Acquired pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) can be associated with lymphoproliferative disease of granular T lymphocytes (T-LDGL), also known as T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia. Fifteen adult patients with PRCA associated with T-LDGL comprise this study. Neutropenia and rheumatoid arthritis were uncommon. All patients responded to immunosuppressive therapy. The 2 most commonly used treatments were prednisone and cyclophosphamide ± corticosteroids, producing overall response rates of 50% and 60%, respectively. Treatment with cyclophosphamide was associated with a more durable remission (median, 60 versus 7.5 months). After a median follow-up of 67 months, 2 patients died of treatment-related complications, one from myelodysplasia and another from cyclosporine-induced renal failure. The clinical course and treatment responses of PRCA associated with T-LDGL in this series were similar to the general group of PRCA. Because T-LDGL is frequently underdiagnosed, it is likely that a significant proportion of idiopathic or primary PRCA is in fact secondary to T-LDGL.
Introduction
Common to the pathophysiology of bone marrow failure syndromes, including aplastic anemia, pure red cell aplasia (PRCA), and a subset of myelodysplastic diseases, is an immune-mediated suppression of marrow progenitor cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes.1-5 Lymphoproliferative disease of granular T lymphocytes (T-LDGL) is a clonal disorder of cytotoxic T lymphocytes that usually manifests as neutropenic infections and is associated with autoimmune disorders, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis. T-LDGL can present as failure of hematopoiesis or immune-mediated destruction in any one or a combination of the several myeloid cell lines, including red cells, neutrophils, and platelets. The frequent associations of these bone marrow failure syndromes with T-LDGL and recent findings on pathogenic mechanisms of T-LDGL suggest that T-LDGL may share a similar pathology to these other syndromes.6,7 We have previously reported that T-LDGL is a disorder frequently associated with PRCA.8 In our institutional series of 203 patients with T-LDGL, 15 (7%) patients presented as PRCA.6 This report reviews our clinical experience in 15 patients with PRCA in the setting of T-LDGL. This series included an update on 9 patients previously reported.8
Study design
After receiving the approval of the institutional review board of the Mayo Foundation, our database of patients with T-LDGL was reviewed for associated PRCA. A diagnosis of PRCA was made on the basis of clinical and bone marrow findings. Anemia with reticulocyte count of less than 1% had to be present. On bone marrow examination, there was almost complete absence of erythropoietic precursors or maturation arrest at the pronormoblastic stage. Maturation of other hematopoietic cell lines was normal. Other known causes of PRCA were excluded. Published criteria for T-LDGL was used.9 Complete response (CR) was defined as normalization of hemoglobin. Partial response (PR) was defined as an increase in hemoglobin level by 2 g/dL or more or by a 50% reduction in transfusion requirements. Any response less than partial was considered no response (NR). The percentage and absolute counts of granular lymphocytes in the peripheral blood were calculated as previously reported.7 Multiparametric flow cytometry of the peripheral blood or bone marrow and immunohistochemical staining of bone marrow biopsy was used to study lymphocytic immunophenotype. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement study was performed by using either the Southern blot analysis or polymerase chain reaction.
Results and discussion
We found 15 patients having PRCA associated with T-LDGL. In all cases, the diagnosis of PRCA was made concurrently with T-LDGL. Of those 15 patients, 8 were women. The median age at diagnosis was 66 years (range, 28-88 years). Associated medical conditions included B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (2), B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (1), thymoma (1), porphyria cutanea tarda (1), rheumatoid arthritis (1), inflammatory bowel disease (1), and polyendocrine failure (1). In the patient with a history of thymoma, thymectomy was performed 6 years before the diagnosis of T-LDGL and PRCA. All patients presented with symptoms because of anemia and were transfusion dependent. Except for pallor, there were no other physical findings. Laboratory findings are shown in Table 1. Absolute lymphocytosis in the peripheral blood was noted in only 6 patients. In the rest of the patients without absolute lymphocytosis, increase in granular lymphocytes could be identified by examination of the peripheral blood or the bone marrow.
Laboratory findings of 15 patients with pure red cell aplasia associated with lymphoproliferative disease of granular T lymphocytes
| . | Median (range) . | Normal values . |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 7.8 (5.0-10.5) | 12.0-17.5 |
| Mean corpuscular volume (fL) | 90 (83.0-117.9) | 81.2-98.3 |
| White cell count (× 109/L) | 6.6 (3.4-37.0) | 3.5-10.5 |
| Absolute neutrophil count (× 109/L) | 3.09 (0.12-5.41) | 1.70-7.0 |
| Absolute lymphocyte count (× 109/L) | 2.31 (1.06-29.97) | 0.90-2.90 |
| Absolute granular lymphocyte count (× 109/L) | 0.45 (0.30-7.21) | 0.10-0.50 |
| Granular lymphocyte (%) | 31 (10-59) | 5-25 |
| . | Median (range) . | Normal values . |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 7.8 (5.0-10.5) | 12.0-17.5 |
| Mean corpuscular volume (fL) | 90 (83.0-117.9) | 81.2-98.3 |
| White cell count (× 109/L) | 6.6 (3.4-37.0) | 3.5-10.5 |
| Absolute neutrophil count (× 109/L) | 3.09 (0.12-5.41) | 1.70-7.0 |
| Absolute lymphocyte count (× 109/L) | 2.31 (1.06-29.97) | 0.90-2.90 |
| Absolute granular lymphocyte count (× 109/L) | 0.45 (0.30-7.21) | 0.10-0.50 |
| Granular lymphocyte (%) | 31 (10-59) | 5-25 |
Clonal T-cell receptor gene rearrangement, 15 of 15 patients; positive direct antiglobulin test, 1 of 10 patients; positive antinuclear antibody test, 4 of 6 patients; rheumatoid factor, 1 of 4 patients; antineutrophil antibody, 0 of 2 patients. Cytogenetic studies, (n = 10 patients). Normal (8); loss of Y chromosome (1); complex abnormality (1). Peripheral blood flow cytometry, (n = 12 patients). CD3+/CD8+ (8); normal (4). Immunophenotypes studied include CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, CD3/CD8, and CD3/CD4.
Bone marrow immunohistochemistry, (n = 9 patients). Increase in CD3+ and CD8+ cells (9); increase in CD57+ cells (8).
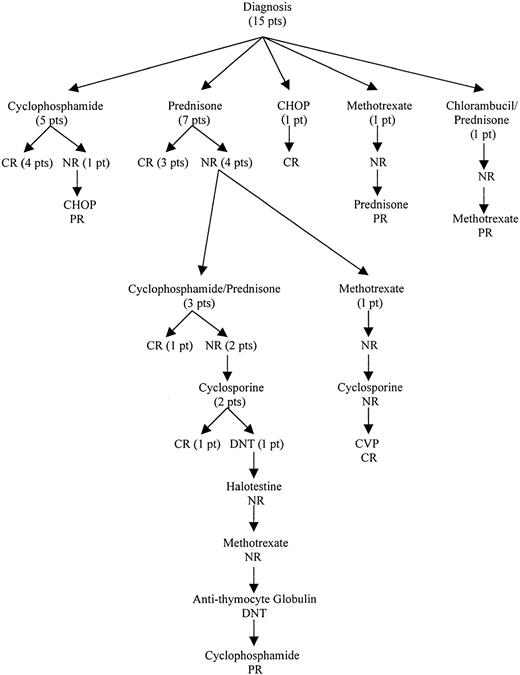
Seven patients were initially treated with prednisone (3 CR, 4 NR), and 5 patients received a combination of cyclophosphamide and corticosteroids (4 CR, 1 NR). Other initial treatments included chlorambucil/prednisone (1/1 NR), methotrexate (1/1 NR), and cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/vincristine/prednisone (1/1 CR). The treatment outcome from initial therapy until a response was obtained is outlined in Figure 1. In patients who initially responded to cyclophosphamide (5), the remission duration ranged from 22 to 120 months. All responded again to cyclophosphamide. In contrast, all prednisone responders (3) relapsed within 5 to 10 months of treatment. They were retreated with either oral cyclophosphamide (1 CR, 1 NR) or prednisone (1 CR). Salvage treatments used included cyclosporine, methotrexate, fluoxymesterone, antithymocyte globulin, or combination chemotherapy. The usual dosages of immunosuppressive agents used were prednisone, 1 mg/kg/d; cyclophosphamide, 50-100 mg/d; cyclosporine, 10 mg/kg/d; and methotrexate, 7.5-15 mg/wk. In general, a specific treatment was tried for at least 2 to 3 months unless side effects were not tolerated. The use of cytotoxic agents was limited to a total of 6 to 12 months after a response was achieved, whereas noncytotoxic immunosuppressive agents were given as long as necessary to control the disease. After a median follow-up of 67 months (range, 22-113 months), 13 patients were alive; 10 patients had PR, and 3 patients were in unmaintained CR. Continued therapy was necessary in all of the patients in PR. The clinical course was characterized by frequent relapses, although durable responses could be achieved. Two patients died of treatment-related complications, one from acute myeloid leukemia arising from myelodysplasia after cyclophosphamide treatment and another from cyclosporine-induced renal failure.
Treatment outcomes of patients with PRCA associated with T-LDGL from diagnosis until first response.
CR indicates complete response; PR, partial response; NR, no response; DNT, did not tolerate; CHOP, cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/vincristine/prednisone; CVP, cyclophosphamide/vincristine/prednisone; pt, patient.
Treatment outcomes of patients with PRCA associated with T-LDGL from diagnosis until first response.
CR indicates complete response; PR, partial response; NR, no response; DNT, did not tolerate; CHOP, cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/vincristine/prednisone; CVP, cyclophosphamide/vincristine/prednisone; pt, patient.
It is now evident that a close association exists between T-LDGL and PRCA.8,11,12 In our experience, PRCA is the second most common hematologic disease found in T-LDGL patients, exceeded only by autoimmune hemolytic anemia.2 In this subset of T-LDGL with concomitant PRCA, it is notable that rheumatoid arthritis and neutropenia were infrequently associated (1 and 2 patients, respectively). A careful examination of the peripheral blood is always necessary as lymphocytosis was observed in less than half of our cases. Similarly, bone marrow involvement by granular lymphocytes was mostly subtle. Peripheral blood flow cytometry detected an abnormal T-cell population in only 8 of the 12 patients studied. This finding was probably because of the limited antibody panel we used (Table1) for routine T-cell analysis. A more detailed analysis of the CD8+ subset, including determinations of CD16, CD56, and CD57, might have provided us more information. Initial case reports and series of T-LDGL included only cases that were obvious on clinical grounds, ie, those with evident lymphocytosis and symptoms, features consistent with a later diagnosis.13,14 As is true when there is a better awareness of a newly described disease, T-LDGL earlier in its natural history is being recognized in a more recent reported series.10 In fact, the diagnostic criteria for T-LDGL were modified to reflect this recognition.15 Nevertheless, we believe that T-LDGL remains a disease that is underdiagnosed.
The 2 most commonly used treatments in our series were prednisone alone and cyclophosphamide with or without concurrent low-dose corticosteroids. As initial therapy, cyclophosphamide ± corticosteroids produced a better overall response rate (CR + PR) than prednisone alone (80% versus 43%). When uses such as initial and salvage therapies were considered together, the overall response rates for cyclophosphamide ± corticosteroids and prednisone were similar (60% and 50%, respectively). Treatment with cyclophosphamide was, however, associated with a longer duration of response, 60 months (range, 22-117 months) versus 7.5 months (range, 5-43 months). Cyclosporine and methotrexate were used in the setting of treatment failure from other agents, with responses noted in 2 of 3 and 1 of 3 patients, respectively. These responses were durable, but, in each case, the treatment had to be maintained to achieve continued remission. All patients achieved remission after sequential immunosuppressive therapy. This finding suggests that T-LDGL association may be prognostic of a good response to immunosuppression. Considering that the clinical course and treatment responses of PRCA associated with T-LDGL are similar to the general group of PRCA and that T-LDGL is probably an underdiagnosed disorder, it is likely that a significant proportion of idiopathic or primary PRCA is, in fact, secondary to T-LDGL.
We thank Janice Hodnefield, Barbara Todd, and William Wittrock for their laboratory assistance.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Robert L. Phyliky, Mayo Clinic, Division of Hematology, 200 First St, SW, Rochester, MN 55905; e-mail:phyliky.robert@mayo.edu.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal