Key Points
A novel mouse model elucidates the impact of Pml NB disruption on APL pathogenesis and response to targeted therapy.
The mode of action of this disruption appears to be via the perturbation of the NHEJ and HR pathways.
Abstract
A hallmark of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is altered nuclear architecture, with disruption of promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies (NBs) mediated by the PML–retinoic acid receptor α (RARα) oncoprotein. To address whether this phenomenon plays a role in disease pathogenesis, we generated a knock-in mouse model with NB disruption mediated by 2 point mutations (C62A/C65A) in the Pml RING domain. Although no leukemias developed in PmlC62A/C65A mice, these transgenic mice also expressing RARα linked to a dimerization domain (p50-RARα model) exhibited a doubling in the rate of leukemia, with a reduced latency period. Additionally, we found that response to targeted therapy with all-trans retinoic acid in vivo was dependent on NB integrity. PML-RARα is recognized to be insufficient for development of APL, requiring acquisition of cooperating mutations. We therefore investigated whether NB disruption might be mutagenic. Compared with wild-type cells, primary PmlC62A/C65A cells exhibited increased sister-chromatid exchange and chromosome abnormalities. Moreover, functional assays showed impaired homologous recombination (HR) and nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair pathways, with defective localization of Brca1 and Rad51 to sites of DNA damage. These data directly demonstrate that Pml NBs are critical for DNA damage responses, and suggest that Pml NB disruption is a central contributor to APL pathogenesis.
Introduction
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is 1 of the commonest subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), with the vast majority of cases harboring the t(15;17) chromosomal translocation, involving the fusion of the genes encoding promyelocytic leukemia (PML) and the transcription factor retinoic acid receptor α (RARα).1-3 The outcome for APL patients has been transformed with the advent of molecularly targeted therapies, that is, arsenic trioxide (ATO) and all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), which bind to the PML and RARα moieties of PML-RARα, respectively. These 2 drugs act in synergy to trigger PML-RARα degradation, by promoting apoptosis (ATO) and cellular differentiation (ATRA), inducing clinical remission.4-7
PML is localized in PML nuclear bodies (NBs),8-10 discrete subnuclear structures of which PML is a crucial component.11-13 Indeed, PML not only promotes NB biogenesis and maintains its integrity,3,14,15 but also is involved in the recruitment and localization of ∼100 proteins into this complex (eg, SUMO-1, CBP, DAXX, BLM).16 The posttranslational modifications of PML, including its SUMOylation, are critical steps in the formation of mature PML NBs.3,17-19 PML NBs are dynamic multiprotein complexes,16 involved in various major processes such as stem cell self-renewal, cell death, and transcription.20
Cells use different DNA repair pathways depending on the type of damage, and the phase of the cell cycle in which the damage occurs. DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) produced by ionizing radiation (IR), for example, can be repaired by 2 major mechanisms: the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) repair pathways. NHEJ, which is mostly active during the G1 phase of the cell cycle, mediates direct ligation of the broken DNA ends in an error-prone manner. HR is, by contrast, largely error free, and arises in the G2 phase using sister chromatids as templates for repair. Failure in DNA DSB repair may lead to genomic instability and, consequently, cancer predisposition.21
Numerous studies have highlighted the importance of the capacity of the PML-RARα fusion protein to oligomerize (conferred by the PML moiety) in APL pathogenesis, in contrast to wild-type (WT) RARα, which lacks this property.22,23 Moreover, it is also unambiguous that PML-RARα expression has a major impact on nuclear architecture leading to NB disruption into nuclear microspeckles, which is a diagnostic hallmark of APL.3 This phenomenon has been proposed as a key step in leukemogenesis,24 but this has not been formally explored in vivo until now. Furthermore, NB disruption is reversed by ATO or ATRA treatment,25 suggesting that normalization of nuclear architecture may be important for response to targeted therapies. To address these issues, we have generated a novel knock-in mouse model, where targeted Pml NB disruption was achieved through mutation of 2 key zinc-binding cysteine residues (C62A/C65A) in the RING domain of Pml. Our mouse model highlights the essential cooperative role of the NB disruption induced by PML-RARα expression in APL development, and the importance of reformation of NBs in generating an efficient response to differentiating drug (ATRA). Additionally, our data reveal that Pml NBs are determinants of the quality of DNA damage repair via both NHEJ and HR repair pathways.
Materials and methods
Animal experimental guidelines
All animal experimentations were performed in accordance with the terms of UK Home Office guidelines. The Home Office Project license number under which these experiments were conducted is PPL 70/7720.
Transplantation experiments
All transplant recipient mice were 8 to 12 weeks old at the time of transplantation. Unfractionated bone marrow (BM) cells (0.5 × 106 to 1 × 106) were transplanted into sublethally irradiated mice (4.5 Gy) via tail-vein injection. PML-RARα leukemic BM cells were transplanted into sublethally irradiated FVB/N Hsd mice. Moribund mice were humanely sacrificed, and leukemia was routinely confirmed by May-Grünwald Giemsa staining, peripheral blood analyses, or independent confirmation by a veterinarian.
Leukemia samples used for transplantation experiments were as follows: numbers 1707, M1/28, and 1787 for PmlWT+p50-RARα; numbers 1403, 626, and 628 for PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα; numbers 1111/3, 935/5, and 1097/1 for PML-RARα.
For ATRA in vivo experiments, placebo or ATRA 21-day-release pellets (5 mg; Innovative Research of America) were subcutaneously implanted 7 days posttransplantation as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis
Cells were lysed on ice in radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer containing protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) and 20 mM N-ethylmaleimide (Sigma-Aldrich). Lysates were precleared with Sepharose 4B beads (GE Healthcare), and then immunoprecipitated with the relevant antibody or isotype control as previously described.26 Immunoprecipitates and whole-cell lysates were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (Millipore). Membranes were blocked in 5% bovine serum albumin, and then incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. Immunodetection was performed using enhanced chemiluminescence western blotting substrate (ThermoFisher), or using infrared imaging (Odyssey LI-COR).
Flow cytometry assays
The Lin−Sca-1+c-Kit+ (LSK) population was defined as previously described.27 Briefly, lineage-depleted (Dynabeads; ThermoFisher) BM cells were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies against Sca-1, and c-Kit (Biolegend), and the lineage cocktail (B220, CD3, CD4, CD8, Ter119, Mac-1, and Gr-1; Biolegend). CD11b/Gr-1 population analysis was performed as previously described.28 Flow cytometry was performed on a BD LSRFortessa cell analyzer, and data were analyzed with FlowJo software (Tree Star).
In vivo cell-cycle analysis
Mice were injected with 50 mg/kg 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) 2 hours before BM harvest.29 Cells were processed using a Click-iT EdU Flow Cytometry Assay kit (ThermoFisher).
Nitro blue tetrazolium reduction assay
Nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT; 0.1%) (Sigma-Aldrich) was added to leukemic BM cells on poly-d-lysine–coated coverslips, and incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37°C. Images were taken under an Eclipse Ti-E Inverted Imaging System (Nikon), and autoanalyzed with NIS software. At least 1100 cells were counted per sample.
NHEJ and HR activity assay
All cell types were nucleofected using the Amaxa kit (Lonza) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were cotransfected with linearized NHEJ reporter plasmid or linearized HR reporter plasmid (kind gifts of Vera Gorbunova, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY) and pDsRed-Express-N1 plasmid (Clontech; as transfection efficiency control) as previously described.30,31 Lineage-depleted BM cells were isolated 12 hours before nucleofection.32 Flow cytometry was performed on a BD LSRFortessa cell analyzer, and data were analyzed with FlowJo software (TreeStar).
Results
Generation of a PmlC62A/C65A knock-in mouse model and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα mice
To investigate the functional consequences of Pml NB disruption, we engineered a knock-in mouse model by substituting 2 zinc-binding cysteine residues for 2 alanine residues located in the RING domain at positions 62 and 65, via site-directed mutagenesis and subsequent homologous recombination in mouse embryonic stem cells (supplemental Figure 1A-E, available on the Blood Web site). For simplicity, homozygous mutant mice will be referred to as PmlC62A/C65A. PmlC62A/C65A mice are developmentally normal, and do not die of spontaneous leukemias or tumors.
The importance of RARα dimerization in APL pathogenicity has been reported previously.33 To explore whether RARα dimerization operates conjointly with NB disruption, PmlC62A/C65A mice were crossbred with p50-RARα transgenic mice,34 in order to generate PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα mice; here, RARα dimerization is artificially forced by linking to the dimerization domain of the NF-κB p50 subunit.33,34 All of the mouse models used in this study have been color coded, as summarized in supplemental Figure 1F.
PmlC62A/C65A expression causes dispersion of NB constituents, deficiency of Pml SUMOylation, and expansion of the LSK compartment
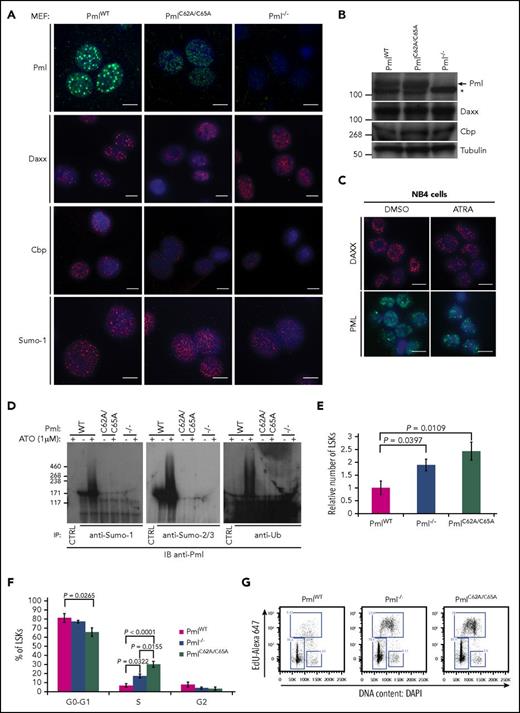
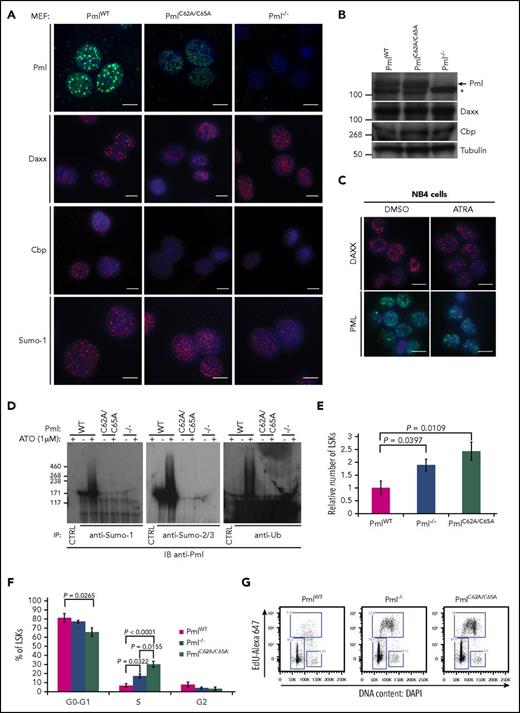
We next investigated whether endogenous PmlC62A/C65A expression induced Pml NB disruption, as previously described when overexpressed in human cell lines.15,35,36 We performed immunofluorescence staining to analyze the localization of well-known NB constituents. Initially, Pml staining was used as a first-line control of Pml NB disruption; this confirmed that PmlC62A/C65A was dispersed in primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) compared with WT Pml (PmlWT). Additionally, whereas Daxx, Cbp, and Sumo-1 formed clear and bright foci in PmlWT MEFs, a diffuse nuclear pattern was observed in PmlC62A/C65A and Pml−/− cells17,37 (Figure 1A). We confirmed that these differences did not result from variations in the level of protein expression (Figure 1B). The PmlC62A/C65A mutant replicated the NB disruption seen in primary human APL cells, with dispersion of PML and NB constituents (eg, DAXX), and as shown in the PML-RARA–expressing NB4 human cell line. As expected, treatment of NB4 cells with ATRA led to relocalization of DAXX and PML into NBs38 (Figure 1C).
PmlC62A/C65Aexpression induces mislocalization of NB constituents, Pml SUMOylation deficiency, and expansion of the LSK compartment. (A) Representative confocal microscopy images are presented for Pml (green), Daxx, Cbp, and Sumo-1 (red) staining in PmlWT, PmlC62A/C65A, and Pml−/− MEFs. Nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Expression levels demonstrated by western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates extracted from PmlWT, PmlC62A/C65A, and Pml−/− MEFs. The asterisk (*) indicates a nonspecific band. Tubulin was used as loading control. (C) Representative images of DAXX (red) and PML (green) staining in NB4 cells treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or ATRA (1 μM). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) MEFs were treated with or without ATO (1 μM) for 1 hour, as indicated, followed by immunoprecipitation (IP) by control immunoglobulin G (IgG; CTRL) or with antibodies against the indicated protein. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblot (IB) with an anti-Pml antibody in order to reveal the SUMOylated or ubiquitinated forms of Pml. Data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. (E) Relative number of LSK cells in BM at 8 weeks (n ≥ 3). (F) Cell-cycle phase distribution of LSK cells labeled with Click-iT EdU in vivo (n ≥ 3). (G) Representative dot plots of cell-cycle status of LSK population. (E-F) Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analyses were performed.
PmlC62A/C65Aexpression induces mislocalization of NB constituents, Pml SUMOylation deficiency, and expansion of the LSK compartment. (A) Representative confocal microscopy images are presented for Pml (green), Daxx, Cbp, and Sumo-1 (red) staining in PmlWT, PmlC62A/C65A, and Pml−/− MEFs. Nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Expression levels demonstrated by western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates extracted from PmlWT, PmlC62A/C65A, and Pml−/− MEFs. The asterisk (*) indicates a nonspecific band. Tubulin was used as loading control. (C) Representative images of DAXX (red) and PML (green) staining in NB4 cells treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or ATRA (1 μM). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) MEFs were treated with or without ATO (1 μM) for 1 hour, as indicated, followed by immunoprecipitation (IP) by control immunoglobulin G (IgG; CTRL) or with antibodies against the indicated protein. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblot (IB) with an anti-Pml antibody in order to reveal the SUMOylated or ubiquitinated forms of Pml. Data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. (E) Relative number of LSK cells in BM at 8 weeks (n ≥ 3). (F) Cell-cycle phase distribution of LSK cells labeled with Click-iT EdU in vivo (n ≥ 3). (G) Representative dot plots of cell-cycle status of LSK population. (E-F) Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analyses were performed.
The PML RING domain is essential for PML SUMOylation.14,15,37,39 Immunoprecipitations of Sumo-1 or Sumo-2/3 revealed that endogenous PmlWT was SUMOylated in MEFs at a basal level, and hyper-SUMOylated following ATO treatment (Figure 1D). Moreover, post-ATO treatment, PmlWT was found to be ubiquitinated. None of these smears of bands were detected in PmlC62A/C65A cells, or as expected in Pml−/− cells (negative control)26 (Figure 1D). Collectively, we confirmed that the C62A/C65A mutation induces NB disruption in a fashion similar to that observed in the context of PML-RARα. These data also demonstrate that the integrity of the RING domain is required not only for PML SUMOylation, but also for the ATO-induced PML degradation pathway.
In vivo, PmlC62A/C65A mice did not exhibit alterations in peripheral blood count parameters. However, the number of LSK hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells was greatly increased, and this increase was even more significant than that seen in the absence of Pml (ie, Pml−/− mice) (Figure 1E; supplemental Figure 2). Cell-cycle analysis revealed that the higher number of LSK cells in PmlC62A/C65A mice, and to a lesser extent in Pml−/− mice, was attributable, at least in part, to an acceleration of cell-cycle progression (Figure 1F-G). Unlike LSK cells, PmlWT, Pm−/−, and PmlC62A/C65A primary MEFs did not present any variations in their cell-cycle nor cell-death profiles (supplemental Figure 3), thus making MEFs a more suitable model to analyze downstream cellular functions.
Pml NB disruption promotes APL pathogenesis
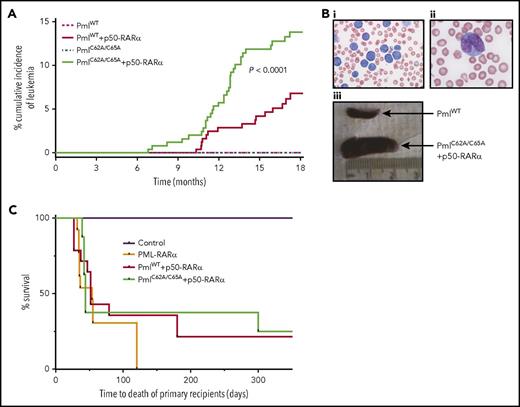
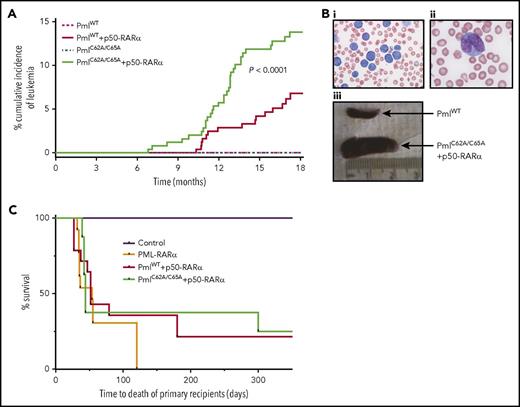
Although no disease was detected over an 18-month observation period in PmlWT (0 of 249) or PmlC62A/C65A (0 of 251) mice, both PmlWT+p50-RARα (15 of 252) and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα (32 of 251) mice developed APL spontaneously (Figure 2A-B). These leukemias were characterized by hyperleukocytosis, anemia, and thrombocytosis, and validated by postmortem examination, revealing, for example, pale BM and splenomegaly (mean weight of healthy adult spleen, 25.75 mg; PmlWT+p50-RARα leukemic spleen, 458 mg; PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα leukemic spleen, 642 mg; PML-RARα leukemic spleen as control, 580 mg). The cumulative incidence of APL differed significantly between PmlWT+p50-RARα and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα genotypes, with a frequency at 18 months of 6.8% and 13.8%, respectively, leading to a penetrance comparable to that observed in PML-RARα transgenic models40-42 (Figure 2A). Moreover, the latency period before the onset of leukemia was significantly reduced in the context of NB disruption compared with PmlWT+p50-RARα (to 213 days of age vs 310 days; P < .008; Figure 2A). These results demonstrate cooperativity between NB disruption and RARα dimerization in the initiation of APL.
Pml NB disruption improves induction of APL. (A) Kaplan-Meier curve showing cumulative incidence of APL in PmlWT (n = 249), PmlC62A/C65A (n = 251), PmlWT+p50-RARα (n = 252), and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα (n = 251). (Bi-ii) Representative pictures of blood smear of moribund PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα mice showing hyperleukocytosis (May-Grünwald Giemsa staining; original magnification ×20 (i) and ×100 (ii)). (Biii) Representative spleens of PmlWT healthy control and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα leukemic mice. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mouse primary recipients transplanted with PmlWT+p50-RARα (n = 14) and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα (n = 8) leukemic BM cells, from 3 independent leukemias each. Mouse recipients transplanted with PML-RARα leukemic BM cells (n = 13) from 3 independent leukemic samples. This graph represents pooled data from 2 independent experiments. (A,C) Log-rank tests were used to compare survival curves.
Pml NB disruption improves induction of APL. (A) Kaplan-Meier curve showing cumulative incidence of APL in PmlWT (n = 249), PmlC62A/C65A (n = 251), PmlWT+p50-RARα (n = 252), and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα (n = 251). (Bi-ii) Representative pictures of blood smear of moribund PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα mice showing hyperleukocytosis (May-Grünwald Giemsa staining; original magnification ×20 (i) and ×100 (ii)). (Biii) Representative spleens of PmlWT healthy control and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα leukemic mice. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mouse primary recipients transplanted with PmlWT+p50-RARα (n = 14) and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα (n = 8) leukemic BM cells, from 3 independent leukemias each. Mouse recipients transplanted with PML-RARα leukemic BM cells (n = 13) from 3 independent leukemic samples. This graph represents pooled data from 2 independent experiments. (A,C) Log-rank tests were used to compare survival curves.
We then assessed APL-initiating activity by transplanting primary APL-derived cells into recipient mice. The vast majority of mice transplanted with leukemic PmlWT+p50-RARα (11 of 14) or PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα (6 of 8) unsorted BM cells developed APL (Figure 2C). The latency period to disease was similar to that previously observed upon transplantation of PML-RARα leukemic blasts.40 None of the mice that received a mock transplant (phosphate-buffered saline) developed any disease. Secondary and tertiary transplants of unsorted BM cells retained the capacity to initiate APL for these 3 genotypes.
The similarities we observed between PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα and PML-RARα mice thus strengthen evidence for the crucial contribution of Pml NB disruption to APL pathogenesis.
Pml NBs are involved in the response to ATRA treatment
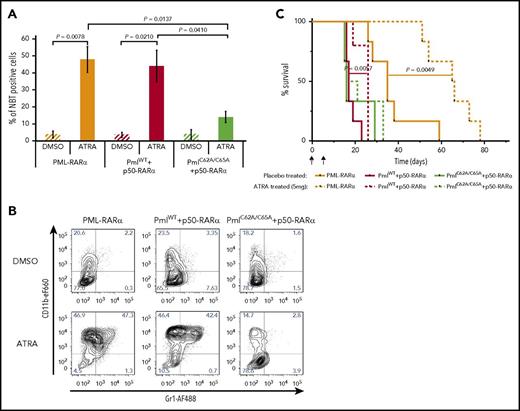
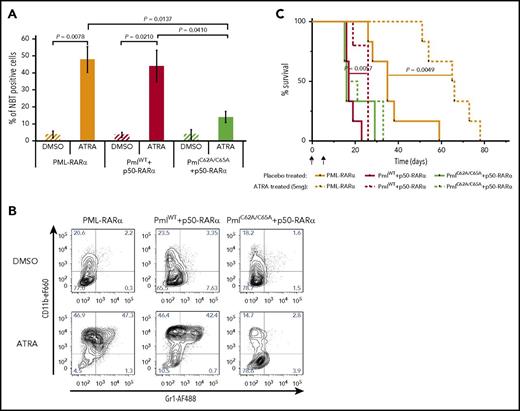
Induction of myeloid differentiation is the hallmark of response to ATRA.43 To analyze the effect of NB disruption on ATRA-induced differentiation, we first performed an in vitro NBT assay. When unsorted leukemic BM cells, isolated from recipients transplanted with PML-RARα or PmlWT+p50-RARα cells, were incubated with ATRA, the percentage of differentiated cells was greatly enhanced compared with cells treated with the vehicle control (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]) (Figure 3A). Interestingly, PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα cells treated with ATRA did not present a significant increase in the percentage of differentiated cells (Figure 3A). The absence of granulocytic differentiation following ATRA exposure in PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα–derived APL cells was confirmed by analysis of CD11b and Gr1 expression (Figure 3B). In vivo, ATRA-treated mice posttransplantation also confirmed these results: survival was significantly improved only for PML-RARα– and PmlWT+p50-RARα–transplanted mice, compared with placebo-treated mice (Figure 3C). These data reveal the importance of Pml NB reformation for an effective response to the differentiating drug.
Response to ATRA treatment is compromised when Pml NBs are disrupted. (A) Differentiation of BM cells from secondary recipients determined by in vitro NBT assay following treatment with DMSO (vehicle control) or ATRA (1 μM) (n ≥ 4). A minimum of 1100 cells were counted per sample using Nikon NIS Elements C software. Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analysis was performed. (B) Representative contour plots of leukemic blasts treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or ATRA (1 µM) for the myeloid differentiation markers CD11b and Gr1. (C) Survival of secondary recipients treated with ATRA (5 mg) or placebo pellets from day 7 posttransplantation (n ≥ 5). This graph represents pooled data from 3 independent experiments. The log-rank test was used. I, implantation; T, transplantation.
Response to ATRA treatment is compromised when Pml NBs are disrupted. (A) Differentiation of BM cells from secondary recipients determined by in vitro NBT assay following treatment with DMSO (vehicle control) or ATRA (1 μM) (n ≥ 4). A minimum of 1100 cells were counted per sample using Nikon NIS Elements C software. Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analysis was performed. (B) Representative contour plots of leukemic blasts treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or ATRA (1 µM) for the myeloid differentiation markers CD11b and Gr1. (C) Survival of secondary recipients treated with ATRA (5 mg) or placebo pellets from day 7 posttransplantation (n ≥ 5). This graph represents pooled data from 3 independent experiments. The log-rank test was used. I, implantation; T, transplantation.
Pml NBs are involved in the maintenance of genome integrity and are essential for optimal DNA DSB repair via the NHEJ and HR pathways
The PML-RARA translocation is undoubtedly an initiating event in APL pathogenesis, but is not sufficient by itself for the full development of APL. Indeed, it is now well-established that APL is a multistep disease, requiring additional cooperating mutations, thus explaining the long latency period prior to leukemia onset.44-48 To determine whether the 3 different genotypes generated APL with similar mutational spectra, we performed whole-exome sequencing on samples from PmlWT+p50-RARα and PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα spontaneous leukemias, and on PML-RARα transplant samples. Interestingly, some of the mutated genes were common to human APL (eg, Kras, Ptpn11, and Usp9y) or human AML (eg, Pten and Jak2),48-51 and some of the copy-number variants were common to human APL/AML (eg, Kdm6a and Ezh2) or human myelodysplastic syndromes (eg, Cul1)46,52,53 (supplemental Figure 4; supplemental Table 1).
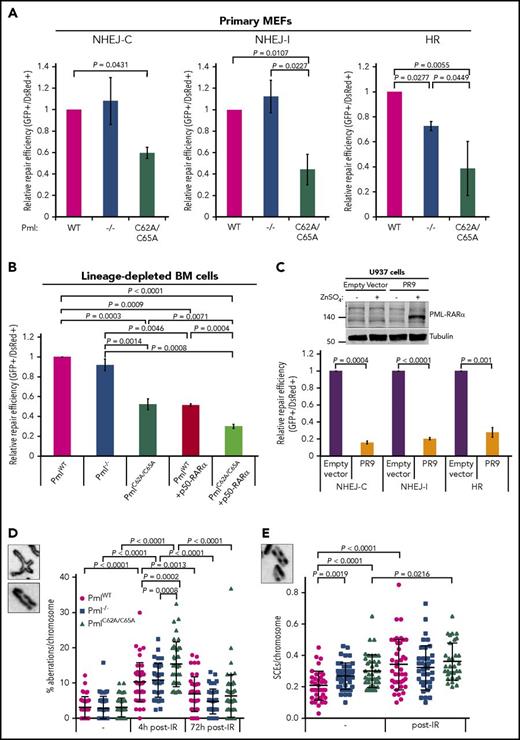
Then, we speculated that loss of NB integrity might affect DNA DSB repair pathways.13,54 To investigate the efficiency of the NHEJ and HR pathways, we used a well-established system of reporter assays.30,31 Pml−/− primary MEFs did not exhibit any defect in the NHEJ pathway when compared with PmlWT cells (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 3A). They did, however, present a significant reduction in the efficiency of the HR pathway, as previously reported.13 Strikingly, both NHEJ (with compatible and incompatible DNA ends) and HR pathway activities were diminished in PmlC62A/C65A MEFs. Similar results for the NHEJ pathway have been obtained with lineage-depleted BM cells isolated from the PmlC62A/C65A mouse model, compared with PmlWT (Figure 4B). The forced dimerization of RARα also affected the efficiency of the NHEJ pathway to a level similar to that observed in PmlC62A/C65A cells (Figure 4B). Moreover, an additive effect was observed in PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα cells compared with PmlWT+p50-RARα cells (Figure 4B). Importantly, similar results were obtained with an inducible PML-RAR⍺–expressing cell line (Figure 4C), thus reinforcing the resemblance observed between PmlC62A/C65A– and PML-RARα–induced NB disruption.
Efficiency of NHEJ and HR altered by Pml NB disruption. (A) Efficiency of NHEJ-C (compatible DNA ends), NHEJ-I (incompatible DNA ends), and HR pathways in primary MEFs (n = 3). The efficiency of repair was measured by quantification of green fluorescent protein (GFP) fluorescence expression, which can only occur when linearized plasmids are accurately ligated (NHEJ-C) or repaired (NHEJ-I and HR). (B) Efficiency of NHEJ-C in lineage-depleted BM cells (n ≥ 5). (C) Efficiency of NHEJ-C, NHEJ-I, and HR in U937-Empty vector and U937-PR9 cell lines, 48 hours after ZnSO4 treatment of induction of PML-RARα expression (n = 4). Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates from U937-Empty vector and U937-PR9 cell lines treated with (+) or without (−) ZnSO4 confirming PML-RARα expression. Tubulin was used as loading control. (A-C) Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analyses were performed. (D) Percentage of chromosomal aberrations (breaks, gaps, and rearrangements) in MEFs at the indicated time post-IR (n > 40 metaphase spreads from 3 independent experiments). Representative images (inset; original magnification ×100) of a chromatid rearrangement and a chromatid gap. (E) Sister chromatid exchange (SCE) rate per chromosome in MEFs, nontreated or treated with IR (n > 30 metaphase spreads from 3 independent experiments). Representative image (inset; original magnification ×100) of SCEs. (D-E) The 2-tailed Mann-Whitney U test was used.
Efficiency of NHEJ and HR altered by Pml NB disruption. (A) Efficiency of NHEJ-C (compatible DNA ends), NHEJ-I (incompatible DNA ends), and HR pathways in primary MEFs (n = 3). The efficiency of repair was measured by quantification of green fluorescent protein (GFP) fluorescence expression, which can only occur when linearized plasmids are accurately ligated (NHEJ-C) or repaired (NHEJ-I and HR). (B) Efficiency of NHEJ-C in lineage-depleted BM cells (n ≥ 5). (C) Efficiency of NHEJ-C, NHEJ-I, and HR in U937-Empty vector and U937-PR9 cell lines, 48 hours after ZnSO4 treatment of induction of PML-RARα expression (n = 4). Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates from U937-Empty vector and U937-PR9 cell lines treated with (+) or without (−) ZnSO4 confirming PML-RARα expression. Tubulin was used as loading control. (A-C) Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analyses were performed. (D) Percentage of chromosomal aberrations (breaks, gaps, and rearrangements) in MEFs at the indicated time post-IR (n > 40 metaphase spreads from 3 independent experiments). Representative images (inset; original magnification ×100) of a chromatid rearrangement and a chromatid gap. (E) Sister chromatid exchange (SCE) rate per chromosome in MEFs, nontreated or treated with IR (n > 30 metaphase spreads from 3 independent experiments). Representative image (inset; original magnification ×100) of SCEs. (D-E) The 2-tailed Mann-Whitney U test was used.
To determine whether these defects in DNA DSB repair pathways were due to a reduced kinetics of repair and/or reduced quality of repair, we analyzed MEF metaphase spreads. First, these revealed a significantly greater number of chromosome aberrations in PmlC62A/C65A cells in response to IR, compared with PmlWT and Pml−/− cells (Figure 4D). Second, a significantly higher number of spontaneous sister chromatid exchange (SCEs) was also found in PmlC62A/C65A cells, compared with WT cells (Figure 4E). Additionally, the rate of SCE formation in PmlC62A/C65A cells was similar to that observed in Pml−/− cells.
Altogether, these data indicate that NB dispersion gives rise to a higher level of recombination activity in primary cells, and further suggests that mice lacking Pml NBs may have an unstable genome.
Investigation of the defective NHEJ pathway in PmlC62A/C65A cells uncovers 53BP1 and Brca1 alteration
We tracked the time course of γH2AX foci formation and disappearance, a well-established indicator of DNA DSBs, in MEFs and in lineage-depleted BM cells, pre- and post-IR exposure (supplemental Figures 5 and 6A-B). An obvious induction of γH2AX foci was observable 1 hour post-IR, compared with untreated cells. The kinetics of repair were identical for all genotypes studied (supplemental Figure 6A-B). This result was confirmed by western blot analyses because equivalent levels of γH2AX, between genotypes, were observed at each time point (supplemental Figure 6C).
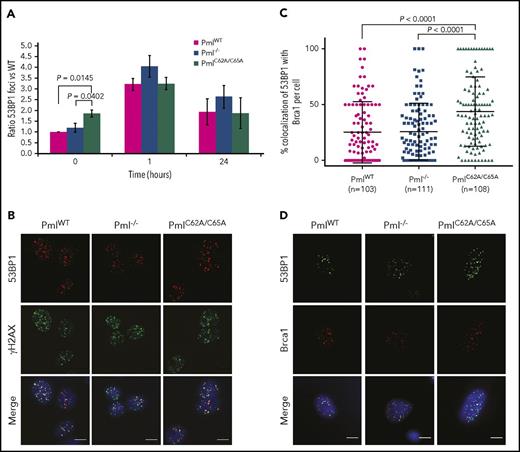
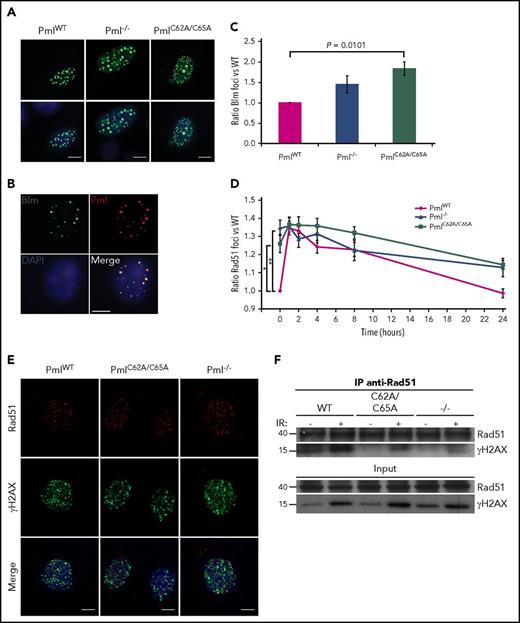
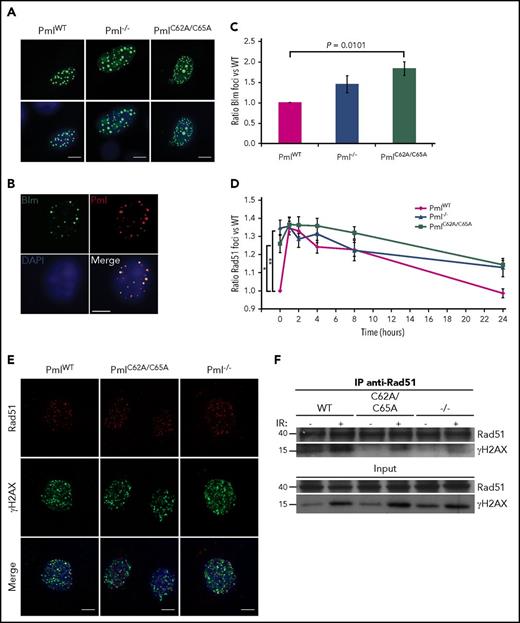
Examining the NHEJ pathway–specific factors, we found that the number of 53BP1 foci was altered in PmlC62A/C65A MEFs, with no variation in protein expression (Figure 5A; supplemental Figures 6C and 7). Indeed, PmlC62A/C65A MEFs presented significantly more 53BP1 foci in the context of spontaneous DNA lesions when compared with PmlWT and Pml−/− cells. 53BP1 was found to colocalize normally with γH2AX, as shown in Figure 5B. 53BP1 and Brca1 are central in the regulation of the balance between NHEJ and HR pathways.55 Interestingly, following IR exposure, 53BP1 and Brca1 foci colocalized at a higher level in PmlC62A/C65A MEFs (mean, 43.81%) compared with PmlWT and Pml−/− cells (mean, 25.27% and 25.82%, respectively; Figure 5C-D). These data revealed that Pml NB integrity is required for correct functional crosstalk between DNA repair proteins involved in the switch between NHEJ and HR pathways. Consequently, the erroneous localization of Brca1 in PmlC62A/C65A cells may also be part of the disturbance observed in the HR pathway.
Elevated colocalization between 53BP1 and Brca1 foci in PmlC62A/C65Acells. (A) Ratio of 53BP1 foci in MEFs over a 24-hour time course following IR exposure (n = 3 per time point). Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analysis was performed. *P < .05. (B) Representative images of irradiated MEFs immunostained for 53BP1 (red), γH2AX (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of 53BP1 and Brca1 foci colocalization 1 hour post-IR in MEFs from 3 independent experiments. Only cells coexpressing 53BP1 and Brca1 foci were counted. Significance was assessed by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. (D) Representative images of irradiated MEFs immunostained for 53BP1 (green), Brca1 (red), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm.
Elevated colocalization between 53BP1 and Brca1 foci in PmlC62A/C65Acells. (A) Ratio of 53BP1 foci in MEFs over a 24-hour time course following IR exposure (n = 3 per time point). Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analysis was performed. *P < .05. (B) Representative images of irradiated MEFs immunostained for 53BP1 (red), γH2AX (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of 53BP1 and Brca1 foci colocalization 1 hour post-IR in MEFs from 3 independent experiments. Only cells coexpressing 53BP1 and Brca1 foci were counted. Significance was assessed by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. (D) Representative images of irradiated MEFs immunostained for 53BP1 (green), Brca1 (red), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm.
Investigation of the defective HR pathway reveals the importance of Pml NB integrity for the correct localization of Rad51 at DSBs
We then analyzed 2 main factors of the HR pathway: Blm and Rad51. Unfortunately, none of the commercial antibodies tested against Blm produced positive signals in immunofluorescence assays. As a surrogate, we therefore overexpressed GFP-Blm in primary MEFs (Figure 6A). In order to determine whether overexpressed Blm accumulates in a fashion similar to the endogenous protein, costaining with Pml was performed in WT cells. As expected, Blm and Pml colocalized56 (Figure 6B). In a similar manner to 53BP1, the number of foci for Blm and Rad51 differed at the basal level, reflecting a disturbance in the HR pathway in PmlC62A/C65A and Pml−/− MEFs, compared with PmlWT cells (Figure 6C-D; supplemental Figures 8 and 9). When protein localization was analyzed, no mislocalizations were observed for Blm foci. Regarding Rad51, confocal analyses strikingly revealed that Rad51 minimally colocalized with γH2AX in PmlC62A/C65A and Pml−/− cells, compared with PmlWT MEFs (Figure 6E). These observations were validated by coimmunoprecipitation experiments. Notably, although the same amount of Rad51 was immunoprecipitated, the amount of γH2AX pulled down was lower in PmlC62A/C65A and Pml−/− compared with PmlWT lysates (Figure 6F).
Reduced colocalization between Rad51 and γH2AX foci in PmlC62A/C65Aand Pml−/−cells. (A) Representative images of PmlWT, Pml−/−, and PmlC62A/C65A MEFs overexpressing GFP-Blm (GFP-Blm, green; DAPI, blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Representative costaining images of Blm/Pml in PmlWT MEF overexpressing GFP-Blm (GFP-Blm, green; Pml, red; DAPI, blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Ratio of GFP-Blm foci in MEFs (n = 3). (D) Ratio of Rad51 foci in MEFs over a 24-hour time course following IR exposure (n = 3 per time point). (C-D) Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analyses were performed. *P < .05; **P < .01. (E) Representative images of irradiated MEFs immunostained for Rad51 (red), γH2AX (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments. Cells treated without (−) or 1 hour post-IR (+) exposure were lysed and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Rad51 antibody and immunoblotted with anti-γH2AX antibody. Input is shown in the lower panels. The blots shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Reduced colocalization between Rad51 and γH2AX foci in PmlC62A/C65Aand Pml−/−cells. (A) Representative images of PmlWT, Pml−/−, and PmlC62A/C65A MEFs overexpressing GFP-Blm (GFP-Blm, green; DAPI, blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Representative costaining images of Blm/Pml in PmlWT MEF overexpressing GFP-Blm (GFP-Blm, green; Pml, red; DAPI, blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Ratio of GFP-Blm foci in MEFs (n = 3). (D) Ratio of Rad51 foci in MEFs over a 24-hour time course following IR exposure (n = 3 per time point). (C-D) Two-tailed unpaired Student t test analyses were performed. *P < .05; **P < .01. (E) Representative images of irradiated MEFs immunostained for Rad51 (red), γH2AX (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments. Cells treated without (−) or 1 hour post-IR (+) exposure were lysed and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Rad51 antibody and immunoblotted with anti-γH2AX antibody. Input is shown in the lower panels. The blots shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Collectively, our data provide further evidence that Pml NBs are essential for effective DNA repair response, and that their disruption is in part responsible for the deficiency observed in the context of PML-RARα expression.
Discussion
APL development is invariably associated with translocations of the RARA gene, and numerous studies have been carried out to determine how the resulting fusions contribute to the pathogenesis of this disease. These include studies of the importance of the fusion partners, but these have been directed more toward their oligomerization potential. As a result, the role played by Pml NB disruption in APL pathogenesis had not been studied in a comprehensive way. Nevertheless, 2 particular studies have provided preliminary evidence for the importance of Pml NB disruption in leukemogenesis. Using truncated versions of the PML-RARα fusion protein, they hypothesized that the PML moiety was required not solely for the dimerization of RARα, and that the observed Pml NB disruption might play an active role in APL pathogenesis.57,58 Here, we used a novel knock-in mouse model, in which Pml NBs are disrupted in a similar fashion to that observed in the context of PML-RARα expression, in order to dissect their impact.
Using this model, we showed definitive evidence for the involvement of Pml NB disruption in APL initiation, in synergy with the forced dimerization of RARα. We also showed that an effective response to ATRA treatment requires Pml NB integrity. These data validate the proposed hypothesis that NBs contain essential factors for nuclear hormone receptor signal transduction,11,59,60 and demonstrate that the WT Pml allele plays an important role in tumor regression following ATRA treatment of PML-RARα APL.61 These points are of importance because ATRA and its derivatives are under investigation not only for the treatment of other AML subtypes,62,63 but also for other malignancies.64-68 Furthermore, the PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα mouse model substantially recapitulates APL pathogenesis as observed in PML-RARα APL mouse models.
Previous studies have investigated the connection between Pml NBs and DNA damage repair. However, owing to the models used, PML-RARα54,69 or Pml−/− cells,13,70 it was impossible to establish a direct link between the 2. On the one hand, the consequences of disruption could not be disassociated from those due to alterations in the RARα signaling; on the other hand, the absence of Pml expression is not necessarily equivalent to Pml mislocalization and Pml NB disruption, as it has been exemplified in this study. Indeed, we report here that both NHEJ and HR repair pathways are drastically altered by the loss of Pml NB integrity, whereas only the HR pathway was impaired in Pml−/− cells. Repair through NHEJ was considerably more altered in PmlC62A/C65A+p50-RARα cells than in PmlC62A/C65A or PmlWT+p50-RARα cells, revealing that Pml NB disruption and the forced dimerization of RARα had a cooperative effect on DNA damage responses. Surprisingly, no alterations in the kinetics of repair following IR exposure were noticeable because clearance of γH2AX foci was similar in all genotypes analyzed. Based on these results, it was possible to refute the hypothesis that the higher number of γH2AX foci observed in PML-RARα cells71 is exclusively due to Pml NB dispersion.69,70 Also, PML-RARα is able to initiate leukemia, but additional events are needed to lead to complete leukemic transformation as observed in various transgenic mouse models.40-42 It is thus plausible that the acquisition of cooperating mutations46,72 is facilitated by the loss of Pml NB integrity. This hypothesis is further strengthened by published reports, which have established that the majority of de novo mutations are random events in AML/APL.48-50
The NHEJ and HR pathways involve a large number of different factors, including 53BP1 for the NHEJ pathway, and Brca1, Blm, and Rad51 for the HR pathway.21 Here, we found an excess of 53BP1, Blm, and Rad51 foci in PmlC62A/C65A cells compared with PmlWT cells. Interestingly, in recent years, SUMO and ubiquitin signals have been characterized as essential components in DNA damage responses,55,73 and indeed, deficient SUMOylation of Blm and/or Rpa has been shown to impair Rad51 localization.74-76 Our results, therefore, suggest a scenario in which the putative incorrect SUMOylation of Blm and/or Rpa (due to SUMOs being inadequately localized in PmlC62A/C65A cells) might partially explain our observation of Rad51 mislocalization. 53BP1 foci, which were found in excess only in the context of PmlC62A/C65A expression, were still located at sites of damage, suggesting that the DNA DSB-specific histone signature, including ubiquitination, is not affected by Pml NB disruption.77 It would be of interest, therefore, to carry out further analyses of 53BP1 phosphorylation, the localization of its partners (eg, Rif1), and, indubitably, the SUMOylation of 53BP1 itself,78,79 in order to establish the causes and consequences of this excess of 53BP1 foci. Moreover, 53BP1 dysregulation might also have repercussions in the HR pathway because 53BP1 and Brca1 are key regulators of the balance between NHEJ and HR repair pathways during the S-G2 phases of the cell cycle.80-84 Also, the SUMO pathway is an important regulator of Brca1 functions.85-87 Finally, the discrepancies observed between the absence of Pml NBs and their disruption (ie, Pml−/− vs PmlC62A/C65A mutants) could also be linked to their distinct impact on Sumo-2/3: whereas Sumo-2/3 formed abnormally large foci in Pml−/− cells, a diffuse pattern was observed in PmlC62A/C65A cells (supplemental Figure 10A). These data are consistent with the role of Pml as a dynamic anchor regulated by SUMOylation.3,16 Indeed, because Pml is expressed in PmlC62A/C65A cells, and because the SUMOylome is severely reduced but still extant (supplemental Figure 10B-E), some proteins could still be recruited by Pml through its SUMO-interaction motif, for example, and might subsequently become sequestrated and/or mislocalized. In accordance with this hypothesis, our finding that 53BP1 SUMOylation was not affected in the same way in Pml−/− and PmlC62A/C65A cells could explain, at least partially, the disparity observed in the NHEJ pathway (supplemental Figure 10F-G). Thus, further study is needed to establish whether Pml NB disruption significantly affects the SUMOylome, and its potential downstream impacts on DNA damage responses (supplemental Figures 10 and 11).
Overall, we found strong evidence for the essential pathogenic role of PML-RARα expression–induced NB disruption in APL development, and also of the importance of NB reformation for an effective response to targeted therapy. Our data also underline the significant contribution of Pml NBs to the effectiveness of DNA damage repair processes, and the manner in which their disruption, mediated by the PML-RARα oncoprotein, can assist APL pathogenesis.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to all members of the Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) Flow Cytometry Core Facility, and particularly to Pj Chana and Susanne Heck. The authors thank Alka Saxena of the BRC Genomics Core Facility, Emanuele de Rinaldis and Venu Pullabhatla of the BRC Bioinformatics Core Facility, and Michael Simpson (King’s College London) for their support in whole-exome sequencing analysis. The authors are indebted to Ian Kesterton (Viapath–Cytogenetics, Guy’s Hospital, London) for his help with cytogenetics analysis. The authors also thank staff of the Biological Services Units (Franklin Wilkins Building [FWB] and New Hunt’s House [NHH]) at King’s College London for excellent animal care. The authors would also like to deeply and gratefully acknowledge the central contributions, unwavering support, inspiring scientific leadership, and friendship of David Grimwade without whom this work could not have been completed.
This work was supported by a specialist program grant from Bloodwise (13043; previously called Leukaemia and Lymphoma Research) and King’s College London. All BRC facilities are funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) BRC based at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London. In addition, this work was supported by grant R01-CA95274 from the US National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute.
Authorship
Contribution: E.V. designed, performed, analyzed, and interpreted experiments and supervised the study; E.M. performed experiments; E.W.S. generated the knock-in mouse model; A.J. performed whole-exome sequencing analysis; C.J.P. performed postmortem examinations; R.K.H. performed statistical analysis on mouse cohorts; P.S. and S.C.K. provided essential reagents, and mouse models; E.S. and D.G. conceived the initial project and supervised the study; and the manuscript was prepared by E.V., E.S., and D.G. with assistance from the other authors.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for A.J is Department of Life Sciences, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom. The current affiliation for P.S. is German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE), Bonn, Germany.
David Grimwade died on 16 October 2016.
Correspondence: Edwige Voisset, Department of Medical and Molecular Genetics, King’s College London, Guy’s Hospital, Floor 8, Tower Wing, London SE1 9RT, United Kingdom; e-mail: edwige.voisset@kcl.ac.uk; and Ellen Solomon, Department of Medical and Molecular Genetics, King’s College London, Guy’s Hospital, Floor 8, Tower Wing, London SE1 9RT, United Kingdom; e-mail: ellen.solomon@kcl.ac.uk.