Abstract
Abstract 2037
Monosomy 7 and deletion 7q (‘del 7’) are associated with poorer prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS). Less is known, however, of the influence of chromosome 7 deletions with additional chromosomal abnormalities on the outcomes of allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT). We hypothesized that multiple abnormalities in addition to ‘del 7’ lead to worse transplant results, and investigated this hypothesis in a cohort of AML (n=101) and MDS (n=100) patients transplanted between year 1990 and 2011 in our institution.
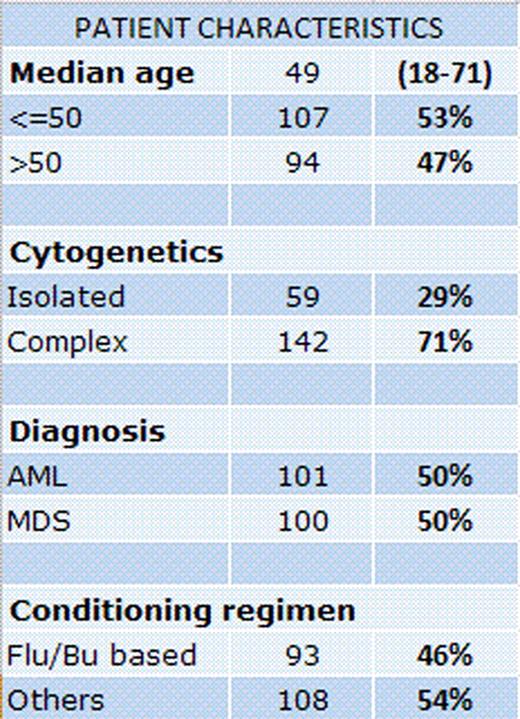
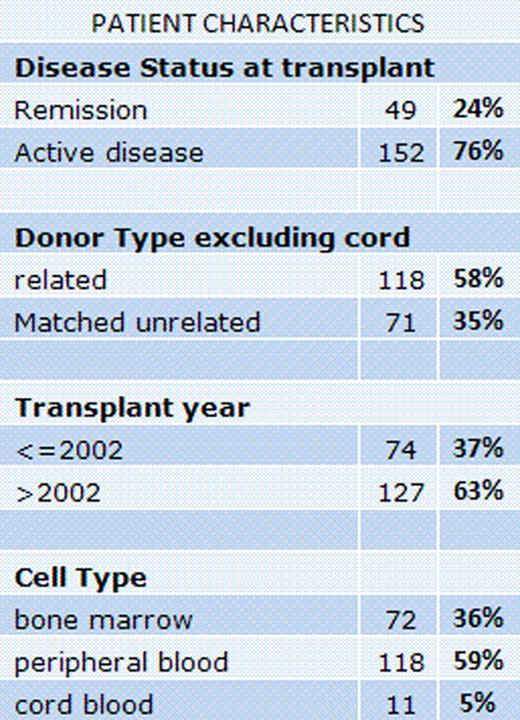
Patient and disease characteristics are shown in the table. Year 2002 marks the year in which allele level HLA class I typing was incorporated, and also when most patients received the preparative regimen of busulfan 130 mg/m2 and fludarabine × 4 days +/− clofarabine. Covariates considered in the statistical analysis were age, ‘del 7’ alone versus multiple, conditioning (busulfan-fludarabine-based versus others), disease status, donor type, stem cell source, treatment-related disease, year of treatment (before and after 2002), and IPSS (MDS only).
AML: 60% had active disease at transplant. Median follow-up of AML survivors was 36 months (range, 0.7 – 237). ‘Del 7’ alone was present in 27 patients, while 74 had ‘del 7’ with complex cytogenetics. Preparative regimen was busulfan/fludarabine-based (n=42) or others (n=59). Donors were related (n=47) or unrelated (n=54). Grafts were bone marrow (n=35), peripheral blood (n=60), or cord blood (n=6). 39 patients were transplanted before 2002. Multivariate analysis showed that survival was independently influenced by age (>50 years) (HR=2; 95% CI 1.2–3.3; p=0.006), use of busulfan/fludarabine-based preparative regimen (HR=0.6; 95%CI 0.3–0.9; p=0.04), and remission at transplant (HR=0.4; 95%CI 0.2–0.7; p=0.001). Same factors influenced PFS.
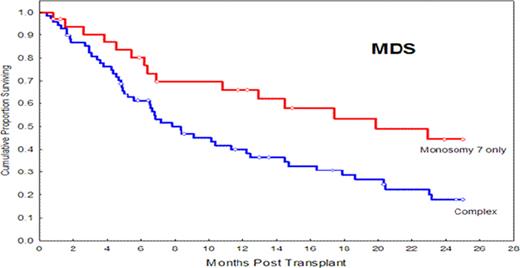
MDS patients: median follow-up in survivors was 17 months (range, 0.8– 197); 32 patients had ‘del 7’ and 68 had ‘del 7’ with complex abnormalities. 54 patients had treatment-related MDS. IPSS score was <= 1.5 in 60 patients and >1.5 in 38 patients, and 92 patients had active disease at transplant. Preparative regimens were Flu/Bu based (n=51), and others (n=49). Donor type was related (n=52) and unrelated (n=48). Grafts were bone marrow (n=37), peripheral blood (n=58) and cord blood (n=5); 35 patients were transplanted before 2002. Multivariate analysis showed that survival was influenced by absence of other chromosomal abnormalities in addition to ‘del 7’ (HR=0.5; 95% CI 0.3–0.8; p=0.01), transplant after year 2002 (HR=0.6; 95%CI 0.3–0.9; p=0.03), and IPSS >= 1.5 (HR=2; 95%CI 1.2–3.4; p=0.006). Same factors influenced PFS.
Presence of complex chromosomal abnormalities in addition to monosomy 7 or deletion 7q did not independently influence outcomes of AML patients, but was an independent predictor of survival and PFS in MDS patients undergoing allogeneic transplantation.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal