Abstract
We recently found that a low number of circulating dendritic cells (DC) is predictive of increased relapse, acute GVHD, and poor survival following allogeneic SCT (
Reddy V et al, Blood 2004;103(11):4330–5
). Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is an immunostimulatory cytokine involved in the activation of naïve T cells by DC (Rissoan et al. Science 1999;283(5405):1183–6
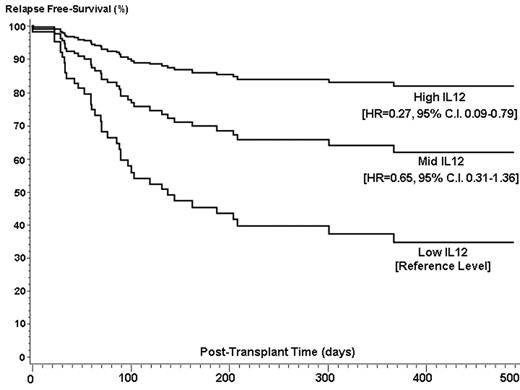
). We hypothesized that patients with high levels of circulating IL-12 in the post transplant period have improved relapse free survival. We studied 134 patients, 120 of whom were evaluable and transplanted during the period of July 1999 to April 2004. Seventy-two patients had transplants from related and 48 from unrelated donors, for predominantly high risk (88%) hematologic malignancies. Median follow up was 1158 days (range 70–1792). Blood samples were collected as baseline prior to conditioning, on day 0 prior to stem cell infusion and during the first week (day 4 and/or 7) after transplant. Plasma IL-12 levels were measured by ELISA. To determine the independent effect of post-transplant IL-12 levels and clinical outcomes, a cluster analysis was performed on the logarithmically transformed mean IL-12 concentration at days 4 and 7 post-transplant. The analysis generated a low, medium and high IL-12 group. Forty-six patients had low levels of IL-12 (median=2 pg/ml, range 0–6.5), 49 patients had medium (median=20.5 pg/ml, range 7–75.5) and 25 patients had high levels (median=181 pg/ml, range 84–623). There was a significant association between IL-12 level and onset of relapse. Using a multivariate Cox model with the low group level as reference, the high IL-12 group level had an adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of 0.27 (95% C.I. 0.09–0.79) and the medium group level a HR of 0.65 (95% C.I. 0.31–1.36). Incidence of relapse at 500 days by Kaplan-Meier analysis by IL-12 group were 23.0% (high group), 40.3% (medium group), and 48.8% (low group). Covariates in the multivariate models were gender match, disease risk, graft source, patient age, donor relation. There was a significant relationship between IL-12 levels and composite death and relapse, the high IL-12 group had a HR of 0.37 (95%C.I.=0.17–0.80) and the medium group a HR of 0.85 (95%.C.I. 0.50–1.45). There was no association between IL-12 levels and risk of AGVHD (p-value=0.51). In addition to IL-12, disease risk was a significant risk factor for the composite endpoint of relapse or death (HR=5.4, p-value=0.0052). The model generated for the outcome of relapse only did not have any additional significant risk factors. In conclusion, high post-transplant levels of IL-12 are associated with less relapse and improved relapse free survival after transplantation. This data suggests that IL-12 administration should be considered as a possible component in studies addressing treatment of relapse after transplantation.Author notes
Corresponding author
2005, The American Society of Hematology
2004

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal