Abstract
Background: Patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who do not achieve a complete response (CR) following CD19-targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell (CAR T) therapy are less likely to obtain durable benefit. Greater tumor burden pre-CAR T has been shown to predict lower CR rate and shorter survival. Recently, patterns of failure studies have identified baseline lesion characteristics including size, SUV, and extranodal location as associated with increased risk of post-CAR T failure. It is not yet known how bridging radiotherapy (BRT) prior to CAR T can alter subsequent patterns of failure.
Methods: We reviewed DLBCL patients treated from 2017 to 2021 with BRT for any intent in the period from 30d pre-leukapheresis to CAR T infusion. Comprehensive BRT fields were defined as no avidity above liver mean outside of the BRT field. Bulky disease was defined as a max diameter of ≥7.5cm in any dimension. PET response was evaluated by Lugano criteria. Pattern of failure analysis was performed to identify failure sites as pre-existing (present pre-CAR T) vs. new and as in-field, marginal, or distant with respect to BRT. Marginal was defined as failure outside of the area receiving prescription dose but within 1cm of BRT field edge. One patient with a cutaneous target was excluded from size-based analyses. Significance was assessed by Fisher's exact test or T-test.
Results: Thirty-five patients were identified with a median age of 66. Most were advanced stage (74%) at BRT with a median of 3 prior lines of systemic therapy. Twelve (35%) had bulky disease at any site pre-BRT (median max diameter 5.9 cm; range 1.1 - 24) with highest overall SUV median 19.8 (range 3.4 - 47); 83% (n=29) had ≥1 extranodal site (bone: n=13; CNS: n=4). Most common BRT sites were head/neck (n=10), pelvis (n=6), and extremity (n=5). BRT targeted the largest lesion in 85% (median 5.8 cm; 32% bulky) and the site of highest SUV in 81% (median 18.7); 49% (n=17) of targets were extranodal. BRT fields were comprehensive in 39%; median radiation treatment volume was 751cc (range 18 - 5856). Twenty-four patients (63%) received ≥30 Gy (median 30 Gy; range 20 - 54). Systemic therapy was given during the bridging period to 31% (n=11). Patients received axicabtagene (n=20), tisagenlecleucel (n=11), lisocabtagene (n=3), or experimental CAR T (n=1).
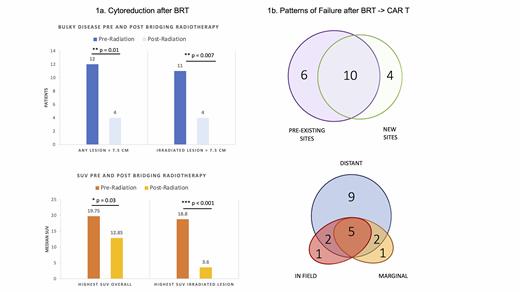
On PET after BRT and pre-infusion (median 12d from BRT), 85% (n=23) had achieved partial response (PR) or better in-field (CR: n=7) though 63% had kinetically active disease with out-of-field progression (PD) and 19% (n=5) had marginal PD. Despite short interval restaging, there was a significant reduction in patients with bulky disease after BRT both within the irradiated field (p=0.007) and at any site (p=0.01). (Fig 1a) A median 81% SUV reduction in the irradiated site was noted with a significant decrease in max SUV in both the irradiated (p<0.001) and any (p=0.03) site. Following CAR T, 82% (n=26) achieved in-field CR and 68% (n=21) overall CR. With median post CAR T follow up of 11.5 mo (range 1.5 - 40), 20 patients (57%) ultimately failed at any site. Most failures (18/20) involved sites distant to the BRT field, however the predominant failure pattern remained within lesions that were present prior to CAR T (16/20). (Fig 1b) Eight patients failed in-field and 8 patients failed marginally; the majority (7/8 in both cases) also experienced distant failure. Comprehensive BRT was not significantly associated with decreased risk of pre-existing site failure. In the subset of patients with a bulky lesion irradiated (n=11; median lesion size 11cm), 73% (n=8) achieved a CR in-field post CAR T and of those 8, only one progressed in-field at 22 mo post CAR T.
Conclusion: BRT significantly reduced the number of patients with bulky disease at any site at time of CAR T and significantly reduced the overall highest lesional SUV. Marginal failure rates of 19% and 23% at interim scan post-BRT and after CAR T, respectively in conjunction with the pattern of post CAR T failure predominantly in pre-existing sites, may suggest a need for more generous fields when a BRT approach is used in this population with rapidly proliferating disease. Further work and larger sample sizes are needed to evaluate the impact of dose on local control in bulky lesions as well as to investigate whether comprehensive BRT affects outcomes or patterns of failure.
Palomba: Juno: Patents & Royalties; Notch: Honoraria, Other: Stock; Novartis: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; PCYC: Consultancy; Wolters Kluwer: Patents & Royalties; Seres: Honoraria, Other: Stock, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Magenta: Honoraria; Ceramedix: Honoraria; WindMIL: Honoraria; Nektar: Honoraria; Rheos: Honoraria; Priothera: Honoraria; BeiGene: Consultancy; Lygenesis: Honoraria; Pluto: Honoraria. Shouval: Medexus: Consultancy. Batlevi: Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Viatris: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; Dava Oncology: Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Regeneron: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; TouchIME: Honoraria; Juno/Celgene: Consultancy; Medscape: Honoraria; BMS: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Life Sciences: Consultancy; Pfizer: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Moderna: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center: Current Employment; Bayer: Research Funding; GLG Pharma: Consultancy; Xynomic: Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Epizyme: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Autolus: Research Funding. Brentjens: Gracell Biotechnologies, Inc: Consultancy, Ended employment in the past 24 months; BMS: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; sanofi: Patents & Royalties; Caribou: Patents & Royalties. Dahi: Kite / Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Giralt: JAZZ: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AMGEN: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; JENSENN: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; PFIZER: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; SANOFI: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CELGENE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Actinnum: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Park: BMS: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Innate Pharma: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Minerva: Consultancy; Servier: Consultancy; Kura Oncology: Consultancy; PrecisionBio: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Intellia: Consultancy; Artiva: Consultancy; Curocel: Consultancy; Autolus: Consultancy; Affyimmune: Consultancy. Scordo: Angiocrine Bioscience: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite - A Gilead Company: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; i3 Health: Other: Speaker; Omeros Corporation: Consultancy; McKinsey & Company: Consultancy. Sauter: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; GSK: Consultancy; Gamida Cell: Consultancy; Precision Biosciences: Consultancy; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genmab: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi-Genzyme: Consultancy, Research Funding. Shah: Amgen: Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceutica: Research Funding. Perales: Merck: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Cidara: Honoraria; Miltenyi Biotec: Honoraria, Other; Kite/Gilead: Honoraria, Other; Equilium: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria, Other; Medigene: Honoraria; Karyopharm: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria; NexImmune: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Other; Nektar Therapeutics: Honoraria, Other; Sellas Life Sciences: Honoraria; Omeros: Honoraria; MorphoSys: Honoraria.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal