Abstract
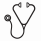
Background: Nilotinib is a BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor with approximately 50-fold higher inhibitory activity than imatinib in preclinical studies.
Aim: We initiated a phase II study (in 2005) to evaluate the efficacy of frontline nilotinib in pts with newly diagnosed CML-CP. The primary objective of this report was to estimate major molecular response (MMR) and complete molecular response (CMR: minimum 100,000 ABL copies) rates with prolonged follow-up, and the impact of MMR and CMR on long-term outcome.
Methods: Pts with Ph-positive or BCR-positive CML in early CML-CP [i.e., time from diagnosis 12 months] with <1 month of prior interferon-alpha and/or imatinib were eligible. Nilotinib was initiated at a dose of 400 mg twice daily. Results for CCyR and MMR are reported as intent-to-treat unless specifically annotated as response among evaluable pts (eval).
Results: 140 pts have been treated as of August 1, 2014. Herein we focus on the initial 109 pts who have a minimum follow-up of 12 months. The median (med) follow-up for these 109 pts is 52.2 months (range, 0.9 to 108.0+). The med age was 50 years (range, 17 to 86). 73% of pts had Sokal low risk. 17 (16%) had received imatinib for <1 months (med 18 days; range, 5 to 29 days).
Overall, 92% (100/109) pts achieved a complete cytogenetic response [CCyR] with a med time to CCyR of 2.9 months (range, 2.1 to 8.1+). The rates of CCyR at 3, 6, 12 and 18 months were 80% (eval:83%), 86% (eval:95%), 83% (eval:99%), and 77% (eval:100%), respectively.
Overall, MMR and CMR were achieved in 90% (98/109) and 45% (49/109) of the pts. Med time to MMR and CMR was 3.3 months (range, 2.4 to 48.0+) and 23.1 months (range, 3.2 to 86.0+), respectively. BCR-ABL/ABL at 3 months was <10% in 94% (eval:100%) and <1% in 89% (eval: 94%). BCR-ABL/ABL at 6 months was <1% in 81% (eval:89%) and <0.1% in 65% (eval:72%) in pts evaluated at these time points. MMR was observed in 65% (eval:72%) at 6 months, 71% (eval:87%) at 12 months, and 70% (eval:90%) at 18 months. CMR was observed in 9% (eval:11%) at 6 months, 14% (eval:17%) at 12 months, and 15% (eval:19%) at 18 months. We further analyzed the association between CCyR and molecular response (Table 1). For example, among the 84 pts who were in CCyR at 18 months: MMR was achieved in 90% of these pts including MR3 in 31%, MR4 in 13%, MR4.5 in 27%, and CMR in 19%.
Estimated 3-year and 5-year overall survival (OS) is 98% and 91%, respectively. Estimated 3-year and 5-year failure-free survival (FFS) is 82% and 73%, respectively. On an intent-to-treat analysis the FFS among pts who achieved CMR was superior to those who did not achieve CMR (P<0.001, respectively). On a landmark analysis, which included only those pts who received nilotinib for a minimum of 24 months (med time to CMR among pts who achieved CMR=23.1 months) the FFS among pts who achieved CMR was superior to those who did not achieve CMR (P=0.008) (Figure 1).
Dose-reductions were performed in 41 (38%) pts: 30 pts required 1 dose-reduction and 11 pts required 2 or more dose-reductions. The most frequent reasons for dose-reductions included increased liver enzymes (n=8), rash (n=5), pain/arthralgia (n=4), cardiac and QTc (n=4), fatigue (n=5), and neutropenia (n=2). The actual med dose remains 800 mg daily. 29 (27%) pts are off study due to toxicity in 8 (cardiac=3, liver enzymes=4, fatigue=1), inadequate response in 5 (3 never achieved adequate and 2 lost adequate response), progression to blast-phase in 3, death in 5 (all 5 non-CML related causes), 8 due to pt choice (financial=1, non-compliance=3, pt choice=1)
Conclusion: Nilotinib 400 mg twice daily is very effective. The cumulative rates of CCyR, MMR and CMR were 92%, 90%, and 45%, respectively. CMR rates continue to improve with long-term follow-up. Attainment of CMR is associated with improved long-term outcome.
Molecular response rates among pts who achieve CCyR
| . | CCyR . | MR3 but not MR4 . | MR4 but not MR4.5 . | MR4.5 but not CMR . | CMR . | No MMR . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 months | 87/105 (83%) | 39/87 (45%) | 5/87 (6%) | 8/87 (9%) | 2/87 (2%) | 33/87 (38%) |
| 6 months | 94/99 (88%) | 35/94 (38%) | 6/94 (6%) | 20/94 (21%) | 10/94 (11%) | 23/94 (24%) |
| 12 months | 90/91 (99%) | 38/90 (42%) | 3/90 (3%) | 23/90 (26%) | 15/90 (17%) | 11/90 (12%) |
| 18 months | 84/84 (100%) | 26/84 (31%) | 11/84 (13%) | 23/84 (27%) | 16/84 (19%) | 8/84 (10%) |
| . | CCyR . | MR3 but not MR4 . | MR4 but not MR4.5 . | MR4.5 but not CMR . | CMR . | No MMR . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 months | 87/105 (83%) | 39/87 (45%) | 5/87 (6%) | 8/87 (9%) | 2/87 (2%) | 33/87 (38%) |
| 6 months | 94/99 (88%) | 35/94 (38%) | 6/94 (6%) | 20/94 (21%) | 10/94 (11%) | 23/94 (24%) |
| 12 months | 90/91 (99%) | 38/90 (42%) | 3/90 (3%) | 23/90 (26%) | 15/90 (17%) | 11/90 (12%) |
| 18 months | 84/84 (100%) | 26/84 (31%) | 11/84 (13%) | 23/84 (27%) | 16/84 (19%) | 8/84 (10%) |
PCyr, partial cytogenetic response; Min, mimimal; Inev, inevaluable; IM, insufficient metaphase
FFS CMR versus no CMR by landmark analysis for pts who received at least 24.0 months of nilotinib
FFS CMR versus no CMR by landmark analysis for pts who received at least 24.0 months of nilotinib
Daver:Novartis: Research Funding. Jabbour:Novartis: Advisory board membership Other, Research Funding. Cortes:Novartis: Advisory Board membership Other, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract