Abstract
A common genetic risk factor for venous thrombosis among Caucasoid subpopulations is a polymorphism, nt G1691A, in blood coagulation factor V that replaces Arg506 with Gln and imparts resistance of factor Va to the anticoagulant, activated protein C. Haplotype analyses using six dimorphic sites in the factor V gene for 117 Caucasian subjects of Jewish, Arab, Austrian, and French origin who were homozygous for nt A1691 compared with 167 controls (nt G1691) support a single origin for this polymorphism. The nt G1691A mutation is estimated to have arisen circa 21,000 to 34,000 years ago, ie, after the evolutionary divergence of Africans from non-Africans and of Caucasoid from Mongoloid subpopulations.
THROMBOSIS AND BLOOD coagulation reactions play major roles in cardiovascular diseases. The pathogenesis of these diseases involves many inherited and acquired risk factors. Studies of hereditary thrombophilia, defined as an increased tendency towards venous thrombotic disease in relatively young adults (<45 years old), provide insights into factors that regulate thrombosis. The protein C (E.C. 3.4.21.69) pathway provides one of the body's major defense systems for regulation of thrombosis, and the anticoagulant plasma protease, activated protein C (APC), exerts its anticoagulant effect through destruction of the coagulation cofactors, factors Va and VIIIa, due to proteolysis of specific Arg-X bonds.1,2 The syndrome termed APC resistance3 has been found remarkably in ∼20% to 60% of cases of venous thrombosis,4-6 and three groups simultaneously reported that APC resistance in greater than 90% of cases is caused by a single point mutation in exon 10 of the factor V gene, nt G1691A, that causes replacement of Arg506 by Gln.7-9 This mutation renders activated factor V resistant to proteolytic downregulation by APC,8,10-12 because inactivation of factor Va is normally caused by sequential APC cleavages at Arg506 and Arg306.13 Defects in the anticoagulant plasma proteins, protein C, protein S, and antithrombin III, are identifiable in ∼10% to 15% of thrombophilic patients,14-17 and a combination of one of these genetic risk factors or hyperhomocysteinemia with APC resistance due to factor V (nt A1691) markedly increases the risk of venous thrombosis.18-21 Caucasoid subpopulations, including Europeans, Jews, Israeli Arabs, and Indians, possess this factor V polymorphism with allelic frequencies ranging from 1% to 8.5%4-9,22; in contrast, this polymorphism is apparently not found among African Blacks, Chinese, Japanese, native North and South American (Amerind), or Greenland Inuit subpopulations22-30 (Seligsohn and Zivelin, unpublished results). This study used haplotype analysis of the factor V gene to assess whether the point mutation in factor V, nt G1691A, likely has a single origin, ie, whether it exists due to a founder effect, or whether it might be a frequent recurrent mutation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
To make the respective polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products for each restriction analysis, the cleavage site, size of PCR product, and forward (F ) and reverse (R) primers were as follows: (1) nt327 (exon 2), 170 bp, F5′CCAGTTTGAATCTTTCTGTAAC3′ and R5′TTTAGATGCATGTGAATGCC3′; (2) nt495 (exon 4), 352 bp, F5′GCTATCCCAGATTTGAGAGTGG3′ and R5′GACAGAACTCCTGACCATTCC3′; (3) nt1470 (exon 9), 132 bp, F5′CGTGTTCAAAAATATGGCCAGC3′ and R5′CTAGTTGGATTCAGTAGAAGTG3′; (4) nt1806 (exon 11), 224 bp, F5′CTGTTCCATTGGTCTATGCG3′ and R5′GTACTCTGACTTACTGCTCATG3′; (5) nt2298 (exon 13), 824 bp, F5′GAACTTGGATGTTAACTTCC3′ and R5′GAGTAACAGATCACTAGGAGG3′; and (6) nt5380 (exon 16), 154 bp, F5′CTACATAAGGACAGCAACATGCaT3′ and R5′CGTGAAACTCATGGGATTT3′. The lower letter a in the forward primer for exon 16 indicates substitution of C to introduce a Nde I restriction site. The PCR products were generated in 25-μL reaction mixtures that contained 100 to 200 ng of genomic DNA, 100 pmol each of primers, 0.125 U of Taq polymerase (Appligene, Illkirch, France), 200 μmol/L of each dNTP, 1.5 mmol/L MgCl2 , and 1× PCR buffer. The reactions were subjected to 30 cycles of 45 seconds of denaturation at 94°C; 45 seconds of annealing at 50°C for exons 2, 13, and 16 and at 55°C for exons 4, 9, and 11; and 45 seconds of extension at 72°C for all exons except 13, which had an extension time of 90 seconds. The PCR products were submitted directly to restriction digestion without further purification. Digests using restriction enzymes (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA) were obtained according to the manufacturer's instructions with 5 U of enzyme in 10 μL of reaction mixture. The restriction digestion mixtures were run on 4% Metaphor gel (FMC Bioproducts, Rockland, ME) for exons 2, 9, and 16; 3% agarose gel for exons 4 and 11; and 2% agrose gel for exon 13. Blood samples were obtained using appropriate informed consent according to institutional protocols. Polymorphisms in exons 4, 13, and 16 were previously reported.7,8,31 Polymorphisms in exons 2, 9, and 11 were identified during sequence analysis of the factor V cDNA from different subjects using methods as follows. Buffy coats were collected from whole blood/acid citrate dextrose (ACD) and RNA was prepared using RNA-Stat 60 (TelTest “B”, Friendswood, TX). No attempt was made to exclude platelets because platelets contain RNA derived from the parent megakaryocytes. The RNA was reverse-transcribed from oligo-dT using the cDNA Cycle Kit (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA). The single-stranded cDNA was used as a template for PCR amplification using factor V-specific primers. The light chain-coding sequence was amplified using primers FV9 (5′TGAGATCATT CCAAAG GAAG3′) and FV14 (5′TTGAGGTCTTAAAGAGTCTC3′) in the presence of 1.5 mmol/L MgCl2 using 30 cycles of 2 minutes at 56°C, 3 minutes at 72°C, and 1 minute at 94°C. Amplification of the heavy chain-coding sequence was the same except that the reaction used FV2 (5′TGCCATT CTC CAGAGCTA GG3′) and FV13 (5′CAGGAAAGGAAGCATGTTCC3′) in the presence of 1.0 mmol/L MgCl2 . Amplification primers were removed from PCR products using Wizard PCR Prep columns (Promega, Madison, WI). Sequencing reactions incorporating 35S-dATP (Amersham, Arlington Heights, IL) were performed without further template purification using the fmol Cycle Sequencing Kit (Promega) and various internal primers derived from the factor V cDNA sequence.32
Polymorphisms in Factor V Gene From 167 Normal Subjects and 117 Subjects With Homozygous APC Resistance Based on ASRA
| Exon . | Nucleotide Polymorphism . | Distance From nt 1691 (kb) . | nt G1691 Normals (N = 334) A1 Allele Frequency (range) . | nt A1691 Homozygotes (N = 234) A1 Allele Frequency (range) . | P* . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | A 327 G | 32.7 | 0.72 (0.55-0.84) | 0.92 (0.88-0.95) | <10−6 |
| 4 | G 495 A | 11.6 | 0.81 (0.73-0.93) | 0.97 (0.92-1.0) | <10−6 |
| 9 | C 1470 T | 0.8 | 0.89 (0.76-0.97) | 1.0 | <10−5 |
| 11 | G 1806 A | 3.2 | 0.89 (0.76-0.97) | 1.0 | <10−5 |
| 13 | C 2298 T | 7.0 | 0.76 (0.65-0.88) | 0.99 (0.98-1.0) | <10−6 |
| 16 | A 5380 G | 20.0 | 0.70 (0.50-0.88) | 0.99 (0.98-1.0) | <10−6 |
| Exon . | Nucleotide Polymorphism . | Distance From nt 1691 (kb) . | nt G1691 Normals (N = 334) A1 Allele Frequency (range) . | nt A1691 Homozygotes (N = 234) A1 Allele Frequency (range) . | P* . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | A 327 G | 32.7 | 0.72 (0.55-0.84) | 0.92 (0.88-0.95) | <10−6 |
| 4 | G 495 A | 11.6 | 0.81 (0.73-0.93) | 0.97 (0.92-1.0) | <10−6 |
| 9 | C 1470 T | 0.8 | 0.89 (0.76-0.97) | 1.0 | <10−5 |
| 11 | G 1806 A | 3.2 | 0.89 (0.76-0.97) | 1.0 | <10−5 |
| 13 | C 2298 T | 7.0 | 0.76 (0.65-0.88) | 0.99 (0.98-1.0) | <10−6 |
| 16 | A 5380 G | 20.0 | 0.70 (0.50-0.88) | 0.99 (0.98-1.0) | <10−6 |
All polymorphisms are silent except for G5380A in exon 16 that predicts replacement of Val1736 by Met. Nucleotides are numbered according to cDNA numbering of Jenny et al33 and distances from nt 1691 to other nt are based on Cripe et al.31 The A1 allele contained the nucleotide more frequently found in the controls and corresponded to negative (−) genotypes for nt A327 and nt G495 and positive (+) genotypes for nt C1470, nt G1806, nt C2298, and nt A5380. APC-resistant subjects (nt A1691 homozygous; N = 117) were composed of the following subgroups: 30 Jews of various origins, 24 Israeli Arabs, 29 Austrians, 29 French, and 5 miscellaneous Caucasian subjects. Control subjects (nt G1691 homozygous; N = 167) were composed of six groups: 29 Austrians, 21 French, 28 Ashkenazi Jews, 30 North African Jews, 29 Iraqi Jews, and 30 Israeli Arabs.
P value based on χ2 analysis of comparing the observed genotypes of the APC-resistant homozygotes (nt A1691) for the indicated polymorphism to the expected calculated genotypes based on the normal subjects (nt G1691).
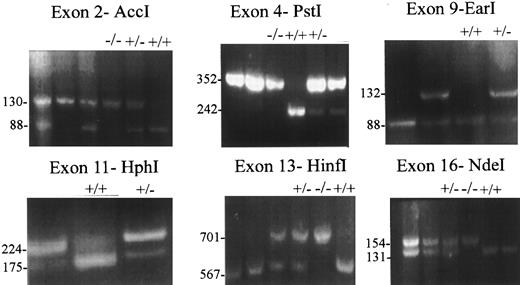
ASRA of six dimorphic sites in the factor V gene. Six restriction sites in exons 2, 4, 9, 11, 13, and 16 of the factor V gene were characterized using standard PCR techniques and the enzymes Acc I, Pst I, Ear I, Hph I, HinfI, and Nde I, as indicated (see the Materials and Methods). In each case, the site was scored positive (+) if it was cleaved and negative (−) if it was not. Examples of typical cleavage patterns, eg, +/+, +/−, and −/−, for individual subjects for each dimorphism are given. Numbers alongside the gel photos indicate the size (in basepairs) of the bands.
ASRA of six dimorphic sites in the factor V gene. Six restriction sites in exons 2, 4, 9, 11, 13, and 16 of the factor V gene were characterized using standard PCR techniques and the enzymes Acc I, Pst I, Ear I, Hph I, HinfI, and Nde I, as indicated (see the Materials and Methods). In each case, the site was scored positive (+) if it was cleaved and negative (−) if it was not. Examples of typical cleavage patterns, eg, +/+, +/−, and −/−, for individual subjects for each dimorphism are given. Numbers alongside the gel photos indicate the size (in basepairs) of the bands.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The factor V gene in chromosome 1q21-25 covers approximately 80 kb and contains 25 exons.31-35 Six polymorphic sites spanning 53 kb in exons 2, 4, 9, 11, 13, and 16 (Table 1) were chosen for allele-specific restriction analyses (ASRA; Fig 1) of DNA samples from 117 APC-resistant subjects homozygous for nt A1691 and 167 normal controls homozygous for nt G1691. The genotypes for nt1691 in exon 10, which defines APC resistance, were verified by PCR and restriction analysis.7 8 The average frequencies of the more common alleles, designated A1, for the six other dimorphisms ranged from 0.70 to 0.89, based on analysis of 334 alleles from 167 normal controls (Table 1). In sharp contrast, based on analysis of 234 alleles from the 117 subjects homozygous for nt A1691, the average frequencies of the A1 alleles ranged from 0.92 to 1.0 for the six dimorphisms (Table 1). Remarkably, all of the 234 alleles bearing nt A1691 bore only the A1 allele in exons 9 and 11, whereas only 2 of 234 alleles for exon 13 and 3 of 234 alleles for exon 16 bore the A2 allele. The linkage disequilibrium between nt A1691 and nt1470 or nt1806 was complete, between nt A1691 and nt2298 or nt5380 was almost complete, and between nt A1691 and nt495 or nt327 was very extensive (Table 1). Based on χ2 analysis, the P value for allelic frequency differences in each exon between normals (nt G1691) and APC-resistant subjects (nt A1691) was less than 10−5 (Table 1).
Factor V Haplotype Distribution for Normal Subjects and for Subjects With Homozygous APC-Resistance Based on Use of Six Dimorphisms in Exons 2, 4, 9, 11, 13, and 16
| Haplotype . | Controls (nt G1691) . | Homozygous (nt A1691) . | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | Exon 2 . | Exon 4 . | Exon 9 . | Exon 11 . | Exon 13 . | Exon 16 . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . |
| a | − | − | + | + | + | + | 83 | 0.488 | 204 | 0.879 |
| b | + | − | + | + | + | + | 25 | 0.147 | 18 | 0.078 |
| c | − | + | + | + | + | + | 24 | 0.141 | 8 | 0.034 |
| d | − | − | + | + | − | − | 17 | 0.100 | 1 | 0.004 |
| e | − | − | + | + | + | − | 4 | 0.024 | 1 | 0.004 |
| f through n Comprising 9 additional haplotyes | 17 | 0.100 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Haplotype . | Controls (nt G1691) . | Homozygous (nt A1691) . | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | Exon 2 . | Exon 4 . | Exon 9 . | Exon 11 . | Exon 13 . | Exon 16 . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . |
| a | − | − | + | + | + | + | 83 | 0.488 | 204 | 0.879 |
| b | + | − | + | + | + | + | 25 | 0.147 | 18 | 0.078 |
| c | − | + | + | + | + | + | 24 | 0.141 | 8 | 0.034 |
| d | − | − | + | + | − | − | 17 | 0.100 | 1 | 0.004 |
| e | − | − | + | + | + | − | 4 | 0.024 | 1 | 0.004 |
| f through n Comprising 9 additional haplotyes | 17 | 0.100 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
A positive sign indicates cleavage by the restrictive enzyme used for each dimorphism (see Fig 1 and Table 1). The 167 normal subjects (nt G1691) presented 170 informative and 164 uninformative alleles, whereas the 117 APC-resistant subjects (nt A1691) gave 232 informative and 2 uninformative alleles.
Factor V Haplotype Distribution of Normal and Homozygous APC-Resistant Subjects Based on Use of Three Dimorphisms in Exons 2, 4, and 9 Located 5′ to nt 1691
| Haplotype . | Controls (nt G1691) . | Homozygous (nt A1691) . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exon 2 . | Exon 4 . | Exon 9 . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . |
| − | − | + | 156 | 0.578 | 207 | 0.885 |
| + | − | + | 56 | 0.207 | 19 | 0.081 |
| − | + | + | 40 | 0.148 | 8 | 0.034 |
| 3 additional haplotyes | 18 | 0.067 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Haplotype . | Controls (nt G1691) . | Homozygous (nt A1691) . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exon 2 . | Exon 4 . | Exon 9 . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . |
| − | − | + | 156 | 0.578 | 207 | 0.885 |
| + | − | + | 56 | 0.207 | 19 | 0.081 |
| − | + | + | 40 | 0.148 | 8 | 0.034 |
| 3 additional haplotyes | 18 | 0.067 | 0 | 0 | ||
The normal and APC-resistant subjects gave 270 and 234 informative alleles and 64 and 0 uninformative alleles, respectively.
To assess a founder effect for the nt 1691 mutation, haplotype analysis based on multiple dimorphisms in alleles from a large number of APC-resistant subjects was limited to only subjects homozygous for nt A1691 to minimize the number of uninformative alleles. The use of only homozygotes maximized the number and percentage of informative alleles and avoided assumption-dependent mathematical treatment of ASRA data for generation of probable haplotypes. Among controls, based on a six-marker haplotype definition involving the six dimorphic sites listed in Table 1, there were 14 different haplotypes observed for controls but only five haplotypes for the APC-resistant subjects. For the APC-resistant subjects, 232 of 234 alleles were informative, whereas 170 of 334 of the controls' alleles were informative (Table 2). Notably, the most frequent haplotype, −/−/+/+/+/+, designated type a in Table 2, was present in 49% of controls versus 88% of APC-resistant subjects. All alleles from APC-resistant subjects could be obtained by single cross-over events starting with the −/−/+/+/+/+ type a haplotype containing the nt G1691A mutation. These data very strongly support the hypothesis that the mutation of nt G1691 to A was a single event that occurred on the background of haplotype a (Table 2), although it cannot be completely excluded that the mutation arose a very limited number of times on the haplotype a of −/−/+/+/+/+.
To increase the number of normals' informative alleles from 170 of 334 (51%), the data for exons on each side of nt1691 were separately analyzed as three-marker haplotypes based on nt1691 plus three dimorphisms. Using this haplotype definition (see Table 1), 270 of 334 (81%) control alleles and all 234 of 234 nt A1691 alleles were informative (Table 3). Eighty-nine percent of APC-resistant subjects' factor V alleles (nt A1691) versus 58% of controls' alleles (nt G1691) possessed the −/−/+ haplotype. Similarly, when a three-marker haplotype definition involves the three dimorphisms in exons 11, 13, and 16 (see Table 1), then 208 of 334 (62%) control alleles and 232 of 234 APC-resistant alleles were informative (Table 4). Ninety-nine percent of APC-resistant subjects versus 76% of controls possessed the +/+/+ haplotype defined in Table 4. Based on χ2 analysis, the P value for this difference is less than 10−6. These haplotype analyses, like those described above, strongly support the hypothesis that the mutation of nt G1691 to A was a single mutational event in one ancestor.
Factor V Haplotype Distribution of Normal and Homozygous APC-Resistant Subjects Based on Use of Three Dimorphisms in Exons 11, 13, and 16 Located 3′ to nt 1691
| Haplotype . | Controls (nt 1691G) . | Homozygous (nt 1691A) . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exon 11 . | Exon 13 . | Exon 16 . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . |
| + | + | + | 158 | 0.760 | 230 | 0.991 |
| + | − | − | 25 | 0.120 | 1 | 0.004 |
| + | − | + | 11 | 0.053 | 0 | 0 |
| + | + | − | 6 | 0.029 | 1 | 0.004 |
| 3 additional haplotypes | 8 | 0.038 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Haplotype . | Controls (nt 1691G) . | Homozygous (nt 1691A) . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exon 11 . | Exon 13 . | Exon 16 . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . | Alleles (N) . | Fraction . |
| + | + | + | 158 | 0.760 | 230 | 0.991 |
| + | − | − | 25 | 0.120 | 1 | 0.004 |
| + | − | + | 11 | 0.053 | 0 | 0 |
| + | + | − | 6 | 0.029 | 1 | 0.004 |
| 3 additional haplotypes | 8 | 0.038 | 0 | 0 | ||
The normal and APC-resistant subjects gave 208 and 232 informative alleles and 126 and 2 uninformative alleles, respectively.
A recent report also suggested that haplotype analysis apparently supported a founder effect for the mutation of nt G1691 to A.36 However, data in that report involved three completely linked dimorphisms and one very rare dimorphism located in a region spanning only 535 bp in exon 13 and were restricted to analysis of factor V alleles from only 6 homozygotes. An additional 42 heterozygous APC-resistant subjects were examined but presented notable limitations for absolute definition of haplotype; the analysis reportedly involved an overall P value of .046. The study design presented here (Tables 1-4) using large numbers of subjects homozygous for nt A1691 overcomes the obvious limitations of that study36 and achieves P values less than 10−6.
The time for the origin of the nt 1691 mutation may be speculated using the approximate estimate that, on average, 1 centiMorgan equals 1 Mb of sequence and equations that approximate the probability of recombination in each generation.37 For these calculations, we also assumed a single mutational origin for nt G1691A and the absence of back mutations such that recombination events account for the distribution of haplotype frequencies. Nineteen of 234 nt A1691 alleles evidence a cross-over altering the genotype at nt327 in exon 2, whereas 8 of 234 evidence a cross-over altering nt495 in exon 4 (Table 3). Assuming the minimum genomic distance between nt1691 and nt327 is 32.7 kb,31 1,050 generations of 20 years or 21,000 years are required to account for the data. Given the genomic distance between nt 1691 and nt 495 of 11.6 kb, 1,700 generations of 20 years or 34,000 years are required to account for the data. Because more cross-overs have occurred at the greater distance of exon 2 compared with exon 4, the mutation date estimate for exon 2 of 21,000 years ago is more likely than that for exon 4 of 34,000 years ago. Cognizant of the assumptions required for these calculations, we speculate that the factor V mutation at nt 1691 arose in a single Caucasoid ancestor approximately 21,000 to 34,000 years ago.
The estimated age of 21,000 to 34,000 years for the nt 1691 mutation in a founder Caucasoid fits very well with the known racial and geographic distributions of the mutation.22-30 These distributions suggest that the nt G1691A polymorphism is restricted to Caucasoid subpopulations yet widely spread among Indo-European groups, ranging from India to the Middle East, around the Mediterranean Sea to northern and western Europe. Based on a variety of genetic, linguistic and archaeological evidence38-43 (see Cavalli-Sforza et al44 for summary), it is currently argued that the evolution of Homo sapiens sapiens involved separation of non-Africans from Africans around 100,000 years ago, with Southeast Asians, including Pacific peoples, and Northeast Asians, including Amerinds, arising from separations that occurred around 60,000 years ago. The origin of modern Caucasoid subpopulations is estimated to be approximately 40,000 years ago. Thus, the estimated age of 21,000 to 34,000 years for the factor V nt 1691 mutation in a Caucasoid ancestor fits well with current estimates for divergence of human subpopulations.
The factor V nt1691 mutation was discovered as a common risk factor for venous thrombosis,4-9 with heterozygotes at mild eightfold increased risk and homozygotes at elevated 80-fold risk of life-threatening venous thromboembolism.45 Yet, its widespread presence among Caucasians suggests that it may be a balanced polymorphism with some advantages conferred upon heterozygotes. Because it renders factor Va resistant to the anticoagulant, APC, there is a mild hypercoagulable state in individuals with nt A1691 as shown by elevated levels of prothrombin fragment F1 + 2.46-49 Although such a condition would usually be mildly deleterious in heterozygotes, it could be rather useful when an individual is faced with life-threatening bleeding, such as during childbirth, warfare, or other activities carrying high risks of trauma. Especially in premodern times, death from bleeding associated with childbirth, trauma, or warfare was a significant risk that may have been reduced by this factor V mutation. The potential beneficial advantage of mild heterozygous APC resistance is suggested by the recent report that such heterozygosity may ameliorate the bleeding tendency in hemophilia A patients.50
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The skilled technical assistance of S. Yakar is gratefully acknowledged. We appreciate helpful discussions with Dr Ernest Beutler, Dr Neil Risch, and Paul Griffin.
Supported in part by National Institutes of Health Grants No. R37HL52246 and RO1HL21544 and the Stein Endowment Fund (J.H.G.).
Address reprint requests to Uri Seligsohn, MD, Institute of Thrombosis and Hemostasis, Department of Hematology, Sheba Medical Center, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel 52621.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal