Abstract
It is currently thought that acute GVHD cannot be elicited in the absence of Ag presentation by radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs after allogeneic BM transplantation. Because clinical data suggest that sex-mismatched H-Y Ags may be important minor histocompatibility Ags for GVH responses, we directly tested their relevance and ability to initiate GVHD when presented by either the hematopoietic- (host or donor) or the nonhematopoietic-derived APCs. H-Y minor Ag incompatibility elicited both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell driven GVHD lethality. Studies with various well-established BM chimera recipients, in contrast to the current views, have reported that in the absence of functional radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs, H-Y Ag presentation by either the donor hematopoietic-derived or the host nonhematopoietic-derived APCs is sufficient for inducing GVHD. Our data further suggest that infusion of sufficient numbers of alloreactive donor T cells will induce GVHD in the absence of radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs.
Introduction
Ag presentation on radiosensitive host hematopoiesis-derived APCs to the alloreactive donor T cells is considered to be obligatory for the induction of acute GVHD.1-9 However, under certain conditions, whether clinically relevant minor Ags can induce GVHD in the absence of functional radiosensitive host hematopoietic APCs is not known.6-8,10 Clinical data from MHC-matched BMT show that male recipients from female donors (F→M) are at a greater risk of developing GVHD9 and show H-Y–specific alloresponses.11-14 These clinical data suggest a strong correlation between H-Y Ag disparity and GVHD. However, in the context of HLA-matched clinical F→M BMT, the donors are also likely to be mismatched with the recipients at multiple minor Ags. Therefore, whether H-Y disparity alone is sufficient for causing clinical acute GVHD is not known. The experimental evidence for the causative role of H-Y Ags in GVHD and mortality has not been reported. Furthermore, the relevance of donor T-cell alloreactivity against a single minor Ag and mechanisms of its presentation in causing GVHD are not known.1-5 Although some studies have suggested that high doses of TCR transgenic (Tg) T cells can cause GVHD, its severity was limited and was in the context of MHC mismatch or against minor Ags with unknown clinical relevance.15,16 With the use of both H-Y–specific Tg and non-Tg T cells in multiple well-established BM chimeras we demonstrate, in contrast to the existing notion, that presentation of clinically relevant minor H-Y Ag by host radiosensitive hematopoietic-derived APCs is not obligatory for induction of acute GVHD.3,6-8,10,17 Our data further suggest that in the absence of radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs, when sufficient numbers of alloreactive donor T cells are infused, nonhematopoietic-derived cells such as endothelial and certain epithelial cells activate alloreactive T cells, might induce GVHD.
Methods
Mice
Male and female C57BL/6 (B6, H-2b, CD45.2+), B6 Ly5.2 (H-2b, CD45.1+), and BALB/c (H-2d) mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. B6-background H2-Ab1−/− mice (B6.129-H2-Ab1tm1Gru N12, CD45.2+), β2 microglobulin deficient (β2m−/−) B6 mice (H-2b, CD45.2+), anti–H-Y TCR Tg mice Marilyn (RAG-2− background, CD4+Tg, H-2b, CD45.2+, I-Ab-restricted),17 Rachel(RAG-2− background, CD4+Tg, H-2b, CD45.2+, I-Ab-restricted),17 and MataHari (RAG-1− background, CD8+Tg, H-2b, CD45.2+, H-2Db-restricted) mice18 were obtained from Taconic. All animals were cared for under regulations reviewed and approved by the University Committee on Use and Care of Animals of the University of Michigan, based on University Laboratory Animal Medicine guidelines.
Generation of BM chimeras
We administered 1100 cGy total body irradiation (137Cs source) to mice and then injected them intravenously with 5 × 106 BM cells with 5 × 106 whole spleen cells from donor mice on day −1. For generating MHC class I–deficient (β2m-KO) BM chimeras, recipient mice were treated with 200 μg of anti-NK1.1 mAb (PK136) on days −2 and −1.6 The peripheral blood from sentinel mice were analyzed for donor chimerism at 3 months and found to show > 98% donor chimerism in all cell lineages. The CD11c+ cells in the splenocytes from these animals also showed > 95% donor chimerism.
BMT
BMTs were performed as described before.10 Briefly, splenic T cells were enriched by autoMACS with anti-CD4, -CD8 microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec). T cells from BM were depleted by autoMACS with anti-CD90 microbeads. These isolated T cells showed naive phenotype (CD62Lhigh CD44low) and no activated markers (CD69+, 1.3%-2.2%; CD25+, 0.2%-0.5%). Recipient animals received 800-1100 cGy total body irradiation (137Cs source) on day −1. They were then injected with T cell–depleted (TCD) BM cells (5 × 106) plus splenic CD4+ or CD8+ T cells from wild-type (WT)–B6, H-Y TCR Tg Marilyn, Rachel, or MataHari donors on day 0. For studies in which the recipients were BM chimeras, we induced GVHD 3-5 months after the generation of BM chimera according to a standard protocol as described previously.7,10
Systemic and histopathologic analysis of GVHD
We monitored survival after BMT daily and assessed the degree of clinical GVHD weekly by a previously described scoring system. We also assessed acute GVHD by detailed histopathologic analysis of primary GVHD target organs, as described.19 The tissue sections were examined with an Olympus BX40 microscope. Representative images were taken using a ProgRes C3 digital camera. The objective lens was 20×/0.40/0.17. Oil was not used. All images were obtained at room temperature. The digital images were subsequently analyzed using ProgRes CapturePro Version 2.8.0 software.
FACS analysis
FACS analyses were performed as described before.10 The mAbs used were FITC-, PE-, allophycocyanin-, peridinin chlorophyll protein complex and cyanine 5.5–conjugated anti–mouse CD4, CD8, CD45.2, CD25, CD69, IFN-γ, Foxp3, granzyme B, and CD107a (eBioscience). The procedure was performed as described previously10 For intracellular staining (Foxp3, IFN-γ, granzyme B, and CD107a), the splenocytes were incubated for 5 hours with CD3Ab, CD28Ab, and brefeldin A (eBioscience). Then cells were stained for cell-surface markers, fixed, permeabilized, and stained for intracellular markers according to the manufacture's protocol.
Cytokine ELISA
Concentrations of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17 were measured in serum by ELISA (BD Biosciences PharMingen, R&D Systems, and BioLegend, respectively), in duplicate according to the manufacturer's protocol and read at 450 nm with the use of a microplate reader (Model 3550; Bio-Rad).
Immunization, ex vivo expansion, and detection of H-Y Ag-specific T cells
H-Y Ag-specific T cells were expanded as described before.20 Briefly, 10 × 106 irradiated B6 male splenic cells were injected intraperitoneally into female B6 mice on day 19 before allo-HCT. On day 5 before allo-HCT, B6 female–derived splenocytes were harvested and then restimulated with B6 male–derived BM dendritic cells (DCs) for 120 hours. On day 0, these expanded H-Y Ag-specific T cells were harvested and isolated with MACS and analyzed for H-Y Ag-specific T cells with H-Y peptide tetramer [Db/WMHHNMDLI (Uty), made by National Institutes of Health Tetramer Core Facility].
DC culture and isolation
To obtain DCs, BM cells from male B6 WT mice were cultured with murine recombinant GM-CSF (PeproTech Inc) for 7 days and isolated as described previously.21
Isolation of lymphocytes, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells from liver and small intestine
MLR
For measurement of MLR cultures, splenic T cells were separated by MACS and then cultured with B6 male–derived liver endothelial cells or small intestine epithelial cells for 120 hours. Incorporation of 3H-thymidine (1 μCi/well [0.037 Bq/well]) by proliferating T cells during the final 24 hours of culture was measured by a Betaplate reader (Wallad).
Statistical analysis
The Mann-Whitney U test was used for the statistical analysis of in vitro data and clinical scores. We plotted survival curves with Kaplan-Meier estimates, and the Wilcoxon rank test was used to analyze survival data. A P value < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
H-Y Ag disparity is sufficient to induce CD8+-mediated GVHD
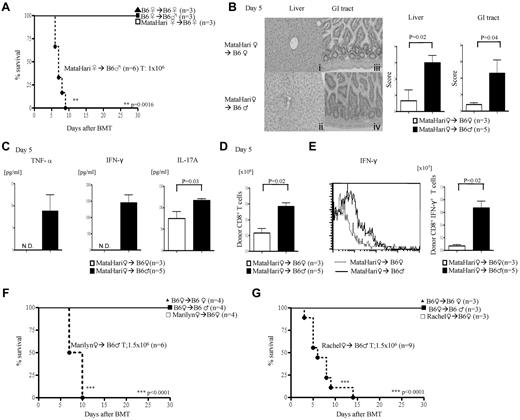
We first tested whether disparity across single H-Y will induce acute GVHD. Anti–H-Y monospecific, H-2b–restricted TCR Tg17,18 mice were used as donors in MHC-matched (F→M) BMT. We used T cells from female MataHari mice, an H-Y–specific CD8+ TCR Tg on the B6.RAG.KO background, that recognizes the WMHHNMDLI peptide from the Uty gene, presented by H-2Db.21 Lethally irradiated female and male B6 animals were transplanted with TCD BM from WT female (B6) mice along with 1 × 106 splenic T cells from either WT or MataHari B6 female donors. All of the syngeneic recipients survived, ruling out potential pathogenic effects from lymphopenic expansion of MataHari T cells (Figure 1A). By contrast, all of the allogeneic male recipients that received MataHari T cells died rapidly (Figure 1A) with signs of severe clinical score (score on day 7, MataHari F→B6M 6 ± 1.3 vs MataHari F→B6F 0.5 ± 0.3; P < .05), and gastrointestinal (GI) and hepatic histopathologic (Figure 1B) GVHD, with elevated levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17A (Figure 1C). MataHari donor T cells also showed significantly greater expansion (Figure 1D), numbers of IFN-γ–secreting cells (Figure 1E), expression of activation markers (CD69 and CD25), and enhanced cytotoxicity (CD107a and granzyme B; supplemental Figure 1A-C, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article) only in the allogeneic male but not the female recipients. These data show that this is an allospecific phenomenon and not a consequence of homeostatic expansion or nonspecific activation of H-Y Ag-specific T cells in the context of radiation-induced cytokine storm.
Single H-Y Ag-specific T cells induce CD8+ and CD4+ T cell–mediated GVHD. (A) Survival in CD8+-mediated GVHD after infusion of 1 × 106 CD8+ T cells from MataHari donors. Data are from 1 of 4 similar experiments. (B-E) GVHD analysis on day 5. Data are from 1 of 3 similar experiments. (B) Histopathologic analysis of liver (i-ii) and GI tract (iii-iv) by H&E stain (left) and scores (right). (C) Serum levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17A (ND indicates not detected). (D) Allo-H-Y Ag-specific donor CD45.2+CD8+ T-cell expansion in spleen. (E) Donor CD45.2+CD8+IFN-γ+ in spleen with representative histogram of IFN-γ expression gated by CD45.2+CD8+ T cells (left) and the absolute number of CD45.2+CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells in spleen (right). (F-G) Survival CD4+ GVHD. Data shown are from 1 of 3 similar experiments.
Single H-Y Ag-specific T cells induce CD8+ and CD4+ T cell–mediated GVHD. (A) Survival in CD8+-mediated GVHD after infusion of 1 × 106 CD8+ T cells from MataHari donors. Data are from 1 of 4 similar experiments. (B-E) GVHD analysis on day 5. Data are from 1 of 3 similar experiments. (B) Histopathologic analysis of liver (i-ii) and GI tract (iii-iv) by H&E stain (left) and scores (right). (C) Serum levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17A (ND indicates not detected). (D) Allo-H-Y Ag-specific donor CD45.2+CD8+ T-cell expansion in spleen. (E) Donor CD45.2+CD8+IFN-γ+ in spleen with representative histogram of IFN-γ expression gated by CD45.2+CD8+ T cells (left) and the absolute number of CD45.2+CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells in spleen (right). (F-G) Survival CD4+ GVHD. Data shown are from 1 of 3 similar experiments.
H-Y–specific CD4+ T cells cause GVHD
To rule out strain-dependent artifacts, we evaluated whether H-Y–specific T cells from 2 other different strains of donor mice, Marilyn and Rachel (H2b), also induced GVHD only in the allogeneic male recipients. CD4+ T cells from Marilyn are specific for the H-Y peptide NAGFNSNRANSSRSS from the Dby gene complexed with Ab, and those of Rachel are specific for Ab complexed with an unknown male-specific peptide.17 Infusion of CD4+ H-Y Tg T cells from either Marilyn or Rachel donors along with BM from WT female B6 donors induced 100% mortality with signs of severe clinical GVHD only in the male recipients (Figure 1F-G). Histopathologic examination (supplemental Figure 2A); levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17 (supplemental Figure 2B-D); and expansion of H-Y Ag-specific donor T cells (supplemental Figure 2E) and IFN-γ+ donor T cells (supplemental Figure 2F) were greater, whereas the Foxp3+ T cells were decreased in the allogeneic (supplemental Figure 2G) males compared with the syngeneic female recipients of Rachel T cells.
H-Y Ag disparate GVHD results from transplanting sufficient numbers of alloreactive precursor T cells
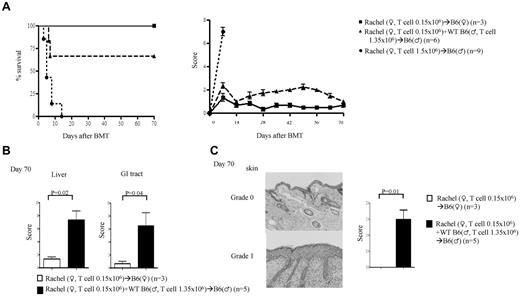
Single minor Ag disparity has been suggested not to be sufficient for causing GVHD.3 By contrast, our data suggested that a single H-Y Ag disparity can drive GVHD. We therefore hypothesized that the induction of GVHD by single minor Ag disparity is a function of transferring sufficient numbers of alloreactive precursor cells. To test this, we next decreased the dose of CD4+ (Rachel) T cells 10-fold (0.15 × 106) and mixed them with (1.35 × 106) syngeneic male CD4+ T cells (∼ 1:9 ratio). All of the female recipients survived, whereas all of the male animals showed clinical signs of GVHD and mortality (33.3%), albeit less than those that received 1.5 × 106 Rachel T cells (Figure 2A). The presence of GVHD was confirmed by histopathology in the GI tract, liver (Figure 2B), and skin (Figure 2C), the target organs of GVHD. However, transfer of 100-fold less (0.015 × 106) Rachel T cells did not cause any mortality or significant clinical GVHD (data not shown). Furthermore, similar to polyclonal donor T cells, the ability of these H-Y–specific T cells to cause GVHD correlated with the intensity of host irradiation (supplemental Figure 2H).24 These results suggest that transplanting sufficient numbers of T-cell precursors against a single minor histo-incompatible Ag caused GVHD.
Donor T-cell precursor frequency is critical for induction of GVHD. Rachel T cells were transplanted along with TCD BM from B6♀ donors into lethally irradiated syngeneic B6♀ or allogeneic B♂ animals. The recipients were monitored for (A) survival and GVHD score. (B) Histopathology scores for liver and GI tract. (C) Skin H&E (left) and score (right). Data are from 1 of 3 similar experiments.
Donor T-cell precursor frequency is critical for induction of GVHD. Rachel T cells were transplanted along with TCD BM from B6♀ donors into lethally irradiated syngeneic B6♀ or allogeneic B♂ animals. The recipients were monitored for (A) survival and GVHD score. (B) Histopathology scores for liver and GI tract. (C) Skin H&E (left) and score (right). Data are from 1 of 3 similar experiments.
Polyclonal T cells cause GVHD after H-Y Ag-mismatched BMT
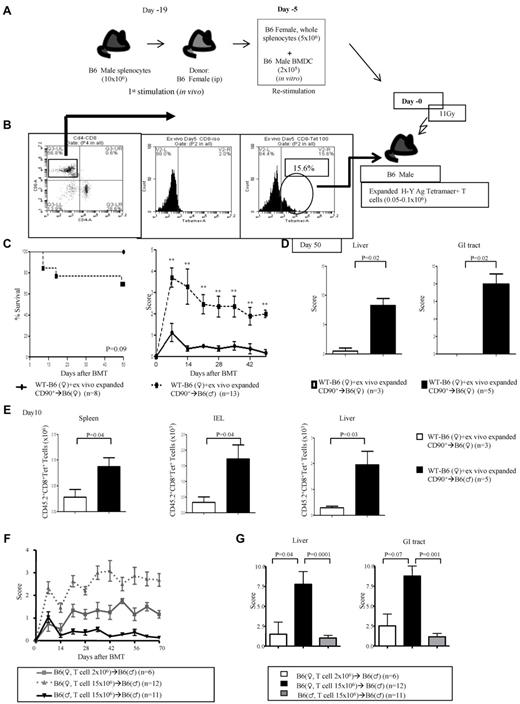
To formally rule out the possibility of an artifact from the Tg nature of the donor T cells, we primed naive WT B6 female donors with B6 male splenocytes (Figure 3A). The donor B6 female splenocytes were harvested and restimulated ex vivo with BM-derived DCs from B6 male animals. The H-Y–specific T cells were confirmed with H-Y peptide tetramer [Db/WMHHNMDLI (Uty)], and ∼ 0.1 × 106 of these cells were transferred into lethally irradiated B6 male and female hosts along with BM cells from female donors (schema shown in Figure 3A-B). The B6 male recipients showed greater mortality, significant clinical severity (Figure 3C), and GVHD-specific histopathology of the target organs (Figure 3D). Significantly greater donor H-Y–specific T cells were recovered from the representative GVHD-specific target organs such as the spleen, intraepithelial lymphocytes, and liver of the male hosts (Figure 3E).
Polyclonal H-Y Ag-specific T cells induce GVHD. (A-B) Experimental schema: polyclonal T cells from WT B6♀ mice that are specific for H-Y Ags were generated after in vivo and subsequent ex vivo priming. These T cells were then transplanted along with TCD BM from B6♀ donors into lethally irradiated syngeneic B6♀ or allogeneic B6♂ animals. The animals were monitored for (C) survival and GVHD score. Data are from 2 combined experiments. **P < .01 compared with female recipients. (D) GVHD histopathology, scores of liver and GI tract and (E) lymphocyte infiltration in the spleen, intestine, and liver. Data are from 1 of 2 similar experiments. (F) Unprimed B6♀ T cells induce GVHD in allogeneic B6♂ recipients. CD90+ T cells (2 × 106 or 15 × 106) donor T cells were harvested from WT B6 female donors and transplanted without priming along with TCD BM into irradiated (11 Gy) syngeneic B6♀ and allogeneic B6♂ animals. The animals were monitored for clinical GVHD severity. (G) Histopathologic analysis, GVHD damage scores of liver and GI tract 70 days after allo-hematopoietic cell transplantation
Polyclonal H-Y Ag-specific T cells induce GVHD. (A-B) Experimental schema: polyclonal T cells from WT B6♀ mice that are specific for H-Y Ags were generated after in vivo and subsequent ex vivo priming. These T cells were then transplanted along with TCD BM from B6♀ donors into lethally irradiated syngeneic B6♀ or allogeneic B6♂ animals. The animals were monitored for (C) survival and GVHD score. Data are from 2 combined experiments. **P < .01 compared with female recipients. (D) GVHD histopathology, scores of liver and GI tract and (E) lymphocyte infiltration in the spleen, intestine, and liver. Data are from 1 of 2 similar experiments. (F) Unprimed B6♀ T cells induce GVHD in allogeneic B6♂ recipients. CD90+ T cells (2 × 106 or 15 × 106) donor T cells were harvested from WT B6 female donors and transplanted without priming along with TCD BM into irradiated (11 Gy) syngeneic B6♀ and allogeneic B6♂ animals. The animals were monitored for clinical GVHD severity. (G) Histopathologic analysis, GVHD damage scores of liver and GI tract 70 days after allo-hematopoietic cell transplantation
To further rule out any potential artifact because of “priming” of T cells before BMT, we performed BMT with 2 × 106 naive T cells from B6 female donors, which barely caused discernable GVHD in male animals. However, transfer of substantially higher numbers, 15 × 106, of donor T cells induced significant clinical and histopathologic GVHD (Figure 3F-G). These results indicate that a single H-Y Ag disparity is sufficient and that epitope spreading is not obligatory for induction of GVHD.
Expression of H-Y Ags in induction of GVHD
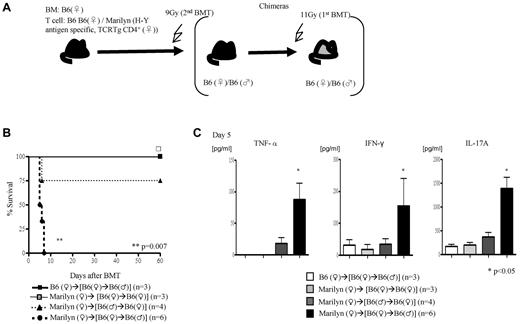
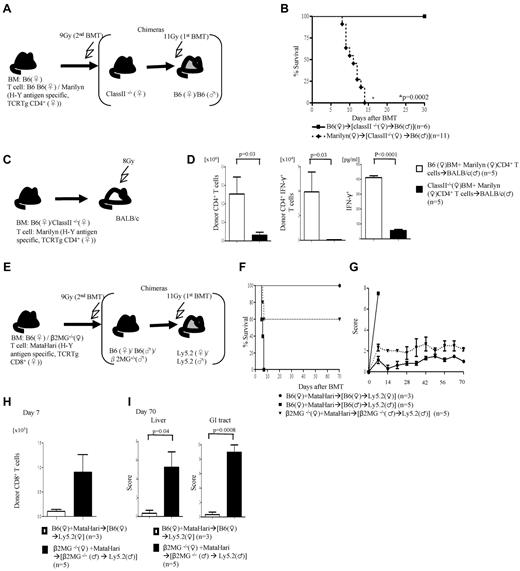
We then next analyzed the requirement of the expression and presentation of H-Y Ags on either the nonhematopoietic or hematopoietic host tissues for induction of GVHD. We generated F→M or M→F BM chimeras such that the H-Y Ags are encoded only by the host nonhematopoietic target tissues or only by the radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived cells, respectively (Figure 4A). These chimeras were then used as BMT recipients and injected with female TCD BM cells plus 1.5 × 106 CD4+ T cells from WT B6 male or from Marilyn donors (experimental schema shown in Figure 4A). The F→M recipients that received cells from syngeneic donors survived, whereas 100% of this group of chimeras that received Marilyn CD4+ T cells died of severe GVHD (Figure 4B; clinical score 8 ± 1 on day 7) and showed significantly greater serum levels of TNFα, INF-γ, and IL-17A (Figure 4C). By contrast, only 25% of the M→F chimeras that received cells from Marilyn CD4+ T cells died (Figure 2G) of modest GVHD (score 4.5 ± 0.9 and 3 ± 0.3 vs 1.5 ± 0 and 1.2 ± 0.2 in syngeneic controls on days 7 and 14, respectively; P < .05). These data are consistent with previous observations25 and further show that minor Ag expression on host target tissues is required for causing severe GVHD.
Alloantigen expression and GVHD. (A) Experimental schema: the F→F, F→M, and M→F chimeras were generated such that male Ags are either not expressed or expressed only on the target tissues or only on the hematopoietic-derived cells. These chimeras were then irradiated and transplanted with Marilyn T cells along with TCD WT B6♀ BM cells and were monitored for (B) survival and (C) Serum levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17A on day 5. Data are from 1 of 2 similar experiments.
Alloantigen expression and GVHD. (A) Experimental schema: the F→F, F→M, and M→F chimeras were generated such that male Ags are either not expressed or expressed only on the target tissues or only on the hematopoietic-derived cells. These chimeras were then irradiated and transplanted with Marilyn T cells along with TCD WT B6♀ BM cells and were monitored for (B) survival and (C) Serum levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17A on day 5. Data are from 1 of 2 similar experiments.
Presentation of H-Y Ags by the radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs is not obligatory
We next explored whether host hematopoietic-derived APCs are obligatory for induction of GVHD. We generated (class II−/− F→B6M) chimeras with the use of thymectomized B6 male mice (to prevent development of autoimmunity in these mice)26 such that the H-Y Ag is expressed on target tissues but cannot be presented to donor CD4+ T cells by the host hematopoietic-derived APCs (schema shown in Figure 5A). All of the syngeneic (class II−/− F→B6M) chimeras survived, whereas 100% of the animals that received cells from Marilyn donors died after BMT (Figure 5B). These data indicate that in the absence of functional Ag presentation on radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs, the H-Y Ag can be efficiently presented by either donor hematopoietic APCs and/or directly by the host nonhematopoietic tissues and cause GVHD.
Presentation by donor and host nonhematopoietic APCs. (A) Experimental schema: B6♂ animals underwent thymectomy and were used for generation of (class II−/−♀→B6♂) chimeras. Three months later, these chimeras were irradiated and transplanted with either B6 or Marilyn T cells and monitored for (B) survival. Data are from 2 combined experiments. (C) Donor APCs alone stimulate GVH responses. Experimental schema: TCD BM from either WT or class II−/− B6♀ were transplanted along with WT or Marilyn T cells into lethally irradiated BALB/c males. (D) Total donor H2Kd+CD4+ T-cell expansion, H2kd+CD4+IFN-γ+ T-cell number, and serum IFN-γ concentration from day 7. Data are from 1 of 2 similar experiments. (E-I) Induction of GVHD in the absence of donor and radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs. (E) Experimental schema: B6Ly5.2 female and male animals were lethally irradiated, treated with anti–natural killer (NK) Ab and transplanted with either WT B6 or β2m−/− BM. Three months later, these chimeras were transplanted with TCD BM from either WT or β2m−/− B6♀ animals along with MataHari T cells. The animals were monitored for (F) survival and (G) clinical score. Data from 1 of 3 similar experiments are shown. (H) Donor CD45.2+CD8+ T cells expansion in spleen and (I) histopathology scores of liver and GI tract. Data from 1 of 2 similar experiments are shown.
Presentation by donor and host nonhematopoietic APCs. (A) Experimental schema: B6♂ animals underwent thymectomy and were used for generation of (class II−/−♀→B6♂) chimeras. Three months later, these chimeras were irradiated and transplanted with either B6 or Marilyn T cells and monitored for (B) survival. Data are from 2 combined experiments. (C) Donor APCs alone stimulate GVH responses. Experimental schema: TCD BM from either WT or class II−/− B6♀ were transplanted along with WT or Marilyn T cells into lethally irradiated BALB/c males. (D) Total donor H2Kd+CD4+ T-cell expansion, H2kd+CD4+IFN-γ+ T-cell number, and serum IFN-γ concentration from day 7. Data are from 1 of 2 similar experiments. (E-I) Induction of GVHD in the absence of donor and radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs. (E) Experimental schema: B6Ly5.2 female and male animals were lethally irradiated, treated with anti–natural killer (NK) Ab and transplanted with either WT B6 or β2m−/− BM. Three months later, these chimeras were transplanted with TCD BM from either WT or β2m−/− B6♀ animals along with MataHari T cells. The animals were monitored for (F) survival and (G) clinical score. Data from 1 of 3 similar experiments are shown. (H) Donor CD45.2+CD8+ T cells expansion in spleen and (I) histopathology scores of liver and GI tract. Data from 1 of 2 similar experiments are shown.
To rule out strain-specific effects and to further determine whether donor T cells respond to minor H-Y Ag when all host (hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic) APCs are incapable of Ag presentation, recipient BALB/c (H2d) male mice were irradiated (800 cGy) and injected with TCD BM from either WT or class II−/− B6 along with 0.5 × 106 purified CD4+ T cells from allogeneic Marilyn donors (experimental schema shown in Figure 5C). Because the H-Y Ag-specific cells from the allogeneic Marilyn B6 donors are H2b restricted, they can recognize the H-Y Ag from the male BALB/c recipients only when presented by the donor-derived H2b APCs. The donor Marilyn CD4+ T cells showed significantly greater proliferation and IFN-γ expression and elevated level of serum IFN-γ only in the BALB/c males that received WT B6 BM (Figure 5D).
Induction of GVHD in the absence of functional Ag presentation by the donor or radiosensitive host hematopoietic APCs
Next, to directly determine whether in the absence of functional donor or radiosensitive host hematopoietic APCs, the nonhematopoietic host tissues alone can directly present minor H-Y Ag to donor T cells and cause GVHD, we designed the following experimental system. We created (β2m−/−→B6M) chimeras with β2 microglobulin (β2m−/−) mice such that the H-Y Ag is expressed on target tissues but cannot be presented to donor CD8+ T cells by the radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs (experimental schema shown in Figure 5E). They were transplanted with 1 × 106 CD8+ T cells from MataHari donors along with BM from the β2m−/− female B6 donors (such that H-Y Ag cannot be presented to donor CD8+ T cells by the donor hematopoietic-derived APCs). All of the syngeneic chimeras survived, whereas the allogeneic WT chimeras died of GVHD (Figure 5F). Importantly, the β2m−/−→B6M animals that received T cells from MataHari donors along with BM from β2m−/− female B6 animals also showed significantly greater mortality (Figure 5F), clinical GVHD (Figure 5G), expansion of the H-Y–allospecific T cells (Figure 5H), and GVHD-specific histopathology (Figure 5I) compared with the syngeneic animals.
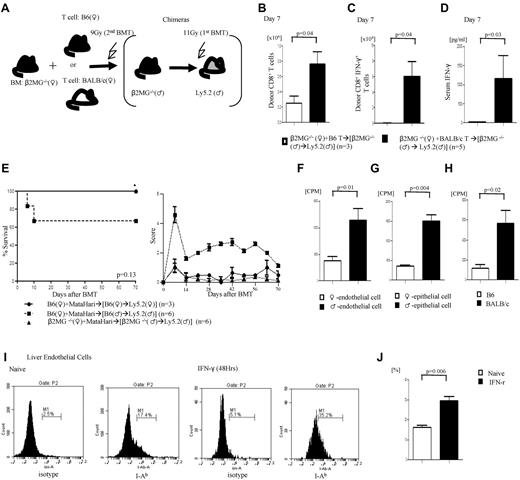
To further rule out strain and Tg T cell–dependent artifacts we used similar β2m−/−→B6M chimeras and transplanted them with T cells from either syngeneic B6 (Ly5.1) or MHC disparate BALB/c female donors (schema shown in Figure 6A). Donor T-cell expansion (Figure 6B) and IFN-γ+T cells (Figure 6C) and serum levels (Figure 6D) were significantly greater in animals that received allogeneic BALB/c T cells despite the absence of functional donor or radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs.
Alloantigen presentation and GVHD in the absence of radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs. (A) Experimental schema: β2m−/−♂→B6♂ chimeras were generated as described in “Methods.” They were then irradiated with 9 Gy and transplanted with TCD BM from β2m−/− animals along with T cells from B6♂ or BALB/c♀ donors and analyzed for donor T-cell expansion. (B) Total donor CD45.1+CD8+ or H2kd+CD8+ T cells expansion. (C) Donor CD8+IFN-γ+ T cell number and (D) serum levels of IFN-γ. Data from 1 of 2 similar experiments are shown. (E) GVH responses induced by host nonhematopoietic APCs depend on T-cell precursor frequency. Survival and GVHD score. Data from 1 of 2 similar experiments are shown. (F-H) Male nonhematopoietic cells can stimulate both H-Y Ag-specific T cells and allogenic T cells. (F-G) Marilyn CD4 T cells against male liver endothelial cells (H) and epithelial cells of small intestine (G). (H) B6 male–derived liver endothelial cells can stimulate allogeneic BALB/c T cells. (I-J) Class II expression on liver endothelial cells gated by CD146+ cells, (right) naive and (left) IFN-γ stimulation for 48 hours (I). (J) Bar graph of class II expression on liver endothelial cells. Data are from 1 of 3 similar experiments.
Alloantigen presentation and GVHD in the absence of radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs. (A) Experimental schema: β2m−/−♂→B6♂ chimeras were generated as described in “Methods.” They were then irradiated with 9 Gy and transplanted with TCD BM from β2m−/− animals along with T cells from B6♂ or BALB/c♀ donors and analyzed for donor T-cell expansion. (B) Total donor CD45.1+CD8+ or H2kd+CD8+ T cells expansion. (C) Donor CD8+IFN-γ+ T cell number and (D) serum levels of IFN-γ. Data from 1 of 2 similar experiments are shown. (E) GVH responses induced by host nonhematopoietic APCs depend on T-cell precursor frequency. Survival and GVHD score. Data from 1 of 2 similar experiments are shown. (F-H) Male nonhematopoietic cells can stimulate both H-Y Ag-specific T cells and allogenic T cells. (F-G) Marilyn CD4 T cells against male liver endothelial cells (H) and epithelial cells of small intestine (G). (H) B6 male–derived liver endothelial cells can stimulate allogeneic BALB/c T cells. (I-J) Class II expression on liver endothelial cells gated by CD146+ cells, (right) naive and (left) IFN-γ stimulation for 48 hours (I). (J) Bar graph of class II expression on liver endothelial cells. Data are from 1 of 3 similar experiments.
Ag presentation by hematopoietic-derived APCs is not obligatory but required for induction of optimal GVHD
To investigate the potential mechanisms for induction of GVHD in the absence of radiosensitive host APCs we posited that infusion of sufficient numbers of alloreactive donor T-cell precursors are required for induction of GVHD. We once again used the β2m−/−→B6M chimeras (Figure 5E), such that the H-Y Ag is expressed on target tissues but cannot be presented to donor CD8+ T cells by the radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs. We transplanted 10-fold less (0.1 × 106) CD8+ T cells from MataHari donors along with BM from the β2m−/− female B6 donors into the β2m−/−→B6M and B6→B6M animals. All of the syngeneic chimeras survived, whereas 30% of the allogeneic WT chimeras died of GVHD (Figure 6E). Importantly, the β2m−/−→B6M animals that received only 0.1 × 106 CD8+ T cells from MataHari donors showed nonlethal GVHD modest clinical severity (Figure 6E). These data suggest that induction of GVHD in the absence of alloantigen presentation by the radiosensitive host and donor hematopoietic APCs is less efficient than that induced by the radiosensitive host or donor hematopoietic APCs. Thus, minor Ag presentation on host or donor hematopoietic-derived APCs, although not obligatory, induces more robust GVHD severity.
Allogeneic T cells can be activated by nonhematopoietic-derived cells
Next, to address which nonhematopoietic cells might be presenting alloantigens to donor T cells, we analyzed whether host endothelial and epithelial cells would directly stimulate donor T cells. Isolated epithelial cells were analyzed for both epithelial cell–specific marker and CD11c+ expression to rule out any possible contamination with professional APCs. The epithelial cells showed expression of epithelial markers without any evidence of CD11c+ expression (supplemental Figure 4A).The liver endothelial and small bowel epithelial cells from the allogeneic male animals caused significantly greater proliferation of Marilyn T cells compared with cells from syngeneic female cells (Figure 6F-G). The B6 liver endothelial cells also caused greater proliferation of polyclonal CD4+ T cells from allogeneic BALB/c animals, showing that this is not merely a response germane to TCR Tg T cells (Figure 6H). Consistent with their ability to stimulate alloreactive T cells, both the endothelial and the epithelial cells express MHC class II, which is further enhanced by the addition of IFN-γ to simulate an inflammatory milieu (Figure 6I-J; supplemental Figure 3). These data suggest that in the context of postconditioning inflammation, nonhematopoietic cells such as certain endothelial, epithelial, or other cells might contribute to activation of alloreactive T cells and induce GVHD.
Discussion
Collectively, our data with T cells specific for clinically relevant H-Y Ags and also with polyclonal donor T cells in multiple murine models (summarized in supplementary Table 1) challenge the currently held notions that alloantigen presentation by radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs is obligatory for induction of GVHD.6,10 The data suggest that in the context of inflammation, infusion of sufficient numbers of alloreactive donor T cells can induce GVHD even in the absence of radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs. Although our data did not formally address the role of Langerhans cells (the only professional hematopoietic-derived APCs that have been shown to be radioresistant and survive in these chimeras),27 our data, when taken collectively in light of recent observations by Li et al,28 suggest that Langerhans cells and other radioresistant hematopoietic APCs, if any, are unlikely to have contributed to the induction of GVHD.
The previous observations that show an obligatory role for radiosensitive host APCs is probably a consequence of transplanting insufficient allospecific T cells.6,10 By contrast, our data show that, when sufficient numbers of highly avid and minor Ag-specific T cells are transplanted, GVHD can be induced in the absence of radiosensitive host or donor hematopoietic-derived APCs. These observations were germane to H-Y–specific and polyclonal T cells across multiple models. Infusion of 5 × 106 donor T cells in the MHC-matched multiple minor C3H.SW→(β2m−/−→B6M) model (that was used in previous reports) also resulted in expansion of donor T cells, showing that the induction of GVH responses is probably a function of the transferring appropriate numbers of alloreactive donor T cells (supplemental Figure 4B).
The putative nonhematopoietic cells that might present alloantigens to donor T cells and induce GVHD include endothelial or epithelial cells as suggested by the ability of these cells to activate alloreactive H-Y–specific and polyclonal T cells. The ability of endothelial cells to stimulate allogeneic T cells is consistent with observations in humans.29,30 However, the direct and/or relative contributions of these cells and the radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs will need further investigation and the development of requisite tools. Furthermore, the site of activation of alloreactive donor T cells by these putative nonhematopoietic APCs, the requirement of secondary lymphoid organs and/or directly in the target tissues remains to be determined. Nonetheless, our data (Figures 3F and 4E) indicate that the intensity of GVHD severity may be less in the absence of radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived APCs.
The sufficiency of single H-Y Ag disparity in causing GVHD mortality is in agreement with experimental organ rejection observations9,18,31 but in contrast to earlier observations in BMT.2,3 This could be a consequence of (1) limited expression of the single immune-dominant minor Ag in contrast to the ubiquitous expression of the H-Y Ag,32,33 and also (2) infusion of insufficient numbers of T-cell precursors against the Ag. Nonetheless, our data are also consistent with recent observations of the sufficiency of single minor Ag disparity in causing GVHD34 and further expand the observation to clinically relevant, H-Y, minor Ags.
Given the previous observations on the requirement of functional radiosensitive host hematopoietic APCs for induction of GVL responses,7,35,36 our data raise the intriguing possibility that GVHD and GVL can perhaps be differentially regulated at the level of Ag presentation. Although direct allopresentation by host cells can cause GVHD, direct presentation of tumor-specific Ags and alloantigens by the tumors (that have developed a multitude of tumor intrinsic immune-evasive pathways) may be insufficient for generation of an effective GVL response. It is therefore probable that cross-presentation of tumor Ags is required for optimal GVL. Because cross-presentation of Ags is primarily a function of subsets of professional APCs, it stands to reason that enhancing cross-presentation on the specific professional APC subsets might facilitate an effective GVL response without aggravating GVHD.
Our observations have additional significant clinical ramifications. They show a causal role for H-Y Ags in clinical GVHD and suggest that identification and tolerizing against relevant immune-dominant minors might prevent GVHD. Our data indicate that GVHD can be induced even in the absence of minor Ag presentation by the radiosensitive host or donor hematopoietic-derived cells. Because host hematopoietic-derived APCs can also negatively regulate GVH responses,37,38 our data indicate that strategies that promote the regulatory APC subsets39-42 might be more effective than elimination of hematopoietic-derived activating APC subsets.28,43-45 Importantly, our data indicate that regulating the process of Ag presentation, rather than targeting any specific host hematopoietic-derived cellular subsets that are capable of activating alloreactive donor T cells, might be a more desirable strategy for mitigating GVHD.
There is an Inside Blood commentary on this article in this issue.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Polly Matzinger, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, for the Matahari, Marilyn, and Rachel mice and for critical reading of the manuscript; Dr David Ginsburg, University of Michigan, for critical reading of the manuscript; and Janet Hoff for expert technical assistance.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants AI-075284 and HL-090775, P.R.).
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: T.T. designed and performed research, analyzed the data; and wrote the paper; I.T. designed and performed research; Y.S., E.N., and R.E. performed research; C.L. performed pathologic analysis; T.F. designed research; R.K. designed research and wrote the paper; and P.R. designed research, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Pavan Reddy, 3312 CCC, 1500 E Medical Center Dr, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-0942; e-mail: reddypr@umich.edu.