Abstract
A new mutation is described in the X-linked geneGATA1, resulting in macrothrombocytopenia and mild dyserythropoietic features but no marked anemia in a 4-generation family. The molecular basis for the observed phenotype is a substitution of glycine for aspartate in the strictly conserved codon 218 (D218G) of the amino-terminal zinc finger loop of the transcription factor GATA1. Zinc finger interaction studies demonstrated that this mutation results in a weak loss of affinity of GATA1 for its essential cofactor FOG1, whereas direct D218G-GATA1 binding to DNA was normal. The phenotypic effects of this mutation in the patients' platelets have been studied. Semiquantitative RNA analysis, normalized for β-actin messenger RNA, showed extremely low transcription of the GATA1 target genes GPIbβ and GPIXbut also a significantly lower expression of the nondirectly GATA1-regulated Gsα gene, suggestive of incomplete megakaryocyte maturation. In contrast, GPIIIa expression was close to normal in agreement with its early appearance during megakaryocyte differentiation. Flow cytometric analysis of patient platelets confirmed the existence of a platelet population with abnormal size distribution and reduced GPIb complex levels but with normal GPIIIa expression. It also showed the presence of very immature platelets lacking almost all membrane glycoproteins studied (GPIbα, GPIbβ, GPIIIa, GPIX, and GPV). Patients' platelets showed weak ristocetin-induced agglutination, compatible with the disturbed GPIb complex. Accordingly, electron microscopy of the patients' platelets revealed giant platelets with cytoplasmic clusters consisting of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and abnormal membrane complexes. In conclusion,GATA1 mutations can lead to isolated X-linked macrothrombocytopenia without anemia.
Introduction
X-linked thrombocytopenia is a well-known clinical condition, found most often in the context of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) and consisting of thrombocytopenia, defective humoral and cellular immunity, and eczema. Mutations in the WASPgene lead either to the full-blown WAS picture or to isolated X-linked thrombocytopenia.1 The platelets in this syndrome are typically small sized. However, hereditary macrothrombocytopenia with or without associated thrombopathy has been identified in a variety of syndromes, such as the May-Hegglin anomaly, Bernard-Soulier syndrome, Fechtner syndrome, or Epstein syndrome.2 Very recently, the May-Hegglin anomaly and Fechtner syndrome have been linked to mutations in the nonmuscle myosin heavy chain 9 gene on chromosome 22.3 4 Patients with X-linked macrothrombocytopenia are not well recognized.
GATA1 is the founding member of the GATA-binding family of transcription factors and has been shown to be an essential protein for normal erythropoiesis and megakaryocyte differentiation.5,6 The human gene encoding GATA1 has been mapped to Xp11.23.7 Shivdasani et al8developed a lineage-selective knockout mouse of GATA1, leading to megakaryocyte-specific loss of GATA1 expression and established the critical role of this transcription factor for megakaryocyte growth and platelet development. Vyas et al9 further characterized the macrothrombocytopenia in these mice with abnormal platelet number and platelet ultrastructure and moderate defects in platelet activation.
Very recently Nichols et al10 described for the first time a mutation in the GATA1 gene in a family with X-linked dyserythropoietic anemia and macrothrombocytopenia. This missense mutation (V205M) leads to a reduced interaction of the N-terminal zinc finger of GATA1 with its essential cofactor FOG1 (for Friend of GATA1).
Here we describe a family with another mutation in the same zinc finger of GATA1, showing pronounced X-linked macrothrombocytopenia and some features of dyserythropoiesis but with no marked anemia. We describe the hematologic features of the affected members and of the female carriers. Moreover, the influence of the GATA1 mutation on FOG1 and DNA binding, on platelet function, and on the expression of platelet-specific glycoproteins is studied.
Patients, materials, and methods
Electron microscopy of platelets
Platelet-rich fractions were available from 5 affected patients (V:3, V:7, V:8, V:15, and V:16) and from one female carrier (IV:4) as well as from 2 normal controls. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was prepared by centrifugation (15 minutes at 150g) of whole blood anticoagulated with 3.8% (wt/vol) trisodium citrate (9:1). The platelet-rich fractions were immediately fixed overnight at 4°C in 2.5% glutaraldehyde, 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.2. After centrifugation at 800g for 10 minutes, a condensed pellet of platelets was formed. After postfixation in 1% OsO4, 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.2 and dehydration in graded series of ethanol, the pellets were embedded in epoxy resin. Ultrathin sections were cut, stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and examined in a Zeiss EM 10 electron microscope (Oberkochen, Germany).
RNA isolation and complementary DNA synthesis
Total RNA was extracted from platelets using the TRIzol (Gibco BRL, Gaithersburg, MD) reagent according to the manufacturer's protocol. Total platelet RNA was first treated with DnaseI, Amplification grade (1 U/μg RNA; Gibco BRL) before reverse transcription using the oligo (dT)-primed first strand complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis kit with M-MLV reverse transcriptase (RT; Gibco BRL).
Genetic analysis of GATA1
GATA1 cDNA was amplified using primers GATA1-F1 (ATCCCCAGAGGCTCCATGGAG) and GATA1-R1 (TCTGTGCCCTCATGAGCTGAGCG). Primer GATA1-R2 (GTTTACTGACAATCAGGCGCTTC) was used for sequencing by the BigDye terminator chemistry (Perkin-Elmer Cetus, Norwalk, CT) on an ABI310 (PerkinElmer) sequencer of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-generated cDNA fragments from patients and controls. A genomic sequence from chromosome Xq11.23 (accession No. AF196971) included theGATA1 gene. The region including exon 4 of the humanGATA1 gene was amplified and sequenced with the primers GATA1-ex4U (GCCAGGGAGTGTGTGAACTG) and GATA1-ex4R (GTCTTACCAGGCGCTTCTTG). Genomic DNA from 72 normal females was screened for the presence of the 653 A→G (D218G) mutation by single-stranded conformation polymorphism analysis.
Statistical analysis
Lod scores were calculated using the MLINK program of the Fastlink package (version 4.1P) for an X-linked recessive disorder and with conservative assumptions: allele-frequency of 1/10 000 for the disease mutation.11
Glutathione-S-transferase fusion protein/FOG1 binding assay
GATA1 Nf, GATA1 Nf D218G, and GATA1 Nf V205M (residues 197-251) fragments were generated by PCR, confirmed by DNA sequencing, and cloned in the expression vector pGEX-4T-2 (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden). Different FOG1 fragments [consisting of finger 1 (241-291), fingers 5 to 7 (587-867), finger 9 (948-997), and fingers 5 to 9 (587-997)] were cloned in pcDNA3.1/His (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA), and S35-labeled FOG1 was produced by in vitro transcription/translation using the TNT system (Promega, Madison, WI). Primer sequences are available on request. In vitro binding studies were done as described previously.12 13
Glutathione-S-transferase fusion protein/DNA binding assay
A 29–base pair (bp) double-stranded DNA oligonucleotide containing the mouse α-globin GATA site (GATCTCCGGCAACTGATAAGGATTCCCTG) was 5′ end biotinylated.13Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) fusion proteins (1 μg) were incubated in binding buffer (150 mM NaCl, 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 0.1% Igepal, 10 μM ZnSO4, 0.25% bovine serum albumin [BSA], 1 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 1.5 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride [PMSF]) containing 100 nM biotinylated DNA in the absence or presence of competing nonbiotinylated oligonucleotide (0-3.2 μM) for 1 hour at room temperature. After washing the GST fusion proteins coupled Sepharose beads 3 times in 1 mL binding buffer, the bound biotinylated oligonucleotide was detected by complex formation with streptavidin- and biotin-substituted horseradish peroxidase (ABC detection kit; DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark).14
Semiquantitative RT-PCR
The cDNA content was normalized by using primers for β-actin. The following primer sets were used to generate specific fragments: β-actin beta5F (ACCAACTGGGACGACATGGAG) and beta3R (CGTGAGGATCTTCATGAGGTAGTC), GPIbβ beta1F (TGCAAGCTTCTCGCCATGGGCTCCGGGCCG) and beta1R (GGCTGCTCAGGACTCCTCTCCTTAAGACG), GPIX IX1F (GAGGGATCCTGTCCCATGCCTGCCTGGGG) and IX1R (CTCCGGGACCTAACTCGGTCCCCATGGCTT), and Gsα GNASF (GGCTGCCTCGGGAACAGTAAG) and GNASR (TAATCATGCCCTATGGTGGGTG). For GPIbβ and GPIX, a nested PCR reaction was performed with the following external primer sets: for GPIbβ beta2F (ACGCCTCCCGCTGCAGAGTAAG) and beta2R (GTTTGCAGGCCCGTGTTGCCC), and for GPIX IX2F (GGAGAAGGCTGAGACCCGAG) and IX2R (GGACCTGCCTCAGGGACTGG). All reactions were performed in duplicate on RNA samples without added RT during cDNA synthesis, generating no reaction products (data not shown).
Platelet immunoblot analysis
Platelets isolated from citrated blood were directly lysed in ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 1% Igepal CA-630 (Sigma Chemical, St Louis, MO), 2 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM PMSF, 2 mmol/L dithioerythritol (DTE), 1% aprotinin, and 2 mM NaF. The samples were then briefly sonicated (2 times for 10 seconds) and incubated on ice for 60 minutes. Lysates were cleared of insoluble debris by centrifugation at 14 000gfor 20 minutes at 4°C. Platelet protein fractions were mixed with Laemmli sample buffer (5% sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS] reducing buffer), resolved by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) on 7% (for GPIbα), 12.5% (for GPIbβ), or 10% (for Gsα) acrylamide gels, and transferred to Hybond ECL-nitro-cellulose membrane (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech). The blots were blocked for 1 hour at room temperature in Tris-buffered saline with Tween (TBS-T; 0.1% Tween-20) supplemented with 5% nonfat dry milk. Incubation with primary (overnight at 4°C) and secondary antibody (2 to 3 hours at room temperature) was performed in TBS-T with 5% nonfat milk. The primary antibodies used were produced in our laboratory and used at 50 μg/mL. Blots were revealed with a monoclonal anti-Gsα antibody (α3), a monoclonal anti-GPIbα antibody (G27C9), or a polyclonal anti-GPIbβ antibody. The secondary antibody was conjugated with horseradish peroxidase, and staining was performed with the Western blotting enhanced chemiluminescence detection reagent (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech).
Flow cytometric analysis of platelet GPIb/GPIIIa in PRP
PRP from citrated blood was prepared as described above, and 10 μL was diluted with 40 μL PBS in the presence of a GPIIb/IIIa antagonist (G4120; 1 μg/mL; Genentech, San Francisco, CA) to prevent platelet aggregate formation and a monoclonal antibody (30 μg/mL, except for Ib9D5, 50 μg/mL). The GPIbα-directed monoclonal antibody G27C9, an anti-GPIIIa monoclonal antibody 16N7C2, an anti-GPIbβ monoclonal antibody Ib9D5, and a platelet nonspecific anti-GST monoclonal antibody were made in our laboratory.15 After incubation for 15 minutes at room temperature, samples were centrifuged for 10 minutes at 2000g, and platelets were resuspended in 50 μL PBS/G4120 with a secondary fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated goat antimouse antibody. After incubation for 15 minutes at room temperature, 500 μL PBS was added, and samples were analyzed in a flow cytometer (FACS Calibur; Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA).
Flow cytometric analysis of platelet GPIb/GPIIIa in whole blood
Citrated blood (15 μL) was incubated with 40 μL PBS/G4120 and specific primary antibodies as described above. After incubation with a secondary FITC-conjugated goat antimouse immunoglobulin antibody, samples were centrifuged and resuspended in 30 μL PBS/G4120 with simultaneous addition of perCP-conjugated monoclonal anti-GPIIIa antibody (CD61) to recognize the platelet population. Samples were incubated for 15 minutes, and 500 μL PBS was added before analysis by FACS.
Platelet aggregation
Blood was obtained from drug-free healthy donors and from patients V:3, V:7, and V:8 and anticoagulated with 3.8% (wt/vol) trisodium citrate (9:1) or acid citrate dextrose (ACD), pH 6.5 (9:1). PRP/ACD, obtained as described above by centrifugation (15 minutes at 150g), was recentrifuged in an equal volume ACD (1000g for 15 minutes) to concentrate the platelets, and the pellet was resuspended in autologous platelet-poor plasma (PPP-trisodium citrate). The platelet count was adjusted to 130 000 platelets/μL PPP. In vitro platelet aggregation was performed on a Chrono-Log Aggregometer (Chronolog, Havertown, PA) by simultaneously recording 2 tracings. Aggregation studies involved addition of collagen (2 μg/mL) or ristocetin (1.3 mg/mL) with or without 1 minute preincubation with a neutralizing monoclonal anti-GPIbα antibody (G19H10, 15 μg/mL).16
Results
Patient description and hematologic analysis
The propositus (patient V:3; Figure1) is a 41-year-old man with congenital thrombocytopenia. A bone marrow examination performed at the age of 2 years revealed increased megakaryocytosis, which led at that time to the diagnosis of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenia. He received treatment with steroids, resulting in a small and transient rise in platelet number. Throughout life he experienced mucocutaneous bleeding, spontaneously or after minor trauma. He underwent surgery for evacuation of a muscular hematoma and was once hospitalized for hematuria.
Pedigree of affected family, light microscopy of red blood cells, and electron microscopy of platelets.
(A) Patients with the X-linked thrombocytopenia are represented by filled symbols, female carriers by dotted circles. (B) Light microscopy (magnification × 1000) of dysmorphic red blood cells in peripheral blood smear of affected patient after May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining, showing anisocytes, poikilocytes, megalocytes, and acanthocytes. (C) Electron microscopy (magnification × 12 600) of platelets. Left panel: platelets of a normal individual. Discoid platelets and more round forms with normal organelles and granules. Right panel: platelets of affected patient (representative of the 6 patients studied). Enlarged round platelet showing a cytoplasmic cluster composed of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and abnormal membrane complexes. Note paucity of alpha granules.
Pedigree of affected family, light microscopy of red blood cells, and electron microscopy of platelets.
(A) Patients with the X-linked thrombocytopenia are represented by filled symbols, female carriers by dotted circles. (B) Light microscopy (magnification × 1000) of dysmorphic red blood cells in peripheral blood smear of affected patient after May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining, showing anisocytes, poikilocytes, megalocytes, and acanthocytes. (C) Electron microscopy (magnification × 12 600) of platelets. Left panel: platelets of a normal individual. Discoid platelets and more round forms with normal organelles and granules. Right panel: platelets of affected patient (representative of the 6 patients studied). Enlarged round platelet showing a cytoplasmic cluster composed of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and abnormal membrane complexes. Note paucity of alpha granules.
The family history (Figure 1A) was compatible with X-linked thrombocytopenia with patients V:7, V:8, V:13, V:14, V:15, V:16, V:17, V:20, V:23, and VI:6 known with chronic macrothrombocytopenia in various hematologic departments. The clinical features of V:7 and V:8 have been described previously in abstract form.17
More detailed hematologic data of some affected family members, obligate carriers, and a healthy family member are listed in Table 1. Thrombocytopenia is not accompanied by anemia, and white blood cell counts and differential counts were completely normal. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate, when measured, was uniformly low.
Hematologic profiles of affected family members (V:3, V:7, V:8, and V:16), obligate carriers (IV:4, IV:1, and VI:5), and a healthy family member (V:6)
| . | Hgb (g/dL) (10.5-16) . | Hct (%) (35-45) . | RBCs (× 106/μL) (3.9-5.2) . | RDW (%) (11.5-14.5) . | LDH (U/L) (150-460) . | Plts (× 103/μL) (150-400) . | ESR (mm/h) . | HgbF (%) (0-2) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V:3 | 13.4 | 44 | 4.38 | 15.7 | 1607 | 12, 20, 35 | 0-1 | 0.88 |
| V:7 | 14.1 | 44 | 4.83 | 15.0 | 36 | |||
| V:8 | 13.5 | 41 | 4.5 | 15.1 | 12 | |||
| V:16 | 12.4 | 39 | 4.36 | 32, 53, 72 | 2 | |||
| IV:4 | 12.6 | 39 | 4.31 | 13.3 | 297 | 0.66 | ||
| IV:1 | 11.8 | 39 | 4.28 | 13.7 | 326 | |||
| VI:5 | 10.4 | 33 | 3.77 | 13.9 | 230 | |||
| V:6 | 14.4 | 43.8 | 4.98 | 348 |
| . | Hgb (g/dL) (10.5-16) . | Hct (%) (35-45) . | RBCs (× 106/μL) (3.9-5.2) . | RDW (%) (11.5-14.5) . | LDH (U/L) (150-460) . | Plts (× 103/μL) (150-400) . | ESR (mm/h) . | HgbF (%) (0-2) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V:3 | 13.4 | 44 | 4.38 | 15.7 | 1607 | 12, 20, 35 | 0-1 | 0.88 |
| V:7 | 14.1 | 44 | 4.83 | 15.0 | 36 | |||
| V:8 | 13.5 | 41 | 4.5 | 15.1 | 12 | |||
| V:16 | 12.4 | 39 | 4.36 | 32, 53, 72 | 2 | |||
| IV:4 | 12.6 | 39 | 4.31 | 13.3 | 297 | 0.66 | ||
| IV:1 | 11.8 | 39 | 4.28 | 13.7 | 326 | |||
| VI:5 | 10.4 | 33 | 3.77 | 13.9 | 230 | |||
| V:6 | 14.4 | 43.8 | 4.98 | 348 |
All individuals have normal MCV and MCH values. Normal values are shown in parentheses.
Hgb indicates hemoglobin; Hct, hematocrit; RBCs, red blood cells; RDW, red blood cell distribution width; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; Plts, platelets; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; HgbF, fetal hemoglobin.
Peripheral blood smears of affected patients invariably demonstrated giant platelets and dysmorphic red blood cells (anisocytes, poikilocytes, megalocytes, and acanthocytes are shown in Figure 1B). Platelet survival, measured in 2 patients using homologous indium111–labeled platelets, showed a normal life span. Light microscopy of the bone marrow of patients V:7 and V:8 revealed normoblasts with punctate basophilia, karyorhexis, budding, and pycnosis. The megakaryocytes appeared dysplastic, with megakaryoblasts, micromegakaryocytes, vacuolization of cytoplasma, and asynchronous maturation of nucleus and cytoplasma. The bone marrow examinations of V:3, V:14, and V:15 only evidenced increased megakaryocytosis.
Electron microscopy of the platelets of affected patients V:3, V:7, V:8, V:15, V:16, and V:17 revealed increased platelet size; furthermore, platelets were rounder than the characteristic discoid shape of normal platelets (Figure 1C). In addition, in a high number of these platelets, clusters composed of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and abnormal membrane complexes were seen in the center and in the periphery of their cytoplasm. A paucity of alpha granules was obvious. The platelets of the female carrier IV:4 (data not shown) did not show abnormalities and were comparable to the controls.
Single amino acid substitution in the N-terminal zinc finger of GATA1
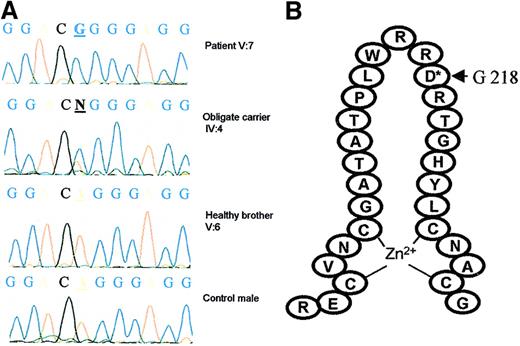
We first studied, in the 2 branches of this family, the segregation of polymorphic markers located around GATA1 and observed identical haplotypes in family members V:7 and V:17 (data not shown). We next sequenced the GATA1 cDNA and found a hemizygous base pair substitution (A to G) at nucleotide position 653 in 2 affected brothers (V:7 and V:8). The mother (IV:4), who is an obligate carrier, is heterozygous for the missense mutation, and the healthy brother has a normal sequence (Figure 2A). The mutation was confirmed on genomic DNA and screened in all available family members. The affected family members V:3, V:14, V:17, and V:20 and the obligate carriers IV:1, IV:21, and V:21 were also respectively hemizygous and heterozygous for the GATA1 mutation. The unaffected male V:6 did not carry the mutation, neither did we detect the 653 A→G substitution in peripheral blood leukocyte DNA from 72 normal females (data not shown).
Mutational analysis of GATA1.
(A) Sequencing analysis of GATA1 cDNA in patient V:7, obligate carrier IV:4, a healthy brother V:6, and a control male. A base pair substitution A to G was found at nucleotide position 653 in V:7 (hemizygous) and IV:4 (heterozygous). (B) This mutation results in a replacement of aspartate for glycine at position 218, located in the loop of the amino-terminal GATA1 zinc finger.
Mutational analysis of GATA1.
(A) Sequencing analysis of GATA1 cDNA in patient V:7, obligate carrier IV:4, a healthy brother V:6, and a control male. A base pair substitution A to G was found at nucleotide position 653 in V:7 (hemizygous) and IV:4 (heterozygous). (B) This mutation results in a replacement of aspartate for glycine at position 218, located in the loop of the amino-terminal GATA1 zinc finger.
These data enable us to calculate a maximal 2-point lod score of 2.804 at no recombination, thereby proving cosegregation of the D218G mutation with X-linked thrombocytopenia in this family.
GATA1-FOG1 and GATA1-DNA binding studies
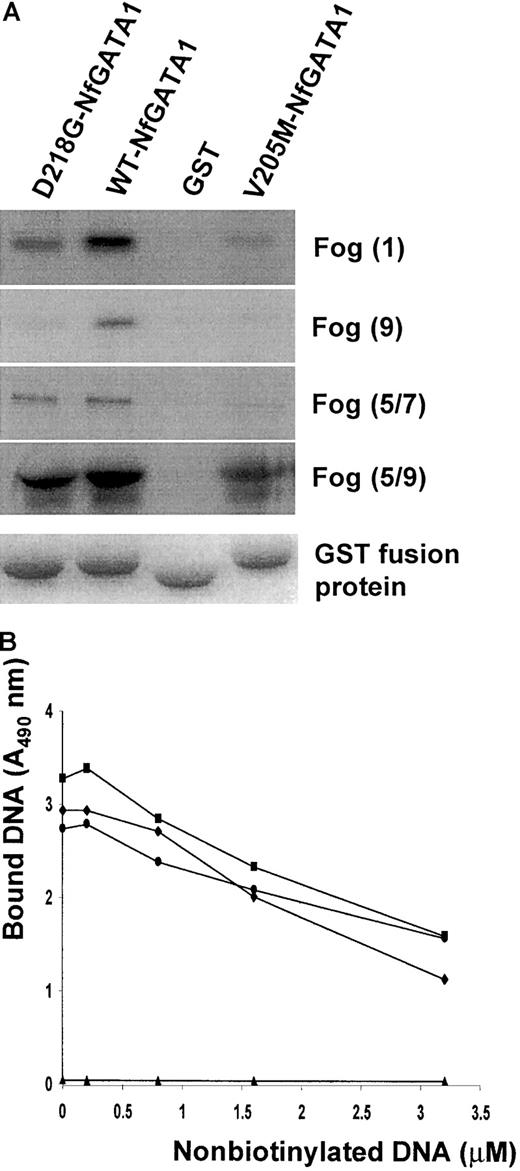
GATA1-FOG1 interaction experiments were performed to study the effect of the D218G mutation in GATA1 on the binding to its cofactor FOG1. We studied the binding between the N-terminal zinc finger of GATA1 and different FOG1 fingers known to be important in GATA1 recognition.19 The recently reported GATA1 mutant V205M was also produced and tested as a control in our assay.10The wild-type GATA1 N finger/GST (197-251) was able to sequester almost all input in vitro translated FOG1 in contrast to the mutant N fingers (Figure 3A). The D218G mutant has a weaker affinity for all FOG1 fingers compared to the wild-type GATA1 but clearly interacts more strongly than the V205M mutant. Control GST-bound beads were unable to bind any FOG1.
GATA1/FOG1 and GATA1/DNA interaction studies.
(A) Different in vitro transcription/translated FOG1 fingers (finger 1, finger 9, fingers 5 to 7, and fingers 5 to 9) were incubated with various GST fusion proteins (GATA1 Nf-D218G, GATA1 Nf, and GATA1 Nf-V205M) or with GST immobilized on glutathione agarose beads. After washing the beads, bound proteins were eluted and resolved by SDS-PAGE. The autoradiogram in the top panel shows the amount of retained S35-labeled FOG1. The lower panel shows the Coomassie blue staining of the gel confirming equal GST fusion protein sample loading. (B) DNA binding competition assay (representative for 3 experiments). The amount of biotinylated DNA (100 μM) bound by GST/GATA1 fusion proteins was plotted against the concentration of nonlabeled competitor DNA. Control GST-bound beads (▴) gave no DNA binding. ♦, WT-NfGATA1; ▪, D218G-NfGATA1; ●, V205M-NfGATA1.
GATA1/FOG1 and GATA1/DNA interaction studies.
(A) Different in vitro transcription/translated FOG1 fingers (finger 1, finger 9, fingers 5 to 7, and fingers 5 to 9) were incubated with various GST fusion proteins (GATA1 Nf-D218G, GATA1 Nf, and GATA1 Nf-V205M) or with GST immobilized on glutathione agarose beads. After washing the beads, bound proteins were eluted and resolved by SDS-PAGE. The autoradiogram in the top panel shows the amount of retained S35-labeled FOG1. The lower panel shows the Coomassie blue staining of the gel confirming equal GST fusion protein sample loading. (B) DNA binding competition assay (representative for 3 experiments). The amount of biotinylated DNA (100 μM) bound by GST/GATA1 fusion proteins was plotted against the concentration of nonlabeled competitor DNA. Control GST-bound beads (▴) gave no DNA binding. ♦, WT-NfGATA1; ▪, D218G-NfGATA1; ●, V205M-NfGATA1.
Similar binding studies using GST fusion proteins of either wild-type or mutant GATA1 N fingers were performed to assess the effect of the D218G mutation on direct GATA1 DNA binding. The classical electrophoretic mobility shift assay (data not shown) as well as an equilibrium DNA competition method revealed no significant impairment of DNA binding in any of the mutants tested (Figure 3B).
Study of platelet gene expression
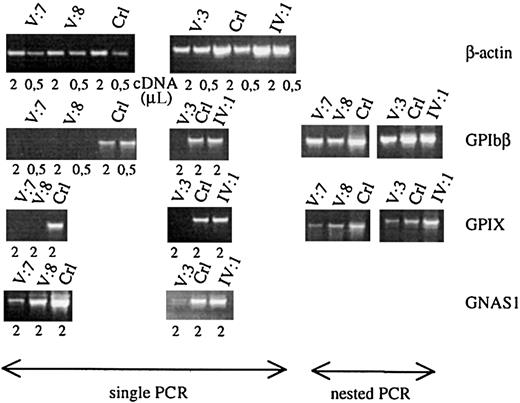
The promoters of many megakaryocyte-expressed genes have a GATA1 recognition site, as is the case for GPIbα, GPIbβ, GPIIb, GPIX, PF4, c-MPL, and p45 NF-E2.20-25 We studied theGPIbβ and GPIX gene expression in the total platelet population of patients V:3, V:7, and V:8 and in the carrier IV:1 and compared it with that of control platelets (Figure4). GATA1-defective platelets indeed showed a strongly decreased GPIbβ and GPIX messenger RNA (mRNA) expression. Only when performing nested PCR reactions, were signals obtained for GPIbβ and GPIX. In contrast, the β-actin normalized expression of GPIIIa was close to normal (data not shown). No abnormalities in expression levels of these glycoprotein mRNAs were seen in the obligate carrier. To study whether this low level of glycoprotein RNA expression is only due to the lack of direct GATA1-FOG1 transcriptional regulation of the genes themselves or also due to a decreased maturation state of the platelets, we also studied the expression of the Gsα gene. This widely expressed gene(GNAS1) is, as far as we know, not a direct transcriptional target of GATA1 but its expression is up-regulated during terminal megakaryocytic maturation. We found a significantly decreased Gsα mRNA expression in the patients' platelets (Figure 4).
Platelet glycoprotein mRNA studies.
Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of the genes for β-actin, GPIbβ, GPIX, and Gsα (GNAS1) using platelet RNA of affected patients (V:7, V:8, and V:3), obligate carrier (IV:1), and controls (Crl). Starting from the same amount of platelet RNA, patients and controls have comparable levels of β-actin expression. All patients have a very weak expression of the GATA1-regulated genesGPIbβ and GPIX, only showing a visible fragment after performing a nested PCR. Patients also show a weaker signal for the nondirectly GATA1-regulated gene GNAS1.
Platelet glycoprotein mRNA studies.
Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of the genes for β-actin, GPIbβ, GPIX, and Gsα (GNAS1) using platelet RNA of affected patients (V:7, V:8, and V:3), obligate carrier (IV:1), and controls (Crl). Starting from the same amount of platelet RNA, patients and controls have comparable levels of β-actin expression. All patients have a very weak expression of the GATA1-regulated genesGPIbβ and GPIX, only showing a visible fragment after performing a nested PCR. Patients also show a weaker signal for the nondirectly GATA1-regulated gene GNAS1.
Platelet membrane glycoprotein studies in PRP
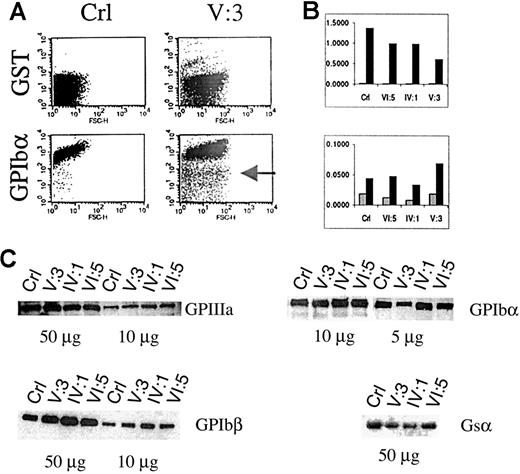
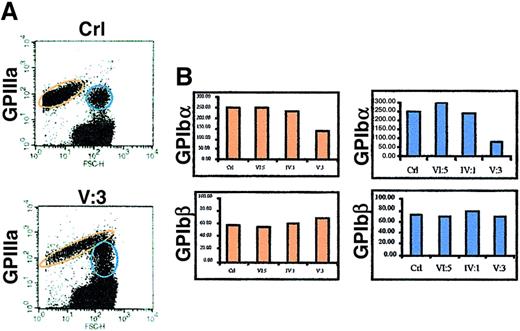
Flow cytometric analysis of platelets in PRP showed that the platelet size in patient V:3 is 2 to 3 times larger than in controls (Figure 5 A). The platelet size of the obligate carriers IV:1 and VI:5 was normal. A series of immunofluorescent labelings were done to compare the expression of GPIbα, GPIbβ, GPIX, GPV, and GPIIIa. Correction for background fluorescence was made using an irrelevant antibody against GST. Most platelets of patient V:3 expressed all glycoproteins although disturbed (see below), but a distinct fraction of the platelets is almost negative for every marker tested, indicating the existence in the circulation of very immature platelets with the same size distribution as the mature platelets (shown for GPIbα in Figure 5A). The membrane distribution of GPIIIa was analyzed versus that of GPIb as a function of the platelet size, and a parallel increase of GPIIIa and GPIb expression with platelet size was found (data not shown). A murine monoclonal antibody against GPIIIa recognized a similar epitope density on platelets of the propositus V:3 as on those from controls, whereas the GPIbα and GPIbβ expressions were abnormal. GPIbα subunit expression was only half of normal and seemed to be slightly reduced in obligate carriers (Figure 5B). Surprisingly, the amount of GPIbβ seemed higher in the propositus than in controls. We also studied the GPIX and GPV expressions but found no significant differences with control platelets. Western blot analysis of the GPIIIa expression confirmed normal GPIIb/IIIa protein, justifying the use of GPIIIa as a parameter to normalize the expression of GPIbα and GPIbβ during FACS analysis (Figure 5C). Furthermore, platelet protein fractions of patient V:3 have more GPIbβ and less GPIbα than control platelets, corroborating the findings presented in Figure 5B. Similar to the gene expression studies, abnormal platelet maturation was analyzed indirectly by studying Gsα expression in the platelets. During normal maturation of megakaryoblastic cells, the large splice variant of Gsα protein (52 kd) is up-regulated.26 However, when we analyzed Gsα expression in patient platelets using a monoclonal antibody (α3) that recognizes specifically this Gsα subtype, we found a weaker signal in patient V:3 and in carrier IV:1 (Figure 5C), again suggestive of incomplete platelet maturation.
Platelet glycoprotein expression analysis in PRP.
(A) Flow cytometry of a platelet nonspecific protein (GST) and GPIbα in the platelets of a control (Crl) or patient V:3. The platelets of V:3 are at least 2 to 3 times larger than control platelets, and a subgroup seems immature with very low levels of GPIbα (indicated by an arrow). (B) Normalized (versus GPIIIa expression) FACS results for the expression of GST, GPIbα, and GPIbβ in control (Crl), obligate carriers (VI:5 and IV:1), and patient V:3. ░, GST/GPIIIa; ▪, GPIbα/GPIIIa (upper panel) and GPIbβ/GPIIIa (lower panel). (C) Platelet glycoprotein expression using Western blot analysis to study the expression of GPIIIa, GPIbα, and GPIbβ. The expression of the GATA1-independent large Gsα subunit (52 kd) was also studied.
Platelet glycoprotein expression analysis in PRP.
(A) Flow cytometry of a platelet nonspecific protein (GST) and GPIbα in the platelets of a control (Crl) or patient V:3. The platelets of V:3 are at least 2 to 3 times larger than control platelets, and a subgroup seems immature with very low levels of GPIbα (indicated by an arrow). (B) Normalized (versus GPIIIa expression) FACS results for the expression of GST, GPIbα, and GPIbβ in control (Crl), obligate carriers (VI:5 and IV:1), and patient V:3. ░, GST/GPIIIa; ▪, GPIbα/GPIIIa (upper panel) and GPIbβ/GPIIIa (lower panel). (C) Platelet glycoprotein expression using Western blot analysis to study the expression of GPIIIa, GPIbα, and GPIbβ. The expression of the GATA1-independent large Gsα subunit (52 kd) was also studied.
Platelet membrane glycoprotein studies in whole blood
To ensure that all platelets were included in our analysis, flow cytometry was also performed in total blood. To differentiate platelets from other blood cells and to include giant platelets, a double-labeling technique was applied, based on our finding that the GPIIIa levels were not disturbed in patient platelets. Again clear abnormalities were observed in the distribution of platelet size of patient V:3 (Figure 6A). The platelet population (circled in red) showed giant platelets 4 to 5 times larger than normal platelets. The largest platelets were not seen in PRP (Figure 5A), most probably because they were lost during centrifugation. The very immature platelets observed in PRP were hardly detected in this window because the amount of platelets in whole blood analyzed is only 10% of the platelets examined in PRP. The bar graphs, normalized to the control GST antibody, showing GPIbα and GPIbβ expressions by platelets within the red ellipse, again revealed a pronounced decrease of GPIbα but not of GPIbβ expression in patient V:3 compared with control or carrier platelets (Figure 6B). For GPIX and GPV, no significant differences were observed (data not shown). Flow cytometry experiments in whole blood also revealed a second weaker GPIIIa-positive platelet population (indicated by blue circles), located on top of the negative red blood cell population (Figure 6A). The glycoprotein expression levels in these 1:1 platelet erythrocyte conjugates revealed a still more pronounced drop of GPIbα expression compared with normal conjugates (Figure 6B). This is not the case for the control or carrier platelets. Again for GPIX and GPV no significant differences were found.
Platelet glycoprotein expression analysis in whole blood.
(A) An antibody (perCP labeled) against GPIIIa was used to identify platelets in blood samples. The platelets of patient V:3 are at least 4 to 5 times larger than control platelets (localized in the normal platelet population, shown in the red ellipses). A platelet subpopulation was observed (shown in blue circles) consisting of 1:1 platelet red blood cell conjugates. (B) Bars showing the normalized expression of GPIbα and GPIbβ in the 2 platelet populations (red versus blue). No abnormalities were seen for the carriers VI:5 and IV:1.
Platelet glycoprotein expression analysis in whole blood.
(A) An antibody (perCP labeled) against GPIIIa was used to identify platelets in blood samples. The platelets of patient V:3 are at least 4 to 5 times larger than control platelets (localized in the normal platelet population, shown in the red ellipses). A platelet subpopulation was observed (shown in blue circles) consisting of 1:1 platelet red blood cell conjugates. (B) Bars showing the normalized expression of GPIbα and GPIbβ in the 2 platelet populations (red versus blue). No abnormalities were seen for the carriers VI:5 and IV:1.
Platelet functional studies
We have investigated to what degree the reduced GPIbα levels on patient platelets affect von Willebrand factor–dependent platelet aggregation (Figure 7). The response to collagen is weak (34%) in PRP of patient V:3 compared with the control (75%) probably because of the presence of some erythrocytes in the PRP. However, the agglutination of platelets in response to ristocetin seems to be more strongly reduced (17%) in comparison to the control (92%). Preincubation with the monoclonal antibody G19H10 resulted in complete inhibition of the ristocetin-induced platelet agglutination. This finding indicates that the patient's platelets have a functionally active GPIb-IX-V receptor complex, although in decreased number. The aggregations shown are representative for 3 patients: aggregations in patients V:7 and V:8 were very similar.
Functional platelet analysis.
Aggregation tracings of the patient V:3 and control (both 130 000 platelets/μL). Arrows indicate the addition of aggregating agents (collagen or ristocetin) or preincubation (1 minute) with G19H10 antibody.
Functional platelet analysis.
Aggregation tracings of the patient V:3 and control (both 130 000 platelets/μL). Arrows indicate the addition of aggregating agents (collagen or ristocetin) or preincubation (1 minute) with G19H10 antibody.
Discussion
The role of the GATA1-FOG1 transcription complex in erythroid and megakaryocyte differentiation has already been illustrated in 3 mouse models. Homozygous disruption of either GATA1 orFOG1 causes embryonic lethality because of a severe erythroid defect.6,27 In contrast, mice with a mutation in the upstream region of GATA1 (GATA1 knockdown mice) show a milder erythroid defect but suffer from severe thrombocytopenia because of absent GATA1 expression in the megakaryocytic lineage.8 28
Very recently, the first GATA1 genetic defect (V205M) was found in patients with dyserythropoietic anemia and thrombocytopenia.10 This single amino acid substitution in GATA1, located in the N-terminal zinc finger, inhibits the interaction with its essential transcription cofactor FOG1. A similar observation in vitro had been made by mutagenesis of the key residues in the N-terminal zinc finger and thus implicated these residues in finger-specific FOG interactions.13 We describe here another mutation (D218G) located in the N-terminal zinc finger loop of GATA1. Mutagenesis of this residue and the neighboring residue (DR218/219NA) was studied by Fox et al13 and revealed FOG1 binding, although reduced. DNA binding was normal as also predicted by the 3-dimensional model of the N-terminal GATA1 zinc finger.29 The biochemical significance of our mutation for the GATA1-FOG1 interaction was studied by an in vitro assay and was compared with the V205M mutant of GATA1. The D218G mutant has a weaker affinity for FOG1, but it clearly interacts more strongly than the previously reported V205M GATA1 mutant. This observation is in agreement with the clinical differences between our kindred and the previously reported patients. The patients described in that study were anemic and severely thrombocytopenic with clear abnormalities not only in the megakaryocytic (low number and dysplastic platelets) but also in the erythrocyte (abnormal in size and shape) lineages.10The patients of our family have an abnormal size and number of dysmorphic platelets but have a normal amount and size with shape abnormalities of the erythrocytes (also confirmed by flow cytometric analysis, data not shown). Furthermore, in the 2 patients described by Nichols et al,10 cryptorchidism was observed, possibly linked to a GATA1 deficiency in the Sertoli cells. In our family no testicular abnormalities are observed, and, as can be concluded from the offspring of patients III:5 and III:8, fertility seems not to be compromised.
We extensively studied the consequences of the GATA1mutation on mRNA and protein expression levels of GATA1-dependent and -independent genes in patient platelets. Similarly to the findings in the megakaryocytes of GATA1 knockdown mice,8 the presently reported GATA1 mutation leads to a decreased GATA1-regulated gene expression and maturation of the patients' platelets. The expression differences cannot be attributed only to an aberrant GATA1/FOG1 transcriptional regulation, since the expression of a nondirect GATA1 target gene such as GNAS1 also is low. The low expression of this gene could be due to a GATA1-dependent secondary effect, resulting from poor megakaryocyte differentiation.GPIIIa expression is close to normal, compatible with the knowledge that this gene has no known GATA1 binding site and is already expressed during early megakaryocyte differentiation.
The in vivo expression of RNA in patient platelets thus corroborates the differences in mRNA profiles (studied for GPIbα, GPIbβ, c-mpl, and p45 NF-E2) observed in cultured megakaryocytes of GATA1 knockdown mice. However, in the GATA1 knockdown mice study, only the megakaryocytes of comparable morphology and size as those from wild-type mice were used, and no platelet mRNA was studied.8 The platelets of these mice were only checked for protein expression levels, and normal levels of GPIb, GPIIb, and c-mpl were found. The investigators explained the apparent discrepancy between the GATA1-deficient megakaryocytes and platelets by speculating that the platelets may be produced by a small subset of megakaryocytes that achieves a quasi-normal degree of maturity. The decreased mRNA levels for the GATA1-dependent genes in the circulating platelets of our patients do not support the hypothesis that platelets originate from just a subset of mature megakaryocytes. However, the GATA1 knockdown situation is not completely comparable to the presence of a mutant GATA1, which could also be the explanation for the observed differences. Indeed, GATA1-regulated gene expression can be entirely the result of GATA1-DNA binding for some genes, whereas others require an intact GATA1-FOG1 complex.
We also studied the glycoprotein expression levels in platelets by flow cytometry and Western blot analysis. Flow cytometric analysis of the patients' platelets in plasma or whole blood both showed a decreased GPIbα expression and a somewhat increased GPIbβ level, whereas GPIIIa expression seemed normal. No significant difference in the glycoprotein (GPIIIa and GPIb-IX-V) distribution in giant versus normal-size platelets was found in the patient. The reason why there is an increase in GPIbβ protein levels, despite decreased GPIbβ mRNA levels, is not clear, but this observation is compatible with findings of Vyas et al.9 Also a similar discordance remains between GPIX RNA and protein levels. Interestingly, in PRP, flow cytometry revealed a platelet subpopulation in the patient, having the size of platelets but a weak to absent glycoprotein expression. This platelet population was never found in controls or in obligate carriers. In whole blood, within the GPIIIa-positive platelets, a subpopulation consisting of erythrocyte-platelet conjugates, also present in the control, could be discerned. The glycoprotein expression in these platelets differs between patient and control: in the control there is no difference in glycoprotein expression in these platelets versus free platelets, but in the patient these platelets seem to have a still weaker expression of GPIbα.
In contrast to the GATA1-defective patients described by Nichols et al,10 we were still able to functionally test patients' platelets. The ristocetin-induced agglutination is weak but is fully GPIb dependent. The low but not absent ristocetin-induced agglutination compared with the collagen-induced aggregation probably results from the disturbed assembly of GPIb subunits. The weak agglutination is in contrast to what is found in patients with Bernard-Soulier syndrome30 in which ristocetin agglutination is completely absent and also in the specific patient described by Ludlow et al,31 in whom the Bernard-Soulier syndrome is the result of a 22q11 microdeletion, with the gene for GPIbβ included in the deletion, on one allele, and a mutation in the GATA1 binding site of the GPIbβ gene on the other allele.
In conclusion, we describe the first family with isolated X-linked macrothrombocytopenia without anemia (but with some dyserythropoietic features), because of a new mutation in GATA1 leading to a weaker interaction with FOG1. These patients release immature platelets in the circulation with a hyperplastic endoplasmic reticulum and a disturbed GPIb-V-IX complex with weakened function. This work suggests that patients with hereditary macrothrombocytopenia or with so-called familial chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura should be screened for mutations in GATA1 and FOG1.
C. V. G. and K. D. are both holders of a fundamental clinical research mandate of the FWO Vlaanderen.
Supported by the FWO Vlaanderen (project G.0306.98).
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Chris Van Geet, Center for Molecular and Vascular Biology, UZ-Gasthuisberg, Herestraat 49, 3000 Leuven, Belgium; e-mail:christel.vangeet@uz.kuleuven.ac.be.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal