Introduction
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cells-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) are commonly associated with Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cells therapy. To assess CAR T cell safety, various grading systems were developed and used in clinical trials: Lee, Penn, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC), CARTOX and CTCAEv5.0 for CRS; and CTCAEv4.03 and CARTOX for ICANS. While these grading systems evaluate mostly uniform symptoms, their intensity gradings differ. The American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) recently developed a simplified consensus grading system for CRS and ICANS. To validate the ASTCT grading, we compared it to the aforementioned gradings.
Methods
We included 2 populations of adult patients (pts) treated at our center: 1) B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) treated with CD1928z CAR T cells from 2010 to 2016 (NCT01044069), and 2) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) or tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel) after FDA approval from 2018. Upon chart review, one expert clinician re-graded all CRS and ICANS. For validation, another expert independently graded a randomly selected sample (20%). A neurologist and an intensivist supervised the review process. CRS/ICANS rates and concordance rates were assessed for all grading systems. In pts with DLBCL (treated with axi-cel or tisa-cel), we used ASTCT grades to predict treatment according to currently available guidelines (axi-cel and tisa-cel FDA insert packages, CARTOX and NCCN guidelines) and compare it to the actual treatment received at our institution.
Results
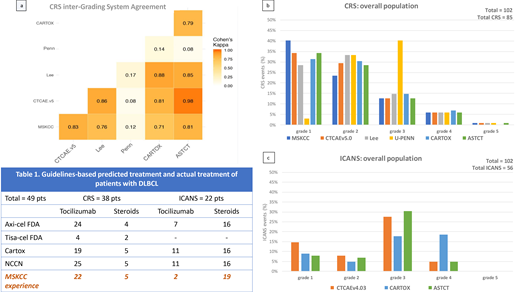
We analyzed 102 pts: 53 B-ALL and 49 DLBCL (axi-cel: 36, tisa-cel: 13). According to ASTCT grading, 82% pts had CRS, 87% in B-ALL and 77% in DLBCL pts (axi-cel: 86%, tisa-cel: 54%). The concordance rate on diagnosis of CRS (yes vs no) across all scores was 99%. Concordance rate grade by grade, instead, was 27%, with major discordance in grades 1 to 3 (figure a-b). The Penn score upgraded 91% pts from gr 1 to 2 (neutropenic fever requiring inpatient antibiotics), and 93% from gr 2 to 3 (fluid responsive hypotension or low-dose oxygen). Grading concordance increased to 78% when Penn was excluded, with other differences due to: 1) CARTOX downgraded 15% of gr 2 pts with hypotension, for systolic blood pressure >90; and 2) CARTOX and Lee upgraded 8% pts for organ damage.
By ASTCT, 50% pts experienced ICANS, 55% in B-ALL and 45% in DLBCL pts (axi-cel: 55%, tisa-cel: 15%). By CTCAEv4.03, ICANS incidence was 55% because 5 pts with headache and slurred speech with trouble word finding didn't meet criteria for ICANS by ASTCT (due to normal ICE score), leading to a 91% global concordance rate. Concordance grade by grade was 57%, mainly due to gr 1 and gr 3-4 ICANS (figure c). CARTOX upgraded 42% of gr 3 pts to gr 4 because of brief generalized seizures which, notably, where mostly seen in B-ALL pts compared to DLBCL (30% vs 6%). Another pt was upgraded from gr 2 to 4 for asymptomatic intracranial pressure >20 mmHg without cerebral edema.
We then looked at implications on management in the DLBCL group (Table 1). For CRS, only 4 pts with gr 3-4 CRS would receive tocilizumab according to tisa-cel's label (doesn't include tocilizumab for gr 2 CRS) compared to 24, 19, 25 pts according to axi-cel's label, CARTOX and NCCN, respectively. In our practice, 22 patients received tocilizumab. For ICANS, steroids use was consistent across all guidelines (16 pts, 5 with gr 2 ICANS and 11 with gr ≥3 ICANS) and almost comparable to our practice (19 pts treated). Conversely, only a few pts at our institution received tocilizumab for ICANS with concurrent CRS (2 pts vs 7, 11, 11 for axi-cel, CARTOX and NCCN, respectively).
Conclusions
Over or under attribution of symptoms due to CAR T cells results in inconsistent scores across different grading systems. Current guidelines for CRS and ICANS management are based on the experience derived from single products and various grading systems, which may result in either overtreating or delaying treatment. As such, they cannot be universally applied. To avoid discrepancies in assessing safety and in managing different product toxicities, we conclude that a unified grading system should be utilized across clinical trials and in clinical practice, and that similar consensus management guidelines be developed and adopted.
Santomasso:Juno/Celgene: Consultancy; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Batlevi:Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Brentjens:Celgene: Consultancy; JUNO Therapeutics: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Giralt:Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Actinium: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Johnson & Johnson: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Miltenyi: Research Funding; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Palomba:MSK (IP for Juno and Seres): Patents & Royalties; Evelo: Equity Ownership; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Noble Insights: Consultancy; Hemedicus: Speakers Bureau; Merck & Co Inc.: Consultancy; Seres Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; STRAXIMM: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Sauter:Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Precision Biosciences: Consultancy; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; Sanofi-Genzyme: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Scordo:Angiocrine Bioscience, Inc.: Consultancy; McKinsey & Company: Consultancy. Shah:Janssen Pharmaceutica: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding. Park:Allogene: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Autolus: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy. Perales:Miltenyi: Research Funding; Kyte/Gilead: Research Funding; Servier: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Medigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Omeros: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Nektar Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bellicum: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; NexImmune: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MolMed: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal