBPβ is essential for the development of monocytes, especially Ly6C− monocytes.
Cell-autonomous and monocyte-specific requirement for C/EBPβ in monopoiesis
Next, we investigated whether the requirement for C/EBPβ in monopoiesis is cell autonomous. Lethally irradiated CD45.1+ mice were reconstituted with BM cells from either CD45.2+ WT or Cebpb−/− mice (Figure 2A). Six weeks after reconstitution, the frequencies of monocyte subsets among CD45.2+ donor-derived BM cells were basically identical to those in the original donor mice, regardless of the donor cell genotype. In brief, when Cebpb−/− cells were transplanted, the frequencies of PB Ly6C+ monocytes and BM Ly6C− monocytes were decreased, and Ly6C− monocytes in the PB almost disappeared among CD45.2+ cells (Figure 2A). Even when competitive BM transplantation was performed (supplemental Figure 2), the contribution of CD45.2+Cebpb−/− cells in PB Ly6C+ cells, BM and PB Ly6C− cells was significantly lower than the contribution of CD45.2+ WT cells, confirming the cell-intrinsic requirement of C/EBPβ for proper monopoiesis.
Cell-intrinsic requirement for C/EBPβ in monopoiesis. (A) Lethally irradiated CD45.1+ mice were reconstituted with BM cells obtained from CD45.2+ WT or Cebpb−/− mice. Flow cytometric analyses of monocyte subsets among CD45.2+ lineage− CD11b+ CD115+ cells in the recipients are shown in the left panel, and the frequencies of the indicated population are shown in the right panel (n = 7 for WT donors and n = 6 for Cebpb−/− donors). (B) BM cells of Mx1-Cre+Cebpbf/f or Mx1-Cre–Cebpbf/f mice (CD45.2) were transplanted into lethally irradiated mice (CD45.1). Flow cytometric analysis of monocyte subsets among CD45.2+ lineage− CD11b+ CD115+ cells in recipient mice is shown in the left panel. The frequencies of monocyte subsets in the BM and PB are shown in the right panel (n = 8). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. **P < .01, ***P < .001. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the adjacent boxed area. FSC, forward scatter.
Cell-intrinsic requirement for C/EBPβ in monopoiesis. (A) Lethally irradiated CD45.1+ mice were reconstituted with BM cells obtained from CD45.2+ WT or Cebpb−/− mice. Flow cytometric analyses of monocyte subsets among CD45.2+ lineage− CD11b+ CD115+ cells in the recipients are shown in the left panel, and the frequencies of the indicated population are shown in the right panel (n = 7 for WT donors and n = 6 for Cebpb−/− donors). (B) BM cells of Mx1-Cre+Cebpbf/f or Mx1-Cre–Cebpbf/f mice (CD45.2) were transplanted into lethally irradiated mice (CD45.1). Flow cytometric analysis of monocyte subsets among CD45.2+ lineage− CD11b+ CD115+ cells in recipient mice is shown in the left panel. The frequencies of monocyte subsets in the BM and PB are shown in the right panel (n = 8). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. **P < .01, ***P < .001. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the adjacent boxed area. FSC, forward scatter.
A recent publication demonstrated that a conditional knockout system utilizing the Mx1 promoter targets Ly6C+ monocytes without inoculation of polyI:C, because Mx1 is constitutively expressed in Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes35 (supplemental Figure 3A). Mx1-Cre–mediated recombination is observed in ∼40% of Ly6C+ monocytes and 90% of Ly6C− monocytes.35 Even if the developmental hierarchy between Ly6C+ monocytes and Ly6C− monocytes is unclear, conditional targeting of Cebpb using the Mx1 promoter is ideal to evaluate the monocyte-specific requirement for C/EBPβ. Indeed, upregulation of Cebpb during monopoiesis was severely impaired in Mx1-Cre+Cebpbf/f mice (supplemental Figure 3B). We first analyzed nonmanipulated Mx1-Cre+Cebpbf/f mice and found that their phenotypes were identical to those of Cebpb−/− mice (supplemental Figure 3C). To exclude the possibility of unexpected Mx1 expression in nonhematopoietic tissue, BM cells of Mx1-Cre+Cebpbf/f mice (CD45.2+) were transplanted into lethally irradiated CD45.1+ mice. The frequency of Ly6C− monocytes was significantly lower in the recipients than in mice that received Mx1-Cre−Cebpbf/f BM cells (Figure 2B). These results strongly suggest that C/EBPβ is specifically required after commitment to monocytes.
Extremely rapid turnover of Ly6C− monocytes in Cebpb−/− mice
The absence of Ly6C− monocytes in Cebpb−/− mice was not accompanied by an increase in any of the upstream progenitors examined (Figure 1B; supplemental Figure 1A). Therefore, we hypothesized that the defects were due to impaired proliferation or enhanced cell loss rather than a block in differentiation. The cell cycle status of MDPs, Ly6C+ monocytes, and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM was assessed by the incorporation of BrdU or propidium iodide staining (supplemental Figure 4). The proportion of cycling cells among Ly6C− monocytes was slightly higher in Cebpb−/− mice but much lower than the proportion among Ly6C+ monocytes. These changes suggest that a feedback mechanism compensates for the loss of Ly6C− monocytes in Cebpb−/− mice but could not compensate for the loss. Next, turnover of monocyte subsets was evaluated by performing in vivo BrdU pulsing experiments (Figure 3; supplemental Figure 5).19 In WT mice (Figure 3, filled lines), BrdU+ Ly6C+ monocytes appeared in the BM and PB on day 1 and then gradually lost this labeling (Figure 3, left). In accordance with a previous report,19 WT Ly6C− monocytes slowly became BrdU+ in the BM and PB, probably reflecting the developmental hierarchy between Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes (Figure 3, right, filled lines). In sharp contrast, in Cebpb−/− mice, much higher frequencies of Ly6C− monocytes in the BM and PB became BrdU+ (dotted lines in Figure 3, right), while the frequency of BrdU+ Ly6C+ monocytes did not significantly differ between WT and Cebpb−/− mice. These results indicated that the turnover of Ly6C−/− monocytes was rapid in Cebpb−/− mice.
Turnover of monocytes is accelerated in Cebpb−/− mice. Time-course analysis of the incorporation of BrdU into Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM and PB after BrdU pulsing (n = 3-8 mice per group). The percentages of BrdU+ cells among the indicated monocyte subsets are shown. *P < .05, **P < .01.
Turnover of monocytes is accelerated in Cebpb−/− mice. Time-course analysis of the incorporation of BrdU into Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM and PB after BrdU pulsing (n = 3-8 mice per group). The percentages of BrdU+ cells among the indicated monocyte subsets are shown. *P < .05, **P < .01.
Apoptosis of Ly6C− monocytes is accelerated in Cebpb−/− mice
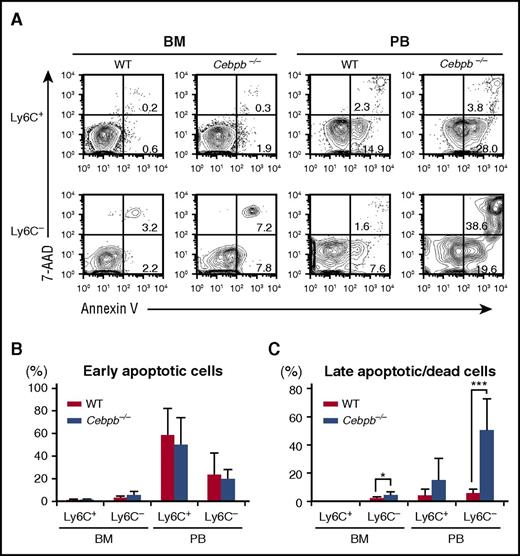
We assessed the death of mature monocytes in the BM and PB by staining with Annexin V and 7-AAD (Figure 4). Among Ly6C+ monocytes, the frequencies of early apoptotic cells (Annexin V+ 7-AAD−) and late apoptotic or dead cells (7-AAD+ Annexin V+) were equivalent in WT and Cebpb−/− mice (Figure 4A-C). By contrast, the frequency of late apoptotic or dead Ly6C− monocytes was significantly higher in Cebpb−/− mice than in WT mice in the BM, and this difference was even more pronounced in the PB (5.84% ± 2.90% in WT mice vs 50.4% ± 22.4% in Cebpb−/− mice, P < .001; Figure 4A,C). In addition, the frequency of Ly6C− monocytes with a depolarized mitochondrial membrane in the PB was higher in Cebpb−/− mice than in WT mice (supplemental Figure 6A-B), suggesting that apoptosis of Ly6C− monocytes was accelerated in Cebpb−/− mice.
Death of Ly6C−monocytes is accelerated in Cebpb−/− mice. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM and PB stained with Annexin V and 7-AAD. (B-C) Frequencies of early apoptotic cells (Annexin V+ and 7-AAD−) and late apoptotic/dead cells (Annexin V+ and 7-AAD+) among the Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocyte populations (n = 7). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < .05, ***P < .001.
Death of Ly6C−monocytes is accelerated in Cebpb−/− mice. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes in the BM and PB stained with Annexin V and 7-AAD. (B-C) Frequencies of early apoptotic cells (Annexin V+ and 7-AAD−) and late apoptotic/dead cells (Annexin V+ and 7-AAD+) among the Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocyte populations (n = 7). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < .05, ***P < .001.
Upregulation of Csf1r in monocytes is impaired in Cebpb−/− mice
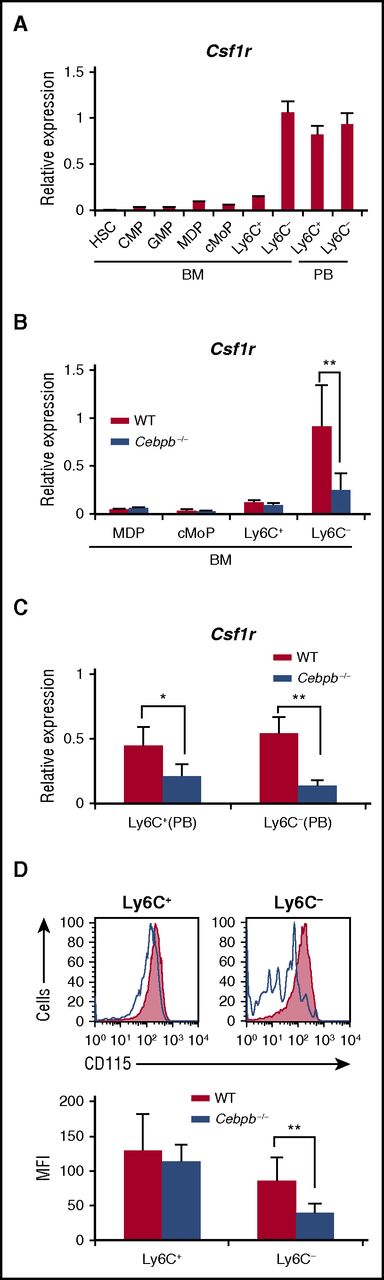
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) is a critical regulator of the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of monocytes and macrophages.36-38 We investigated the involvement of Csf1r in altered monopoiesis in Cebpb−/− mice. During the process of monopoiesis in WT mice, Csf1r mRNA expression was highly induced after differentiation into Ly6C− monocytes in the BM (Figure 5A). Interestingly, this expression pattern resembled that of Cebpb mRNA shown in Figure 1. When Cebpb−/− BM cells were analyzed, upregulation of Csf1r mRNA in Ly6C− monocytes was significantly impaired (Figure 5B). In the PB of WT mice, Csf1r was highly expressed in both Ly6C+ and Ly6C− monocytes (Figure 5A), and this expression was significantly decreased in Cebpb−/− mice (Figure 5C). Accordingly, surface expression of CD115 (Csf1r) on Ly6C− monocytes in the PB was reduced in Cebpb−/− mice (Figure 5D). These data suggest that Csf1r is a target of C/EBPβ during the terminal stage of monopoiesis.
Upregulation of Csf1r in monocyte subsets is impaired in Cebpb−/− mice. (A) Csf1r mRNA expression in purified hematopoietic populations (n = 3). (B) Csf1r mRNA expression in purified hematopoietic populations obtained from BM of WT or Cebpb−/− mice (n = 3). (C) Csf1r mRNA expression in purified monocyte subsets obtained from the PB of WT or Cebpb−/− mice (n = 3). (D) Flow cytometric analysis of CD115 (Csf1r) expression on Ly6C+ (left) and Ly6C− (right) monocytes in the PB of WT (filled lines, n = 3) and Cebpb−/− (unfilled lines, n = 3) mice. Data are presented as mean ± SD. **P < .01, ***P < .001. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the adjacent boxed area. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
Upregulation of Csf1r in monocyte subsets is impaired in Cebpb−/− mice. (A) Csf1r mRNA expression in purified hematopoietic populations (n = 3). (B) Csf1r mRNA expression in purified hematopoietic populations obtained from BM of WT or Cebpb−/− mice (n = 3). (C) Csf1r mRNA expression in purified monocyte subsets obtained from the PB of WT or Cebpb−/− mice (n = 3). (D) Flow cytometric analysis of CD115 (Csf1r) expression on Ly6C+ (left) and Ly6C− (right) monocytes in the PB of WT (filled lines, n = 3) and Cebpb−/− (unfilled lines, n = 3) mice. Data are presented as mean ± SD. **P < .01, ***P < .001. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the adjacent boxed area. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
Csf1r is a downstream target of C/EBPβ
Previous reports revealed a minimum cis-regulatory element of Csf1r, a combination of a 0.5-kb promoter region and a 1.8-kb FIRE located in the second intron31,39 (Figure 6A). There are at least 2 consensus binding sites for C/EBPs within the regulatory elements (one in the promoter and the other in the FIRE region). We hypothesized that C/EBPβ binds to these sites, activates transcription and promotes survival of Ly6C− monocytes. When a construct harboring the luciferase gene flanked by the Csf1r promoter and FIRE was subjected to the reporter assay using Cos-7 cells, C/EBPβ enhanced luciferase activity in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 6B). This enhancement was substantially weakened by mutation of either of the binding sites and completely abrogated by mutation of both binding sites, suggesting that these binding sites are functional in terms of activating transcription of Csf1r by C/EBPβ.
Csf1r is a downstream target of C/EBPβ. (A) Schematic illustration of the Csf1r reporter vector containing the promoter region and FIRE. Open circles indicate the consensus binding sites for C/EBPβ. (B) Activity of the luciferase reporter gene under the control of a combination of the promoter and FIRE of the Csf1r gene in response to different amounts of the C/EBPβ expression vector (0, 1, 5, and 10 ng) (n = 4). Open circles indicate the consensus binding sites for C/EBPβ, and closed circles indicate sites that were mutated to disrupt the binding of C/EBPβ. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. (C-D) mRNA (C) and surface (D) expression of Csf1r (CD115) in EML cells that were engineered to express ER alone or ER fused to C/EBPβ. 4-OHT, 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Shaded histograms indicate isotype controls. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. (E) ChIP-PCR to analyze the direct binding of C/EBPβ to the promoter and FIRE region in the Csf1r locus (n = 2). EML cells expressing C/EBPβ-ER were used for this analysis. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments and are presented as mean ± SD. (F) ChIP analysis showing binding of C/EBPβ to the mouse Csf1r locus in monocyte-derived cells. Data were taken from a study by Bornstein et al.40 Red arrows indicate promoter (Prom) and FIRE regions. IgG, immunoglobulin G.
Csf1r is a downstream target of C/EBPβ. (A) Schematic illustration of the Csf1r reporter vector containing the promoter region and FIRE. Open circles indicate the consensus binding sites for C/EBPβ. (B) Activity of the luciferase reporter gene under the control of a combination of the promoter and FIRE of the Csf1r gene in response to different amounts of the C/EBPβ expression vector (0, 1, 5, and 10 ng) (n = 4). Open circles indicate the consensus binding sites for C/EBPβ, and closed circles indicate sites that were mutated to disrupt the binding of C/EBPβ. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. (C-D) mRNA (C) and surface (D) expression of Csf1r (CD115) in EML cells that were engineered to express ER alone or ER fused to C/EBPβ. 4-OHT, 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Shaded histograms indicate isotype controls. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. (E) ChIP-PCR to analyze the direct binding of C/EBPβ to the promoter and FIRE region in the Csf1r locus (n = 2). EML cells expressing C/EBPβ-ER were used for this analysis. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments and are presented as mean ± SD. (F) ChIP analysis showing binding of C/EBPβ to the mouse Csf1r locus in monocyte-derived cells. Data were taken from a study by Bornstein et al.40 Red arrows indicate promoter (Prom) and FIRE regions. IgG, immunoglobulin G.
To investigate whether C/EBPβ can upregulate Csf1r, EML cells (a mouse HSC line) were engineered to express the C/EBPβ-ER fusion protein or ER alone. Nuclear translocation of C/EBPβ-ER induced by addition of tamoxifen resulted in significantly higher levels of Csf1r mRNA and protein, while ER alone had no effect on Csf1r expression (Figure 6C-D). Using these cell lines, we performed ChIP-PCR to confirm the binding of C/EBPβ to the consensus binding sites in the regulatory elements mentioned above. C/EBPβ was enriched at the promoter and FIRE regions by almost twofold (Figure 6E). Binding of C/EBPβ to these regions was further confirmed by ChIP-sequencing analysis using monocyte-derived cells40 (Figure 6F). Collectively, these data suggest that C/EBPβ positively regulates Csf1r expression, at least in part through direct binding to these regulatory elements.
Discussion
In this study, we revealed a novel role of C/EBPβ in monopoiesis. Cebpb was highly upregulated in mature monocytes, and Cebpb−/− mice had a severely reduced number of Ly6C− monocytes (Figure 1). BM chimera experiments in which Cebpb−/− cells were transplanted into WT mice showed similar defects in Ly6C− monocytes (Figure 2A), demonstrating that C/EBPβ is a cell-intrinsic factor required for Ly6C− monocyte development. In addition, Mx1-Cre–mediated targeting of Cebpb resulted in a decrease in the frequency of Ly6C− monocytes (Figure 2B). These findings clearly demonstrated that C/EBPβ is required by mature monocytes, in which expression of this transcription factor is strongly induced.
Our results clearly showed that death of Ly6C− monocytes was accelerated and that these cells were rapidly turned over in Cebpb−/− mice, clearly suggesting that C/EBPβ is required for the survival of Ly6C− monocytes. To identify a factor required for the survival of Ly6C− monocytes, we focused on Csf1r, which encodes the receptor for M-CSF. We found that Csf1r is a critical downstream target of C/EBPβ, while the serum level of Csf1 was not reduced in Cebpb−/− mice (supplemental Figure 7). Accordingly, recent reports show that administration of an antibody against Csf1r depletes PB Ly6C− monocytes, but not Ly6C+ monocytes, in vivo, suggesting the higher dependency of Ly6C− monocyte survival on M-CSF receptor signaling.41-43
Cell surface expression of Csf1r (CD115) was first observed at the MDP stage, even in the absence of C/EBPβ (Figure 1B). Interestingly, surface expression of Csf1r was maintained at a similar level during differentiation into monocytes, while the mRNA level of Csf1r was highly upregulated in mature monocytes, in which Cebpb mRNA was also highly expressed. Discrepancies between mRNA and protein expression of Csf1r might reflect the instability of surface Csf1r expression in mature monocytes.44 Collectively, these results suggest that the initial induction of Csf1r mRNA in MDPs is regulated by other factors including C/EBPα and that the subsequent sharp increase in Csf1r mRNA in monocytes, which might be required for survival of Ly6C− monocytes, is highly dependent on C/EBPβ.45-48 Further elucidation of the molecular mechanism regulating Csf1r and C/EBPβ is the next key step to understand the regulation of the monocyte/macrophage system.
Recently, 3 molecules have been reported to be involved in the homeostasis of Ly6C− monocytes, namely, Nr4a1, S1PR5, and CX3CR1. Mice in which one of these molecules is knocked out have a reduced number of Ly6C− monocytes.49-51 Interestingly, expression of all these molecules was highly induced during monocyte differentiation and severely decreased in Cebpb−/− monocytes (supplemental Figure 8). Of these molecules, S1PR5 functions in the egress of Ly6C− monocytes from BM.50 However, the egress of Ly6C− monocytes from BM was not impaired in Cebpb−/− mice (supplemental Figure 9). By contrast, in Nr4a1- or CX3CR1-knockout mice, the decreased level of Ly6C− monocytes has been suggested to be due to the accelerated death of these cells.49,51 This suggests that C/EBPβ can control the survival of Ly6C− monocytes through the regulation of Nr4a1 and/or CX3CR1. Indeed, a recent study showed that C/EBPβ binds to the promoter region of Nr4a1 and controls the expression of this gene.52
In this study, we focused on Ly6C− monocytes. However, we noticed that the number of PB Ly6C+ monocytes was also significantly reduced in Cebpb−/− mice (Figures 1 and 2), while turnover and apoptosis of Ly6C+ monocytes were not altered. One plausible explanation for this is that C/EBPβ also regulates the survival of Ly6C+ monocytes in the PB and that the extremely rapid turnover of Ly6C+ monocytes in the PB and their constant release from the BM allow for their detection in the PB of Cebpb−/− mice. mRNA expression of Csf1r was decreased in Cebpb−/− PB Ly6C+ monocytes (Figure 5C). This could be due to a decreased level of Csf1r in PB Ly6C+ monocytes or detection of BM Ly6C+ monocytes, which expressed Csf1r at low level (Figure 5A). In any case, regulation of Csf1r by C/EBPβ may be critical for the survival of monocyte subsets, including PB Ly6C+ and BM and PB Ly6C− cells, all of which expressed Cebpb at an extremely high level (Figure 1A). Further studies are required to elucidate the significance of C/EBPβ in PB Ly6C+ monocytes. In addition, C/EBPβ is required for differentiation of a newly identified Ly6C− monocyte subset called segregated nucleus–containing atypical monocytes (SatMs).53 Because there are many similarities between Ly6C− nonclassical monocytes and SatMs, it will be of interest to elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which C/EBPβ induces differentiation of SatMs.
In summary, we showed that C/EBPβ is involved in the survival of Ly6C− monocytes, in part via Csf1r regulation. These results will facilitate understanding of the mechanisms that regulate monocyte/macrophage homeostasis and uncover the pathophysiologies of various diseases in which monocytes are involved.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Shigekazu Nagata and Esta Sterneck for providing the CD45.1+ mice and Cebpb floxed mice, respectively. They also thank Toshio Kitamura (The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo) for providing Plat-E cells, and Clare Pridans and David A Hume (The Roslin Institute, University of Edinburgh) for providing the Csf1r-EGFP-long FIRE vector. The authors thank Eishi Ashihara (Kyoto Pharmaceutical University), Manabu Minami (Kyoto University), Yoji Andrew Minamishima (Kyushu University), Hideki Hara (Kyoto University), Ikuo Kawamura (Kyoto University), and all members of the Maekawa laboratory for valuable discussions and technical advice. They are also grateful to Yoko Nakagawa and Yoshiko Manabe for their excellent technical assistance.
This work was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) in Japan (H.H., A.Y., Y.M., and T.M.) and by a grant from the Kyoto University Research Development Program “Ishizue” (H.H.). D.G.T. was supported by a STaR Investigator Award, an RCE Core grant, and Tier 3 RNA Biology Center grant MOE2014-T3-1-006 from the National Research Foundation and Ministry of Education (Singapore) and National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute grant CA66996.
Authorship
Contribution: A.T. acquired and analyzed data and drafted the manuscript; H.H. conceived and designed the study, acquired, analyzed, and interpreted data, drafted the manuscript, and obtained funding; A.Y. acquired, analyzed, and interpreted data and drafted the manuscript; N.K., A.S., T.S., T.K., Y.T., and Y.M. acquired and analyzed data; and D.G.T. and T.M. supervised the study and interpreted data.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: H.H. received research funding from Kyowa Hakko Kirin and Novartis Pharma. T.M. received research funding from Bristol-Meyers Squibb K.K. T.K. is an employee of Takara Bio Incorporation. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Hideyo Hirai, Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy, Kyoto University Hospital, 54 Kawahara-cho, Shogo-in, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8507, Japan; e-mail: hhirai@kuhp.kyoto-u.ac.jp.




This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal