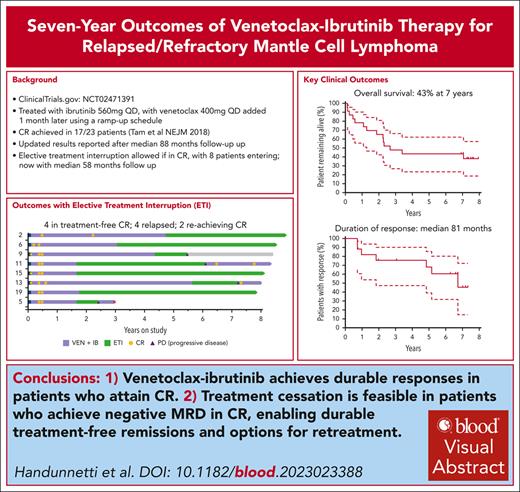
Key Points
In relapsed MCL, venetoclax-ibrutinib achieves 7-year PFS of 30%, TTF of 39%, OS of 43%, and durable remissions in 10 of 17 responders.
ETI in MRD-negative CR allows for durable treatment-free remissions, and retreatment can be effective after relapse.
Visual Abstract
In the phase 2 clinical trial (AIM) of venetoclax-ibrutinib, 24 patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL; 23 with relapsed/refractory [R/R] disease) received ibrutinib 560 mg and venetoclax 400 mg both once daily. High complete remission (CR) and measurable residual disease negative (MRD-negative) CR rates were previously reported. With median survivor follow-up now exceeding 7 years, we report long-term results. Treatment was initially continuous, with elective treatment interruption (ETI) allowed after protocol amendment for patients in MRD-negative CR. For R/R MCL, the estimated 7-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 30% (95% confidence interval [CI], 14-49; median, 28 months; 95% CI, 13-82) and overall survival (OS) was 43% (95% CI, 23-62; median, 32 months; 95% CI, 15 to not evaluable). Eight patients in MRD-negative CR entered ETI for a median of 58 months (95% CI, 37-79), with 4 experiencing disease recurrence. Two of 3 reattained CR on retreatment. Time-to-treatment failure (TTF), which excluded progression in ETI for those reattaining response, was 39% overall and 68% at 7 years for responders. Beyond 56 weeks, grade ≥3 and serious adverse events were uncommon. Newly emergent or increasing cardiovascular toxicity were not observed beyond 56 weeks. We demonstrate long-term durable responses and acceptable toxicity profile of venetoclax-ibrutinib in R/R MCL and show feasibility of treatment interruption while maintaining ongoing disease control. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02471391.
Introduction
In patients with relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma (R/R MCL), clinical trials over the last decade have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of novel targeted therapies1-4 and substantially improved outcomes in this essentially incurable disease.5 The first-in-class Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi), ibrutinib, was approved as continuous monotherapy in R/R MCL with an overall response rate (ORR) of 77%, complete response rate (CRR) of 23%, and median progression-free survival (PFS) of 15.6 months.1 The second-generation BTKis acalabrutinib and zanubrutinib were subsequently approved based on high response rates and favorable PFS in single-arm studies.2,3 The BH3-mimetic venetoclax also has single-agent activity in R/R MCL, with an ORR of 75%, CRR 21%, and median PFS 11.3 months,4 with a 40% ORR in a retrospective study.6 However, durable responses in R/R MCL remain elusive, with disease progression being the most common cause of death.7
Based on preclinical synergy in MCL8-10 and nonoverlapping toxicities, we conducted a phase 2 single-center study of combination venetoclax-ibrutinib (AIM Study).11 When first reported with median follow-up of 16 months, the CRR based on computed tomography scanning at 16 weeks (primary end point) was 42%, significantly higher than the historical 9% CRR observed with ibrutinib at this time point.11 By [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–positron emission tomography (PET) scanning, the CRR was 60% at week 16 and 71% overall. Remissions were deep, with measurable residual disease (MRD) clearance by flow cytometry attained in 67% of patients and by allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction in 38%,11 associated with improved immunological status.12
Now, with a median survivor follow-up of 88 months, we report long-term outcomes, evaluating durability of responses, long-term safety, and an exploratory analysis of elective treatment interruption (ETI) in select patients.
Study design
Study design, eligibility, study end points, and assessments have been previously published.11 In brief, we conducted an investigator-initiated, open-label, single-group, phase 2 trial of ibrutinib 560 mg daily plus venetoclax 400 mg daily in 24 patients with MCL. Patients with R/R MCL and those unsuitable for frontline treatment with chemo-immunotherapy were eligible. In the original protocol version, treatment was continuous until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Prompted by emerging data in chronic lymphocytic leukemia for treatment-free remissions with venetoclax-based regimens,13 a protocol amendment permitted patients in confirmed MRD-negative CR after a minimum 56-week treatment to enter ETI with stringent per protocol surveillance for disease progression (supplemental Data, available on the Blood website). Disease recrudescence permitting reintroduction of study treatment was defined as either unequivocal detection of MRD on blood or bone marrow (BM) on 2 consecutive occasions at least 2 weeks apart or radiological progression.
In patients with R/R MCL, as well as standard time-to-event analyses for PFS, overall survival (OS), and duration of response, efficacy was also evaluated per protocol by a modified PFS that excluded progression events in patients on ETI (supplemental Data), thereby defining time-to-treatment failure (TTF) as an exploratory aim. All patients in the study were evaluated for safety. Disease response used computed tomography and FDG-PET using the Deauville scale,14,15 BM examination, and MRD testing in peripheral blood and BM using 8-color flow cytometry with a minimum sensitivity of 10–3 to 10–4, as previously detailed (supplemental Data).11 For patients followed up for survival events off study, data were collected by review of medical records.
This trial was conducted with approval from the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Human Research Ethics Committee. It adhered to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice Guidelines of the International Conference on Harmonisation. Time-to-event estimates were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method with confidence intervals (CIs) calculated using the log-log transformation. For this analysis, the first author analyzed the data using IBM SPSS Statistics Version 28.0.1.1(14). The data cutoff date was 15 September 2023. All authors had access to primary data.
Results and discussion
Between July 2015 and September 2016, a total of 24 patients were recruited. Twenty-three patients had R/R MCL with median 2 prior lines of therapy (range, 1-6). The median age was 68 years (range, 47-81). TP53 aberrations were present in 48% of cases, and 26% had an NF-κB pathway mutation.11 Median follow-up was 88 months (range, 1.6-95). The sole treatment-naive case is detailed in the supplemental Data.
Long-term outcomes in R/R MCL
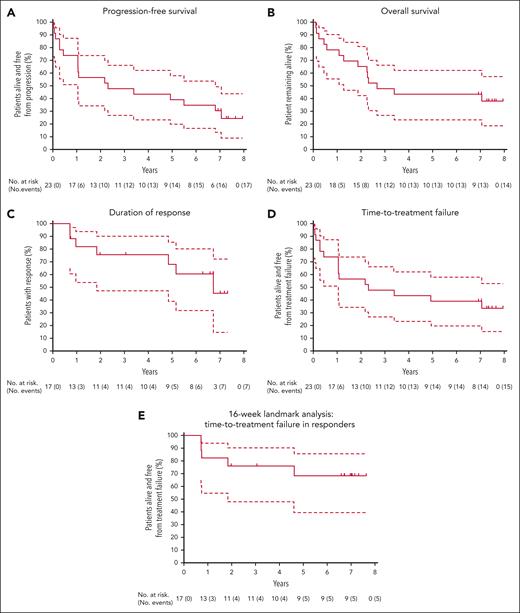
The median PFS (Figure 1A) was 28 months (95% CI, 13-82), and estimated 7-year PFS was 30% (95% CI, 14-49). The median OS (Figure 1B) was 32 months (95% CI, 15 to not evaluable [NE]) and estimated 7-year OS was 43% (95% CI, 23-62). Supplemental Table 1 details all time-to-event analyses of outcomes. Seventeen patients achieved a CR, assessed with FDG-PET, at a median of 4 months (range, 4-24). The median duration of response was 81 months (95% CI, 22 to NE; Figure 1C). Of these 17 patients, 4 died in remission on therapy, 3 had disease progression on continuous therapy, 2 remain in CR on continuous therapy, and 8 undertook ETI.
Key survival outcomes for patients with R/R MCL. Kaplan-Meier plots, with 95% CIs (dashed lines) for PFS (A), OS (B), DOR (C), TTF (D), and 16-week landmark analysis (E) for TTF in responders. Tick marks represent censoring at last follow-up before data cutoff for patients without an event. Note: Patient 2 could not be stringently evaluated by PET until removal of a ureteric stent near site of original disease, with CR by CT/PET formally documented after 2 years on study. For landmark analysis (E), patient 2 was included as a responder at week 16 to reflect the overall clinical assessment at the time. CT, computed tomography.
Key survival outcomes for patients with R/R MCL. Kaplan-Meier plots, with 95% CIs (dashed lines) for PFS (A), OS (B), DOR (C), TTF (D), and 16-week landmark analysis (E) for TTF in responders. Tick marks represent censoring at last follow-up before data cutoff for patients without an event. Note: Patient 2 could not be stringently evaluated by PET until removal of a ureteric stent near site of original disease, with CR by CT/PET formally documented after 2 years on study. For landmark analysis (E), patient 2 was included as a responder at week 16 to reflect the overall clinical assessment at the time. CT, computed tomography.
Figure 2 details the clinical course for all patients with R/R MCL, highlighting the 8 patients who entered ETI (baseline characteristics and pre-ETI treatment toxicity/tolerability are noted in supplemental Tables 2 and 3, respectively). The median time on study treatment before commencing ETI was 23 months (range, 18-61). The median time in remission on ETI was 58 months (95% CI, 37-79). Four patients on ETI had progressive disease (PD) events (detailed in supplemental Table 4). Three resumed venetoclax-ibrutinib treatment, with 2 rapidly reachieving CR (ongoing at 8 and 23 months) and 1 progressing.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax treatment, ETI, disease response, and survival for 23 patients with R/R MCL. Individual patient data are shown in lanes, ordered by duration on study, with key molecular variants detected in corresponding MCL biopsy from each patient at baseline shown to left of the graph. The full molecular data on each MCL sample have previously been fully reported.15 A black square shows the presence of a pathogenic variant for the indicated genes; for TP53 this includes deletions. Arrows at the end of each lane indicate ongoing treatment on study or ongoing surveillance in ETI. Patient 8 elected to come off study treatment while in MRD-negative CR but declined to enter ETI due the logistic constraints of the surveillance schedule. CR, complete response documented by PET; MRD Neg, minimal residual disease negative on BM by flow cytometry, PD; IB, ibrutinib; IB+V, ibrutinib plus venetoclax; PR, partial response with PET; VEN, venetoclax.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax treatment, ETI, disease response, and survival for 23 patients with R/R MCL. Individual patient data are shown in lanes, ordered by duration on study, with key molecular variants detected in corresponding MCL biopsy from each patient at baseline shown to left of the graph. The full molecular data on each MCL sample have previously been fully reported.15 A black square shows the presence of a pathogenic variant for the indicated genes; for TP53 this includes deletions. Arrows at the end of each lane indicate ongoing treatment on study or ongoing surveillance in ETI. Patient 8 elected to come off study treatment while in MRD-negative CR but declined to enter ETI due the logistic constraints of the surveillance schedule. CR, complete response documented by PET; MRD Neg, minimal residual disease negative on BM by flow cytometry, PD; IB, ibrutinib; IB+V, ibrutinib plus venetoclax; PR, partial response with PET; VEN, venetoclax.
TTF for venetoclax-ibrutinib was 39% at 7 years overall (95% CI, 20-58; median, 28 months; 95% CI, 13 to NE; Figure 1D). Using a landmark of 16 weeks, TTF in responders was 68% at 7 years (95% CI, 39-86; Figure 1E).
For the 11 patients with TP53 aberrant MCL, median PFS was 5 months (supplemental Figure 1). Response was achieved in 5 of these patients, with durations of 9 and 37 months and ongoing after 84, 86, and 87 months (2 after recommencement of venetoclax-ibrutinib after relapse during ETI). No responses were observed in the 4 patients whose MCL had both TP53 and SMARCA4 mutations, as previously reported.16
Safety
Overall, 15 of 24 patients have died (supplemental Table 5), 9 due to PD. Two deaths were infection related and occurred in patients with active disease. Notably, non-MCL deaths occurred during ongoing CR in 4 patients: 3 due to secondary malignancies (metastatic small cell lung cancer, therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome that transformed to AML, and glioblastoma multiforme) and 1 due to cardiac failure. The patient with therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome was aged 73 years and had received R-CHOP as his only prior therapy. In the primary analysis, we reported 2 incidences of new onset atrial fibrillation and 2 incidences of cardiac failure, both in patients with a history of anthracycline-related cardiomyopathy, with 1 being fatal.11
Safety beyond 56 weeks was evaluated, specifically for grade ≥3 events and serious adverse events (Table 1). No new cases of cardiac toxicity were observed. Grade 3 diarrhea occurred in 3 incidences, with 2 being serious adverse events. Significant lung infection occurred in 2 patients, including 1 case of cryptococcal infection (postprogression). There was a total of 4 second cancers: the above 3 fatal cases and 1 cutaneous nonmelanoma neoplasm.
Adverse effects beyond 56 weeks of study treatment: grade 3 or higher events and SAEs
| Event, grade ≥3 . | Event frequency (N = 17) (%) . |
|---|---|
| Neutropenia | 1 (6) |
| Hypertension | 1 (6) |
| Cutaneous neoplasm | 1 (6) |
| Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome | 1 (6)∗ |
| Glioblastoma multiforme | 1 (6) |
| Metastatic small cell lung cancer | 1 (6) |
| Febrile neutropenia | 1 (6)∗ |
| Sinusitis | 1 (6)∗ |
| Urosepsis | 1 (6)∗ |
| Infectious enterocolitis | 1 (6)∗ |
| Lung infection | 2 (12)∗ |
| Diarrhea | 3 (17)† |
| Event, grade ≥3 . | Event frequency (N = 17) (%) . |
|---|---|
| Neutropenia | 1 (6) |
| Hypertension | 1 (6) |
| Cutaneous neoplasm | 1 (6) |
| Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome | 1 (6)∗ |
| Glioblastoma multiforme | 1 (6) |
| Metastatic small cell lung cancer | 1 (6) |
| Febrile neutropenia | 1 (6)∗ |
| Sinusitis | 1 (6)∗ |
| Urosepsis | 1 (6)∗ |
| Infectious enterocolitis | 1 (6)∗ |
| Lung infection | 2 (12)∗ |
| Diarrhea | 3 (17)† |
SAEs, serious adverse events.
These events were SAEs.
Two of the events were SAEs.
Now, with >7 years of follow-up, these data indicate that venetoclax-ibrutinib provides long-term benefit for some patients with R/R MCL. Acknowledging the limitations of crosstrial comparisons, reference to other single-arm studies suggests that the median PFS of 28 months and median OS of 32 months observed with venetoclax-ibrutinib surpasses that achievable with either agent as monotherapy in the R/R setting.1,4 It also appears superior to the survival outcomes when using sequential ibrutinib and venetoclax, for which Eyre et al17 reported a median PFS of 3.2 month and OS 9.4 months in patients treated with venetoclax, with PD after a median 4.8 months of exposure duration to ibrutinib.17 Following from our study, the phase 3 multinational, randomized, double-blind SYMPATICO study18 has demonstrated a superior PFS (31.9 vs 22.1 months) and time to next treatment (median, not reached vs 35.4 months) in the ibrutinib plus venetoclax arm compared with ibrutinib plus placebo in patients with R/R MCL. Long-term outcomes from this study are awaited.
Other combinations have also been investigated in R/R MCL, and these data are summarized for context in supplemental Table 6.19-24 In the phase ½ OASIS study evaluating ibrutinib, venetoclax, and obinutuzumab, CRR and ORR similar to this trial were reported, whereas the rate of molecular MRD negativity after 12 weeks was 71.5%, higher than what we observed.19 Treatment was continuous, and the 4-year PFS and OS estimates were both 50%.19 Other ibrutinib containing regimens have been reported, with CRRs of 37% to 56%, all with immature follow-up and 2-year PFS estimates of 59.4% to median 16 months, and 2-year OS estimates of 60.6% to median 22 months.20,22
Other venetoclax containing combinations have also been evaluated in front line and patients with R/R MCL. In treatment-naive MCL, a phase 1 study combining venetoclax, lenalidomide, and rituximab showed high ORR of 96% and CRR of 86%, together with high levels of undetectable MRD without occurrence of dose-limiting toxicities.23 In R/R MCL, a phase 2 study used umbralisib, ublituximab, and venetoclax and demonstrated, similar to our study, the capacity to stop therapy in CR.24 Awaited are results from further studies, including the ENRICH study evaluating rituximab-ibrutinib vs rituximab-chemotherapy in untreated MCL (ISRCTN11038174) and OASIS-II (NCT04802590).
Here, we have provided, to our knowledge, the first exploration of ETI in patients treated with venetoclax-ibrutinib achieving MRD-negative CR, with a median duration on ETI of 58 months. Although the number of patients electing to enter ETI in this study is small, the data establish the proof-of-principle for durable disease control with ETI in deep remission and that patients could respond rapidly to retreatment after PD on ETI. ETI is feasible in this subset of patients but cannot be recommended at this time without formal prospective validation. ETI could also be applicable for patients treated with similar combinations, such as ibrutinib, venetoclax, and obinutuzumab, and potentially other BTKi/BH3-mimetic combinations. We are now exploring 2 limited duration targeted-agent combination regimens in response-adapted treatment of R/R MCL in the AIM2 clinical trial (NCT05864742).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients who participated in this study and their families, referring physicians, study coordinators, Piers Blombery and the Peter MacCallum Molecular Pathology Laboratory, and support staff at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre and Royal Melbourne Hospital.
This study was supported by Janssen, AbbVie, the Victorian Cancer Agency, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (M.A.A. [1177718] and A.W.R. [1174902; 2011139]), the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (S.-J.D. and M.A.D.), and the Peter MacCallum Foundation.
Authorship
Contribution: S.M.H., J.F.S., A.W.R., and C.S.T. contributed to conception and design of the manuscript; patient care and data collection was provided by S.M.H., M.A.A., K.B., P.A.T., G.B., J.D.I., J.F.S, A.W.R., and C.S.T.; analysis and interpretation of the data was performed by S.M.H., R.J.H., M.B., and C.S.T.; S.M.H. wrote the first draft; S.M.H., M.A.A., J.F.S., A.W.R., and C.S.T. supervised the study; and all authors reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.M.H. reports honoraria from BeiGene, AstraZeneca, Janssen, and Roche; and travel grant from AbbVie. M.A.A. reports honoraria from Roche, Takeda, Novartis, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Janssen, and AbbVie; and is a current employee of the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, which received milestone and royalty payments related to venetoclax that is shared with employees. P.A.T. reports research funding and honoraria (advisory board and speaker) from AbbVie and Adaptive Biotechnologies; honoraria (advisory board and speaker) from AstraZeneca and Janssen; honoraria (advisory board) from BeiGene, Genentech, Genmab, and Lilly; honoraria (speaker) from Merck; and research funding and honoraria (advisory board) from Pharmacyclics. R.J.H. reports research funding from Siemens Healthineers; and is a shareholder of Telix Radiopharmaceuticals, PreMIT Pty Ltd, and Precision Molecular Imaging and Theranostics Pty Ltd. S.L. reports consultancy fees from EUSA Pharma; and honoraria from A. Menarini Australia Pty Ltd, Mundipharma Pty Ltd, and Takeda. R.K. reports research funding from CRISPR Therapeutics. D.R. reports honoraria and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Takeda, Novartis, and Amgen; and honoraria from Merck Sharp & Dohme. M.D. reports research funding and honoraria (advisory board) from AbbVie; speaker’s honoraria from AstraZeneca; research funding from Bayer; honoraria (advisory board and speaker) from BeiGene; research funding and honoraria (advisory board and speaker) from Gilead/Kite, Janssen, and Roche; and honoraria (advisory board and speaker) from Lilly/Loxo and Novartis. J.F.S. reports honoraria from and membership on an entity's board of directors or advisory committees in Gilead, BMS, Janssen, and AstraZeneca; membership on an entity’s board of directors or advisory committees in Genor Biopharma; consultancy fees from TG Therapeutics; consultancy fees, honoraria, research funding, and speakers bureau fees from and membership on an entity's board of directors or advisory committees in F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd; consultancy, research funding, and speakers bureau fees from Celgene; honoraria, research funding, speakers bureau fees from and membership on an entity’s board of directors or advisory committees in AbbVie. A.W.R. reports being an inventor on a patent related to venetoclax; employee of Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, which received milestone and royalty income related to venetoclax that is shared with employees; research funding for this research from AbbVie and Janssen; and research funding for past research from BeiGene. C.S.T. reports honoraria from LOXO and AstraZeneca; and honoraria and research funding from BeiGene, AbbVie, and Janssen. The remaning authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Sasanka M. Handunnetti, Department of Clinical Haematology, Princess Alexandra Hospital, 199 Ispwich Rd, Woolloongabba, Brisbane 4102, Australia; email: sasanka.handunnetti@health.qld.gov.au; and Mary Ann Anderson, Department of Clinical Haematology, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre and Royal Melbourne Hospital, 305 Grattan St, Melbourne 3000, Australia; email: maryann.anderson2@mh.org.au.
References
Author notes
Deidentified cohort data, which will be made available 3 months after the publication for a period of 5 years, are available upon request from corresponding author Mary Ann Anderson (maryann.anderson2@mh.org.au).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal