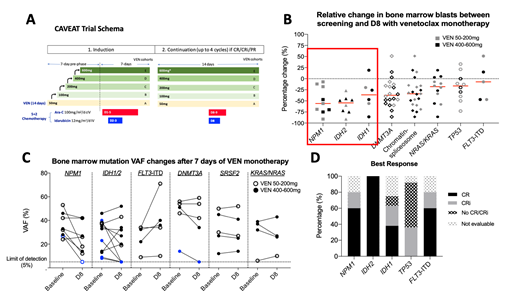
Background:The small molecule BCL-2 inhibitor Venetoclax (VEN) has emerged as a promising frontline therapy in combination with low dose cytarabine (LDAC) or hypomethylating agents in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML)(DiNardo et al, Lancet Oncol 2018, Blood 2019; Wei et al,JCO 2019). The anti-leukemic activity of single agent VEN as monotherapy in newly diagnosed AML is unknown. This information would be useful for studies considering VEN as a maintenance therapy. We have previously presented preliminary outcomes from a phase 1b/2 study: Chemotherapy and Venetoclax in Elderly AML Trial (CAVEAT), which incorporated a 7-day single agent VEN run-in phase prior to combination with chemotherapy (Wei et al, ASH 2018). The study procedures incorporated a bone marrow assessment performed at study screening and on day 8, prior to commencement of chemotherapy (Figure 1A). This allowed us to explore the single agent activity of venetoclax on bone marrow blasts in treatment naïve patients with AML and to assess molecular dynamics of response.
Methods:The CAVEAT trial included 51 de novo or secondary patients with AML aged ≥65 years and considered fit for intensive chemotherapy. The study enrolled patients to 5 VEN dose cohorts (50-100-200-400-600mg). VEN was administered on days 1-14 during induction. Chemotherapy commenced on day 8, with a 7-day VEN monotherapy pre-phase. Molecular studies:a 54-gene myeloid NGS panel (Illumina TruSight) and MassARRAY MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry was performed on DNA extracted from bone marrow aspirates. FLT3-ITD testing was by fragment analysis, PCR and capillary electrophoresis. Minimal residual disease (MRD) testing was performed by digital droplet PCR for IDH mutations (assay sensitivity: 10-4-10-5).
Results: A total of 46 patients had paired BM assessments at screening and on day 8 for comparison. A ≥50% relative reduction in BM blasts was recorded in 13/46 (28%) patients. Figure 1B shows the relative BM blast reduction stratified by molecular subgroups. Patients with NPM1(n=9) or IDH2 (n=8) mutation achieved greater BM blast reductions (median of 56% and 55%, respectively) than IDH1 (n=6), TP53 (n=10) or FLT3-ITD (n=5) mutant cases (median of 37%, 17% and 7%, respectively). Three NPM1 mutant cases with <25% blast reduction had contemporaneous kinase activating mutations (FLT3-ITD, FLT3-TKD and c-KIT). Molecular studies were performed on serial screening and day 8 bone marrow samples in 21 patients (Figure 1C). Variant allele frequency (VAF) reductions were observed in 6/8 (75%) NPM1 and 6/11 (55%) IDH 1/2 mutant cases. 1/8 (13%) NPM1 mutant and 4/11 (36%) IDH 1/2 mutant cases had reduction in molecular burden to below the limit of detection (5%) by day 8. Minimal reduction in VAF was seen in DNMT3A, SRSF2, NRAS/KRAS and FLT3-ITD mutations. 4 out of 5 (80%) FLT3-ITD mutant cases had an increase in VAF at day 8.
Clinically, complete remission (CR) and CR with incomplete count recovery (CRi) rates after chemotherapy were seen for the following mutations: NPM1(80%), IDH2 (100%), IDH1 (62%) and TP53 (36%) (Figure 1D). Despite all four response-evaluable patients with FLT3-ITD achieving CR/CRi, 3/4 relapsed with detectable FLT3-ITD (at 0.8, 1.5 and 12.3 months respectively). Median survival for each genomic sub-group were NPM1 (12.5m), IDH2 (not reached), IDH1 (6.1m),TP53 (3.8m), FLT3-ITD (5.5m).
CyTOF analyses for changes in BCL-2 family expression are underway and results will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusion: Treatment naïve NPM1 and IDH2 mutant AML blasts are highly sensitive to VEN alone and combination with cytarabine and anthracycline chemotherapy results in a high clinical response rate. TP53 and FLT3-ITD mutant cases were more resistant and outcomes were poor despite VEN combined with chemotherapy.
Reynolds:Alfred Health: Employment, Other: Biostatistician for trials funded by the Australian government and Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, GSK, Janssen-Cilag, Merck, Novartis, Takeda, but sponsored by Alfred Health.; AUSTRALASIAN LEUKAEMIA & LYMPHOMA GROUP (ALLG): Consultancy; Novartis AG: Equity Ownership; Novartis Australia: Honoraria. Fong:Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Consultancy; Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Ting:NHMRC: Research Funding. Fleming:Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Ariad: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Moujalled:Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research: Patents & Royalties: Share in venetoclax royalties . Ivey:Novartis: Honoraria. Roberts:AbbVie: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Walter and Eliza Hall Institute: Employment, Patents & Royalties: receives a fraction of its royalty stream related to venetoclax. Wei:AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties: AHW is a former employee of the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute and receives a fraction of its royalty stream related to venetoclax, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Macrogenics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria.
Venetoclax is a BCL-2 inhibitor that is FDA-approved in some indications. This presentation will focus on correlative study results in the CAVEAT trial which combines venetoclax with modified intensive chemotherapy in AML, which is not an approved indication.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal