Abstract
In the hematopoietic system CD77, a glycolipid surface antigen, is restricted to group I Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) cell lines and a subset of germinal center B lymphocytes. Recently, we have reported that recombinant B subunits of Verotoxin, which specifically binds to CD77, induce programmed cell death of CD77+ BL cells. Here, we show that an anti-CD77 monoclonal antibody (38.13) immobilized on tissue culture dishes also induces apoptosis, and we have explored the signal transducing events leading to this cell death. We show that ligation of CD77 antigen causes an increase of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration owing to an influx of extracellular Ca2+ through calcium channels. Chelation of extracellular Ca2+ with EGTA partially prevents anti-CD77–induced apoptosis, indicating that this process is probably Ca2+ dependent. We show that the cross-linking of CD77 provokes an increase of intracellular cAMP levels followed by cAMP-dependent protein kinase activation. We report that BL cells produce ceramide when they are exposed to 38.13 but, unexpectedly, without a concomitant decrease in sphingomyelin or CD77 content. Finally, we provide evidence that C2-ceramide, calcium ionophore, and forskolin (which increases intracellular levels of cAMP) independently induce apoptosis of CD77+ BL cells and, moreover, that C2-ceramide and forskolin strongly synergize to cause cell death. The possible role of CD77-mediated apoptosis in the B cell selection that occurs in germinal centers is discussed.
APOPTOSIS (or programmed cell death) is a form of cell suicide that occurs during embryogenesis, metamorphosis, and tumor regression.1,2 It also plays a major role in the development of the immune system, because clonal selection is effected, in part, by apoptosis.3 In the B cell compartment apoptosis plays a key role during elimination of self-reactive immature B lymphocytes and during affinity maturation of B lymphocytes in germinal centers (GC).4 5
In vitro, apoptosis can be induced by a wide variety of physiological and pharmacological stimuli such as withdrawal or adjunction of various agents (hormones, cytokines, toxins, glucocorticoids), low serum concentration, or radiation. However, the intracellular signaling pathways leading to cell death remain relatively poorly understood. Early studies on glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of immature thymocytes provided evidence that Ca2+ influx plays a key role in early stages of apoptosis. Later, it was also shown that cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is able to potentiate glucocorticoid-induced DNA fragmentation through activation of a cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA).6 More recently, ceramide, a product of sphingolipid metabolism, has also emerged as a mediator in several apoptotic processes. Radiations, tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and Fas cause ceramide generation leading to cell death in a variety of cell types.7 8
We have recently suggested that CD77 may be a new membrane antigen involved in apoptosis of some B cells.9 This neutral glycosphingolipid (the globotriaosylceramide or Gb3) has a very restricted pattern of expression in the hematopoietic system.10 Among normal leukocytes, it is only expressed on a subset of tonsillar B lymphocytes, which are located in the dark zone of germinal centers and which undergo rapid and spontaneous apoptosis when isolated and cultured in vitro.11,12 Among neoplastic cells, CD77 antigen is only found on the so-called “group I” Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) cells,13,14 which have been reported to enter apoptosis upon culture at low serum concentration or exposure to immobilized anti–immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies.15 In contrast, the group III BL cells, which do not express CD77, are mostly resistant to these stimuli. This ability of the CD77+ cells to readily enter apoptosis prompted us to investigate the role of the CD77 molecule in apoptosis. Recently we showed that ligation of CD77 by recombinant B subunits of Verotoxin, the CD77-specific binding subunits of this bacterial toxin, induces apoptosis in CD77+ BL cells.16
Considering that CD77 antigen could thus represent an important new functional molecule for B cells, we have further investigated the cell death signal generated by way of CD77. We report that cross-linked anti-CD77 monoclonal antibodies (MoAb), although less potent that anti-IgM MoAb, induce the programmed cell death of BL cells. We show that ligation of CD77 causes an increase of intracellular Ca2+ concentration (by an influx of extracellular Ca2+), which seems to be a critical step in the apoptotic process because its prevention by EGTA protects, in part, the BL cells. We show that ligation of CD77 induces a rapid increase of cAMP and the activation of PKA. We also show that endogenously produced ceramide accumulates when group I BL cells are exposed to anti-CD77 MoAb and that this elevation does not result from sphingomyelin or CD77 degradation. Finally, we show that C2-ceramide, calcium ionophore, and forskolin (which increases intracellular levels of cAMP) independently induce apoptosis of the CD77+ BL cells. Moreover, we provide evidence that forskolin and C2-ceramide strongly synergize to cause cellular death, therefore suggesting that accumulation of cAMP and generation of ceramide are complementary events in the signal transduction pathway of the CD77-mediated apoptosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell lines.The BL cell lines used in this study were kindly provided by Dr G. Klein (Stockholm, Sweden; Ramos, Daudi, and Namalwa), by Dr G. Lenoir (Lyon, France; BL2), and by Dr C. Gregory (Birmingham, UK; Mutu I and Mutu III). These cell lines were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (GIBCO-BRL, Cergy-Pontoise, France) containing 2 mmol/L L-glutamine, 1 mmol/L sodium pyruvate, 20 mmol/L glucose, and 20 μg/mL gentamicine, and supplemented with 5% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS).
Reagents.38.13 hybridoma (rat IgM anti-CD77) was produced in our laboratory. 5B5 (mouse monoclonal IgM anti-CD77) and HJ6 (mouse monoclonal IgM anti-Gb4) were a gift from Dr M. Nahm (St Louis, MO). DA4.4 (mouse monoclonal IgG1 anti-human IgM) was kindly donated by Dr Y. Richard (Clamart, France). B-B6 (mouse monoclonal IgM anti-CD20) was purchased from Diaclone (Besançon, France). Purified recombinant Verotoxin B chain (VT-B) and purified 38.13 MoAb were kindly provided by Dr C.A. Lingwood (Toronto, Canada). Rabbit anti-rat IgM (RARa), rabbit anti-mouse IgG (RAM-G), and rabbit anti-mouse IgM (RAM-M) were obtained from Zymed (San Francisco, CA). [3H] palmitate and [γ32P] adenosine triphosphate (ATP) were obtained from Amersham (Les Ulis, France). High performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) plates were from Merck (Nogent sur Marne, France). Diacylglycerol (DAG) kinase came from Calbiochem (La Jolla, CA). All other reagents were purchased from Sigma (L'Isle d'Abeau Chesnes, France).
Coating procedure.The coating of RARa, RAM-G, and RAM-M on Petri dishes was performed using a slightly modified version of a previously described procedure.17 Briefly, antibodies at 10 μg/mL final concentration were diluted in 0.05 mol/L Tris-HCl pH 9.5 and immediately poured onto the plates, which were then incubated overnight at 4°C. Dishes were washed two times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and 38.13 MoAb (10 μg/mL) was added to the dishes before overnight incubation at 4°C. After 1 to 2 hours incubation at 4°C with bovine serum albumin (BSA; 1 mg/mL in PBS), cells (5 × 105/mL) were added, and dishes were placed at 37°C.
DNA fragmentation assays.5 × 106 cells were centrifuged in PBS. The pellets were lysed by incubation for 1 hour at 50°C in 10 mmol/L EDTA, 200 mmol/L NaCl, 0.1 mg/mL proteinase K, 0.5% (wt/vol) SDS, and 50 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 8. The DNA was extracted with phenol chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) and then ethanol precipitated. One-tenth volume of 3 mol/L sodium acetate, pH 7.2, was added to the supernatant, which was kept at −80°C overnight. The precipitate containing DNA was centrifuged and dried under vacuum. DNA was then resuspended in 20 μL RNAse buffer (15 mmol/L NaCl and 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.5) containing 0.5 μg/mL DNAse-free RNAse, and incubated at 50°C for 1 hour. DNA was separated by electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel.
Measurement of intracellular calcium.Increases in [Ca2+]i were monitored with the calcium-sensitive dye indo-1/AM. Cells (107/mL) were incubated for 45 minutes at 37°C with 3 μmol/L indo-1/AM in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 5% FCS. After washing, cells were suspended in RPMI (5 × 106/mL), and flow cytometric analysis was performed using a FACS 440 (Becton Dickinson, Pont-de-Cloix, France). Ultraviolet excitation was obtained from an argon ion laser (Spectra-Physics, Les Ulis, France). Violet fluorescence emission was measured at 390-410 nm, blue emission at 480 to 500 nm with band pass filters, and violet-blue separation was performed with a 450-nm dichroic filter. Cells were transferred to a 37°C thermostatically controlled sample cup and analyzed at a rate of 1,000 cells/s. The indo-1 violet/blue fluorescence ratio intensity was digitally calculated and ratio histograms of 5,000 cells were collected every 60 seconds using an MCA 3000 computer in kinetic mode. The percentages of responding cells were digitally calculated by substraction of the negative control curve from the test curve. The efficiency of indo-1 loading was determined at the beginning of each experiment by addition of 10 mmol/L ionomycin.
Intracellular cAMP measurement.Cells were washed and resuspended at 4 × 106/mL in complete medium in presence of 38.13 MoAb or forskolin (10 μmol/L). After various incubation times, the reactions were stopped by addition of cold RPMI 1640 and incubated for 15 minutes at 4°C. Cells were then centrifuged for 1 minute at 13,000 rpm, resuspended in a lysis buffer (50 mmol/L sodium acetate) and placed in a boiling water bath for 2 minutes, followed by refrigeration. The samples were again centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 minutes and supernatants were obtained. cAMP was measured in cell lysates using a cAMP assay kit (RPA 509, Amersham) following the manufacturer's instructions. Values were expressed in pmol ± SD per 106 cells as determined by comparison with a standard curve.
Measurement of cAMP-dependent PKA activity.Cells were washed and resuspended at 2 × 106 cells/mL in complete medium; 38.13 MoAb or other reagents were then added and incubation was performed at 37°C. The reaction was stopped by placing the tubes on ice before centrifuging at 13,000 rpm for 2 minutes at 4°C. Five hundred microliters of lysis buffer (50 mmol/L Tris-HCl, 5 mmol/L EDTA, 0.1 mmol/L sodium orthovanadate, 100 μmol/L calyculin A, 1 mmol/L aprotinin, 1 mmol/L PMSF, 1 mmol/L leupeptin) were added to each tube, and the supernatant was examined for specific PKA activity using a PKA assay kit (GIBCO-BRL) following the manufacturer's instructions.
Lipid studies.3 × 106 cells were incubated for various times at 37°C in complete medium containing 38.13 MoAb, and lipids were then extracted. Ceramide was quantified by the DAG kinase assay as previously described.18 Briefly, cell pellets were extracted three times with 1 mL of chloroform:methanol (2:1) and 500 μL of water. After drying of the organic phase extract, lipids were solubilized and added to 7 μg of DAG kinase and 20 μL of 10 mmol/L [γ32P] ATP (1,000 dpm/pmol). After 40 minutes of incubation at 22°C, the reaction was stopped by extraction of lipids. The ceramide 1-Phosphate (Cer 1-P) was resolved by HPTLC, with the use of a chloroform:acetone:methanol:acetic acid:water (100:40:20:20:10) solvent system. After autoradiography, Cer 1-P was scraped off the plates and quantitated by liquid scintillation counting. Ceramide content was determined by comparison with a standard curve.
For sphingomyelin and CD77 quantification, cells (5 × 106/flask) were cultured for 24 hours in RPMI 1640 containing 20 μCi [3H] palmitate before treatment with 38.13 MoAb for various times. Lipids were then extracted as previously described.19 Briefly, the cell pellets were extracted with 1 mL of methanol:water:concentrated HCl (100:5:1), 2 mL of chloroform, and 0.6 mL of water. The organic lower phase was then dried under N2 , reconstituted with 20 μL of chloroform:methanol (2:1), and lipids were chromatographed on HPTLC plates using chloroform:methanol:acetic acid:water (100:60:20:5). Plates were air-dried and autoradiographed. Labeled lipids were scraped off the plates and quantitated by liquid scintillation counting.
RESULTS
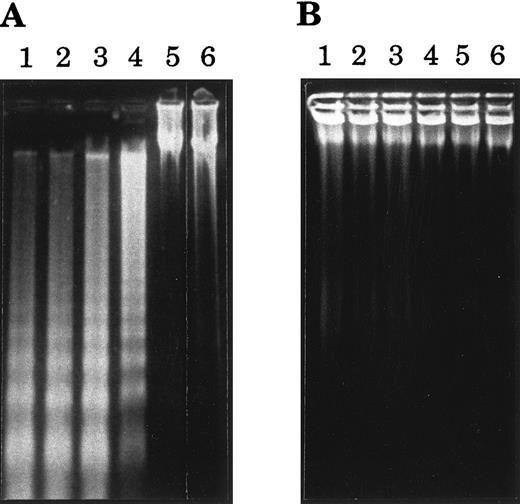
Cross-linked anti-CD77 MoAb induces the apoptotic cell death of BL cells.Our previous observation, that triggering of the CD77 antigen by the B-subunit of the VT-B induced apoptosis of the CD77+ BL cells,16 prompted us to test the effect of an anti-CD77 MoAb (38.13) on the viability of these BL cells. The CD77+ MUTU I cells were therefore incubated for various times with soluble 38.13 MoAb or soluble anti-human IgM (DA4.4 MoAb), which have been shown to induce apoptosis of certain BL cells.20 The viability of cells was then evaluated by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis of cells stained with ethidium bromide (EB). As shown in Table 1, incubation of the cells for up to 48 hours with 38.13 MoAb had a very moderate effect on the viability of the cells (however, at higher concentrations of 38.13 [100 to 200 μg/mL] a higher percentage of dead cells was seen [data not shown]). As expected because MUTU I cells are EBV+ BL cells,20 incubation with DA4.4 moderately decreased their viability, but the effect was clearly higher than the 38.13 effect. Because it has been extensively shown that immobilization of antibodies maximizes their capacity to cross-link cell surface receptors, we then analyzed the effect of plastic-immobilized 38.13 and DA4.4 antibodies on the MUTU I cells. Cells were cultured in Petri dishes that had been previously coated with RARa and 38.13 MoAb or RAM-G and DA4.4 MoAb. Under these conditions, the viability of the MUTU I cells was almost unaffected after 5 hours of incubation with 38.13, slightly decreased after 10 hours, and drastically reduced after 20 and 48 hours. By contrast, the viability of the MUTU I cells was strongly reduced as soon as after 5 hours of incubation with DA4.4 MoAb and almost no detectable live cells could be seen after 20 and 48 hours (Table 1). The induction of cell death by cross-linked 38.13 MoAb was then tested on various CD77+ (Ramos, Daudi, Mutu I) and CD77− (Mutu III, VT500, Namalwa) BL cell lines. As negative controls, cells were incubated with plastic-immobilized B-B6, an anti-CD20 MoAb. CD20 antigen was chosen because it is expressed on most BL cell lines at levels similar to CD77 levels. As shown in Table 2, after 24 hours of incubation with B-B6 MoAb and RAM-M, viability of CD77+ BL cells was maintained at a high level, whereas the percentage of dead cells was strongly increased for cells incubated with 38.13 MoAb and RARa. No effect of anti-CD77 or anti-CD20 MoAbs on viability of CD77− BL cell lines was observed. To confirm that the anti-CD77–induced cell death was caused by apoptosis, various BL cell lines were cultured for 24 hours with immobilized 38.13 MoAb and examined for DNA fragmentation. As shown in Fig 1, extraction and gel electrophoresis of total DNA revealed the apoptotic DNA ladder for the CD77+ BL cell lines BL2, Ramos, Daudi, and MUTU I, and no DNA fragmentation for the CD77− cell lines Namalwa and MUTU III. Taken together these results indicate that cross-linking of CD77 antigen induces apoptosis of BL cells, which is delayed compared with anti-IgM–induced apoptosis.
Kinetics of Cell Death Induced by Soluble or Plastic-Immobilized 38.13 Anti-CD77 MoAb and DA4.4 Anti-IgM MoAb
| . | % of Cell Viability . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | 5 h . | 10 h . | 20 h . | 48 h . |
| Anti-CD77 | 83 ± 6 | 82 ± 5 | 77 ± 5 | 74 ± 6 |
| Anti-IgM | 80 ± 5 | 81 ± 7 | 74 ± 4 | 65 ± 6 |
| RARa | 75 ± 7 | 77 ± 7 | 78 ± 7 | 82 ± 6 |
| RARa + α-CD77 | 79 ± 3 | 67 ± 7 | 30 ± 5 | 39 ± 7 |
| RAM-G | 81 ± 2 | 82 ± 8 | 77 ± 5 | 77 ± 5 |
| RAM-G + α-IgM | 58 ± 7 | 47 ± 6 | 5 ± 3 | 0 |
| . | % of Cell Viability . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | 5 h . | 10 h . | 20 h . | 48 h . |
| Anti-CD77 | 83 ± 6 | 82 ± 5 | 77 ± 5 | 74 ± 6 |
| Anti-IgM | 80 ± 5 | 81 ± 7 | 74 ± 4 | 65 ± 6 |
| RARa | 75 ± 7 | 77 ± 7 | 78 ± 7 | 82 ± 6 |
| RARa + α-CD77 | 79 ± 3 | 67 ± 7 | 30 ± 5 | 39 ± 7 |
| RAM-G | 81 ± 2 | 82 ± 8 | 77 ± 5 | 77 ± 5 |
| RAM-G + α-IgM | 58 ± 7 | 47 ± 6 | 5 ± 3 | 0 |
CD77+ MUTU I BL cells were cultured for various times with anti-CD77 (38.13; 10 μg/mL) or anti-human IgM (DA4.4; 5 μg/mL) MoAb or were incubated in Petri dishes that had been previously coated with: RARa; RARa and 38.13 MoAb (RARa + α-CD77); RAM-G; and RAM-G and DA4.4 MoAb (RAM-G + α-IgM).
Effect of Immobilized 38.13 Anti-CD77 MoAb and B-B6 Anti-CD20 MoAb on BL Cell Viability
| . | % of Cell Viability . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | RARa . | RARa + α-CD77 . | RAM-M . | RAM-M + α-CD20 . |
| CD77+ cells | ||||
| Ramos | 91 ± 7 | 43 ± 9 | 89 ± 9 | 90 ± 7 |
| Daudi | 88 ± 9 | 38 ± 11 | 87 ± 8 | 88 ± 7 |
| Mutu I | 87 ± 6 | 31 ± 7 | 89 ± 7 | 91 ± 7 |
| CD77− cells | ||||
| Mutu III | 92 ± 9 | 88 ± 9 | 90 ± 7 | 91 ± 8 |
| VT500 | 90 ± 8 | 80 ± 10 | 87 ± 10 | 88 ± 8 |
| Namalwa | 89 ± 7 | 86 ± 8 | 83 ± 9 | 87 ± 7 |
| . | % of Cell Viability . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | RARa . | RARa + α-CD77 . | RAM-M . | RAM-M + α-CD20 . |
| CD77+ cells | ||||
| Ramos | 91 ± 7 | 43 ± 9 | 89 ± 9 | 90 ± 7 |
| Daudi | 88 ± 9 | 38 ± 11 | 87 ± 8 | 88 ± 7 |
| Mutu I | 87 ± 6 | 31 ± 7 | 89 ± 7 | 91 ± 7 |
| CD77− cells | ||||
| Mutu III | 92 ± 9 | 88 ± 9 | 90 ± 7 | 91 ± 8 |
| VT500 | 90 ± 8 | 80 ± 10 | 87 ± 10 | 88 ± 8 |
| Namalwa | 89 ± 7 | 86 ± 8 | 83 ± 9 | 87 ± 7 |
CD77+ BL cells and CD77− BL cells were cultured 24 hours on Petri dishes precoated with: RARa; RARa and 38.13 MoAb (RARa + α-CD77); RAM-M; RAM-M and B-B6 MoAb (RAM-M + α-CD20). The percentage of cell viability was obtained by EB staining and FACS analysis.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA from BL cells treated with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb. BL cells were incubated for 24 hours in Petri dishes that had been previously coated with RARa and 38.13 MoAb (A) or with RARa alone (B). DNA was then prepared and analyzed by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, CD77+ BL2 cells; lane 2, CD77+ Ramos cells; lane 3, CD77+ Daudi cells; lane 4, CD77+ MUTU I cells; lane 5, CD77− Namalwa cells; lane 6, CD77− MUTU III cells.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA from BL cells treated with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb. BL cells were incubated for 24 hours in Petri dishes that had been previously coated with RARa and 38.13 MoAb (A) or with RARa alone (B). DNA was then prepared and analyzed by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, CD77+ BL2 cells; lane 2, CD77+ Ramos cells; lane 3, CD77+ Daudi cells; lane 4, CD77+ MUTU I cells; lane 5, CD77− Namalwa cells; lane 6, CD77− MUTU III cells.
Anti-CD77 MoAb induce a sustained influx of Ca2+ into BL cells.Ca2+ ions play an important role in various apoptotic processes, most probably by activating Ca2+-dependent endonucleases. We therefore measured the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) of BL cells triggered by various ligands of CD77. As shown in Fig 2, an increase in the cytosolic [Ca2+] was observed when the CD77+ Ramos cells were treated with two anti-CD77 MoAb (38.13 or 5B5) or with VT-B. The [Ca2+]i began to increase within seconds, reached a maximal level after 2 minutes, and remained high for 10 minutes. Similar results were obtained with Daudi and Mutu I cells (data not shown). In contrast, the [Ca2+]i was not modified when Ramos cells were incubated with HJ6, a MoAb directed against Gb4 glycolipid (produced by addition of a Gal-NAc to Gb3) antigen, or when the CD77− Namalwa cells were treated with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb.
Kinetics of intracellular Ca2+ changes in BL cells treated by various ligands of CD77 antigen. CD77+ Ramos cells were stimulated by 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL), 5B5 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL), VT-B (5 ng/mL), or by HJ6 anti-Gb4 MoAb (10 μg/mL). CD77− Namalwa cells were stimulated by 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL). Ramos cells were also incubated with 2.5 mmol/L EGTA or 25 μg/mL Verapamil before stimulation by 38.13 MoAb. Intracellular Ca2+ was measured using indo-1 indicator. Results are representative of six different experiments. The basal [Ca2+]i, before addition of 38.13 MoAb, was 230 ± 50 nmol/L (mean ± SD, 50 cells) and the [Ca2+]i rise can reach a peak of 540 ± 30 nmol/L.
Kinetics of intracellular Ca2+ changes in BL cells treated by various ligands of CD77 antigen. CD77+ Ramos cells were stimulated by 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL), 5B5 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL), VT-B (5 ng/mL), or by HJ6 anti-Gb4 MoAb (10 μg/mL). CD77− Namalwa cells were stimulated by 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL). Ramos cells were also incubated with 2.5 mmol/L EGTA or 25 μg/mL Verapamil before stimulation by 38.13 MoAb. Intracellular Ca2+ was measured using indo-1 indicator. Results are representative of six different experiments. The basal [Ca2+]i, before addition of 38.13 MoAb, was 230 ± 50 nmol/L (mean ± SD, 50 cells) and the [Ca2+]i rise can reach a peak of 540 ± 30 nmol/L.
To determine whether Ca2+ is mobilized from the extracellular medium or from intracellular Ca2+ stores, experiments were performed in the presence of EGTA, which chelates the extracellular Ca2+. As shown in Fig 2, preincubation of the cells with EGTA totally inhibited the Ca2+ increase induced by 38.13 MoAb, thus indicating that the increase is caused by an influx of extracellular Ca2+ and not by a release from intracellular stores. Verapamil, an L-type Ca2+ channel antagonist, was then used to determine the specificity of the Ca2+ influx. Incubation of the cells with 38.13 MoAb and verapamil completely abolished the Ca2+ rise. Taken together, these results suggest that the increase of the [Ca2+]i is caused by an influx of extracellular Ca2+ through Ca2+ L-type channels and also show that Ca2+ mobilization is one of the early signaling events to occur after CD77 triggering.
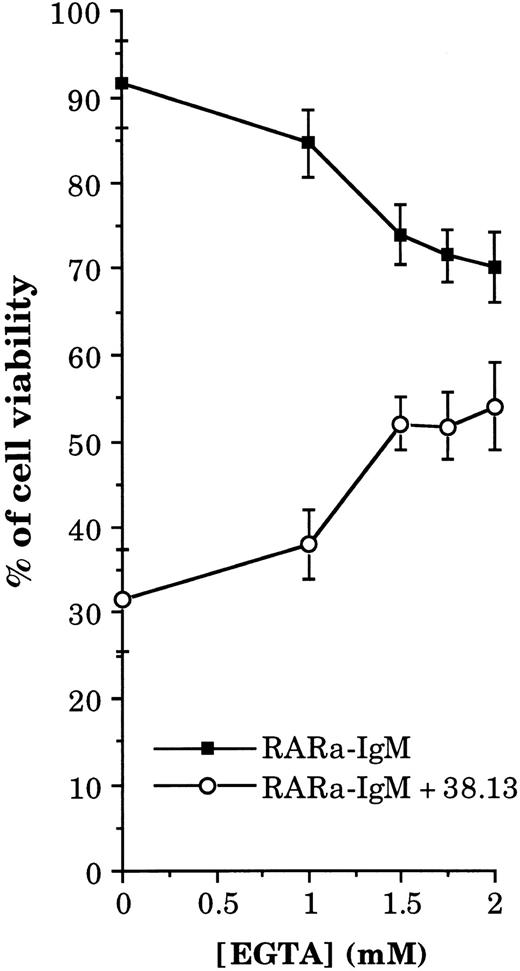
Inhibition of Ca2+ influx protects cells from anti-CD77–induced apoptosis.To assess the role of the Ca2+ influx, we then tested the effect of inhibiting the Ca2+ increase on the anti-CD77–induced apoptosis. Because prior experiments indicated that 1 and 1.5 mmol/L of EGTA partially inhibited the Ca2+ rise and 2 mmol/L totally blocked it (data not shown), we added these concentrations, simultaneously with Ramos cells, to Petri dishes that had been previously coated with 38.13 MoAb and RARa (or RARa alone). Viability of the cells was then evaluated by FACS analysis of EB-stained cells. As shown in Fig 3, 69% of Ramos cells died after 24 hours of incubation with 38.13 MoAb and RARa, whereas with RARa alone most of the cells (91.5%) remained viable. Addition of 1.5, 1.75, and 2 mmol/L of EGTA protected the cells from death because only 48%, 49%, and 45% of cells were killed by treatment with the anti-CD77 MoAb after 24 hours. At higher concentrations of EGTA, the protective effect was abolished by its cytotoxic effect (data not shown). These data suggest that CD77-induced cell death occurs through a calcium-dependent process.
Effect of EGTA on the viability of BL cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. Ramos cells were cultured for 24 hours with various concentrations of EGTA in Petri dishes that had been previously coated with RARa or with RARa and 38.13 MoAb. The percentage of viable cells was obtained by EB staining and FACS analysis.
Effect of EGTA on the viability of BL cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. Ramos cells were cultured for 24 hours with various concentrations of EGTA in Petri dishes that had been previously coated with RARa or with RARa and 38.13 MoAb. The percentage of viable cells was obtained by EB staining and FACS analysis.
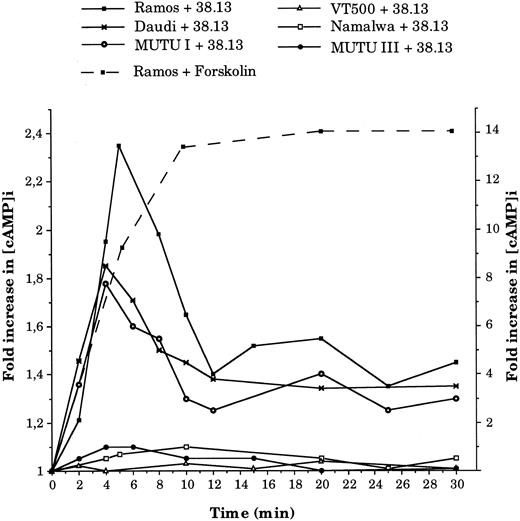
Anti-CD77 MoAb cause an increase in cAMP concentration and activation of PKA.Previous studies have indicated that induction of apoptosis often requires an elevated cAMP level. We therefore measured the intracellular level of cAMP ([cAMP]i) in BL cells treated with 38.13 MoAb. As shown in Fig 4, treatment of CD77+ BL cells (Ramos, Daudi, and MUTU I) with 38.13 MoAb caused a transient increase in [cAMP]i concentration, which was clearly detectable after 2 minutes, peaked at 4 minutes (1.78-fold increase for MUTU I and 1.85 for Daudi) or 5 minutes (2.35 fold increase for Ramos), and then decreased until 12 minutes. However, the [cAMP]i did not return to the initial concentration, and an increase of about 40% was maintained until 30 minutes. In contrast, no change in [cAMP]i level was observed in the CD77− BL cells (Namalwa, MUTU III, and VT 500) incubated with 38.13 MoAb. Positive controls of cAMP generation were obtained by incubating cells with forskolin, a direct activator of adenylate cyclase. As shown in Fig 4, treatment of Ramos cells with 50 μmol/L of forskolin induced a very high increase in [cAMP]i concentration (13.3-fold increase) after 10 minutes, which then remained elevated until 30 minutes. The induction of cAMP triggered by forskolin (50 μmol/L) in the other BL cell lines after 10 minutes were between 7.4- and 12.8-fold increases (data not shown). Addition of other antibodies (B-B6 anti-CD20 MoAb, HJ6 anti-Gb4 MoAb) did not influence the [cAMP]i of CD77+ or CD77− BL cells (data not shown).
Kinetics of intracellular cAMP changes in BL cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. CD77+ Ramos, Daudi, and MUTU I cells, and CD77− Namalwa, MUTU III, and VT500 cells were cultured with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb for various times, and cAMP concentrations were measured. Results are expressed in fold increase (left ordinate) of the basal cAMP level measured before stimulation (Ramos, 5.3; Daudi, 5.4; MUTU I, 2.3; Namalwa, 9; MUTU III, 3.2; VT500, 2.7 pmol/106 cells). The effect of forskolin (50 μmol/L) on cAMP concentrations (fold increase on the right ordinate) in Ramos cells is also shown. Results are representative of seven independent experiments.
Kinetics of intracellular cAMP changes in BL cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. CD77+ Ramos, Daudi, and MUTU I cells, and CD77− Namalwa, MUTU III, and VT500 cells were cultured with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb for various times, and cAMP concentrations were measured. Results are expressed in fold increase (left ordinate) of the basal cAMP level measured before stimulation (Ramos, 5.3; Daudi, 5.4; MUTU I, 2.3; Namalwa, 9; MUTU III, 3.2; VT500, 2.7 pmol/106 cells). The effect of forskolin (50 μmol/L) on cAMP concentrations (fold increase on the right ordinate) in Ramos cells is also shown. Results are representative of seven independent experiments.
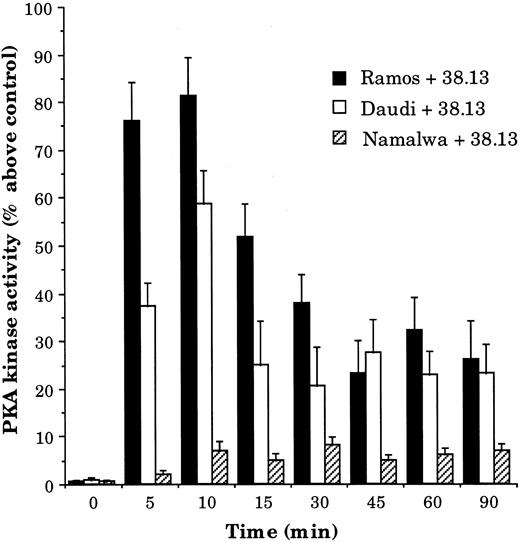
One of the primary elements in the cAMP signal transduction cascade is the activation of PKA, a serine/threonine protein kinase that then phosphorylates appropriate target proteins. The activity of this kinase was consequently measured in CD77+ cells (Ramos and Daudi) incubated for various times with 38.13 MoAb. As shown in Fig 5, PKA activity was increased after 5 minutes, maximum at 10 minutes, declined between 15 and 45 minutes, and then remained stable until 90 minutes (similarly to results seen for [cAMP]i, this level of PKA activity was slightly higher than the prestimulation level). Comparable levels of PKA activation were obtained in Ramos and Daudi cells with 2 other anti-CD77 MoAbs (3D9 and 4A11; data not shown). In contrast, the PKA activity of Namalwa cells was not modified by any of the anti-CD77 MoAb.
Kinetics of PKA activity changes in BL cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. CD77+ Ramos and Daudi cells and CD77− Namalwa cells were cultured with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb, and PKA activities were measured. Initial PKA activity was 3,100 pmol/min/mg of protein for Ramos, 1,975 for Daudi, and 4,500 for Namalwa cells.
Kinetics of PKA activity changes in BL cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. CD77+ Ramos and Daudi cells and CD77− Namalwa cells were cultured with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb, and PKA activities were measured. Initial PKA activity was 3,100 pmol/min/mg of protein for Ramos, 1,975 for Daudi, and 4,500 for Namalwa cells.
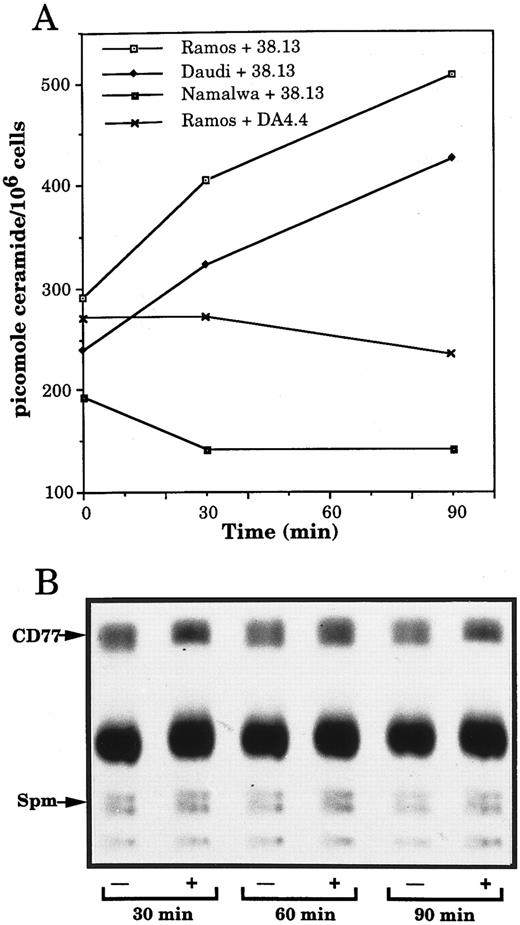
Anti-CD77 MoAb generate ceramide accumulation in BL cells.Recently, ceramide, a sphingolipid molecule usually generated by the hydrolysis of the plasma membrane sphingomyelin, has emerged as a new second messenger of apoptosis. We therefore investigated whether stimulation of CD77 antigen could induce an increase of endogenous ceramide, concomitant to a decrease in sphingomyelin. Furthermore, because ceramide constitutes the lipid portion of glycosphingolipids and could therefore be generated by degradation of the CD77 antigen, we measured the amount of CD77 in the treated or nontreated cells. Figure 6A shows that after 90 minutes of incubation with 38.13, the level of ceramide, measured by the DAG kinase assay, increased in the CD77+ Daudi and Ramos cells, whereas it was not modified in the CD77− Namalwa cells. As a negative control, Ramos cells were also exposed to anti-human IgM, which were previously reported not to induce detectable ceramide accumulation before at least 12 hours of treatment.19 No increase in the level of ceramide of Ramos cells incubated with DA4.4 could be detected (Fig 6A). Because the kinetics of ceramide generation caused by stimulation of the CD77 antigen was delayed compared with the one generally observed in ceramide-initiated apoptosis,18,21 22 control experiments were performed in parallel to treatment of CD77+ BL cells with 38.13: when U937 cells were treated with TNF-α (100 ng/mL), a typical time-course of ceramide generation was observed: ceramide concentration increased from 99 pmol/106 cells before stimulation to 178 and 119 pmol/106 cells after 5 and 10 minutes of stimulation and before returning to basal level (90 pmol/106 cells at 60 minutes).
Changes in ceramide but not sphingomyelin and Gb3/CD77 levels in BL cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. (A) CD77+ Ramos and Daudi cells and CD77− Namalwa cells were cultured with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb; Ramos cells were also cultured with DA4.4 anti-human IgM MoAb. Ceramide was quantitated by the DAG kinase assay. Results are representative of six independent experiments. (B) Ramos cells, prelabeled with 3H-palmitate, were cultured with (+) or without (−) 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb. Lipids were extracted and chromatographed on HPTLC plates using chloroform: methanol: acetic acid: water (100:60:20:5) as solvent system. Radioactive spots were visualized by autoradiography. Sphingomyelin (Spm) and Gb3/CD77 were identified by comigration with standards.
Changes in ceramide but not sphingomyelin and Gb3/CD77 levels in BL cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. (A) CD77+ Ramos and Daudi cells and CD77− Namalwa cells were cultured with 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb; Ramos cells were also cultured with DA4.4 anti-human IgM MoAb. Ceramide was quantitated by the DAG kinase assay. Results are representative of six independent experiments. (B) Ramos cells, prelabeled with 3H-palmitate, were cultured with (+) or without (−) 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb. Lipids were extracted and chromatographed on HPTLC plates using chloroform: methanol: acetic acid: water (100:60:20:5) as solvent system. Radioactive spots were visualized by autoradiography. Sphingomyelin (Spm) and Gb3/CD77 were identified by comigration with standards.
The autoradiogram of an HPTLC of sphingolipids extracted from Ramos cells, prelabeled for 18 hours with 3H-palmitate, indicates that the sphingomyelin and the CD77 contents of the cells are not significantly altered by incubation with 38.13 MoAb (Fig 6B). To confirm that sphingomyelin content does not decrease in the cells treated with 38.13, Ramos cells were also prelabeled for 48 hours with 3H-choline (which specifically incorporates into sphingomyelin).18 After 30, 60, and 90 minutes of incubation with 38.13, sphingolipids were extracted and chromatographed. No significant modifications of the sphingomyelin level were observed. Variations in the amounts of ceramide, sphingomyelin, and CD77 following ligation of CD77 are summarized in Table 3. The amount of ceramide in cells incubated with 38.13 MoAb began to accumulate after 30 minutes, peaked at 60 and 90 minutes, and returned to basal level after 2 hours. No concomitant decrease in the level of sphingomyelin or CD77 could be observed in the cells treated by 38.13 MoAb. Rather, a tendancy toward a slight increase of these compounds could be seen after 90 minutes of stimulation. When U937 cells were treated with 100 ng/mL of TNFα, a decrease in sphingomyelin, concomitant to the increase of ceramide, was observed (data not shown). These results indicate that triggering of CD77 generates ceramide accumulation, which apparently does not result from the hydrolysis of sphingomyelin or Gb3/CD77.
Quantification of Changes in Ceramide, Sphingomyelin, and Gb3/CD77 Levels in Ramos Cells Treated by 38.13 Anti-CD77 MoAb
| . | Incubation Times (min) . | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | 0 . | 15 . | 30 . | 60 . | 90 . | 120 . |
| Ceramide | 1 | 1.03 ± 0.05 | 1.10 ± 0.08 | 1.35 ± 0.12 | 1.77 ± 0.22 | 1.09 ± 0.10 |
| Sphingomyelin | 1 | 1.12 ± 0.07 | 1.00 ± 0.04 | 1.11 ± 0.09 | 1.29 ± 0.19 | 1.12 ± 0.10 |
| CD77 | 1 | 0.97 ± 0.07 | 1.10 ± 0.16 | 1.00 ± 0.12 | 1.17 ± 0.08 | 0.92 ± 0.04 |
| . | Incubation Times (min) . | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | 0 . | 15 . | 30 . | 60 . | 90 . | 120 . |
| Ceramide | 1 | 1.03 ± 0.05 | 1.10 ± 0.08 | 1.35 ± 0.12 | 1.77 ± 0.22 | 1.09 ± 0.10 |
| Sphingomyelin | 1 | 1.12 ± 0.07 | 1.00 ± 0.04 | 1.11 ± 0.09 | 1.29 ± 0.19 | 1.12 ± 0.10 |
| CD77 | 1 | 0.97 ± 0.07 | 1.10 ± 0.16 | 1.00 ± 0.12 | 1.17 ± 0.08 | 0.92 ± 0.04 |
For ceramide, each value is: pmol in 38.13 treated cells ÷ pmol in control cells. For sphingomyelin and Gb3/CD77, each spot of the HPTLC obtained from cells treated or not with 38.13 MoAb was scraped off the plates and quantitated by liquid scintillation counting. Each value is: cpm in 38.13 treated cells ÷ cpm in control cells. Results given are the means ± SD of five independent experiments.
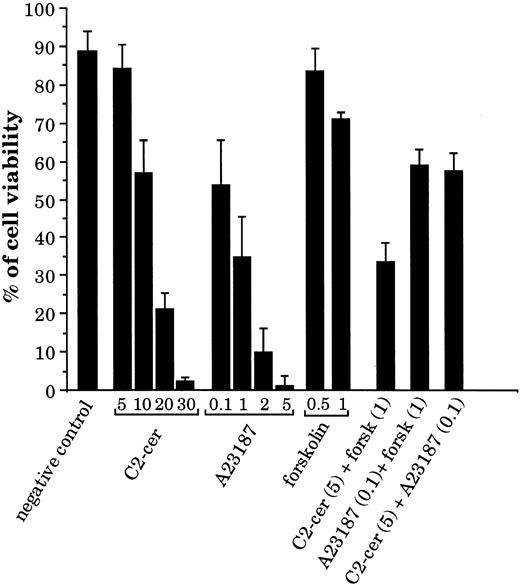
Second messengers generated by CD77 ligation induce BL cell death.Because we have shown that stimulation of CD77 causes accumulation of calcium, cAMP, and ceramide, we have tested whether these second messengers (alone or in combination) can induce apoptosis of the CD77+ cells. As shown in Fig 7, addition of the membrane-permeable ceramide analogue C2-ceramide or of the calcium ionophore A23187 induced apoptosis of the CD77+ Daudi cells in a dose-dependent manner. At high concentrations, forskolin, which increases intracellular cAMP production by adenylate cyclase activation, also induced some cell death. When C2-ceramide and forskolin were added together, a strong synergy of these two compounds was observed in the induction of cell death: viability was 84% for cells incubated with C2-ceramide at 5 μmol/L and 71% with forskolin at 1 mmol/L, but was reduced to 34% when these two compounds were added together. In contrast, forskolin did not synergize with A23187 nor C2-ceramide with A23187. Similar data were obtained with Ramos cells. These results indicate that the CD77-induced second messengers can cause BL cell death by themselves. Most interestingly, these results also suggest that accumulation of cAMP and activation of PKA may not be sufficient signaling events in the apoptosis of CD77+ cells, but that they become highly efficient in conjunction with C2-ceramide.
Effect of C2-ceramide, calcium ionophore, and forskolin on viability of the CD77+ Daudi BL cells. Cells were cultured for 24 hours with various concentrations of C2-cer (from 5 to 30 μmol/L), calcium ionophore A23187 (from 0.1 to 5 μmol/L), or forskolin (0.5 and 1 mmol/L) and also with combinations of these molecules: C2-cer (5 μmol/L) + forskolin (1 mmol/L), A23187 (0.1 μmol/L) + forskolin (1 mmol/L), and C2-cer (5 μmol/L) + A23187 (0.1 μmol/L). The percentage of cell viability was obtained by propidium iodide (PI) staining and FACS analysis.
Effect of C2-ceramide, calcium ionophore, and forskolin on viability of the CD77+ Daudi BL cells. Cells were cultured for 24 hours with various concentrations of C2-cer (from 5 to 30 μmol/L), calcium ionophore A23187 (from 0.1 to 5 μmol/L), or forskolin (0.5 and 1 mmol/L) and also with combinations of these molecules: C2-cer (5 μmol/L) + forskolin (1 mmol/L), A23187 (0.1 μmol/L) + forskolin (1 mmol/L), and C2-cer (5 μmol/L) + A23187 (0.1 μmol/L). The percentage of cell viability was obtained by propidium iodide (PI) staining and FACS analysis.
DISCUSSION
In a previous report, we showed that VT-B, a specific ligand of the Gb3/CD77 antigen, induced apoptosis of BL cells.16 In the present work, we first show that anti-CD77 MoAb are also able to cause apoptosis of BL cells and then demonstrate that various second messenger molecules are produced in response to ligation of the CD77 antigen.
To evaluate the potency of the CD77 signaling for apoptosis, we have first compared the effects of anti-CD77 and anti-human IgM MoAb, cross-linked or not, on the viability of BL cells. We show that soluble anti-CD77 MoAb are very weak inducers of apoptosis, whereas soluble anti-IgM are slightly more efficient; we also show that cross-linking of both antigens increase their ability to transduce a death signal. Similar potentiation of anti-IgM to induce apoptosis of BL cells, after cross-linking of the MoAb by secondary Ab, were previously reported.15,20 Considering that we observed induction of apoptosis by soluble VT-B, we were surprised by the inefficiency of the soluble anti-CD77 MoAb. The precise reason for this discrepancy in effects between the two molecules is unclear. However, because it has been shown that signal transduction through any ligand-receptor complex is greatly influenced by the affinity of the interacting molecules (as demonstrated, for example, for membrane IgM23 ), it is worth noting that Verotoxin has a very high affinity for Gb3/CD77 (affinity constant [Ka] = 5 × 109/mol/L24), whereas 38.13 has a much lower affinity (Ka of about 5 to 8 × 107/mol/L; our unpublished results, June 1984). From these data, we conclude that CD77 antigen, although less potent that membrane IgM, is able to transduce a signal leading to apoptosis. It must also be underlined that the process is much slower in the case of CD77 than it is for IgM.
We then sought to determine what signal transduction pathway is involved in this CD77-mediated apoptosis of BL cells. We have found that ligation of CD77 induces, within minutes, (1) a sustained influx of Ca2+, (2) a transient increase of the intracellular cAMP concentration and of PKA activity, and later on (3) a transient increase in ceramide concentration. Furthermore, we have also obtained evidence that strongly suggests that cAMP and ceramide synergize to cause cell death.
Several studies have shown that modification of the intracellular Ca2+ level is a relatively common trigger for apoptosis; Ca2+ ionophores, which artificially raise the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration, were shown to induce apoptosis in group I BL cells15 as well as in various other cells.25 Most importantly, numerous investigators have observed that the earliest detectable change in cells undergoing apoptosis is a rapid and sustained increase in intracellular Ca2+ level.6 Therefore, our results showing that the anti-CD77 MoAbs or VT-B induced such an increase suggested that this second messenger might be an important mediator of CD77-mediated cell death. Our observation that the Ca2+ chelator EGTA, which prevents the Ca2+ influx, reduced the cell death induced by the 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb substantiates this hypothesis.
Studies of transduction pathways also identified the cAMP signaling system as an important second messenger in controlling apoptosis. It was first shown that membrane-permeant cAMP analogues and agents that induce an increase in endogenous cAMP levels promote cell death in various cells.26,27 Other studies also showed that cAMP may be involved in the CD3- and CD2-mediated apoptosis of human thymocytes,28 in the spontaneous apoptosis of GC B lymphocytes,29 and in the apoptosis of BL cells.30 Our results indicating that ligation of CD77 causes a rapid and transient increase in intracellular cAMP concentration certainly reinforce the notion that this second messenger is involved in the regulation of apoptosis in GC B lymphocytes and in BL cells that express the CD77 antigen.
The generation of cAMP in cells activates one or more PKA isoforms, and thereafter these serine/threonine protein kinases mediate many of the effects of cAMP through phosphorylation of target proteins. In earlier studies, McConkey et al27 suggested that cAMP, through PKA activation, mediates DNA fragmentation in thymocytes. Vintermyr et al31 showed that microinjection of catalytic PKA subunit induces apoptosis in a myeloid leukemia cell line. In this report, we show that ligation of CD77 antigen induces a clear increase in PKA activity, with the kinetics of activation of this enzyme slightly retarded compared with the cAMP accumulation. To our knowledge, our report is the first to demonstrate that ligation of a cell surface antigen that leads to apoptosis of the cells involves a cAMP-mediated activation of PKA.
Since the elucidation of the sphingomyelin cycle which produces ceramide, numerous investigators have shown that this signal transduction pathway is involved in cell growth, in cell differentiation, and in apoptosis. Various studies have shown, for example, that TNFα or Fas/CD95-induced apoptosis are mediated by way of sphingomyelin degradation and generation of ceramide caused by the activation of a sphingomyelinase.7,32 On the other hand, Bose et al33 have described another mechanism where generation of ceramide in daunorubicin-induced apoptosis is caused by activation of ceramide synthase.
In this report we show that ligation of CD77 induces accumulation of ceramide; but we also observe that the ceramide production is not paralleled by any decrease in sphingomyelin concentration, and therefore probably does not result from the hydrolysis of this compound. Furthermore, we also show that this increased ceramide is apparently not produced by the hydrolysis of the Gb3/CD77 antigen. It thus seems rather likely that ligation of the CD77 antigen may increase ceramide synthase activity, and this possibility will be tested in future.
Because, in this study, cAMP and ceramide were generated by soluble 38.13 MoAb, which induce apoptosis only poorly, the role of these two molecules in the apoptotic process could be questioned. Although we have preliminary evidence that VT-B also induces an increase in the concentrations of these molecules, and although it is generally admitted that cross-linking of MoAb does not greatly modify the nature of the second messenger molecules produced (in comparison to soluble MoAb), we have tested the effect of increasing the intracellular concentration of cAMP and ceramide (and of Ca2+), independently or in combination, on the viability of CD77+ BL cells.
We show that C2-ceramide and calcium ionophore A23187 strongly induce apoptosis, whereas forskolin, even at high doses, only slightly reduced cell viability. Moreover, we show that C2-ceramide and forskolin act synergistically for induction of apoptosis in CD77+ BL cells. These results indicate that the second messengers generated by triggering of CD77 are able to cause apoptosis of the BL cells, therefore suggesting that these molecules could be part of the intracellular signaling pathway responsible for CD77-mediated apoptosis. Most importantly, these results also indicate that accumulation of cAMP and of ceramide, in the same cell, potentiate their respective apoptotic capacities. One can therefore hypothesize that CD77-mediated apoptosis involves the cooperation of the various kinases activated by these two molecules. Whether these kinases phosphorylate the same target protein(s) or complementary proteins remain to be determined. Interestingly, a recent report indicates that the synergistic effect of TNFα and interleukin-1β on the downregulation of the M2 muscarinic receptor is also mediated through activation of both ceramide and cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathways.34
Recently a model has been proposed to explain the role of ceramide and other lipid second messengers during proliferation and apoptosis.35 Ceramide would act through activation of the SAPK/JNK and inhibition of the MAPK/ERK pathways,21,36 which are known to be involved in apoptosis,37 whereas sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate, which are metabolites of ceramide, could induce mitogenesis by stimulation of ERK and inhibition of SAPK/JNK. PKC would also be involved in these pathways, because ceramide inhibited its kinase activity,38 and because activation of PKC resulted in an accumulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate.35 Because we provide evidence of a synergy between ceramide and PKA, one can now suggest that PKA probably does not belong to these signaling cascades but rather to a pathway which, nevertheless, at certain point cooperates with the ceramide pathway to enhance the cell death signal. In our model of CD77-mediated apoptosis, it may therefore be hypothesized that the effects of the early activation of PKA are, thereafter, somehow amplified by the ceramide accumulation, perhaps through the SAPK/JNK signaling cascade.
To our knowledge, CD77 was the first glycolipid antigen shown to transduce a signal leading to apoptosis; but numerous previous reports have shown that glycolipids act as transmembrane signaling molecules.39 Recently, it has been shown that the B subunit of Cholera toxin, which binds specifically to GM1 ganglioside, provokes an increase of [Ca2+]i in various types of cells.40,41 Furthermore, it was shown that the B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin, which also binds to GM1, induces the selective apoptosis of mature CD8+ T lymphocytes.42 These results suggest that GM1, like CD77, may mediate a functional activation signal involving a rapid increase in Ca2+ concentration and leading to apoptosis in certain cases. On the other hand, a study by Chatterjee et al43 has shown that anti-GM3 MoAb trigger differentiation of Neuro-2a cells mediated by an induction of adenylate cyclase activity and cAMP accumulation. These results certainly reinforce the notion that glycolipids, such as CD77, are functional cell surface receptors.
What could be the physiological role of CD77? Today, it is now clearly established that death by apoptosis is the fate of the centrocytes that fail to be positively selected during affinity maturation.4,44 During this process, germinal center B cells randomly diversify their Ig genes by a somatic hypermutation mechanism, after which high affinity variants are positively selected. In contrast, the B lymphocytes in which somatic mutations give rise to nonfunctional or low affinity Ig or to autoreactive antibodies must be eliminated. A recent report, where the Ig heavy chain variable region genes from five tonsillar B cell populations were analyzed, indicates that this process of somatic mutation is ongoing in cells which express CD77 antigen.45 To explain this selection mechanism, one could hypothesize that the signal generated by the antigen-antibody interaction is a component of a process involving a balance of stimuli. In that case, all the cells to be selected would be submitted to a negative signal, and only a potent signal caused by the interaction between high affinity receptors and foreign antigens held on follicular dendritic cells would be able to rescue them. Our results suggest that CD77 could be one of the candidates for the negative signal receptor. Further studies on the CD77-mediated signal transduction pathway and a search for the natural ligand of CD77 will be needed to obtain new insights into the physiological function of CD77.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Dr Elisabeth Sweeney for her help in the lipid studies and Drs Marc Lipinski and Pierre Busson for helpful discussions.
Supported in part by grants from the Ligue Nationale Française contre le Cancer and the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC 6915). S.T. is a recipient of a fellowship from the Ligue Nationale Française contre le Cancer.
Address reprint requests to Joëlle Wiels, Laboratoire de Biologie des Tumeurs Humaines, CNRS URA 1156, Institut G. Roussy, 39, rue Camille Desmoulins, 94805 Villejuif Cedex, France.

![Fig. 2. Kinetics of intracellular Ca2+ changes in BL cells treated by various ligands of CD77 antigen. CD77+ Ramos cells were stimulated by 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL), 5B5 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL), VT-B (5 ng/mL), or by HJ6 anti-Gb4 MoAb (10 μg/mL). CD77− Namalwa cells were stimulated by 38.13 anti-CD77 MoAb (10 μg/mL). Ramos cells were also incubated with 2.5 mmol/L EGTA or 25 μg/mL Verapamil before stimulation by 38.13 MoAb. Intracellular Ca2+ was measured using indo-1 indicator. Results are representative of six different experiments. The basal [Ca2+]i, before addition of 38.13 MoAb, was 230 ± 50 nmol/L (mean ± SD, 50 cells) and the [Ca2+]i rise can reach a peak of 540 ± 30 nmol/L.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/90/7/10.1182_blood.v90.7.2757/3/m_bl_0035f2.jpeg?Expires=1763698679&Signature=fQukxVTZ5P9unUeUQV9RQxt0DLjXHWNUT27J4MSjZc2oozQSlswpuTpx8xzzXjYSzrkuYeuebF0yaPbQBjB-6geX-RziyyzppkEz6jt3I7pq62nwPnCsFojgDtkariSxYfTtXsGCRVEYF7-jmOcPKa5akly1dMl6T-4xxigF7VHkU2GterM5DTpuCfXrC4T-StyAh4hqSukJpnyOPjWmjrN~i98a2T9-6-EFR8DrKo6M6qYPw5Ek6nNXtQh1~ii3dT4R~XkWxO2Y1ehxGJzapyoVcKN9KTfHWZMKbVWreTHQJr97bIgjuuT9BpCKcPWffmKgSEL0AsaIL81BzumU6Q__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal