Introduction: Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis and peripheral cytopenia. In about half of patients with lower-risk (LR) MDS, thrombocytopenia is present at the time of diagnosis and associated with shortened survival and an increased risk of progression to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The thrombopoietin receptor agonist (TPO-RA) romiplostim has shown safety and marked efficacy in a still poorly-defined subset of LR-MDS patients with thrombocytopenia.
Methods: The EUROPE multicenter phase 2 trial within the EMSCO network investigated the impact of biomarkers like endogenous thrombopoietin (TPO) level and platelet transfusion events (PTE) on the efficacy of romiplostim (750µg SC qw) treatment in patients with LR-MDS (IPSS low/int-1). Patients were eligible if baseline bone marrow blast count was <5% as assessed by central morphology and platelet counts were ≤30 Gpt/L or ≤50 Gpt/L in case of bleeding history. According to a previously published model of response to TPO-RA (Sekeres at al. BJH 2014), patients were assigned into 3 different cohorts at the time of screening based on their previous PTE as well as centrally assessed TPO serum levels (cohort A: TPO<500 ng/l, PTE<6 units/past year; cohort B: TPO<500 ng/l, PTE≥6 units or TPO≥500 ng/l, PTE<6 units, cohort C: TPO≥500 ng/l, PTE≥6 units). Primary endpoint of the study was the rate of hematologic improvement of platelets (HI-P) according to IWG 2006 criteria after 16 weeks of romiplostim treatment. We here present the analysis for the first 16 weeks of romiplostim treatment.
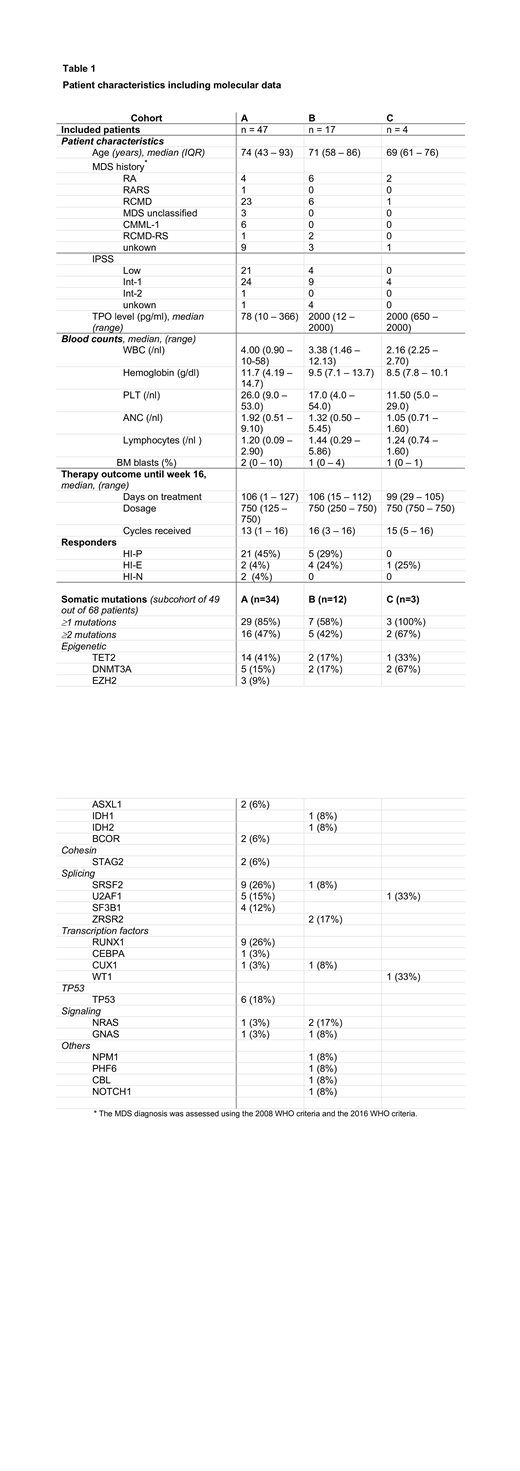
Results: From 2015 to 2018, a total of 68 patients were included in 20 trial sites in Germany, France and Czech Republic. Patients displayed a median age of 74 years and a median platelet count of 25 G/L (range 1-50 G/L) and were stratified into cohort A (n=47), B (n=17) or C (n=4), respectively. All patients received at least one cycle of romiplostim with a median weekly dose of 750μg and a median of 15 cycles of romiplostim until week 16. Reasons for premature study discontinuation before week 16 were investigator/patient decision (n=8), adverse events (n=5), disease progression (n=4) or death (n=1). There were 9 reported severe treatment-related adverse events in seven patients including pulmonary embolism (n=1), subacute stroke (n=1), mucocutaneous hemorrhage (n=1), asthenia (n=1), suspicion of anti-romiplostim antibodies (n=1), progression to AML (n=1) and varicella zoster infection (n=1). Two patients had transient increases in peripheral blasts to more than 10% and 1 patient progressed to AML after 1 month of treatment. HI-P was observed in 26 of 68 (38%) patients, while response was ongoing in 24 of them beyond week 16. Moreover, rate of HI-P lasting for at least 8 weeks was notably higher in cohort A (45%, n=21/47) compared to patients in cohort B and C (24%, n=5/21) (p=0.11). Median peak increase of PLT count in responding patients was 199 G/L in cohort A and 83 G/L in cohort B (p=0.25) and was observed in median after 7 weeks (range 3-16). In addition, responses occurred also in 2 patients in the neutrophil (HI-N) and in 7 patients in the erythroid (HI-E) lineage according to IWG 2006 criteria (Table 1). Explorative analysis showed a correlation between pretreatment platelet transfusion requirement and endogenous TPO-levels (spearman-test, p=0.034). Median pretreatment endogenous TPO-level was lower in responders compared to non-responders (82 vs. 103 pg/ml, p=0.15). Higher response rates occurred in patients with lower TPO-levels (<500 ng/l) and lower pre-treatment transfusion needs (PTE<6 units/past year), but both variables were not significantly associated with response to romiplostim (univariable logistic regression, p= 0.13 and p=0.53, respectively). Evaluation of the mutational profile in a subgroup of 49 patients demonstrated that 67% of responders exhibited spliceosome mutations including SRSF2, SF3B1, U2AF1 and ZRSR2 compared to 35% in non-responders (p=0.06) (Table 1).
Conclusion: This prospective study confirms that romiplostim treatment is highly effective in a subgroup of LR-MDS patients, but neither baseline platelet transfusion requirements nor baseline TPO levels were significantly associated with clinical response to romiplostim. Further translational analyses are ongoing to elucidate potential biomarkers of response.
Platzbecker:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Götze:AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Cony-Makhoul:Pfizer: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Incyte Biosciences: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Park:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Thiede:Daiichi Sankyo: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; AgenDix GmbH: Employment, Equity Ownership; Diaceutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ades:Helsinn Healthcare: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Silence Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Research Funding.
Romiplostim is formally not licensed for the treatment of thrombocytopenia due to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal