The hyperinflammation that characterizes PF is, at least in part, a consequence of inherited complement defects.
Missense mutations in ITGB2 simultaneously impair anti-inflammatory CR3 signaling and enhance proinflammatory CR4 signaling.
Visual Abstract
Extreme disease phenotypes can provide key insights into the pathophysiology of common conditions, but studying such cases is challenging due to their rarity and the limited statistical power of existing methods. Herein, we used a novel approach to pathway–based mutational burden testing, the rare variant trend test (RVTT), to investigate genetic risk factors for an extreme form of sepsis-induced coagulopathy, infectious purpura fulminans (PF). In addition to prospective patient sample collection, we electronically screened over 10.4 million medical records from 4 large hospital systems and identified historical cases of PF for which archived specimens were available to perform germline whole-exome sequencing. We found a significantly increased burden of low-frequency, putatively function-altering variants in the complement system in patients with PF compared with unselected patients with sepsis (P = .01). A multivariable logistic regression analysis found that the number of complement system variants per patient was independently associated with PF after controlling for age, sex, and disease acuity (P = .01). Functional characterization of PF-associated variants in the immunomodulatory complement receptors CR3 and CR4 revealed that they result in partial or complete loss of anti-inflammatory CR3 function and/or gain of proinflammatory CR4 function. Taken together, these findings suggest that inherited defects in CR3 and CR4 predispose to the maladaptive hyperinflammation that characterizes severe sepsis with coagulopathy.
Introduction
Severe sepsis is associated with extremely high levels of systemic inflammation and the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), a consumptive coagulopathy caused by dysregulated activation of blood clotting.1 A small subset of sepsis patients experience a highly thrombotic manifestation of DIC known as purpura fulminans (PF), which is characterized by the sudden onset of diffuse retiform purpura and widespread, uncontrolled microvascular clotting that results in tissue ischemia and necrosis.2 PF is associated with a mortality rate of up to 50%, and survivors are often left with extensive scarring, tissue loss, and dismemberment.2,3
In severe sepsis syndromes such as PF, there is extensive cross talk between inflammation and coagulation.4 Proinflammatory cytokines elaborated during sepsis, including interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), downregulate expression of anticoagulant mediators, upregulate expression of tissue factor (TF), and stimulate release of TF-rich procoagulant microparticles by activated monocytes, macrophages, and endothelium.5-7 Although the exact mechanism by which the coagulation system is activated in PF remains unclear, aberrantly expressed TF is thought to trigger unchecked thrombin generation and subsequent failure of the thrombomodulin-protein C anticoagulant pathway, thereby completing the circuit that links infection, inflammation, and thrombosis.2,8,9
One hypothesized driver of hyperinflammation and DIC in severe sepsis is the complement system (Figure 1A).10-13 Complement promotes inflammation via at least 3 distinct mechanisms: stimulation of immune cells by complement activation peptides C3a and C5a,12,14,15 pathogen lysis and release of lipopolysaccharide and other cellular components,16-18 and opsonization of microorganisms for recognition by complement receptors.14,19,20 The integrin complement receptors 3 and 4 (CR3 and CR4) expressed on leukocytes play a fundamental role in regulating the pro- and anti-inflammatory responses to infection.21-24 CR3 and CR4 are heterodimers composed of a unique α subunit and a shared β subunit (Figure 1B). CR3 is composed of integrin β2 (ITGB2, CD18) paired with integrin αM (ITGAM, CD11b), whereas CR4 is composed of integrin β2 paired with integrin αX (ITGAX, CD11c). During infection, complement fragment C3b is deposited on microbial surfaces where it is converted to iC3b, a potent opsonin that serves as the primary ligand for CR3 and CR4.21,25 Binding of iC3b to CR3 and CR4 leads to phagocytosis of targeted microbes and activation of intracellular signaling. CR3 signaling promotes an anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory cytokine profile whereas CR4 signaling contributes to a proinflammatory state.20-22,26-28
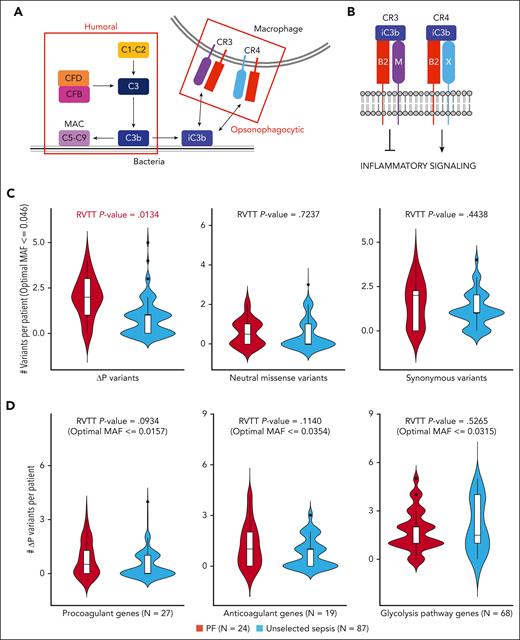
Rare variant analysis of PF. (A) Simplified schematic of the complement system. The complement system is broadly divided into 2 subpathways: humoral and opsonophagocytic. The humoral subpathway is comprised of soluble plasma proteins responsible for destroying microorganisms via formation of the membrane attack complex, which lyses the target cell by permeabilizing its surface. The opsonophagocytic subpathway is comprised of cellular receptors that recognize complement fragments deposited on microbial surfaces and facilitate phagocytosis and pathogen clearance. (B) Heterodimerization of integrin β2 (B2) with integrin αM (M) forms the anti-inflammatory signaling mediator CR3 whereas heterodimerization of B2 with integrin αX (X) forms the proinflammatory signaling mediator CR4. (C) RVTT analyses comparing the European PF cohort (PF) and the NHLBI ARDSnet iSPAAR cohort (unselected sepsis) in terms of ΔP variants (left panel), neutral missense variants (middle panel), and synonymous variants (right panel). (D) RVTT analyses comparing the same 2 cohorts in terms of ΔP variants in procoagulant genes (left panel), anticoagulant genes (middle panel), and glycolysis pathway genes (right panel).
Rare variant analysis of PF. (A) Simplified schematic of the complement system. The complement system is broadly divided into 2 subpathways: humoral and opsonophagocytic. The humoral subpathway is comprised of soluble plasma proteins responsible for destroying microorganisms via formation of the membrane attack complex, which lyses the target cell by permeabilizing its surface. The opsonophagocytic subpathway is comprised of cellular receptors that recognize complement fragments deposited on microbial surfaces and facilitate phagocytosis and pathogen clearance. (B) Heterodimerization of integrin β2 (B2) with integrin αM (M) forms the anti-inflammatory signaling mediator CR3 whereas heterodimerization of B2 with integrin αX (X) forms the proinflammatory signaling mediator CR4. (C) RVTT analyses comparing the European PF cohort (PF) and the NHLBI ARDSnet iSPAAR cohort (unselected sepsis) in terms of ΔP variants (left panel), neutral missense variants (middle panel), and synonymous variants (right panel). (D) RVTT analyses comparing the same 2 cohorts in terms of ΔP variants in procoagulant genes (left panel), anticoagulant genes (middle panel), and glycolysis pathway genes (right panel).
To evaluate the role of complement variants in severe sepsis with coagulopathy, we performed a case-controlled extreme phenotype genomic study utilizing PF as an archetypal extreme sepsis phenotype. Extreme phenotype approaches can amplify the effects of low-frequency germline variants and facilitate genomic research,29,30 particularly when prior biological knowledge is leveraged to focus on pathways where multiple genes function together in a directionally consistent manner.31-33 We found that low-frequency variants in the humoral and opsonophagocytic complement pathways are independently associated with PF, and that several of the opsonophagocytic variants we identified aberrantly augment the inflammatory response. Our data suggest that a hyperinflammatory reaction mediated in part by inherited defects in complement receptor function contributes to the development of severe sepsis with coagulopathy.
Methods
Study samples
The Boston PF cohort is a multi-institutional data set of infectious PF patients treated at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston Medical Center, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, or Massachusetts General Hospital between 1995 and 2019. Approximately one-third of the samples were obtained from archived formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded surgical pathology specimens. The remaining samples were extracted from whole blood or cheek swab specimens from living subjects. Whole-exome sequencing was performed and underwent quality control as described in supplemental Methods, available on the Blood website. Exome sequences from 87 unselected patients with sepsis from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) ARDSnet iSPAAR consortium available in the NIH Database of Genotypes and Phenotypes (dbGaP) were used as the control cohort (dbGaP study accession phs000631.v1.p1).
This study was approved by the institutional review boards of all participating centers. Use of the NHLBI ARDSnet iSPAAR whole-exome sequencing data set and associated clinical data was approved by the Data Access Committee of dbGaP. All sequencing was performed in a fully deidentified manner with informed consent or under an institutional review board–approved waiver of consent for historical samples.
PF case definition
Each PF case was adjudicated through consensus review of the patient’s medical record by a panel of 3 independent experts. A diagnosis of PF required all 3 of the following features: rapid onset of systemic inflammatory response syndrome, evidence of consumptive coagulopathy, and purpuric skin findings. Consumptive coagulopathy was defined by 2 or more of the following: activated partial thromboplastin time ≥45 seconds, International Normalized Ratio ≥1.5, platelets ≤ 100 x 109/L, and/or D-dimer ≥ 3000 ng/mL.
Data analysis
Gene sets
To test the hypothesis that impaired complement function predisposes individuals to PF, the complement system gene set was restricted to positive effectors of complement activity.34,35 For the coagulation gene sets, canonical positive and negative regulators of coagulation were used. For the glycolysis gene set, the Broad Institute’s MSigDB database gene list was used.
Rare variant trend test (RVTT)
Pathway–based mutational burden testing was performed as described in supplemental Methods.
Sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score calculation
SOFA scores36 were calculated for each patient based on review of their medical record (PF cohort) or data available through dbGaP (control cohort). Scores were not computed for patients missing 1 or more parameters. Modeling was performed using GraphPad Prism version 9.3.
CFD cloning, protein expression, and purification
C-terminal His-tagged complement factor D expression vectors were generated, and recombinant proteins were produced and purified, as described in supplemental Methods.
Red blood cell lysis assay
The red blood cell lysis assay was identical to the standard clinical alternative pathway hemolytic assay (AH50)37 except that, instead of normal plasma, complement factor D (CFD)-depleted plasma reconstituted with recombinant wild type (WT) or mutant CFD was used. Please refer to the supplemental Methods.
Generation of CR3 and CR4 stable cell lines
ITGAM, ITGAX, and ITGB2 expression vectors were generated as described in supplemental Methods. HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with different combinations of ITGB2-mCherry constructs and ITGAM-green fluorescent protein (GFP) or ITGAX-GFP constructs using Lipofectamine (Thermo Fisher Scientific). To ensure equivalent subunit expression, the cell lines were sorted for equivalent GFP and mCherry double-positivity using a FACSAria cell sorter (BD Biosciences) under BL2+ sterile conditions. HEK-293T cells were authenticated by short tandem repeat profiling and were periodically tested for Mycoplasma contamination using the Venor GeM Mycoplasma detection kit (Sigma Aldrich).
Immunoblotting of CR3 and CR4 stable cell lines
Cells were lysed in 2% NP-40 in Tris-buffered saline–containing Halt protease inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Fisher Scientific), resolved by sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gene electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), transferred to 0.45 μm polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore), and analyzed by immunoblotting. Primary antibodies used were anti-integrin αM (Cell Signaling Technology, D6X1N), anti-integrin αX (Cell Signaling Technology, D3V1E), anti-integrin β2 (Cell Signaling Technology, D4N5Z), and anti-GAPDH (Cell Signaling Technology, D16H11). Secondary antibodies used were horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, no. 211-032-171) and anti-mouse (Cell Signaling Technologies, no. 7076).
Flow cytometry analysis of CR3 and CR4 stable cell lines
Cell surface CR3 and CR4 expression was assessed by staining cells with allophycocyanin (APC)–labeled anti-CD18 antibody (BD BioSciences, 551060). Flow cytometry was performed using an LSRFortessa flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and data were analyzed using FlowJo software.
Solid-phase iC3b binding assays
Ninety-six-well polystyrene plates were coated with iC3b (200 ng per well) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at 4°C overnight and then blocked with 0.05% polyvinylpyrrolidone. Cells (1 × 105 for CR4-expressing cells or 2 × 105 for CR3-expressing cells) in HEPES (N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-NN-2-ethanesulfonic acid)-buffered saline (HBS) with 1 mM Ca2+, 1 mM Mg2+, and 0.5 mM Mn2+ were added to each well and incubated at 37°C for 20 minutes. Unbound cells were removed by 3 washes with HBS. Adherent cells were stained with 0.5% crystal violet. Excess dye was washed off with distilled water, the remaining dye was solubilized in methanol, and absorbance was measured at 570 nM on a standard plate reader. Data were analyzed using the 1-way analysis of variance with the Dunnett post hoc test after confirming normality of the data with the Shapiro-Wilk test.
Dual-luciferase reporter assays
Ninety-six-well plates (Medisorp, Thermo Scientific) were coated with 1 μg per well iC3b (Complement Tech) or mock solution and incubated at 4°C for 6 hours. Plates were then washed with PBS, blocked with 0.5% polyvinylpyrrolidone in PBS for 1 hour at room temperature, and washed again with PBS. Cells (1 × 106 per well) were seeded in 12-well tissue culture plates. When the cells reached 80% confluency, they were transfected with 75 ng pSI-Check2-hRluc-NFκB-firefly plasmid (Promega) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) and incubated at 37°C for 6 hours. Following transfection, the cells were harvested and seeded onto the iC3b-coated or mock-coated 96-well plates at 5 × 104 cells per well and were incubated at 37°C for 18 hours. Cells were then stimulated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α (Sigma) at 37°C for 4 hours and luciferase activity was measured using a Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega).
Results
Assembly of the Boston PF cohort and curation of whole-exome sequencing data
PF is exceptionally rare. To assemble a patient cohort, we combined prospective sample collection with an automated natural language processing approach to mine the electronic medical records of 10.4 million patients for historical cases of PF with archived pathology specimens suitable for whole-exome sequencing. In total, we collected and sequenced 40 PF patient samples (Table 1; supplemental Table 1). Three PF samples failed quality control (QC) (supplemental Figure 1) and were removed. As controls, we utilized the exome sequences of 87 unselected patients with sepsis from the NHLBI ARDSnet iSPAAR consortium who had significantly lower average disease acuity as measured by SOFA score (P < .0001) (Table 1). We analyzed the PF and control datasets to identify variants in the complement system with gnomAD global minor allele frequncies (MAFs) < 0.05 as well as variants with an optimal in-cohort frequency cutoff selected using a variable thresholds approach.38 Missense variants predicted to be “deleterious” or “possibly deleterious” by either PolyPhen2 or Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant (SIFT) and high-precision loss of function (LoF) variants (stop gained, stop lost, essential splice site, frameshift, and in-frame indel) were grouped together and termed “low-frequency altered-phenotype” (ΔP) variants. To control for population structure, we performed principal component analysis on the study samples (supplemental Figure 2). All 87 controls but only 24/37 PF patients were of European descent, and we therefore limited our primary analysis to individuals of European ancestry. As expected, inclusion of non-European PF patients increased the burden of ΔP variants when compared to the European-only PF patient cohort (supplemental Figure 3). To rule out that other population substructures could introduce bias into our analysis, we evaluated the distribution of ultra-rare (ie, doubleton and tripleton) missense and synonymous variants shared between the European PF and control cohorts and observed no significant differences (supplemental Table 2).
Characteristics of the study cohorts
| . | PF cohort (N = 37) . | Control cohort (N = 87) . |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (% male) | 59.5 | 70.1 |
| Mean age (±SD) | 44.5 ± 23.2 | 61.8 ± 17.2 |
| Race (% Caucasian) | 68.6 | 100% |
| Ventilated (%) | 80.0 | 81.6 |
| Mean platelet count (±SD) | 39.2 ± 35.2 | 203.4 ± 124.8 |
| Mean bilirubin (±SD) | 2.3 ± 2.4 | 1.3 ± 2.2 |
| Mean creatinine (±SD) | 3.6 ± 2.1 | 1.6 ± 1.1 |
| Mean lactate (±SD) | 9.0 ± 5.0 | UK |
| Mean protein C (% ± SD) | 22.8 ± 10.8 | UK |
| In-hospital mortality (%) | 42.4 | 21.8 |
| Mean SOFA score (± SD) | 12.8 ± 3.0 | 7.6 ± 2.8 |
| . | PF cohort (N = 37) . | Control cohort (N = 87) . |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (% male) | 59.5 | 70.1 |
| Mean age (±SD) | 44.5 ± 23.2 | 61.8 ± 17.2 |
| Race (% Caucasian) | 68.6 | 100% |
| Ventilated (%) | 80.0 | 81.6 |
| Mean platelet count (±SD) | 39.2 ± 35.2 | 203.4 ± 124.8 |
| Mean bilirubin (±SD) | 2.3 ± 2.4 | 1.3 ± 2.2 |
| Mean creatinine (±SD) | 3.6 ± 2.1 | 1.6 ± 1.1 |
| Mean lactate (±SD) | 9.0 ± 5.0 | UK |
| Mean protein C (% ± SD) | 22.8 ± 10.8 | UK |
| In-hospital mortality (%) | 42.4 | 21.8 |
| Mean SOFA score (± SD) | 12.8 ± 3.0 | 7.6 ± 2.8 |
Clinical and laboratory data at the time of presentation for patients in the Boston PF cohort (N = 37) and the NHLBI ARDSnet iSPAAR control cohort (N = 87).
SD, standard deviation; UK, unknown.
Pathway–based rare variant burden analysis in distinct phenotypes of sepsis
Across the entire PF cohort (N = 37), we identified 59 unique missense variants in the complement gene set (N = 27 genes; supplemental Table 3) with MAFs < 0.05 (Table 2). We noted that variants in the humoral subpathway were far less well characterized than those affecting opsonophagocytic subpathway genes (supplemental Tables 4-6). Of the 61 total (nonunique) humoral subpathway ΔP variants identified in the PF cohort (all of which were heterozygous), 40 (65.6%) were either high-precision LoF variants or had previously been experimentally found to result in LoF. By contrast, only 7 of 20 (35.0%) opsonophagocytic subpathway ΔP variants met these criteria, and only 1 opsonophagocytic variant had been previously described in the literature. In the control cohort, 54/83 (65.1%) variants qualified as ΔP variants (Table 2; supplemental Tables 4 and 5).
Complement system variants found in the study cohorts
| . | PF-specific variants . | US-specific variants . | Shared variants . | Total PF-associated variants . | Total US-associated variants . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total unique variants | 64 | 63 | 20 | 84 | 83 |
| Neutral | 16 | 19 | 10 | 26 | 29 |
| Missense | 43 | 52 | 16 | 59 | 68 |
| MissenseF | 26 | 33 | 6 | 32 | 39 |
| HP LoF | 22 | 11 | 4 | 26 | 15 |
| ΔP variants | 48 | 44 | 10 | 58 | 54 |
| Humoral variants | 48 | 42 | 17 | 65 | 59 |
| Neutral | 13 | 15 | 9 | 22 | 24 |
| Missense | 30 | 36 | 14 | 44 | 50 |
| MissenseF | 16 | 19 | 5 | 21 | 24 |
| HP LoF | 19 | 8 | 3 | 22 | 11 |
| ΔP variants | 35 | 27 | 8 | 43 | 35 |
| Opsonophagocytic variants | 16 | 21 | 3 | 19 | 24 |
| Neutral | 3 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| Missense | 13 | 18 | 2 | 15 | 20 |
| MissenseF | 10 | 14 | 1 | 11 | 15 |
| HP LoF | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| ΔP variants | 13 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 19 |
| . | PF-specific variants . | US-specific variants . | Shared variants . | Total PF-associated variants . | Total US-associated variants . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total unique variants | 64 | 63 | 20 | 84 | 83 |
| Neutral | 16 | 19 | 10 | 26 | 29 |
| Missense | 43 | 52 | 16 | 59 | 68 |
| MissenseF | 26 | 33 | 6 | 32 | 39 |
| HP LoF | 22 | 11 | 4 | 26 | 15 |
| ΔP variants | 48 | 44 | 10 | 58 | 54 |
| Humoral variants | 48 | 42 | 17 | 65 | 59 |
| Neutral | 13 | 15 | 9 | 22 | 24 |
| Missense | 30 | 36 | 14 | 44 | 50 |
| MissenseF | 16 | 19 | 5 | 21 | 24 |
| HP LoF | 19 | 8 | 3 | 22 | 11 |
| ΔP variants | 35 | 27 | 8 | 43 | 35 |
| Opsonophagocytic variants | 16 | 21 | 3 | 19 | 24 |
| Neutral | 3 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| Missense | 13 | 18 | 2 | 15 | 20 |
| MissenseF | 10 | 14 | 1 | 11 | 15 |
| HP LoF | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| ΔP variants | 13 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 19 |
The number and types of rare unique complement system variants identified in the PF cohort (PF) (N = 37) and the NHLBI ARDSnet iSPAAR unselected sepsis (US) cohort (N = 87).
ΔP variants = MissenseF + HP LoF.
HP LoF, high-precision prediction LoF (stop gained, stop lost, essential splice site, frameshift, and in-frame indel); MissenseF, missense variants predicted in silico to cause altered protein function.
The novel analytic approach we developed, RVTT, allows us to evaluate the aggregate effect of multiple ΔP variants in a biologic pathway even if insufficient power exists to identify individual disease-causing rare variants. In RVTT, the frequency of qualifying rare ΔP variants in directionally consistent genes of a biologic pathway is compared between disease and control cohorts by leveraging the Cochran-Armitage test statistic. If a pathway is related to disease risk, RVTT can reveal whether it is enriched for qualifying variants in the disease cohort relative to controls. This approach was recently used to uncover the contribution of rare variants to Parkinson’s disease.39 We performed RVTT on the European PF cohort (N = 24) and the unselected sepsis control cohort (N = 87) using a fixed gnomAD MAF cutoff of 0.05 and a variable threshold approach with or without an in-cohort MAF cutoff. We observed a significant linear trend in the number of complement system ΔP variants in PF patients compared with controls (RVTT approach with gnomAD cutoff: permutation P = .0168, z score = 2.5; RVTT approach with MAF cutoff up to 0.05: permutation P = .0134, z score = 2.62; RVTT approach without cutoff: P = .0278, z score = 2.72) (Table 3; Figure 1C). Notably, a simple 1-sided combined multivariate and collapsing (CMC) Fisher exact test was only borderline significant (P = .0418) (supplemental Table 7), and none of the complement genes individually showed significant enrichment of ΔP variants in PF cases using gene-based collapsing analyses (supplemental Table 8). These results further support our use of a pathway-based analysis that leverages prior biological knowledge to increase power. To rule out the possibility that the observed ΔP RVTT signal resulted from a technical artifact, we repeated RVTT with synonymous and predicted functionally neutral missense variants in the complement pathway and observed no significant linear trend (Table 3; Figure 1C). To further validate our findings, we also performed RVTT on gene sets comprising canonical pro- and anticoagulant genes (N = 27 and N = 19 genes, respectively) as well as on an unrelated pathway, the glycolysis system (N = 68 genes) (supplemental Table 3). None of the control gene sets demonstrated significant enrichment in ΔP variants in the PF cohort (Table 3; Figure 1D).
Rare variant burden assessed by RVTT in quality-filtered European PF cases (N = 24) and sepsis controls (N = 87)
| Type . | RVTT-fixed test statistic (gnomAD cutoff = 0.05) . | RVTT-fixed Perm P value (gnomAD cutoff = 0.05) . | RVTT-variable selected MAF threshold (no cutoff) . | RVTT-variable test statistic (no cutoff) . | RVTT-variable Perm P value (no cutoff) . | RVTT-variable selected MAF threshold (cutoff = 0.05) . | RVTT-variable test statistic (cutoff = 0.05) . | RVTT-variable Perm P value (cutoff = 0.05) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complement system pathway (N = 27) | ||||||||
| ΔP variants | 2.4951 | .0168 | 0.0833 | 2.7229 | .0278 | 0.0463 | 2.6236 | .0134 |
| Synonymous | 1.5071 | .1368 | 0.25 | 1.1308 | .8166 | 0.0463 | 1.0267 | .4438 |
| Neutral missense | 1.0195 | .323 | 0.3704 | 1.0636 | .8954 | 0.0463 | 0.7881 | .7237 |
| Procoagulant genes (N = 27) | ||||||||
| ΔP variants | 0.9582 | .3075 | 0.0157 | 2.0983 | .1054 | 0.0157 | 2.0983 | .0934 |
| Synonymous | 1.5327 | .1326 | 0.0119 | 2.4547 | .0584 | 0.0119 | 2.4547 | .0575 |
| Neutral missense | 0.5990 | .6026 | 0.3228 | 1.6853 | .3315 | 0.0433 | 0.5990 | .9198 |
| Anticoagulant genes (N = 19) | ||||||||
| ΔP variants | 1.9988 | .0595 | 0.0354 | 1.9988 | .1680 | 0.0354 | 1.9988 | .1140 |
| Synonymous | 1.9414 | .1818 | 0.0354 | 2.0340 | .1359 | 0.0354 | 2.0340 | .0993 |
| Neutral missense | 1.2307 | .1931 | 0.0714 | 1.3959 | .4013 | 0.0354 | 1.2307 | .4541 |
| Glycolysis pathway (N = 68) | ||||||||
| ΔP variants | 0.0536 | .9563 | 0.035 | 1.0827 | .5804 | 0.0315 | 1.0827 | .5265 |
| Synonymous | 0.1035 | .9256 | 0.185 | 1.4843 | .309 | 0.0079 | 0.8554 | .7307 |
| Neutral missense | 0.3942 | .7607 | 0.169 | 1.8254 | .2089 | 0.0118 | 0.6315 | .7491 |
| Type . | RVTT-fixed test statistic (gnomAD cutoff = 0.05) . | RVTT-fixed Perm P value (gnomAD cutoff = 0.05) . | RVTT-variable selected MAF threshold (no cutoff) . | RVTT-variable test statistic (no cutoff) . | RVTT-variable Perm P value (no cutoff) . | RVTT-variable selected MAF threshold (cutoff = 0.05) . | RVTT-variable test statistic (cutoff = 0.05) . | RVTT-variable Perm P value (cutoff = 0.05) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complement system pathway (N = 27) | ||||||||
| ΔP variants | 2.4951 | .0168 | 0.0833 | 2.7229 | .0278 | 0.0463 | 2.6236 | .0134 |
| Synonymous | 1.5071 | .1368 | 0.25 | 1.1308 | .8166 | 0.0463 | 1.0267 | .4438 |
| Neutral missense | 1.0195 | .323 | 0.3704 | 1.0636 | .8954 | 0.0463 | 0.7881 | .7237 |
| Procoagulant genes (N = 27) | ||||||||
| ΔP variants | 0.9582 | .3075 | 0.0157 | 2.0983 | .1054 | 0.0157 | 2.0983 | .0934 |
| Synonymous | 1.5327 | .1326 | 0.0119 | 2.4547 | .0584 | 0.0119 | 2.4547 | .0575 |
| Neutral missense | 0.5990 | .6026 | 0.3228 | 1.6853 | .3315 | 0.0433 | 0.5990 | .9198 |
| Anticoagulant genes (N = 19) | ||||||||
| ΔP variants | 1.9988 | .0595 | 0.0354 | 1.9988 | .1680 | 0.0354 | 1.9988 | .1140 |
| Synonymous | 1.9414 | .1818 | 0.0354 | 2.0340 | .1359 | 0.0354 | 2.0340 | .0993 |
| Neutral missense | 1.2307 | .1931 | 0.0714 | 1.3959 | .4013 | 0.0354 | 1.2307 | .4541 |
| Glycolysis pathway (N = 68) | ||||||||
| ΔP variants | 0.0536 | .9563 | 0.035 | 1.0827 | .5804 | 0.0315 | 1.0827 | .5265 |
| Synonymous | 0.1035 | .9256 | 0.185 | 1.4843 | .309 | 0.0079 | 0.8554 | .7307 |
| Neutral missense | 0.3942 | .7607 | 0.169 | 1.8254 | .2089 | 0.0118 | 0.6315 | .7491 |
RVTT was applied to 3 gene sets: the complement system, the coagulation system, and the glycolysis pathway. For each gene set, ΔP, synonymous, and neutral missense variants were tested. Qualifying low-frequency variants were selected using 3 settings: (1) fixed threshold gnomAD MAF <0.05, (2) variable threshold with no cutoff, and (3) variable threshold with MAF cutoff = 0.05. Significant enrichment of low-frequency ΔP complement variants in PF patients when compared with control patients was observed under all 3 settings.
P values <.05 are in bold type.
The number of complement system variants is independently associated with PF
To determine whether the association of ΔP complement system variants with PF was independent of clinical and demographic parameters, we generated a multivariable logistic regression model incorporating age, sex, and SOFA score, a validated composite measure of illness severity in critically ill patients.36 After adjusting for these covariates, the number of ΔP variants per subject was independently associated with PF in the European PF cohort (odds ratio (OR), 2.61 per ΔP variant; 95% confidence interval, 1.29-6.10; P = .01) and the entire PF cohort (OR, 2.85 per ΔP variant; 95% confidence interval, 1.58-5.9; P = .002) (Table 4). This finding confirms the association found using RVTT and suggests that multiple ΔP variants in a single patient additively contribute to the development of infectious PF.
Multivariable logistic regression model of predictors of PF
| EUR only analysis (N = 111) . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | β . | SE . | OR (95% CI) . | P value . |
| ΔP variants | 0.96 | 0.39 | 2.61 (1.29-6.1)∗ | .01 |
| Sex | −1.58 | 0.93 | 0.21 (0.03-1.18) | .09 |
| Age | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.95 (0.91-0.99)† | .02 |
| SOFA score‡ | 0.67 | 0.16 | 1.96 (1.49-2.87)§ | <.0001 |
| EUR only analysis (N = 111) . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | β . | SE . | OR (95% CI) . | P value . |
| ΔP variants | 0.96 | 0.39 | 2.61 (1.29-6.1)∗ | .01 |
| Sex | −1.58 | 0.93 | 0.21 (0.03-1.18) | .09 |
| Age | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.95 (0.91-0.99)† | .02 |
| SOFA score‡ | 0.67 | 0.16 | 1.96 (1.49-2.87)§ | <.0001 |
| Entire study analysis (N = 124) . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | β . | SE . | OR (95% CI) . | P value . |
| ΔP variants | 1.05 | 0.33 | 2.85 (1.58-5.90)∗ | .002 |
| Sex | −1.02 | 0.81 | 0.36 (0.07-1.72) | .21 |
| Age | −0.06 | 0.02 | 0.94 (0.90-0.98)† | .005 |
| SOFA score‡ | 0.75 | 0.17 | 2.12 (1.59-3.16)§ | <.0001 |
| Entire study analysis (N = 124) . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | β . | SE . | OR (95% CI) . | P value . |
| ΔP variants | 1.05 | 0.33 | 2.85 (1.58-5.90)∗ | .002 |
| Sex | −1.02 | 0.81 | 0.36 (0.07-1.72) | .21 |
| Age | −0.06 | 0.02 | 0.94 (0.90-0.98)† | .005 |
| SOFA score‡ | 0.75 | 0.17 | 2.12 (1.59-3.16)§ | <.0001 |
CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio; SE, standard error.
Per ΔP variant.
Per year of age.
Composite measure comprised of: PaO2, FiO2, mechanical ventilation status, platelet count, Glasgow Coma Scale, total bilirubin level, mean arterial pressure, and creatinine level.
Per one point increase in SOFA score.
Functional characterization of CFD E69K
As a test case to assess the functional impact of PF–associated humoral complement system variants, we characterized a putatively benign variant, an E→K substitution at position 69 in complement factor D (CFD E69K). We chose this variant because residue 69 in CFD is highly conserved across mammalian species (Figure 2A), because the mutation results in a charge change near the catalytic triad (Figure 2B), and because the variant was identified in 2 unrelated PF patients (supplemental Table 4). We generated recombinant CFD WT, CFD E69K, and a catalytically inactive CFD variant (CFD HDS/AAA) (Figure 2C) and tested the ability of each to reconstitute alternative complement pathway activity in CFD-deficient serum. CFD E69K exhibited ∼50% catalytic function compared with CFD WT in a rabbit erythrocyte lysis assay (P < .0001) (Figure 2D). Consistent with these in vitro results, the baseline AH50 activity of one of the CFD E69K-positive patients 4 years after their acute illness was borderline low at 77% (normal range, 77%-159%). The partial LoF phenotype of CFD E69K parallels that of other previously characterized humoral ΔP variants in the PF cohort.40-44
Identification and functional characterization of CFD E69K. (A) Sequence alignment of complement factor D (CFD) showing conservation across diverse species of a negatively-charged residue, glutamic acid (E) or aspartic acid (D), at position 69 (arrowhead). Green shading denotes exact sequence conservation, red shading denotes conservation of amino acid charge. (B) Structural modeling of the catalytic triad of CFD WT (left) compared to CFD E69K (right) (Protein Data Bank: 2XWB). (C) Whole cell lysates from HEK-293T cells expressing CFD WT, CFD E69K (E69K), or catalytic-dead CFD (HDS/AAA), in which the catalytic triad residues histidine 66, aspartic acid 114 and serine 208 were replaced with alanines, were subjected to western blot analysis to quantify the total expression of each variant in each cell line. Untransfected (UT) HEK-293T cells were used as a negative control for CFD expression. (D) Red blood cell lysis assay results for human CFD-deficient serum reconstituted with the indicated CFD variants. Data shown are representative results of at least 3 independent experiments.
Identification and functional characterization of CFD E69K. (A) Sequence alignment of complement factor D (CFD) showing conservation across diverse species of a negatively-charged residue, glutamic acid (E) or aspartic acid (D), at position 69 (arrowhead). Green shading denotes exact sequence conservation, red shading denotes conservation of amino acid charge. (B) Structural modeling of the catalytic triad of CFD WT (left) compared to CFD E69K (right) (Protein Data Bank: 2XWB). (C) Whole cell lysates from HEK-293T cells expressing CFD WT, CFD E69K (E69K), or catalytic-dead CFD (HDS/AAA), in which the catalytic triad residues histidine 66, aspartic acid 114 and serine 208 were replaced with alanines, were subjected to western blot analysis to quantify the total expression of each variant in each cell line. Untransfected (UT) HEK-293T cells were used as a negative control for CFD expression. (D) Red blood cell lysis assay results for human CFD-deficient serum reconstituted with the indicated CFD variants. Data shown are representative results of at least 3 independent experiments.
Functional characterization of missense variants in complement receptors 3 and 4
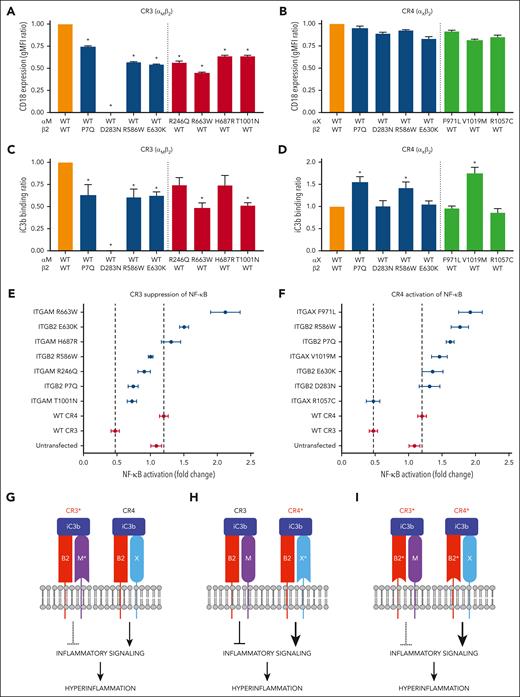
Of the 19 unique, nonsynonymous opsonophagocytic subpathway variants identified in the PF cohort, 14 (73.7%) were in genes encoding CR3 and CR4 subunits (supplemental Table 5; supplemental Figure 4). Of these 14, 11 (78.6%) were missense mutations and 7 were ΔP variants. One of the missense variants, ITGB2 R586W, had previously been characterized in vitro as a partial LoF mutant,45 whereas 4 of the missense variants (ITGAM H687R, ITGAM T1001N, ITGAX V1019M, and ITGB2 P7Q) were predicted in silico to be neutral. Given the dearth of functional data on these variants and given the critical role of CR3 and CR4 in regulating the inflammatory response to infection, we undertook to characterize all 11 unique ITGB2, ITGAM, and ITGAX missense variants from the PF cohort with respect to 3 parameters that impact receptor function: cell surface expression, ligand binding affinity, and activation of intracellular signaling.
We cloned the variants (supplemental Figure 5) and coexpressed each, together with its WT dimerization partner, in HEK-293T cells. We then assessed total and cell surface expression of each variant. Although total expression of the variants was similar to that of their WT counterparts (supplemental Figure 6), cell-surface expression of the CR3 variants was significantly lower than that of WT CR3 (Figure 3A), whereas cell-surface expression of the CR4 variants was similar to that of WT CR4 (Figure 3B). Notably, the D283N variant in the shared β2 subunit resulted in complete loss of CR3 cell-surface expression without affecting surface expression of CR4.
Functional characterization PF-associated CR3/4 variants. (A-B) WT and variant complement receptors were cloned and expressed in HEK-293T cells, and surface expression levels of CR3 (A) and CR4 (B) were evaluated by flow cytometry for integrin β2 (ITGB2/CD18). WT CR3 and WT CR4 are depicted in orange. Receptors containing a variant integrin β2 subunit are depicted in blue, those with a variant integrin αM (ITGAM) subunit are depicted in red, and those with a variant integrin αX (ITGAX) subunit are depicted in green. (C-D) The ability of complement receptor-expressing cells to bind immobilized iC3b was assessed using a solid-phase functional assay. iC3b binding activity of WT and variant CR3 (C) and WT and variant CR4 (D) are shown. ∗P < .05 compared to WT/WT control. (E-F) TNFα-mediated activation of an NF-ĸB dual-luciferase reporter in cells expressing the indicated PF-associated CR3 (E) or CR4 variants (F) in the presence or absence of iC3b. Control HEK-293T cells not expressing CR3 or CR4 (Untransfected) and HEK-293T cells expressing WT CR3 or WT CR4 were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Data are shown as the mean fluorescence intensity ratio of the iC3b-plus condition to the iC3b-minus condition. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. (G) PF-associated variants in ITGAM (M∗) reduce the ability of variant CR3 (CR3∗) to suppress inflammatory signaling. (H) PF-associated variants in ITGAX (X∗) enhance the ability of variant CR4 (CR4∗) to activate inflammatory signaling. (I) PF-associated variants in the shared subunit ITGB2 (B2∗) simultaneously decrease suppression of inflammatory signaling by CR3∗ and increase activation of inflammatory signaling by CR4∗. ITGAM H687R, ITGAM T1001N, ITGAX V1019M, and ITGB2 P7Q were predicted in silico to be neutral. Shown in panels A-F are representative results of at least 3 independent experiments.
Functional characterization PF-associated CR3/4 variants. (A-B) WT and variant complement receptors were cloned and expressed in HEK-293T cells, and surface expression levels of CR3 (A) and CR4 (B) were evaluated by flow cytometry for integrin β2 (ITGB2/CD18). WT CR3 and WT CR4 are depicted in orange. Receptors containing a variant integrin β2 subunit are depicted in blue, those with a variant integrin αM (ITGAM) subunit are depicted in red, and those with a variant integrin αX (ITGAX) subunit are depicted in green. (C-D) The ability of complement receptor-expressing cells to bind immobilized iC3b was assessed using a solid-phase functional assay. iC3b binding activity of WT and variant CR3 (C) and WT and variant CR4 (D) are shown. ∗P < .05 compared to WT/WT control. (E-F) TNFα-mediated activation of an NF-ĸB dual-luciferase reporter in cells expressing the indicated PF-associated CR3 (E) or CR4 variants (F) in the presence or absence of iC3b. Control HEK-293T cells not expressing CR3 or CR4 (Untransfected) and HEK-293T cells expressing WT CR3 or WT CR4 were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Data are shown as the mean fluorescence intensity ratio of the iC3b-plus condition to the iC3b-minus condition. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. (G) PF-associated variants in ITGAM (M∗) reduce the ability of variant CR3 (CR3∗) to suppress inflammatory signaling. (H) PF-associated variants in ITGAX (X∗) enhance the ability of variant CR4 (CR4∗) to activate inflammatory signaling. (I) PF-associated variants in the shared subunit ITGB2 (B2∗) simultaneously decrease suppression of inflammatory signaling by CR3∗ and increase activation of inflammatory signaling by CR4∗. ITGAM H687R, ITGAM T1001N, ITGAX V1019M, and ITGB2 P7Q were predicted in silico to be neutral. Shown in panels A-F are representative results of at least 3 independent experiments.
We next assessed binding of the receptor variants to iC3b. Of the 8 CR3 variants, 6 (75%) demonstrated reduced binding to iC3b compared to WT CR3 (Figure 3C). The binding of each CR3 variant to iC3b was proportional to its surface expression, suggesting that the observed decrease in iC3b binding is a consequence of reduced receptor availability rather than decreased affinity for iC3b. By contrast, 4 of 7 (57.1%) CR4 variants bound iC3b at similar levels to that of WT CR4 and, unexpectedly, 3 of 7 (42.9%) demonstrated increased iC3b binding (Figure 3D). Given that the CR4 variants all expressed at equivalent or slightly reduced cell surface levels compared to WT CR4, the increased ligand binding likely reflects an increased affinity of those variants for iC3b.
Finally, we used a dual-luciferase reporter assay to assess the impact of the CR3 and CR4 variants on TNFα-mediated activation of the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-κB. Relative to untransfected cells, NF-κB activation was suppressed by expression of WT CR3 (Figure 3E) and enhanced by expression of WT CR4 (Figure 3F). All 7 expressed CR3 variants and 6 of the 7 CR4 variants were associated with increased NF-κB activation compared with WT CR3 and WT CR4, respectively. Taken together, these findings suggest that PF-associated CR3 and CR4 variants result in relative loss of anti-inflammatory CR3 function and relative gain of proinflammatory CR4 function (Figure 3G-I).
Discussion
PF is an extreme phenotype of sepsis characterized by overwhelming thrombotic DIC. Crucially, PF patients are a homogenous population with a well-defined syndrome and highly predictable clinical course that remains consistent across ancestries, pathogens, and care settings.2,46,47 PF patients are also younger and have fewer comorbidities than typical sepsis patients, making it more likely that inherited factors drive the disease process. These features lend PF to germline genetic analysis in a way that avoids many of the limitations that have confounded sepsis research.48-51 To identify genetic contributions to severe sepsis, we developed RVTT, a novel statistical method for pathway–based mutational burden testing of rare disease datasets. We eschewed an unbiased approach in favor of leveraging decades of research on the role of complement in immunity, inflammation, and sepsis. RVTT assumes a directionally consistent biological effect among variants occurring in a single pathway and considers these variants collectively, thereby substantially increasing statistical power. Using this novel methodology, we identified an association between low-frequency, putatively deleterious coding variants in the complement system and the development of PF. By contrast, analytical controls evaluating for genomic inflation, including an examination of synonymous variants, other biological pathways, and missense variants predicted to be neutral, all revealed no enrichment in the PF cohort relative to unselected patients with sepsis. The results we obtained through RVTT were further supported by multivariable regression analysis showing an additive increase in risk of PF with each additional complement system variant after controlling for sex, age, and clinical acuity.
Based on our in silico modeling and the functional studies that we and others have performed, at least 23 of the 49 unique PF–associated humoral complement variants we identified are likely hypomorphic mutants. That these mutants retain some function may be key to their role in PF. Severity of meningococcal disease correlates with levels of circulating endotoxin,52,53 which are increased by complement-mediated bacterial lysis.16,18 This could explain the lower mortality associated with meningococcal disease in persons with complete deficiencies of terminal complement components compared to complement-sufficient individuals.54,55 We hypothesize that partial loss of humoral complement function results in suboptimal killing of bacteria while still allowing for significant complement-mediated thrombo-inflammation to occur, resulting in PF (supplemental Figure 7).
The novel variants in CR3 and CR4 we identified in patients with PF result in relative loss of CR3 function and relative gain of CR4 function. CR3 and CR4 have previously been implicated in regulation of the inflammatory response to complement activation in mice. Jawhara et al utilized a murine model of sepsis to demonstrate that monocytes and macrophages promote deleterious proinflammatory functions via CR4 signaling, whereas CR3 exerts significant anti-inflammatory effects.20 The investigators also showed that deletion of CR4 (ITGAX−/−), but not CR3 (ITGAM−/−), confers significant protection against endotoxin-induced mortality.20 These results are consistent with orthogonal findings reported by several groups that CR3 mediates macrophage efflux from sites of inflammation and that loss of CR3 is associated with autoimmunity.27,56-59 Despite a wealth of animal studies pointing to a key role for these receptors in thrombo-inflammation, CR3 and CR4 have not previously been implicated in the human immune response during sepsis.
The PF–associated CR3 variants we identified all result in decreased CR3 surface expression and a corresponding decline in iC3b binding and CR3-mediated suppression of NF-κB activity, a proxy for in vivo inflammatory signaling. This suggests that PF–associated CR3 mutations impair receptor expression, with receptor binding affinity for iC3b left largely intact. By contrast, the PF–associated CR4 mutations we identified do not affect receptor expression. Rather, the mutations appear to enhance CR4 binding to iC3b and/or signaling downstream of CR4. This finding is particularly remarkable given our identification of several single amino acid substitutions in the shared β2 subunit that simultaneously enhance CR4 signaling and reduce CR3 signaling. No cases were identified in which PF-associated variants resulted in a gain of CR3 function relative to CR4. Taken together, our data support a model in which an imbalance between anti-inflammatory signaling through CR3 and proinflammatory signaling through CR4 contributes to the hyperinflammation that is a hallmark of PF.
Our findings could have significant therapeutic implications. Recent structural studies have revealed that, despite sharing considerable sequence identity, CR3 and CR4 each bind iC3b via distinct, non-overlapping mechanisms.24,60-62 Although the αI portion of the CR3 headpiece engages the thioester domain and macroglobulin domains MG1-MG2 and MG6-MG7 of iC3b, CR4 has its major iC3b binding site at MG3-MG4 and a minor binding site near the C345c domain. Furthermore, the key CR3 αI domain residues necessary for binding to iC3b are completely distinct from those at the equivalent positions in CR4.60 These observations present the intriguing possibility that selective CR4 blockade is pharmacologically feasible and could be used to dampen proinflammatory signaling in sepsis. The converse approach, in which CR3 is selectively activated, could also present a therapeutic opportunity in severe sepsis. Indeed, a recent report demonstrated that biased activation of CR3 with a reagent that greatly increases CR3 binding to iC3b can protect against pathologic inflammation and death in a murine cecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis.22
Our study has some important limitations. Firstly, we focused on positive effectors of complement but other genetic loci are likely also involved in the development of PF, which, like sepsis more broadly, is almost certainly a polygenic condition.63 Secondly, our experiments to functionally characterize the PF-associated CR3 and CR4 mutants were carried out in isogenic cell lines that do not normally engage in CR3 and CR4 signaling. To fully define the effects of PF–associated integrin mutations on complement signaling, it will be necessary to generate genetically engineered mouse models that harbor endogenous ITGAM, ITGAX, and ITGB2 mutations. Finally, when comparing 2 cohorts that undergo sequencing on distinct platforms, there is always the possibility that technical artifacts can influence results. We attempted to mitigate this potential issue through rigorous quality control prior to analysis.
Taken together, our data are consistent with a model in which genetically-encoded defects in the complement system contribute to the maladaptive hyperinflammatory response that defines PF and its associated coagulopathy. Further studies will be required to define the role of inherited complement system defects in the broader population of patients with sepsis.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the patients who participated in this study and their families, as well as to George Cannelos, Robert Mayer, Ann LaCasce, and James DiCaprio of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute for their support. The authors also thank members of the Flaumenhaft, Bendapudi, and Losman laboratories for technical assistance.
P.K.B. was supported by Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and the National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (R21 HL153655 and K08 HL136840). S.N. gratefully acknowledges support from the Australian Parkinson’s Mission through funding from the Australian government. J.-A.L. was supported by the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The Boston Medical Center Clinical Data Warehouse for Research, the Partners Research Patient Data Registry, and the BIDMC Clinical Data Repository supported the case-finding strategy and provided data extracts for this research.
Authorship
Contribution: P.K.B. and J.-A.L. conceived of the project, analyzed the data, and assembled and wrote the manuscript; S.S. and S.N. developed the novel rare variant trend test, analyzed the sequencing data, and assisted in drafting the manuscript; P.K.B., J.R., M.C., B.P., J. Krier, E.F., J.C.H., O.P., and V.N. developed and operationalized the specimen collection system; J. Knight supervised the sequencing of the PF samples and aided in bioinformatic analysis; S.N., O.S., A.T.-P., and M.B. performed sequencing quality control and statistical analyses, which was overseen by S.S.; P.K.B., R.M., W.H.D., S.R., and J.-A.L. designed experiments and analyzed data; P.K.B. and J.R. developed and conducted the in vitro assays and analyzed the data; B.R., J.K.O., and R.P. generated the stable cell lines; A.R., J.K.O., R.P., L.T., and L.C. conducted the in vitro assays and analyzed the data; M.Y. performed the in silico structural modeling; and all of the authors read and helped to edit the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for A.R. is Immunology Division, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Melbourne, Australia.
The current affiliation for B.R. is Institut de Génétique Moléculaire de Montpellier, Montpellier, France.
The current affiliation for M.C. is Division of Intramural Research, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD.
The current affiliation for A.T.-P. is Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, Dresden, Germany.
Correspondence: Julie-Aurore Losman, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 450 Brookline Ave, Mayer 422, Boston, MA 02215; email: julieaurore_losman@dfci.harvard.edu.
References
Author notes
RVTT code is available through https://github.com/snz20/RVTT.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal