Abstract
It is well known that iron (Fe) is transported to the mitochondrion for heme synthesis. However, only recently has the importance of this organelle for many other facets of Fe metabolism become widely appreciated. Indeed, this was stimulated by the description of human disease states that implicate mitochondrial Fe metabolism. In particular, studies assessing various diseases leading to mitochondrial Fe loading have produced intriguing findings. For instance, the disease X-linked sideroblastic anemia with ataxia (XLSA/A) is due to a mutation in the ATP-binding cassette protein B7 (ABCB7) transporter that is thought to transfer [Fe-S] clusters from the mitochondrion to the cytoplasm. This and numerous other findings suggest the mitochondrion is a dynamo of Fe metabolism, being vital not only for heme synthesis but also for playing a critical role in the genesis of [Fe-S] clusters. Studies examining the disease Friedreich ataxia have suggested that a mutation in the gene encoding frataxin leads to mitochondrial Fe loading. Apart from these findings, the recently discovered mitochondrial ferritin that may store Fe in ring sideroblasts could also regulate the level of Fe needed for heme and [Fe-S] cluster synthesis. In this review, we suggest a model of mitochondrial Fe processing that may account for the pathology observed in these disease states.
Introduction
Since its discovery, the mitochondrion has been known as an essential and dynamic component of cellular biochemistry. The complexity of the mitochondrion has been gradually revealed by the study of a variety of genetic diseases associated with its function. Thus far, it is clear that Fe plays a crucial role in many facets of mitochondrial metabolism and the consequences of disruption to these pathways are catastrophic. Therefore, it would seem clear that the mitochondrion, a site of dynamically active electron transport and redox activity, would possess sufficient measures for the safe trafficking and metabolism of Fe. However, until recently, knowledge of the Fe metabolism of the mitochondrion has been largely confined to the heme synthesis pathway (for review, see Ponka1 ), and very little was understood concerning the trafficking and storage of Fe in this organelle.
The recent discovery of a plethora of mitochondrial proteins believed to be involved in Fe metabolism has resulted in a marked increase of research in this field. Key proteins identified include frataxin, ATP-binding cassette protein B7 (ABCB7), and the more recently discovered mitochondrial ferritin. These discoveries have provided evidence to support the hypothesis that the mitochondrion is a distinct compartment of Fe metabolism. However, despite these new data, the Fe trafficking pathways within the mitochondrion remain unclear, and in this review we will attempt to analyze and integrate the most recent findings in this intriguing field.
Iron transport, storage, and homeostatic regulation
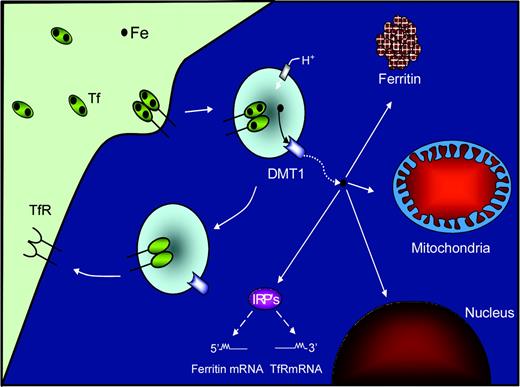
Before discussing the most recent results regarding mitochondrial Fe metabolism, we will first provide a brief overview of the well-characterized molecular pathways of cellular Fe trafficking and utilization. Iron is transported within the serum bound to the Fe-binding protein, transferrin (Tf),2-4 that binds to the transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1; Figure 1). The receptor binds 2 molecules of Fe-loaded Tf,5 resulting in receptor-mediated endocytosis of the Tf-TfR1 complex (for reviews, see Morgan,2 Richardson and Ponka,3 and Hentze et al4 ). A reduction in endosomal pH2,3,6 mediates the release of Fe from Tf.2,7 A protein known as the natural resistance–associated macrophage protein 2 (Nramp2)8 was subsequently demonstrated to be the long sought-after exporter of Fe+2 from endosomes.9-11 This molecule is now known as divalent metal ion transporter 1 (DMT1) but has also been denoted as the divalent cation transporter 1 (DCT1) or solute carrier family 11a member 2 (Slc11a2).
Schematic illustration showing how Fe is acquired for cellular processes by the transferrin-transferrin receptor pathway in nonerythroid cells. Diferric transferrin (Tf) binds to the transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) and is then internalized into cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis. After internalization, Fe is released from Tf by a decrease in endosomal pH and then transported through the endosomal membrane by the divalent metal ion transporter 1 (DMT1). Once transported into the cytosol, the Fe then becomes part of a poorly characterized labile Fe pool. The Fe can be either transported to ferritin, for storage and reutilization, or to the mitochondrion or other organelles such as the nucleus. Iron in the labile pool is thought to regulate the mRNA-binding activity of the iron-regulatory proteins (IRP1 and IRP2) that are important for regulating the expression of TfR1 and ferritin, which are critical for Fe uptake and storage, respectively.
Schematic illustration showing how Fe is acquired for cellular processes by the transferrin-transferrin receptor pathway in nonerythroid cells. Diferric transferrin (Tf) binds to the transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) and is then internalized into cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis. After internalization, Fe is released from Tf by a decrease in endosomal pH and then transported through the endosomal membrane by the divalent metal ion transporter 1 (DMT1). Once transported into the cytosol, the Fe then becomes part of a poorly characterized labile Fe pool. The Fe can be either transported to ferritin, for storage and reutilization, or to the mitochondrion or other organelles such as the nucleus. Iron in the labile pool is thought to regulate the mRNA-binding activity of the iron-regulatory proteins (IRP1 and IRP2) that are important for regulating the expression of TfR1 and ferritin, which are critical for Fe uptake and storage, respectively.
Within the cytosol, Fe can be stored in a large multimeric protein known as ferritin.12 The storage of Fe in this molecule protects the cells from the damaging effects of free Fe and also keeps it sequestered in a bioavailable form. Since Fe is such an important but potentially toxic metal, its uptake, storage, and mobilization pathways are tightly regulated. This homeostatic control mechanism is largely controlled by RNA-binding proteins known as iron-regulatory protein 1 (IRP1) and IRP2, which are responsible for the regulation of Fe uptake and storage by their association with iron-responsive elements (IREs; for reviews, see Richardson and Ponka,3 Hentze et al,4 Harrison and Arosio,12 and Hentze and Kühn13 ). Incorporation of the [4Fe-4S] cluster in IRP1 regulates its RNA-binding activity and, hence, the expression of molecules involved in Fe metabolism (eg, TfR1 and ferritin).13 High cellular Fe levels lead to the formation of an [4Fe-4S] cluster in IRP1 that prevents binding to the 3′-IRE in TfR1 mRNA, leading to its decreased stability and translation.13 In contrast, the inability of IRPs to bind to the 5′-IRE of ferritin mRNA allows its translation into protein that is necessary for Fe storage. Conversely, under Fe deprivation, the [4Fe-4S] cluster in IRP1 does not form and the opposite occurs.13
Mitochondrial iron metabolism
The Fe sequestered by the Tf-TfR1 pathway can be directed to numerous sites within the cell including the mitochondrion (Figure 1). For instance, in hemoglobin synthesizing erythroid cells, this represents a major proportion of Fe uptake from Tf.1 In nonerythroid cells, far less Fe is directed to the mitochondrion with a larger proportion being incorporated into cytosolic Fe-containing molecules. How Fe is directed from the endosome to the mitochondrion remains unclear. However, in erythroid cells, the process of Fe trafficking appears to specifically target this organelle.1,14 For many years, it has been suggested that Fe transported from the endosome to the cytosol enters a poorly characterized Fe pool composed of low Mr ligands15 or high Mr chaperones (Figure 1). To account for the targeting of Fe to the mitochondrion, physical contact between the mitochondrion and the endosome has been suggested in a “kiss and run” hypothesis.1 To date, there has been no direct evidence for either a labile small–molecular-weight Fe pool acting as a kinetic intermediate14 or for direct contact between the mitochondrion and endosome. Hence, the mechanism responsible for targeting Fe to the mitochondrion remains unknown.
Once Fe is transported to the mitochondrion (Figure 2) it can be used in a variety of metabolic pathways, for instance, heme synthesis1 or [Fe-S] cluster biogenesis,16 or it may be stored in the recently described mitochondrial ferritin (m-Ferr; see “Mitochondrial ferritin: a mitochondrial iron storage molecule”). While the mitochondrion uses some of the heme and [Fe-S] clusters generated for its own metabolism, both heme and Fe are probably exported from this organelle via the activity of specific transporters (Figure 2). In the case of heme, the transporter is unknown, whereas the [Fe-S] clusters may be exported to the cytosol via the mitochondrial inner membrane transporter, ABCB7 (Figure 2).17-19
Schematic illustration of a generalized overview of mitochondrial Fe metabolism. Iron is supplied to the mitochondrion from the cytosolic labile Fe pool by an unknown mechanism. It is transported by as yet unidentified transporter(s) into the matrix where it can be directed to a number of different pathways, including storage in mitochondrial ferritin, [Fe-S] synthesis, heme metabolism, or other as yet unknown pathways (see “The mitochondrion is a major site of [Fe-S] synthesis” for further details). ALA indicates δ-aminolevulinic acid; ALAS, δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase; CoPIII, coproporphyrinogen III; Fch, ferrochelatase; [Fe-S], iron sulphur cluster; Fxn, frataxin; IRP1, iron-regulatory protein 1; m-Ferr, mitochondrial ferritin; and PIX, protoporphyrin IX.
Schematic illustration of a generalized overview of mitochondrial Fe metabolism. Iron is supplied to the mitochondrion from the cytosolic labile Fe pool by an unknown mechanism. It is transported by as yet unidentified transporter(s) into the matrix where it can be directed to a number of different pathways, including storage in mitochondrial ferritin, [Fe-S] synthesis, heme metabolism, or other as yet unknown pathways (see “The mitochondrion is a major site of [Fe-S] synthesis” for further details). ALA indicates δ-aminolevulinic acid; ALAS, δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase; CoPIII, coproporphyrinogen III; Fch, ferrochelatase; [Fe-S], iron sulphur cluster; Fxn, frataxin; IRP1, iron-regulatory protein 1; m-Ferr, mitochondrial ferritin; and PIX, protoporphyrin IX.
The mitochondrion is the only site of heme synthesis
Heme biosynthesis occurs in all cells, especially erythroid cells and hepatocytes.1 This subject has been reviewed extensively elsewhere and will only be briefly described here.1 The biosynthesis of heme involves 8 steps, 4 of which occur within the cytosol, while the remaining 4 steps occur within the mitochondrion (Figure 2). In the mitochondrial matrix, δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase (ALAS) catalyzes the first step of the heme synthesis pathway, namely a condensation reaction between glycine and succinyl coenzyme A (CoA) resulting in δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA).20 There are 2 different genes for ALA synthase, one of which is expressed ubiquitously (ALAS1), whereas the expression of the other is specific to erythroid cells (ALAS2). ALA is transported to the cytosol where the next 4 steps take place. ALA dehydratase converts 2 molecules of ALA to the monopyrrole, porphobilinogen (PBG). Two subsequent enzymatic steps, involving PBG deaminase and uroporphyrinogen III synthase, convert 4 molecules of PBG into the cyclic tetrapyrrole, uroporphyrinogen III. This is then decarboxylated to form coproporphyrinogen III (CoPIII), which is transported to mitochondria by an unknown mechanism. The enzyme, CoPIII oxidase, localized in the intermembrane space of mitochondria, catalyzes oxidative decarboxylation of CoPIII to protoporphyrinogen IX.1 Protoporphyrinogen III oxidase, an integral protein of the inner mitochondrial membrane, catalyzes the penultimate step in the heme pathway that generates protoporphyrin IX (PIX). The final step in this pathway involves insertion of one atom of Fe2+ into PIX by the inner mitochondria membrane–associated enzyme, ferrochelatase (Figure 2). The rate-limiting step of heme biosynthesis by erythroid cells has been suggested to be the acquisition of Fe from Tf.1 In contrast, in nonerythroid cells, the rate of heme synthesis is dependent on the formation of ALA.1
The mitochondrion is a major site of [Fe-S] synthesis
Apart from heme synthesis, in the mitochondrion the biomolecular machinery exists for the synthesis of [2Fe-2S] and [4Fe-4S] clusters that play important roles in cellular metabolism, including regulating the uptake of Fe itself (Figure 2). The mitochondrion contains many [Fe-S] cluster–containing proteins including enzymes of the respiratory chain (eg, complex I and III), ferrochelatase, and enzymes of the citric acid cycle such as aconitase and succinate dehydrogenase. There are also cytosolic [Fe-S] cluster–containing proteins including the well-known human IRP1 (Figure 2) but also yeast glutamate synthase (Glt1p)21 and isopropylmalate isomerase (Leu1p).22 There is also an example of a human nuclear [Fe-S] protein, human endonuclease III homolog 1 (hNTH1), which is involved in base excision repair and has homologs in the yeast and mouse.23,24 The biosynthesis of [Fe-S] clusters is complicated, with a high degree of conservation across species.25 As most of the work on [Fe-S] cluster formation has been performed in bacteria and yeast, the discussion below focuses on these systems with reference to mammalian cells where possible (Table 1).
The first enzyme identified as playing a role in [Fe-S] cluster biosynthesis was in the nitrogen-fixing bacteria Azobacter vinlandii and termed NifS.26 NifS is a homodimeric cysteine desulfurase that catalyses the conversion of cysteine to alanine with pyridoxal-5′-phosphate (PLP) as a cofactor.33 During this reaction there is release of elemental sulfur for incorporation into new [Fe-S] clusters.34 Homologs of NifS were later discovered in non–nitrogen-fixing bacteria (Escherichia coli; IscS: iron sulfur cluster) and in higher eukaryotes. The yeast NifS homolog, Nfs1p, was shown to be the functional homolog of E coli IscS.35 Land and Rouault27 were the first to report the cloning of the human homolog to nifs, Nfs1.
The next stage of cluster biosynthesis involves a group of molecules generally referred to as scaffold proteins. The scaffold proteins contain 3 conserved cysteine residues that provide the foundation for the assembly of [2Fe-2S] and [4Fe-4S] clusters.28 In bacteria, the elemental sulfur generated by NifS is donated to the scaffold protein, NifU (Figure 2).30,36-38
The formation of [4Fe-4S] clusters in the E coli NifU homolog, iron-sulfur cluster assembly protein U (IscU) (Figure 3), was shown by Agar et al28 to be the result of sequential higher-order cluster assembly. Initially, IscU contains a single [2Fe-2S]2+ cluster per dimer (Figure 3), which is then converted to a form containing 2 [2Fe-2S]2+ clusters per dimer and then to a structure containing one [4Fe-4S]2+ cluster.
Schematic illustration of the molecules involved in the genesis of [Fe-S] clusters. Nfs1 supplies elemental sulphur for incorporation into a new [Fe-S] cluster with pyridoxal-5-phosphate (PLP) as a cofactor. Homodimeric IscU acts as a scaffold upon which the [Fe-S] cluster is built. Two atoms of Fe are delivered to the cluster machinery and the [Fe-S] cluster components are rearranged to form a single [2Fe-2S] cluster that is bridged between the 2 IscU subunits. Another [2Fe-2S] cluster may be formed on the cluster-containing scaffold complex, leading to the formation of a single [4Fe-4S] cluster (see “The mitochondrion is a major site of [Fe-S] synthesis” for further details).
Schematic illustration of the molecules involved in the genesis of [Fe-S] clusters. Nfs1 supplies elemental sulphur for incorporation into a new [Fe-S] cluster with pyridoxal-5-phosphate (PLP) as a cofactor. Homodimeric IscU acts as a scaffold upon which the [Fe-S] cluster is built. Two atoms of Fe are delivered to the cluster machinery and the [Fe-S] cluster components are rearranged to form a single [2Fe-2S] cluster that is bridged between the 2 IscU subunits. Another [2Fe-2S] cluster may be formed on the cluster-containing scaffold complex, leading to the formation of a single [4Fe-4S] cluster (see “The mitochondrion is a major site of [Fe-S] synthesis” for further details).
In yeast cells, the function of IscU is encompassed by 2 related proteins: Isu1 and Isu2.29 Another protein, Nfu1p, has been proposed to function in the assembly of the [Fe-S] cluster in Isu1/2 or its insertion into an appropriate apoprotein.30,31 In human cells, the function of IscU is performed by a single protein arising from an alternatively spliced mRNA.32 The alternative splicing of human IscU mRNA results in 2 transcripts, the translation of which generates a cytosolic (IscU1) or a mitochondrial (IscU2) isoform. The exact purpose for the 2 isoforms of these proteins is unknown but may reflect a higher degree of regulation for [Fe-S] cluster biosynthesis and the requirement for constant assembly/disassembly of these clusters in [Fe-S]–regulatory proteins (eg, IRP1).13
Mitochondrial ferritin: a mitochondrial iron storage molecule
Recently, the discovery of m-Ferr has led to re-evaluation of how Fe is processed within the mitochondrion and has suggested a level of complexity not previously imagined. The m-Ferr molecule is encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5q23 and is synthesized as a 30-kDa precursor that is targeted to the mitochondrion by a 60–amino acid leader sequence.39,40 The leader sequence is cleaved in the mitochondrion to produce 22-kDa subunits that have a ferroxidase center and form homopolymeric ferritin shells that bind Fe-like ferritin H-chain.41 Unlike cytoplasmic ferritin, m-Ferr mRNA lacks an IRE and may be transcriptionally regulated by Fe.40,41 The expression of the molecule is correlated with tissues that have high numbers of mitochondria (eg, testis) rather than with tissues involved in Fe storage (eg, the liver). Interestingly, m-Ferr was shown to be highly expressed in sideroblasts of patients with X-linked sideroblastic anemia (XLSA) but not in normal erythroblasts.39,42 In XLSA, high levels of Fe accumulate in the mitochondrion resulting in ringed sideroblasts due to a defect in ALAS2 activity.43 Indeed, most of the Fe deposited in perinuclear mitochondria of ringed sideroblasts was present in the form of m-Ferr.42
Mitochondrial transporters
It is unknown how cytosolic and nuclear [Fe-S] proteins acquire their cluster from IscU. One hypothesis is that the proteins are imported into the mitochondria, the [Fe-S] clusters are inserted, and the mature proteins are then transported out of the matrix.16 A more favorable hypothesis may be that the newly formed [Fe-S] cluster is transported out of the matrix and then inserted into target proteins by the cytosolic NifS/NifU machinery.16,35 The export of [Fe-S] clusters in yeast is known to involve an inner mitochondrial membrane channel of the ABC (adenosine triphosphate [ATP]–binding cassette) family, ABC transporter of the mitochondrion 1 protein (Atm1p).44 It is not known how Atm1p transports [Fe-S] clusters to the cytosol. However, it has been suggested that a linear or near-linear form of [2Fe-2S] and [4Fe-4S] may be involved, forming partial bonds with channel amino acids during transport.45 Interestingly, yeast atm1 mutants have an unstable mitochondrial genome and have white mitochondria that completely lack cytochromes.46 Atm1 mutants also show a 30-fold increase in mitochondrial Fe44 and reduced activity of cytosolic, but not of mitochondrial, [Fe-S] cluster–containing enzymes. A fraction of the excess mitochondrial Fe is still available for heme and [Fe-S] cluster biosynthesis. The human and mouse homologs to yeast atm1 (abcb7) have been identified18,47,48 and also appear to be involved in [Fe-S] cluster metabolism (see “X-linked sideroblastic anemia with ataxia (XLSA/A)”).
As described above, it is unknown how Fe bound to Tf is delivered to the mitochondrion and then transported into the mitochondrial matrix. In yeast, import of Fe into mitochondria is mediated, at least in part, by 2 transporters designated as mitochondrial solute carrier protein 3 (MRS3) and MRS4.49 In mammalian mitochondria, no such transporters have been identified. However, the export of free Fe from mammalian mitochondria may involve a promising candidate from the ABC half-type transporter family, namely, MTABC3 (mammalian mitochondrial ABC protein 3 or ABCB6).50 This molecule has been shown to rescue the mitochondrial Fe accumulation, mitochondrial DNA damage, and respiratory dysfunction in the atm1 mutant yeast cell strain.50 While atm1 is an ortholog of ABCB7, the product of which is presumably involved in the export of [Fe-S] clusters (see “X-linked sideroblastic anemia with ataxia (XLSA/A)”), it is possible that MTABC3 is involved in the transport of a different form of Fe.
Clues to further understanding iron trafficking: genetic diseases involving mitochondrial Fe metabolism
Advances in understanding the molecular events involved in Fe trafficking have resulted from the examination of animal models where defects in Fe metabolism were known to exist.9,11 Similarly, and more recently, examination of a variety of human diseases and the characterization of the molecular defects involved have resulted in important insights into the metabolic pathways of mitochondrial Fe trafficking. In the section below, we will describe the revolutions in understanding that have resulted from assessment of genetic diseases such as XLSA, X-linked sideroblastic anemia with ataxia (XLSA/A), and Friedreich ataxia (FA).
X-linked sideroblastic anemia
XLSA results from a deficiency of ALAS2,43 the first enzyme in the heme biosynthetic pathway of erythroid cells.1 The defect results in hyperferremia and potential death from hemochromatosis. In some cases, XLSA can be partially rescued by supplementation with pyridoxine,51 which is the cofactor of ALAS2.52 Despite disruption to heme biosynthesis and an increase in mitochondrial Fe loading, no neuropathy was observed in this disease, in contrast to that found in XLSA/A (see “X-linked sideroblastic anemia with ataxia (XLSA/A)”). The lack of neuropathy in these patients relates to the specific molecular defect involved. In this case, ALAS2 expression is confined to erythroid tissues only, while the synthesis of heme in neural tissues is mediated by ALAS1.1
The fact that mitochondrial Fe loading occurs suggests that Fe continues to enter the mitochondrion despite a lack of heme precursor in XLSA. Similar observations can be found in vitro in experiments on reticulocytes, where inhibition of heme synthesis leads to mitochondrial Fe accumulation.14,53 Considering this, it is possible that the end product of the heme biosynthetic pathway regulates entry of Fe into the mitochondrion.1 As mentioned above, it has been recently reported that mitochondrial Fe accumulation of XLSA may be incorporated into m-Ferr, as the expression of this latter molecule is markedly increased in this disease.42 This observation indicates that m-Ferr plays a critical role in the Fe metabolism of the mitochondrion in this disease state.
X-linked sideroblastic anemia with ataxia (XLSA/A)
Mutations within the human abcb7 gene result in XLSA/A,17-19,47,48,54 a rare condition resulting in mitochondrial Fe accumulation and the formation of ring sideroblasts. However, mitochondrial Fe accumulation in other tissues has not been documented. Symptoms of XLSA/A include a nonprogressive ataxia in early childhood, elevated free erythrocyte PIX levels, coordination difficulties, and mild anemia. In line with the proposed function of yeast atm1p, Csere et al48 identified ABCB7 as a mitochondrial protein which when expressed in yeast cells was able to restore growth defects of atm1 mutants. These ABCB7-expressing cells showed reduced mitochondrial Fe loading and had normal levels of cytochromes, suggesting ABCB7 was the functional homolog of atm1p. In addition, mutation of ABCB7 resulted in a disruption in the maturation of cytosolic [Fe-S] proteins and complementation of atm1 mutants by ABCB7-restored cytosolic [Fe-S] protein maturation. These data indicate that an essential function of mitochondria is to supply [Fe-S] clusters to the cytosol, and disruption to this process, via mutation of ABCB7/atm1p, is thought to result in the mitochondrial Fe loading observed in XLSA/A.
Hypochromic microcytic erythrocytes18,19,54 suggest a decrease in heme synthesis in developing erythroid cells of XLSA/A patients. However, it is difficult to explain how the disruption of [Fe-S] cluster export can interfere with Fe insertion into PIX. The disturbance in mitochondrial Fe metabolism in XLSA/A could be due several possibilities, including that Fe import into the mitochondrion and its export is regulated by an “Fe sensor” similar to IRPs in the cytosol. Alternatively, the Fe import by the mitochondrion may be regulated by feedback inhibition by exported Fe or an [Fe-S] protein. In this case, the export of such an Fe-containing molecule signals to the cytosol to appropriately modify Fe transport into the mitochondrion. It is also conceivable that the loss of Fe release from the mitochondrion in the form of [Fe-S] clusters induces changes leading to mitochondrial Fe loading. Finally, disrupted export of [Fe-S] clusters from the mitochondria may interfere with the reduction of Fe3+, which then accumulates since it cannot be used by ferrochelatase.55 The ataxia observed in XLSA/A maybe related to the damage mediated by the Fe loading in the mitochondrion and/or disruption to mitochondrial Fe homeostasis in neural cells. This disease is clearly different from that observed in XLSA where there is a deficiency of ALAS2.43 The expression of this latter enzyme is confined to erythroid tissues only and thus XLSA does not result in ataxia.
Friedreich ataxia
Friedreich ataxia (FA) is the most common inherited spino/cerebellar ataxia resulting in confinement to a wheelchair and death during middle age due to cardiomyopathy.56-58 The genetic defect accounting for about 98% of FA cases was identified by Campuzano et al59 as a trinucleotide (GAA)n repeat hyperexpansion within the first intron of the FA gene, FRDA.59,60 The end result of this expansion is mitochondrial Fe accumulation, especially in tissues of high mitochondrial content, such as nerve and cardiac tissue.61-63 An excess of “free Fe” in the redox-active environment of the mitochondrion of FA patients has been suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of this disease.64 Indeed, free-radical scavengers such as idebenone have been shown to be somewhat protective against the cardiomyopathy observed in this disease.65 This has been hypothesized to be due to the participation of Fe in Fenton chemistry resulting in damage to essential biologic molecules.66
FRDA encodes a 210–amino acid protein known as frataxin, which has a specific association with the mitochondrial inner membrane.67 The crystal structure of human frataxin has been determined and a novel protein fold in the molecule has been identified.68,69 A cluster of 12 acidic residues on one surface of the protein forms a large, negatively charged region believed to be a site of ligand interaction. In terms of Fe, a potential binding site at position 177 (H177) was found to bind one atom of Fe per frataxin monomer.68 Other experiments showed that the human frataxin monomer was unable to bind Fe with any significant affinity and lacked any obvious Fe-binding site or motif.69 Furthermore, titration of purified human frataxin with an excess of Fe did not result in protein aggregation.69
More recently, frataxin has again been investigated as a potential Fe-binding protein70,71 and was suggested to perform the function of a “mitochondrial ferritin.” In vitro assays have shown that incubation of frataxin monomers with excess Fe results in polymerization to high–molecular-weight molecules with ferroxidase activity.72 However, considering the discovery of a functional m-Ferr in human tissues (see “Mitochondrial ferritin: a mitochondrial iron storage molecule”), the seemingly redundant role of frataxin as a mitochondrial Fe storage protein is puzzling but not excluded. Indeed, frataxin could play some role as an Fe chaperone.
Previous studies have shown that the expression of frataxin protein is not regulated in response to intracellular Fe levels, in contrast to the effect of Fe on TfR1 expression.73 The current and most convincing data indicates frataxin may be involved in the formation of [Fe-S] clusters. The link between frataxin and [Fe-S] cluster assembly and/or export suggests an essential role.74 Interestingly, yeast frataxin was shown to play a direct role in the formation of [Fe-S] clusters, and the export of Fe from yeast mitochondria required the formation of these clusters.75 A role for frataxin in assembly of the [Fe-S] cluster of ferredoxin was observed76 and later the import of [Fe-S] clusters into yeast ferredoxin was reduced in frataxin-deficient cells.77 Likewise, the formation of [Fe-S] clusters in mitochondrial extracts from yeast cells deficient in yeast frataxin homolog 1 protein (Yfh1p) was found to be reduced78 and other studies found frataxin was directly involved in the generation of [Fe-S] clusters.79
Frataxin has been suggested to be involved in either the transfer of Fe to Isu or to perform a chaperone-type role in [Fe-S] cluster assembly.80,81 By loading purified human frataxin with Fe, Yoon and Cowan80 demonstrated that frataxin can bind 6 to 7 Fe atoms and by doing so is in an “active” form that is capable of binding IscU when the purified proteins are mixed in vitro. Interestingly, the Fe-loaded frataxin was able to donate Fe to the cluster assembly sites within the IscU. However, these authors labeled frataxin by incubating it for 6 hours with a very high Fe concentration in the absence of a donor ligand such as citrate or nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA).80 Therefore, the “bound Fe” may be nonspecifically adsorbed to the protein and no control experiments were performed to assess if this was the case. The binding of frataxin to Isu was proposed to occur before the formation of the [Fe-S] cluster and was also enhanced by the presence of Fe2+.81
More recent studies suggested that Fe-loaded frataxin acted as a high-affinity binding partner for ferrochelatase, mediating the final step in the heme-biosynthesis pathway.82 Based on studies indicating that frataxin levels decrease during erythroid differentiation, and the fact that holo-frataxin has differential affinities for IscU and ferrochelatase, these authors indicate that frataxin could act as an Fe-delivery molecule for [Fe-S] cluster assembly or heme synthesis.82 However, these studies82 were performed by simply mixing the purified proteins and no control studies were used to assess if the Fe transfer observed was due to nonspecific interactions.
Frataxin has also been implicated to play some role in heme metabolism, as PIX is able to decrease frataxin expression, suggesting the protein may act as a metabolic switch.73 In this case, excess PIX may signal a requirement for heme synthesis, reducing frataxin expression and resulting in a diversion of Fe from one pathway (eg, [Fe-S] cluster synthesis) to another (eg, heme metabolism).73 Alternatively, frataxin could be involved in delivering Fe to these pathways. In this model, Fe-loaded frataxin donates its “cargo” to the [Fe-S] cluster assembly machinery or to ferrochelatase depending upon metabolic requirements.
Some similarities exist between the neurodegenerative diseases FA and XLSA/A. Both diseases result in mitochondrial Fe accumulation and appear to be due to the uncoupling of normal [Fe-S] cluster synthesis. This strongly suggests that both frataxin and ABCB7 are required for normal Fe homeostasis in mammalian mitochondria. It is possible that frataxin is not directly involved in [Fe-S] cluster synthesis and that its decreased expression in FA causes a downstream disruption of cluster metabolism. Perhaps frataxin acts as a metabolic switch between these mitochondrial Fe metabolizing pathways, and when frataxin is reduced (such as in FA), Fe is not appropriately distributed among them. This suggestion is discussed further below as part of a general model of mitochondrial Fe homeostasis.
A hypothetical model of mitochondrial Fe metabolism: is frataxin a regulator of Fe trafficking?
Taken together, the current data concerning mammalian mitochondrial Fe metabolism suggests an intricate and complicated web of supply and demand involving at least 2 major Fe-requiring pathways, that is, the generation of [Fe-S] clusters and heme synthesis. Furthermore, the identification of m-Ferr (see “Mitochondrial ferritin: a mitochondrial iron storage molecule”) suggests a molecular mechanism for mitochondrial Fe storage. These pathways cannot be considered in isolation and an overall hypothetical model of mitochondrial Fe trafficking needs to be proposed.
Figure 4 summarizes major known biochemical pathways that occur in the mammalian mitochondrion under physiologic circumstances, namely, the transport of Fe into the mitochondrion by a transporter, the use of Fe in heme synthesis, the generation of [Fe-S] clusters, or its storage in m-Ferr. It is likely that like cytosolic Fe metabolizing pathways, these Fe-utilization pathways are tightly regulated, since “free” Fe is toxic when not properly used.66 Mitochondrial-generated [Fe-S] clusters are thought to be transported into the cytosol by ABCB7.19,48 Heme produced in the mitochondria can also be transported to the cytosol by an uncharacterized mechanism.1 It is known that heme-binding protein with a molecular mass of 22 kDa (p22HBP) binds heme with high affinity83,84 , and it was suggested to be involved in transport of heme from the mitochondrion to the cytosol.83 The majority of evidence suggests a role for frataxin in the assembly of [Fe-S] clusters.74,76,77,80 However, most of these data are derived from studies assessing yeast cells or the purified proteins and the exact function of mammalian frataxin remains unclear.
Schematic illustration of heme and cluster synthesis and metabolism. (A) Schematic illustration of normal heme and [Fe-S] cluster synthesis, (B) PIX induction of heme synthesis and the inhibition of frataxin (Fxn) expression and [Fe-S] cluster metabolism, and (C) a proposed mechanism of the disrupted mitochondrial [Fe-S] cluster biosynthesis and Fe metabolism in Friedreich ataxia (FA). (A) Under physiologic conditions, Fe is used for the synthesis of heme or the genesis of [Fe-S] clusters. (B) PIX has been shown to decrease frataxin expression and we hypothesize that frataxin acts as a PIX-sensitive metabolic switch that regulates the use of Fe for heme synthesis. In this way, increased PIX levels indicate a requirement for heme synthesis that decreases frataxin expression and results in diversion of Fe to this pathway from [Fe-S] cluster assembly or Fe storage. Hence, we propose that this may be the role for frataxin under physiologic conditions. (C) Since frataxin expression is low in FA, [Fe-S] cluster synthesis is impaired. Moreover, because there is no intense demand for heme synthesis in nonerythroid tissues, the excess Fe not used for [Fe-S] cluster synthesis is incorporated into m-Ferr. Initially, the Fe accumulation in m-Ferr may be protective and would explain the delay in pathogenesis of FA until many years after birth. However, in the absence of marked Fe utilization in nonerythroid cells for the generation of heme, the m-Ferr may degrade to “hemosiderin-like” material that is redox-active and could lead to the mitochondrial damage observed in FA.
Schematic illustration of heme and cluster synthesis and metabolism. (A) Schematic illustration of normal heme and [Fe-S] cluster synthesis, (B) PIX induction of heme synthesis and the inhibition of frataxin (Fxn) expression and [Fe-S] cluster metabolism, and (C) a proposed mechanism of the disrupted mitochondrial [Fe-S] cluster biosynthesis and Fe metabolism in Friedreich ataxia (FA). (A) Under physiologic conditions, Fe is used for the synthesis of heme or the genesis of [Fe-S] clusters. (B) PIX has been shown to decrease frataxin expression and we hypothesize that frataxin acts as a PIX-sensitive metabolic switch that regulates the use of Fe for heme synthesis. In this way, increased PIX levels indicate a requirement for heme synthesis that decreases frataxin expression and results in diversion of Fe to this pathway from [Fe-S] cluster assembly or Fe storage. Hence, we propose that this may be the role for frataxin under physiologic conditions. (C) Since frataxin expression is low in FA, [Fe-S] cluster synthesis is impaired. Moreover, because there is no intense demand for heme synthesis in nonerythroid tissues, the excess Fe not used for [Fe-S] cluster synthesis is incorporated into m-Ferr. Initially, the Fe accumulation in m-Ferr may be protective and would explain the delay in pathogenesis of FA until many years after birth. However, in the absence of marked Fe utilization in nonerythroid cells for the generation of heme, the m-Ferr may degrade to “hemosiderin-like” material that is redox-active and could lead to the mitochondrial damage observed in FA.
Previous investigations have shown that the immediate heme precursor, PIX, decreases frataxin expression and it was hypothesized that frataxin acts as a PIX-sensitive metabolic switch.73 In this way, increased PIX levels indicate a requirement for heme synthesis that decreases frataxin expression and results in diversion of Fe to this pathway from [Fe-S] cluster assembly or Fe storage (Figure 4A). Hence, we propose that this may be the role for frataxin under physiologic conditions.73
In FA, frataxin expression is low and this is thought to lead directly or indirectly to mitochondrial Fe accumulation in nonerythroid cells.57-63 It is known that mitochondrial [Fe-S] cluster levels are decreased in FA, but it is not clear whether this is due to the sensitivity of these moieties to oxidative stress85 or the possible role of frataxin in [Fe-S] synthesis.76-81 The tissues affected in FA are composed of nonerythroid cells (eg, neurons and cardiomyocytes) that have a basal level of heme synthesis.1 Considering this, we propose a second hypothesis in nonerythroid cells of FA patients where, because there is no intense demand for heme synthesis, the excess Fe is not used for [Fe-S] cluster synthesis but is incorporated into m-Ferr (Figure 1C). This would account for the fact that defects in [Fe-S] cluster generation occur before Fe accumulation in the conditional frataxin knockout (KO) mouse.63 Initially, the Fe accumulation in m-Ferr may be protective and could explain the delay in pathogenesis of the disease until many years after birth.57 In the absence of intense Fe utilization in nonerythroid cells for heme synthesis, m-Ferr may potentially degrade to a hemosiderin-like molecule86-88 that is redox-active, leading to the subsequent mitochondrial damage seen in FA (Figure 4B).
Hemosiderin is a degradation product of cytosolic ferritin and while there has been a report that hemosiderin may protect against Fe-mediated oxidative stress,88 the majority of evidence suggests that hemosiderin plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of Fe-overload disease.87 Due to its soluble nature, ferritin does not usually give a Perl reaction90 and this staining is only generally seen for insoluble hemosiderin. Electron micrographs of ferritin and hemosiderin show obvious morphological differences in Fe-overloaded tissue (Figure 5A). These should be compared to the deposits in the mitochondrion of X-linked sideroblastic anemia patients (Figure 5B) and in the muscle creatinine kinase (MCK) conditional frataxin knockout mouse (Figure 5C). The Fe deposits in FA patients (reviewed in Wickramasinghe91 ) and the conditional frataxin knockout mice stain positive using Perl stain63 are consistent with hemosiderin rather than ferritin. Indeed, electron micrographs of the mitochondrial Fe deposits in the conditional frataxin knockout mouse (Figure 5C)63 are similar to those published of insoluble hemosiderin, but not cytoplasmic ferritin (Figure 5A).93,94 Using electron microscopy, the mitochondrial Fe deposits in sideroblasts from XLSA patients (Figure 5B) are more similar to those observed in the FA knockout mouse (Figure 5C) and hemosiderin (Figure 5A) than that of Fe-loaded ferritin (Figure 5A). Determination of the nature of the Fe deposits and the identification of a “mitochondrial hemosiderin” may be critical in determining the pathology of FA and direct experimental validation is clearly required. At present, it is unknown how m-Ferr would be degraded to form a hemosiderin-like material, as in the cytosol this may be accomplished by lysosomes.95,96 However, protein turnover within the mitochondrion must occur and a system for protein degradation in mitochondria has been described.97,98
Transmission electron micrographs. Transmission electron micrographs of (A) electron dense deposits consistent with hemosiderin and ferritin in the liver of a hemochromatosis patient (reprinted from Stal et al92 with permission); (B) electron dense deposits in sideroblasts from a patient suffering X-linked sideroblastic anemia (reprinted from Wickramasinghe et al91 with permission from S. Karger AG, Basel); and (C) electron dense deposits in the mitochondrion of a muscle creatine kinase (MCK) conditional frataxin knockout mouse (reprinted from Puccio et al63 with permission from Nature [www.nature.com], copyright 2001).
Transmission electron micrographs. Transmission electron micrographs of (A) electron dense deposits consistent with hemosiderin and ferritin in the liver of a hemochromatosis patient (reprinted from Stal et al92 with permission); (B) electron dense deposits in sideroblasts from a patient suffering X-linked sideroblastic anemia (reprinted from Wickramasinghe et al91 with permission from S. Karger AG, Basel); and (C) electron dense deposits in the mitochondrion of a muscle creatine kinase (MCK) conditional frataxin knockout mouse (reprinted from Puccio et al63 with permission from Nature [www.nature.com], copyright 2001).
Support for this hypothesis above has recently been obtained using yeast cells deficient in the frataxin homolog, Yfh1p.99 Expression of m-Ferr in these cells rescued the respiratory deficiency caused by the loss of Yfh1p, protecting the activity of [Fe-S] enzymes and enabling frataxin-deficient cells to grow.99 This suggests that m-Ferr may potentially be protective and would at least explain the delay in the pathogenesis of FA until it is processed to a redox-active mitochondrial hemosiderin. Clearly, further studies are required to test this.
The model of mitochondrial Fe utilization described above and in Figure 4C would also account for the lack of significant pathology in the erythron of FA patients, as low frataxin levels correlate with Fe utilization for heme production in erythroid cells.73 This may prevent Fe loading of m-Ferr in these latter cells. Indeed, we showed that frataxin expression is reduced upon erythroid differentiation.73
The hypothetical models described in Figure 4A-C provide the basis for experimental validation. Clearly, the precise roles these proteins play in mitochondrial Fe metabolism are still yet to be determined and many questions remain. However, it is clear that the mitochondrion is a critical site for many Fe-utilizing pathways, making it a dynamo of cellular Fe metabolism.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, November 4, 2004; DOI 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3856.
Supported by a fellowship and project grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears in the front of this issue.
The authors acknowledge the careful reading of the manuscript by Dr Neil Davies (Iron Metabolism and Chelation Program, Children's Cancer Institute Australia). Dr Ralph Watts of the Iron Metabolism Program is kindly thanked for his expert assistance with the figures. Children's Cancer Institute Australia for Medical Research is affiliated with the University of New South Wales and Sydney Children's Hospital. The authors thank members of the Iron Metabolism and Chelation Program for their comments on the manuscript prior to submission.

![Figure 2. Schematic illustration of a generalized overview of mitochondrial Fe metabolism. Iron is supplied to the mitochondrion from the cytosolic labile Fe pool by an unknown mechanism. It is transported by as yet unidentified transporter(s) into the matrix where it can be directed to a number of different pathways, including storage in mitochondrial ferritin, [Fe-S] synthesis, heme metabolism, or other as yet unknown pathways (see “The mitochondrion is a major site of [Fe-S] synthesis” for further details). ALA indicates δ-aminolevulinic acid; ALAS, δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase; CoPIII, coproporphyrinogen III; Fch, ferrochelatase; [Fe-S], iron sulphur cluster; Fxn, frataxin; IRP1, iron-regulatory protein 1; m-Ferr, mitochondrial ferritin; and PIX, protoporphyrin IX.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/105/5/10.1182_blood-2004-10-3856/6/m_zh80050574830002.jpeg?Expires=1769105485&Signature=Dr8XVOA2yUnYTRihg5YD9w5abDE22pt6aLwB3cQdybEv9PjI3MrCY9agTrNLFet7qbsc6EGt8Uykn3i0fWnO2S17FO8K3fskd-TDzP3fFa9VE1dY~fEW3v8rFPAP6I4SA9e6-Wye0LXkRUXOgSDavpHko5ZaRHuO3yJ1d2yRJ~i-Th~yh9XRFWa~2KnBc7mp3ETfHXGiR6H0~YX5nolKXUwoW9YShVCdceWayAs0NIy6xyYmxMTfal29ak-HuOEvsVToMXDKHMsko3bbspHKZgdyA0eIq50cqQ0qub6tvDf5WyMYT4kw5a-JsWRvsZD0NO9Mgt8w8OpVGeP11dC77w__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![Figure 3. Schematic illustration of the molecules involved in the genesis of [Fe-S] clusters. Nfs1 supplies elemental sulphur for incorporation into a new [Fe-S] cluster with pyridoxal-5-phosphate (PLP) as a cofactor. Homodimeric IscU acts as a scaffold upon which the [Fe-S] cluster is built. Two atoms of Fe are delivered to the cluster machinery and the [Fe-S] cluster components are rearranged to form a single [2Fe-2S] cluster that is bridged between the 2 IscU subunits. Another [2Fe-2S] cluster may be formed on the cluster-containing scaffold complex, leading to the formation of a single [4Fe-4S] cluster (see “The mitochondrion is a major site of [Fe-S] synthesis” for further details).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/105/5/10.1182_blood-2004-10-3856/6/m_zh80050574830003.jpeg?Expires=1769105485&Signature=1tIA6bV4sOC1cILi6A9ZzWAATY1oT~4keTbqOynKCFJ6VAYoiTAidz8VLMFeJQohpv-JIAFftv-rCeYYINOcHO4I0LEUgo6xF3ntRf5aco5WZm~IMjT8ATK-wgn7tw5NF8jc~ivoYtSffeFk2DDqCfGIX96fFbQRR1Pj-8pTd2bS4bOMoGhFDE6cTOGMT8n4mahDu2L3goI5dEmAGiDFok42~d0KWuFLZQs9~ehmhD85jXTjsOShxqewYGItPKZOGnO4~nJNPqyamR8HGbhPhzf7PtsGrciAA279QKL-qs-se1HMLM6V36VdJ167b1EiNfMoNSvIsCTCD-wHga-zGg__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![Figure 4. Schematic illustration of heme and cluster synthesis and metabolism. (A) Schematic illustration of normal heme and [Fe-S] cluster synthesis, (B) PIX induction of heme synthesis and the inhibition of frataxin (Fxn) expression and [Fe-S] cluster metabolism, and (C) a proposed mechanism of the disrupted mitochondrial [Fe-S] cluster biosynthesis and Fe metabolism in Friedreich ataxia (FA). (A) Under physiologic conditions, Fe is used for the synthesis of heme or the genesis of [Fe-S] clusters. (B) PIX has been shown to decrease frataxin expression and we hypothesize that frataxin acts as a PIX-sensitive metabolic switch that regulates the use of Fe for heme synthesis. In this way, increased PIX levels indicate a requirement for heme synthesis that decreases frataxin expression and results in diversion of Fe to this pathway from [Fe-S] cluster assembly or Fe storage. Hence, we propose that this may be the role for frataxin under physiologic conditions. (C) Since frataxin expression is low in FA, [Fe-S] cluster synthesis is impaired. Moreover, because there is no intense demand for heme synthesis in nonerythroid tissues, the excess Fe not used for [Fe-S] cluster synthesis is incorporated into m-Ferr. Initially, the Fe accumulation in m-Ferr may be protective and would explain the delay in pathogenesis of FA until many years after birth. However, in the absence of marked Fe utilization in nonerythroid cells for the generation of heme, the m-Ferr may degrade to “hemosiderin-like” material that is redox-active and could lead to the mitochondrial damage observed in FA.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/105/5/10.1182_blood-2004-10-3856/6/m_zh80050574830004.jpeg?Expires=1769105485&Signature=wZ1YsE4ToPiwpqZda9F8NtoFK035H3wQZYWy7EjoxUjrCz9mdTkB9ORBExmUe10dIpTHTyIAuaKBfmrl6GQULGzBtW5oumkf~Kza67p94OCzdJ90vEk01hwexEjff8yq7SGe-o6YlC0qMLULhI~HFfQMiLkEVZC1VrOGfUbWU54cwahGY9toMEpb25UA7Qm5gooV8ZgsEmMA8EfK8S-S8rGTuw7rbmeHlccR1msRWdzJU-CpUSDQ8wDlcfkaNgnQWndlSxEKHChdM4AcK6exFkR7Wo3-NSCGtm3IuSxOoPUnknDvUfLA0pRZ42xtl~xWhUfAIhCKgGWJ1Es6Wabgaw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![Figure 5. Transmission electron micrographs. Transmission electron micrographs of (A) electron dense deposits consistent with hemosiderin and ferritin in the liver of a hemochromatosis patient (reprinted from Stal et al92 with permission); (B) electron dense deposits in sideroblasts from a patient suffering X-linked sideroblastic anemia (reprinted from Wickramasinghe et al91 with permission from S. Karger AG, Basel); and (C) electron dense deposits in the mitochondrion of a muscle creatine kinase (MCK) conditional frataxin knockout mouse (reprinted from Puccio et al63 with permission from Nature [www.nature.com], copyright 2001).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/105/5/10.1182_blood-2004-10-3856/6/m_zh80050574830005.jpeg?Expires=1769105485&Signature=VJS1Dxp9RN4dx83zDq6HKv6LAsis4Rc5KLbYsjbD2sDM~rc13qH1Yh~uiOQCJmYjwq1~mXvvJDy6AaFEYT11jSUuhisEF7Ddjfam60lNLvlVoe2c~jkR19qRhsZ3CnI1GCvf0J10qj7OUhvMnffKuyaMK2VAtb-EJw5ag~J0sOYi5fLWcEfqYVBUguMDrr010VmAeWfyvWsvdLw~SczQCdyZfQdYhKxPlMpfWFdhDj~rzHJYjuzoFuoK-GGxyXDU9klSJhNvODYF9g80Rdp1C3AsyTvynqiQjmnvC7duNNgYgry3HvQz6YYueUn-jmkbhTDLuhVYx87Cbb6vpLL8fw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
