Abstract
Genetic loss-of-function studies in murine tumor models have been essential in the analysis of downstream mediators of oncogenic transformation. Unfortunately, these studies are frequently limited by the availability of genetically modified mouse strains. Here we describe a versatile method allowing the efficient expression of an oncogene and simultaneous knockdown of targets of interest (TOI) from a single retroviral vector. Both oncogene and TOI-specific miR30-based shRNA are under the control of the strong viral long terminal repeat promoter, resulting in a single shared RNA transcript. Using this vector in a murine syngeneic BM transplantation model for BCR-ABL–induced chronic myeloid leukemia, we find that oncogene expression and target knockdown in primary hematopoietic cells with this vector is efficient both in vitro and in vivo, and demonstrate that Raf1, but not BRAF, modulates BCR-ABL–dependent ERK activation and transformation of hematopoietic cells. This expression system could facilitate genetic loss-of-function studies and allow the rapid validation of potential drug targets in a broad range of oncogene-driven murine tumor models.
Introduction
Malignant cells frequently have rewired signaling networks required for growth and survival. Identification of essential nodes within these oncogene-mediated signaling networks will be crucial for the development of novel anticancer therapies. In vivo tumor models1-3 have been vital for the identification of signaling pathways underlying malignant transformation, an important aspect in the validation of potential therapeutic targets. A powerful approach to pin down essential components of oncogenic signaling cascades in vivo has been the use of murine BM transplantation (BMT) models in combination with knockout BM cells.4-10 However, using knockout mice to define critical signaling cascades or potential drug targets can be time-consuming and may in some cases be impossible. Some knockout mice have severe defects leading to embryonic lethality, others may not yet be available or have to be crossed back to a syngeneic background to prevent graft rejection, limiting efficiency and utility of this approach.
The discovery of RNA interference (RNAi) introduced a new approach to inactivating genes in live cells. Subsequently, the development of vector-expressed hairpin siRNAs (shRNA) paved the way for prolonged, stable knockdown of genes.11 For in vivo application of siRNA-mediated gene suppression, shRNAs have been accommodated for the expression from retroviral and lentiviral vectors.12 The improvements in shRNA delivery systems have made gene inactivation by RNAi a rapid, versatile, and efficient approach to study gene function.13,14 The combination of retroviral hairpin siRNA delivery and retroviral infection/transplantation models in mice should alleviate the inherent problems of transgenic/knockout mice such as lack of suitable genetically modified mice because of embryonic lethality, time-consuming breeding or backcrossing and limited availability. Furthermore, a functional incomplete siRNA-mediated knockdown may mimic target inhibition by a potential drug more closely than a knockout, where gene function is completely abolished. However, expression of the oncogene and the target-of-interest (TOI)–specific shRNA from 2 different vectors may lead to uncoupling of expression and escape of oncogene transformed cells for example, by silencing of the shRNA or by outgrowth of single-infected cells.
Here we describe a reliable, highly versatile retroviral single vector system in which a potent and durable knockdown of variable TOIs by miR30-based shRNAs can be combined with efficient expression of a desired oncogene or other transgene. Directly coupling oncogene expression with TOI knockdown was achieved by cloning an oncogene directly downstream of a miR30-based shRNA (miRTOI) under control of the MSCV retroviral long-terminal repeat (LTR) polymerase (Pol) II promoter, resulting in one shared RNA transcript. By coupling expression of the shRNA to the driving oncogene, we minimize the chances for escape and ensure stable and durable TOI knockdown in every transformed cell.
To validate our vector system, we turned to a well-established murine retroviral syngeneic BMT model of BCR-ABL induced myeloproliferative neoplasm2,15 to investigate the role of Raf1 and BRAF in BCR-ABL–mediated leukemogenesis. Raf kinases are key enzymes to activate the MAPK/ERK cascade,16 one of the central pathways activated by BCR-ABL.17 Using our coupled expression system, we here show that Raf1 but not BRAF modulates the BCR-ABL–mediated induction of a chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)–like disease in mice.
Methods
Growth factors and Abs
Recombinant murine IL-3 (mIL-3), IL-6 (mIL-6), and SCF (mSCF) were purchased from R&D Systems. BCR-ABL and Abl was detected by immunoblotting using an Abl-specific Ab 8E9 (BD Biosciences), β-actin Ab was from Sigma-Aldrich (AC-15). Tyrosine phosphorylation was detected using a mixture of monoclonal anti-phosphotyrosine Ab 4G10 (Millipore) and PY20 (BD Biosciences). Raf1 (C-12), BRAF (H-145), and STAT5 A/B (C-17) Abs came from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, p53 Ab came from NovoCastra (CM5). Abs detecting phosphorylated AKT (Ser-473), phosphorylated ERK1/ERK2, pan-AKT, and pan-ERK1/ERK2 were purchased at Cell Signaling Technology. Monoclonal phospho-specific STAT5 A/B Ab was a generous gift from Tom Wheeler (Hamilton, New Zealand).
Plasmids
PLMPmiRCtrl was generated by subcloning the target-specific hairpin sequence from pSM2c (nonsilencing shRNA vector for Ctrl miR; Open Biosystems on BioCat) to pLMP (Open Biosystems) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Twenty-one–mer sequences for miRRaf1(1-3) were calculated using the RNAi Central algorithm, miRRaf1(4-6), and miRBRAF were calculated using the siRNA prediction software biopredsi (www.biopredsi.org, developed by Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, provided by Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research) and were adapted to miR30-based shRNA according to pLMP manufacturer's instructions. Oligonucleotide sequences serving as PCR templates are: miRCtrl: TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGATCTCGCTTGGGCGAGAGTAAGTAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTACTTACTCTCGCCCAAGCGAGAGTGCCTACTGCCTCGGA; miRRaf1(1): 5′-TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGCTGGTGGCTGACTGTGTGAAGATAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTATCTTCACACAGTCAGCCACCAATGCCTACTGCCTCGGA-3′; miRRaf1(2): 5′-TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGGGCTGCCGCCTCTCTGATTGGAGATAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTATCTCCAATCAGAGAGGCGGCATTGCCTACTGCCTCGGA-3′; miRRaf1(3): 5′-TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGCAAGAAAGCCAGGAATACAGGTTAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTAACCTGTATTCCTGGCTTTCTTATGCCTACTGCCTCGGA-3; miRRaf1(4): 5′-TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGACAGGAACACAAAGGTAAGAAATAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTATTTCTTACCTTTGTGTTCCTGGTGCCTACTGCCTCGGA-3′; miRRaf1(5): 5′-TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGATCAGGTATAAGTATTGTTTAATAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTATTAAACAATACTTATACCTGAGTGCCTACTGCCTCGGA-3′; miRRaf1(6): 5′-TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGCGACATGAAATCCAACAATATATAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTATATATTGTTGGATTTCATGTCTTGCCTACTGCCTCGGA-3′; miRBRAF(1): 5′-TGCTGTTGACAGTGAGCGCAAGGGTGGAGATGAACTATAATAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTATTATAGTTCATCTCCACCCTTATGCCTACTGCCTCGGA-3′; pLMPmiRp53 vector was kindly provided by S. Lowe (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, NY). pMmiRTOI-BCR-ABL was cloned in 3 steps. First, the multiple cloning site (MCS) of the MIG-R1 vector was modified. To this purpose pcDNA3.1/Zeo(+) (Invitrogen) was PmeI digested and the small fragment spanning the MCS of pcDNA3.1/Zeo(+) between the 2 PmeI sites was ligated into HpaI-digested MIG-R1 vector resulting in MIG-Z. Then pBluescript BCR-ABL p185 was digested with EcoRI and the BCR-ABL–encoding fragment was placed into the EcoRI site of MIG-Z. Finally, pMmiRTOI–BCR-ABL was generated by introducing a PCR product from pLMPmiRTOI (miRRaf1(1), miRBRAF(1), miRp53, and miRCtrl), digested with BamHI and BglII into BamHI-digested MIG-Z BCR-ABL construct (primer BamHI miR forward, 5′-TGAGGATCCTAGGGATAACAGGGTAATTG-3′ and BglII miR reverse, 5′-TGACAATTGAGATCTAAAAAAGTGATTTAATTTATACC-3′). Supplemental constructs: pSuper.retro.puro shRNARaf1(1-4) plasmids were cloned according to the manufacturer's instructions (Oligoengine). pMBCR-ABL–shRaf1 was cloned in 2 steps. First, a PCR product spanning H1 promoter and shRNARaf1 was digested with XhoI and inserted into SalI linearized MIG-R1 vector resulting in MIG H1 shRNARaf1. Second, pBluescript BCR-ABL p185 was digested using EcoRI and introduced into EcoRI site of MIG H1 shRNARaf1. Cloning details for generation of pMmiRTOI–BCR-ABLp210 are available on request.
Cell culture
The IL-3–dependent murine myeloid cell line 32D and the IL-3–dependent mouse pro-B-cell line Ba/F3 (both DSMZ) were cultured in RPMI 1640 (PAA Laboratories) supplemented with 10% FCS (PAA Laboratories), 2 ng/mL IL-3, penicillin/streptomycin, and l-glutamine. Phoenix E helper virus-free ecotropic packaging cells (G. Nolan, Stanford, CA) and NIH/3T3 cells (DSMZ) were maintained in DMEM (PAA Laboratories) supplemented with 10% FCS. Cells were cultured in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2.
Retrovirus preparation and generation of cell lines
A total of 2 × 106 Phoenix E cells were plated on 60-mm dishes and transiently transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) 18 hours later according to the manufacturer's instructions. Medium was replaced after 12 hours and retroviral stocks were collected at 12-hour intervals beginning 24 hours after transfection. Retroviral titer were determined by transduction of 5 × 104 NIH/3T3 cells with serial dilutions of retrovirus supplemented with 4 μg/mL polybrene (Sigma-Aldrich). The 48-hour posttransduction percentage of infected cells was determined by flow cytometric analysis of EGFP expression. Titer was calculated by multiplication of the total number of EGFP-positive cells with dilution factor of the respective retroviral supernatant. To generate stably retroviral infected cell lines derived from 32D or Ba/F3 cell line origin, 5 × 104 cells were transduced by 2 to 4 rounds of spin infection (1200g, 32°C, 90 minutes) every 12 hours in retroviral supernatant supplemented with 2 ng/mL IL-3, 4 μg/mL polybrene (Sigma-Aldrich), and 20% RPMI 1640.
In vivo leukemogenesis studies
A suspension of 1 × 106 Ba/F3 cells infected with pMmiRRaf1-BCR-ABL or pMmiRCtrl-BCR-ABL, previously maintained with 2 ng/mL IL-3 supplement was injected into 6- to 8-week-old female Balb/c mice through tail vein injection. Ba/F3-derived leukemic cells were rescued after 2 weeks from spleens of the mice immediately after killing and cultured in RPMI 1640 containing 10% FCS for 7 days.
Transduction of murine BM and syngeneic transplantation model
Murine BM was collected and transduced as described previously.18 Briefly, BM was harvested from female BALB/c donor mice 4 days after injection of 150 mg/kg 5-fluorouracil (5-FU; Medac) and prestimulated overnight in BBMM medium (IMDM, 30% FCS, 1% BSA) containing growth factors (10 ng/mL mIL-3, 10 ng/mL mIL-6, 50 ng/mL mSCF). Cells were transduced by 4 rounds of spin infection (1200g, 32°C, 90 minutes) every 12 hours in retroviral supernatant (viral titers of 3.2-4.2 × 104) supplemented with growth factors, 4 μg/mL polybrene (Sigma-Aldrich), and 20% BBMM. Infection efficiency was determined by FACS analysis 12 hours after last spin infection round (infection efficiencies of 10%-12%) and adjusted to 10% EGFP-positive cells. The median EGFP intensity was comparable, indicating comparable oncogene expression levels. Subsequently, cells were resuspended in HBSS (Sigma-Aldrich) and were used for methylcellulose assays or for transplantation. For transplantation, cells were mixed with untransduced BM to adjust to 2.5% EGFP-positive cells (5000 EGFP-positive cells with 195 000 EGFP-negative cells), and injected into the tail veins of lethally irradiated female BALB/c recipient mice. Animals that received a transplant were monitored for signs of disease development by serial measurement of peripheral blood (PB) counts. Mice were caged in special caging system with autoclaved food and acidified water at the Technical University of Munich in accordance with national and institutional guidelines for animal care.
Clonal growth in methylcellulose
To analyze clonal growth, retrovirally transduced BM cells were resuspended in HBSS in a concentration of 1-4 × 104 cells containing 2 × 103 EGFP+ cells per 100 μL and mixed with 1.8 mL of MethoCult 4230 (StemCell Technologies) and 100 μL of imatinib solution (final concentration from 100nM to 2μM) or vehicle HBSS. One thousand EGFP+ BM cells in 1 mL of methylcellulose medium were plated in duplicates in 12-well plates and colonies were photographed and counted on day 10.
Quantitative PCR
RNA from cell lines and tissues was isolated with the RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN). cDNA was generated using the Titan One Tube RT-PCR Kit (Roche Applied Science). qRT-PCR was performed using Platinum SYBR Green qPCR SuperMIX UDG (Invitrogen) using primers specific for murine GAPDH (fw: GGTCATCCCAGAGCTGAACGG, rev: CCTGCTTCACCACCTTCTTG) and murine Raf1 (fw1: TCTGAAGGTGAGAGGCCT, rev1: GGCATCGGTGTTCCAATCT, fw2: GTGATGCTGTCTACTCGGA, rev2: GGTCAACCACCTTTAGGATC). SD was calculated as described by Livak and Schmittgen.19
Results
An alternative strategy to achieve simultaneous expression of cDNAs and shRNAs in individual cells
Although it is possible to simultaneously overexpress an oncogene and down-regulate a TOI by double infection of cells with 2 retro- or lentiviral constructs, one encoding the oncogene, the other encoding for a TOI-specific shRNA (shRNATOI), and either FACS sort or select the cells with antibiotics, this strategy suffers from several drawbacks. It is cumbersome and requires extensive ex vivo manipulation of cells, which may compromise for example the quality of HSCs, which cannot easily be kept in culture for extended periods of time. Furthermore, expression of both constructs is influenced by the number and genomic location of proviral integrations, which can lead to variable results. Therefore, we designed a vector, which encodes both transgene mRNA and shRNATOI on a single construct, thereby directly linking oncogene and shRNATOI expression.
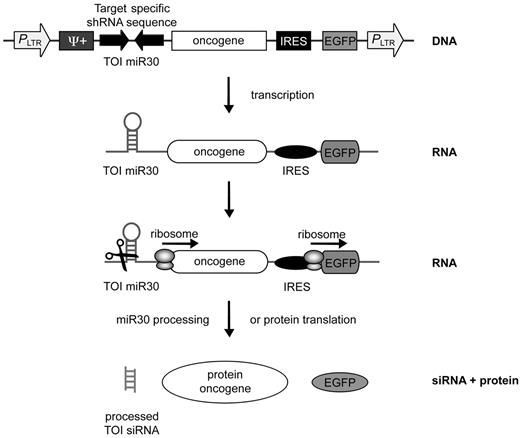
Most retroviral vectors express the oncogene under control of the LTR promoter, a very strong RNA Pol II promoter. In contrast, “classic” shRNAs are usually expressed from RNA Pol III promoters such as U6 or H1. Initially, we used a MSCV-based retroviral vector, which can express an oncogene via an LTR promoter followed by EGFP translated from an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES). In the 3′ region of the construct, individual shRNATOI expressed from a H1 promoter were cloned adjacent to the EGFP (pMBCR-ABL-shTOI, supplemental Figure 1A, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). This vector design led to good oncogene expression (in this case the p185 BCR-ABL cDNA) and reasonable knockdown of the TOI (in this experiment Raf1) in NIH/3T3 cells (supplemental Figure 2). To further improve knockdown efficiency, we inserted a second tandem shRNATOI targeting Raf1 with its own H1 promoter in same orientation (supplemental Figure 1B) or opposite orientation (supplemental Figure 1C). However, these modifications did not lead to further improved knockdown efficiencies (data not shown). Suboptimal knockdown with these constructs might be because of the relatively weak RNA Pol III promoters, driving the conventional shRNAs. MiR30-based shRNAs (miRTOI) can be expressed from the powerful LTR Pol II promoter and are effective in gene knockdown even when present as a single copy in the genome.20,21 Therefore we designed an MSCV-based retrovirus encoding both the target-specific Pol II–driven miR30-based shRNA and the oncogene on a single construct, both under the control of the same LTR promoter (pMmiRTOI-oncogene, Figure 1). Importantly, coupling target-specific miRTOI and oncogene by simultaneous expression from a single common transcript should hinder silencing of the miRTOI over time even in the presence of a strong negative selection and should enable expression of both constructs in every transduced cell without time consuming selection or cell sorting of double-positive cells (Figure 1). In addition, we established a sequence and ligation independent cloning strategy22 for easy exchange of the miRTOI cassette (supplemental Figure 3).
A retroviral vector system encoding an oncogene and an shRNA under the control of a single promoter. Schematic representation of the single-vector design of pMmiRTOI oncogene. Oncogene and a miR30-based TOI-specific shRNA are expressed from the same RNA Pol II promoter LTR. EGFP is expressed via an IRES. The DNA is transcribed by RNA Pol II resulting in one unique mRNA transcript encoding for target-specific miR, oncogene and EGFP as fluorescent marker. Dicer processes miR30 sequence of the transcript or ribosomes initiate translation of the oncogene and EGFP.
A retroviral vector system encoding an oncogene and an shRNA under the control of a single promoter. Schematic representation of the single-vector design of pMmiRTOI oncogene. Oncogene and a miR30-based TOI-specific shRNA are expressed from the same RNA Pol II promoter LTR. EGFP is expressed via an IRES. The DNA is transcribed by RNA Pol II resulting in one unique mRNA transcript encoding for target-specific miR, oncogene and EGFP as fluorescent marker. Dicer processes miR30 sequence of the transcript or ribosomes initiate translation of the oncogene and EGFP.
MiR30-based shRNAs targeting Raf1 show efficient knockdown when coupled to BCR-ABL expression
Next we wished to confirm the functionality of this vector system in a clinically relevant leukemia model. We decided to investigate the role of Raf1 in the well-established BCR-ABL–driven murine retroviral syngeneic CML transplantation model.2,9,15,23 Previous studies demonstrated a role for Raf1 in activation of the MAPK/ERK signaling cascade,16,24,25 one of the central signal transduction cascades of BCR-ABL.17,26,27 In addition, Raf1 has been implicated in BCR-ABL–mediated transformation in vitro.26 However, the role of Raf1 has not been assessed in a CML transplantation mouse model in vivo, possibly because Raf1 knockout BM is not available because of embryonic lethality of Raf1−/− mice.28 Because Raf1 is a drugable kinase, it is of great interest as a potential molecular target in CML.
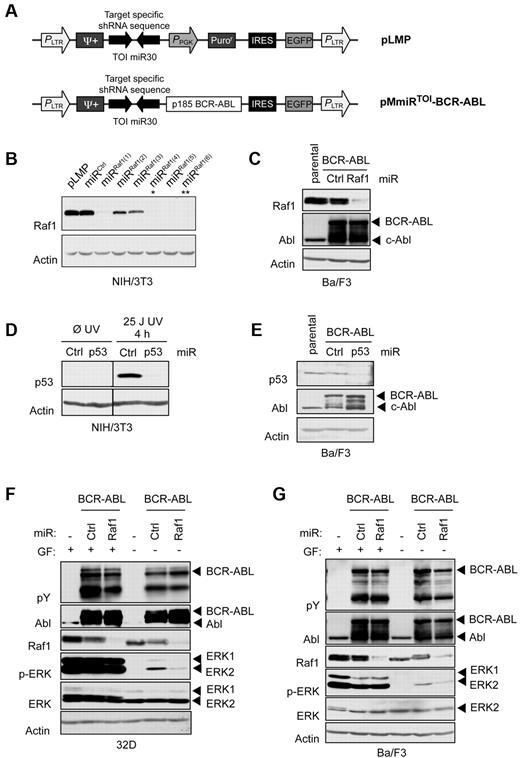
Thus, we cloned 6 different miR30-based Raf1 shRNAs (miRRaf1) into the retroviral pLMP vector (Figure 2A top panel).20 Three of 6 pLMPmiRRaf1 constructs were effective, resulting in nearly undetectable Raf1 protein levels in NIH/3T3 cells (Figure 2B). We subcloned the most efficient miRRaf1 cassette (indicated by a single asterisk) into the BCR-ABL–encoding pMmiRTOI-oncogene vector, resulting in pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL (Figure 2A bottom panel) and analyzed the efficacy of parallel oncogene expression and target knockdown. Both knockdown of the target and oncogene expression with this vector were highly effective (Figure 2C).
Effective target silencing and oncogene expression can be obtained from one unique mRNA. (A) Retroviral vectors used to deliver shRNAs to mammalian cells. PLMP vector encodes for a miR30-based target-specific shRNA under LTR promoter control. PMmiRTOI–BCR-ABL vector encodes for target-specific miR and p185 BCR-ABL. Provirus layouts are shown with open arrows indicating active promoters and 2 inverted block arrows representing shRNA stem sequence. (B) Western blot analysis of NIH/3T3 cells transduced with different Raf1 miR in pLMP after puromycin selection. (C) Ba/F3 cells retrovirally infected with pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL or pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL construct. (D) Western blot analysis of NIH/3T3 cells transduced with p53 miR in pLMP after puromycin selection. To induce p53, cells were UV irradiated 4 hours prior harvesting. (E) Western blot analysis of Ba/F3 cells retrovirally infected with pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL or pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL. (F-G) Raf1 knockdown disrupts BCR-ABL–dependent MAPK signaling. 32D (F) or Ba/F3 cells (G) retrovirally infected with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL were maintained in IL-3–containing medium, then starved for 4 hours and analyzed for MAPK signaling by Western blot as indicated.
Effective target silencing and oncogene expression can be obtained from one unique mRNA. (A) Retroviral vectors used to deliver shRNAs to mammalian cells. PLMP vector encodes for a miR30-based target-specific shRNA under LTR promoter control. PMmiRTOI–BCR-ABL vector encodes for target-specific miR and p185 BCR-ABL. Provirus layouts are shown with open arrows indicating active promoters and 2 inverted block arrows representing shRNA stem sequence. (B) Western blot analysis of NIH/3T3 cells transduced with different Raf1 miR in pLMP after puromycin selection. (C) Ba/F3 cells retrovirally infected with pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL or pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL construct. (D) Western blot analysis of NIH/3T3 cells transduced with p53 miR in pLMP after puromycin selection. To induce p53, cells were UV irradiated 4 hours prior harvesting. (E) Western blot analysis of Ba/F3 cells retrovirally infected with pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL or pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL. (F-G) Raf1 knockdown disrupts BCR-ABL–dependent MAPK signaling. 32D (F) or Ba/F3 cells (G) retrovirally infected with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL were maintained in IL-3–containing medium, then starved for 4 hours and analyzed for MAPK signaling by Western blot as indicated.
In addition, we also cloned a p53-specific miR30-based shRNA (miRp53) in the BCR-ABL–encoding pMmiRTOI-oncogene vector and showed functionality of the miRp53 in both vectors (Figure 2D-E). p53 knockdown previously has been shown to lead to an acceleration of BCR-ABL–induced leukemogenesis in mice29 and thus could serve as a positive readout control in further experiments. In summary, these data demonstrate that miRTOI expressed together with the BCR-ABL oncogene on one single mRNA transcript driven by the LTR Pol II promoter leads both to effective TOI knockdown and expression of the oncogene.
Next we examined the effects of simultaneous Raf1 knockdown and BCR-ABL expression on ERK activation in 2 hematopoietic cytokine-dependent cell lines. We infected 32D cells (IL-3–dependent murine myeloid cell line, Figure 2F) and Ba/F3 (IL-3–dependent murine pro-B-cell line, Figure 2G) with pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL or pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL retroviruses. On BCR-ABL expression, these cell lines become growth factor independent. Transduced cells were cultured with IL-3 or starved for 4 hours in IL-3 and serum-free medium, subsequently harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis. Also in these cells, the pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL vector led to both robust oncogene expression and effective TOI knockdown. In the absence of growth factors, Raf1 knockdown resulted in a significant reduction of ERK phosphorylation in BCR-ABL–positive 32D and Ba/F3 cells (Figure 2F-G). However, this effect of the Raf1 knockdown was not observed in IL-3–stimulated cells. Thus, Raf1 seems to be important for BCR-ABL–induced activation of the MAPK/ERK cascade but dispensable for IL-3–mediated ERK activation.
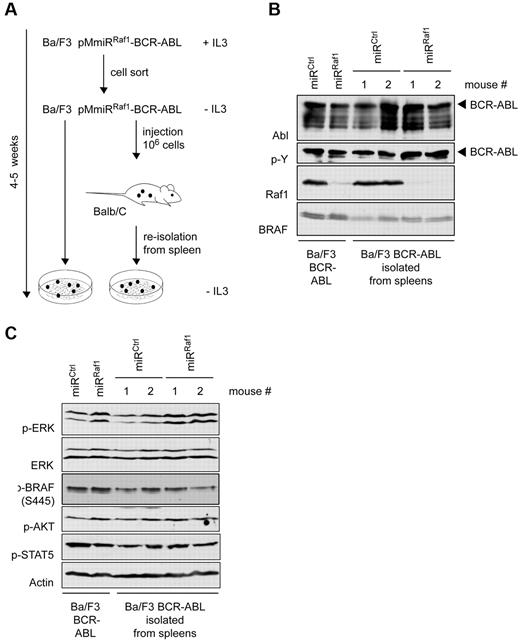
Next we analyzed whether our construct enabled sustained knockdown over a longer period of time both in vitro and in vivo as knockdown of Raf1 might confer negative selection pressure and, for example, lead to silencing of the shRNA expression over time. To this end, Ba/F3 cells were transduced with pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL or pMmiRCtrl-BCR-ABL. Cells were sorted for EGFP, deprived of IL-3, and then either kept in culture or injected into syngeneic Balb/c mice. Four to 6 weeks later cultured cells or spleen cells from diseased mice were analyzed for BCR-ABL expression and knockdown efficiency (Figure 3A).
Target silencing and oncogene expression are both effective and persistent. (A) Scheme of experimental setup: FACS-sorted Ba/F3 cells expressing pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL as shown in Figure 2G, were deprived of IL-3 and either kept in culture or injected intravenously into BALB/c mice. After 2 weeks, cells were reisolated from mouse spleens and cultured for 1 more week. After 4-5 weeks cultured cells or spleen cells from 2 individual mice per group were analyzed for (B) BCR-ABL expression and Raf1 knockdown efficiency by Western blot analysis. (C) The membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti–p-ERK, anti–p-AKT, and anti–p-STAT5 Abs as indicated.
Target silencing and oncogene expression are both effective and persistent. (A) Scheme of experimental setup: FACS-sorted Ba/F3 cells expressing pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL as shown in Figure 2G, were deprived of IL-3 and either kept in culture or injected intravenously into BALB/c mice. After 2 weeks, cells were reisolated from mouse spleens and cultured for 1 more week. After 4-5 weeks cultured cells or spleen cells from 2 individual mice per group were analyzed for (B) BCR-ABL expression and Raf1 knockdown efficiency by Western blot analysis. (C) The membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti–p-ERK, anti–p-AKT, and anti–p-STAT5 Abs as indicated.
Western blot analysis showed sustained BCR-ABL expression and strong Raf1 knockdown (> 90%) over a period of > 4 weeks both in vitro and in vivo (Figure 3A). Interestingly, miRRaf1-encoding cells showed reactivation of p-ERK over time, indicating that activation of the MAPK/ERK cascade is indispensable for the survival of BCR-ABL–positive cells (Figure 3B). Because the Raf1 knockdown remained complete over time, other mechanisms may lead to ERK activation. One possible candidate might be BRAF, another Raf family member and activator of MAPK/ERK cascade, but neither BRAF protein expression (Figure 3B) nor its activation was elevated (Figure 3C). Alternatively secreted or circulating cytokines might reactivate ERK independent of BCR-ABL signaling. IL-3, for example, is able to activate ERK in the absence of Raf1 (Figure 2F-G).
Effects of Raf1 suppression on BCR-ABL–mediated colony growth of primary HSCs in methylcellulose
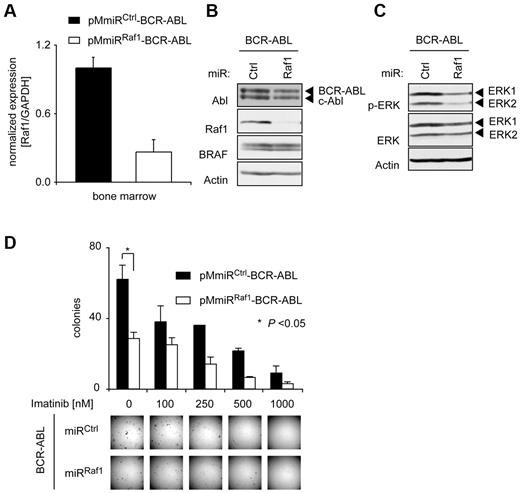
We next tested the functionality of the pMmiRTOI–BCR-ABL vector in primary murine BM (BM) cells. Primary murine BM cells, harvested from 5-FU–pretreated donor mice, were transduced with pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL or pMmiRCtrl-BCR-ABL retrovirus, BCR-ABL expression and Raf1 knockdown was confirmed (Figure 4A and B) and cells were starved for 6 hours in cytokine-free, serum-reduced medium. Again, simultaneous BCR-ABL expression and Raf1 knockdown led to a reduction in the phosphorylation of ERK (Figure 4C).
Raf1 depletion attenuates BCR-ABL–induced transformation of murine BM cells in vitro. 5-FU–enriched mouse BM-derived progenitor cells were infected either with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL retrovirus. (A) Expression levels of Raf1 were analyzed by qRT PCR (TaqMan) in EGFP+ cells 5 days after transduction. Results were normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. (B) Raf1 knockdown efficacy was verified by Western blot. (C) Retrovirally infected BM cells were starved for 6 hours in RPMI medium containing 3% FCS and no cytokines and p-ERK status was determined by Western blot. (D) Results of methylcellulose colony formation assays. PMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL and pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL–expressing murine BM cells were plated in methylcellulose without growth factors in the absence or presence of imatinib as indicated. Representative photographs of methylcellulose colonies of pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL–transduced BM cells are shown and CFUs were quantified 10 days after plating. Results shown are from 1 of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicates. P values were determined by Student t test.
Raf1 depletion attenuates BCR-ABL–induced transformation of murine BM cells in vitro. 5-FU–enriched mouse BM-derived progenitor cells were infected either with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL retrovirus. (A) Expression levels of Raf1 were analyzed by qRT PCR (TaqMan) in EGFP+ cells 5 days after transduction. Results were normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. (B) Raf1 knockdown efficacy was verified by Western blot. (C) Retrovirally infected BM cells were starved for 6 hours in RPMI medium containing 3% FCS and no cytokines and p-ERK status was determined by Western blot. (D) Results of methylcellulose colony formation assays. PMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL and pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL–expressing murine BM cells were plated in methylcellulose without growth factors in the absence or presence of imatinib as indicated. Representative photographs of methylcellulose colonies of pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL–transduced BM cells are shown and CFUs were quantified 10 days after plating. Results shown are from 1 of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicates. P values were determined by Student t test.
To determine the role of Raf1 in BCR-ABL–mediated transformation of primary BM cells, cells were plated into methylcellulose in the absence of growth factors and colonies were quantified 10 days later. We observed smaller colonies and a significant reduction in colony numbers by Raf1 knockdown compared with control cells, indicating that Raf1 mediates BCR-ABL–induced ERK activation and plays an important role in the transformation of primary hematopoietic cells by BCR-ABL in vitro (Figure 4D).
To test whether a combination of Raf1 knockdown and BCR-ABL kinase inhibition could further reduce colony formation, we used the BCR-ABL inhibitor imatinib. Although imatinib alone is able to suppress colony formation of BCR-ABL–positive BM cells, additional Raf1 knockdown potentiates imatinib-induced growth inhibitory effects in this assay (Figure 4D). Similar results were obtained using a vector encoding for the BCR-ABLp210 instead of the BCR-ABLp185 isoform (supplemental Figure 5A-B). In addition, we investigated the impact of Raf1 knockdown on leukemogenesis mediated by imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutants BCR-ABLT315I and BCR-ABLY253H. The transforming capacity of both mutants was strongly reduced on Raf1 down-regulation (supplemental Figure 5C-D). Thus, a combination of Raf1 and Abl inhibition may be a promising approach in BCR-ABL–positive disease.
Inactivation of Raf1 by RNAi delays onset of leukemia in a murine model of CML
First, to exclude general toxicity of Raf1 knockdown in hematopoietic cells, we tested the effect of Raf1 down-regulation alone on normal hematopoiesis in vitro as well as in vivo. On Raf1 knockdown, there was no difference observed regarding colony-forming ability in semisolid medium in vitro (supplemental Figure 6). Furthermore, mice transplanted with Raf1 knockdown BM reconstituted normally (supplemental Figure 7A-B) and Raf1 knockdown had no effect on short- or long-term generation of myeloid, B, or T cells (supplemental Figure 7C), indicating that Raf1 knockdown does not interfere with normal hematopoiesis. This finding is in agreement with a recent report demonstrating no obvious phenotype of Raf1 knockout in adult mice.30
Then, to confirm the applicability of the vector system for in vivo approaches, we generated mice developing BCR-ABL–positive leukemia by the retroviral syngeneic transplantation method. To this end BM derived from 5-FU–pretreated donor mice was infected with pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL, pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL, or pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL retroviruses and injected into the tail veins of lethally irradiated recipient BALB/c mice (see “Methods,” for summary of all transplantations see Table 1). All mice that received pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL–infected cells developed a CML-like disease with a very short latency and 100% penetrance characterized by a high percentage of EGFP+, Mac1/Gr-1+ cells in their peripheral blood within 18 days (Figure 5B). The mice succumbed to leukemia within 5 weeks, demonstrating that the pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL construct can efficiently induce a CML-like disease in this model (Figure 5A). Recipients of pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL–transduced BM cells showed a substantially prolonged survival (Figure 5A). Onset and progression of the disease was significantly delayed in Raf1 knockdown animals as depicted by lower proportion of leukemic white blood cells (WBCs) in the peripheral blood (Figure 5B) and lower peripheral leukocyte counts (Figure 5C). These results were verified using a second independent miRRaf1 (Figure 2B indicated by double asterisks, and supplemental Figure 8).
Summary of transplantation experiments
| Genotype . | No. of mice . | Mean fluorescence . | EGFP+ cell transplantations . | Total cell transplantations . | Median survival time, d (range) . | Median WBC day 18, ×103/μL (range) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 5 | 63.7 | 5000 | 200 000 | 23.2 (19-30) | 85 (42-135) |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 4 | 60.5 | 5000 | 200 000 | 31.3 (26-34) | 52 (23-88) |
| pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL | 5 | 59.6 | 5000 | 200 000 | 22.2 (19-27) | 129 (46-242) |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 3 | 178.6 | 5000 | 200 000 | 25.0 (22-27) | 188 (169-209) |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 3 | 160.8 | 5000 | 200 000 | 40.0 (34-50) | 98 (20-150) |
| pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL | 3 | 138.7 | 5000 | 200 000 | 21.3 (19-24) | ND |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 5 | 31.0 | 5000 | 190 000 | 24.6 (22-28) | 107 (78-140) |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 5 | 23.9 | 5000 | 190 000 | 33.4 (24-41) | 69 (40-124) |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 5 | 31.1 | 5000 | 190 000 | 29.8 (18-37) | 52 (31-86) |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 4 | 27.5 | 5000 | 190 000 | 41.0 (32-46) | 26 (10-39) |
| pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL | 5 | 32.5 | 5000 | 190 000 | 29.2 (25-32) | 82 (31-168) |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 5 | 34.2 | 5000 | 200 000 | 25.0 (19-29) | ND |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 5 | 28.0 | 5000 | 200 000 | 34.3 (31-38) | ND |
| pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL | 5 | 35.0 | 5000 | 200 000 | 24.4 (21-30) | ND |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 10 | 65.6 | 5000 | 200 000 | 25.7 (21-29) | 101 (33-228) |
| pMmiRRaf1(6)–BCR-ABL | 10 | 50.9 | 5000 | 200 000 | 39.6 (25-70) | 23 (5-70) |
| Genotype . | No. of mice . | Mean fluorescence . | EGFP+ cell transplantations . | Total cell transplantations . | Median survival time, d (range) . | Median WBC day 18, ×103/μL (range) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 5 | 63.7 | 5000 | 200 000 | 23.2 (19-30) | 85 (42-135) |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 4 | 60.5 | 5000 | 200 000 | 31.3 (26-34) | 52 (23-88) |
| pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL | 5 | 59.6 | 5000 | 200 000 | 22.2 (19-27) | 129 (46-242) |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 3 | 178.6 | 5000 | 200 000 | 25.0 (22-27) | 188 (169-209) |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 3 | 160.8 | 5000 | 200 000 | 40.0 (34-50) | 98 (20-150) |
| pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL | 3 | 138.7 | 5000 | 200 000 | 21.3 (19-24) | ND |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 5 | 31.0 | 5000 | 190 000 | 24.6 (22-28) | 107 (78-140) |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 5 | 23.9 | 5000 | 190 000 | 33.4 (24-41) | 69 (40-124) |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 5 | 31.1 | 5000 | 190 000 | 29.8 (18-37) | 52 (31-86) |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 4 | 27.5 | 5000 | 190 000 | 41.0 (32-46) | 26 (10-39) |
| pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL | 5 | 32.5 | 5000 | 190 000 | 29.2 (25-32) | 82 (31-168) |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 5 | 34.2 | 5000 | 200 000 | 25.0 (19-29) | ND |
| pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL | 5 | 28.0 | 5000 | 200 000 | 34.3 (31-38) | ND |
| pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL | 5 | 35.0 | 5000 | 200 000 | 24.4 (21-30) | ND |
| pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL | 10 | 65.6 | 5000 | 200 000 | 25.7 (21-29) | 101 (33-228) |
| pMmiRRaf1(6)–BCR-ABL | 10 | 50.9 | 5000 | 200 000 | 39.6 (25-70) | 23 (5-70) |
WBC indicates white blood cell.
Raf1 depletion attenuates BCR-ABL–induced leukemogenesis in a murine transfection/transplantation model. Mice transplanted with pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL show delayed onset and slower progression of disease. (A) Raf1 knockdown in BCR-ABL–positive cells prolongs overall survival of mice in a BM transplantation model. Kaplan-Meier plot detailing survival times of mice transplanted with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL (n = 23) or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL (n = 21) in 5 independent experiments. (B) Proportion of leukemic WBCs in the peripheral blood of mice that received transplants at indicated time points (day 15: pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL n = 10; others n = 9). P value was determined by Student t test. (C) White blood cell counts from peripheral blood of mice that received transplants of one experiment at indicated time points (n = 3 for each group). (D) p53 knockdown in BCR-ABL–positive cells has no significant impact on overall survival in a BM transplantation model. Kaplan-Meier plot detailing survival times of mice transplanted with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL (n = 8) or pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL (n = 8) in 2 independent experiments. (E-F) Target knockdown is durable in a BM transplantation model. qRT PCR (TaqMan) analysis of splenocytes isolated from moribund mice with > 80% EGFP-positive splenocytes. (E) Raf1 and (F) p53 mRNA levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. Values were determined from 2-3 mice per group measured in duplicates.
Raf1 depletion attenuates BCR-ABL–induced leukemogenesis in a murine transfection/transplantation model. Mice transplanted with pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL show delayed onset and slower progression of disease. (A) Raf1 knockdown in BCR-ABL–positive cells prolongs overall survival of mice in a BM transplantation model. Kaplan-Meier plot detailing survival times of mice transplanted with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL (n = 23) or pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL (n = 21) in 5 independent experiments. (B) Proportion of leukemic WBCs in the peripheral blood of mice that received transplants at indicated time points (day 15: pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL n = 10; others n = 9). P value was determined by Student t test. (C) White blood cell counts from peripheral blood of mice that received transplants of one experiment at indicated time points (n = 3 for each group). (D) p53 knockdown in BCR-ABL–positive cells has no significant impact on overall survival in a BM transplantation model. Kaplan-Meier plot detailing survival times of mice transplanted with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL (n = 8) or pMmiRp53–BCR-ABL (n = 8) in 2 independent experiments. (E-F) Target knockdown is durable in a BM transplantation model. qRT PCR (TaqMan) analysis of splenocytes isolated from moribund mice with > 80% EGFP-positive splenocytes. (E) Raf1 and (F) p53 mRNA levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. Values were determined from 2-3 mice per group measured in duplicates.
As expected, p53 knockdown in this system slightly although nonsignificantly accelerated the progression of leukemia in this highly aggressive CML model (Figure 5D).29 Sustained and efficient Raf1 and p53 knockdown could be demonstrated in spleen cells of diseased mice, highlighting the efficient and durable in vivo knockdown conferred by this vector design (Figure 5E-F). Thus, development of leukemia was delayed but not completely abolished in Raf1 knockdown mice. pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL–expressing cells, as shown in Figure 3C, showed reactivation of p-ERK over time. Therefore, compensatory mechanisms may lead to ERK activation, because the Raf1 knockdown remained complete over time. One possible candidate might be BRAF, another Raf family member and activator of the MAPK/ERK cascade.
BRAF is dispensable for BCR-ABL–dependent transformation
Two studies suggested an involvement of BRAF in BCR-ABL–mediated transformation by overexpressing or deleting the BRAF inhibitor SPA-1.31,32 As BRAF knockout mice are embryonic lethal33 studies using BRAF knockout BM have not been performed. Here we analyzed the function of BRAF in comparison to Raf1 for BCR-ABL–mediated transformation using our vector system. Interestingly, in contrast to Raf1, BRAF knockdown had no impact on BCR-ABL–dependent activation of ERK in vitro (Figure 6A). In addition, BRAF depletion in primary murine BM cells did not alter colony-forming numbers and shape in a methylcellulose assay, suggesting that BRAF is dispensable for BCR-ABL–mediated transformation in this assay (Figure 6B). We finally also investigated the role of BRAF for BCR-ABL–mediated leukemogenesis in the previously described murine CML model (for summary of all transplantations see Table 1). Neither knockdown of Raf1 nor of BRAF had an influence on the phenotype of the disease (supplemental Figure 4). However, in contrast to Raf1, BRAF knockdown did not affect BCR-ABL–dependent leukocytosis, leukemic burden in the peripheral blood (Figure 6D-E) or overall survival despite very efficient BRAF knockdown (Figure 6C,F).
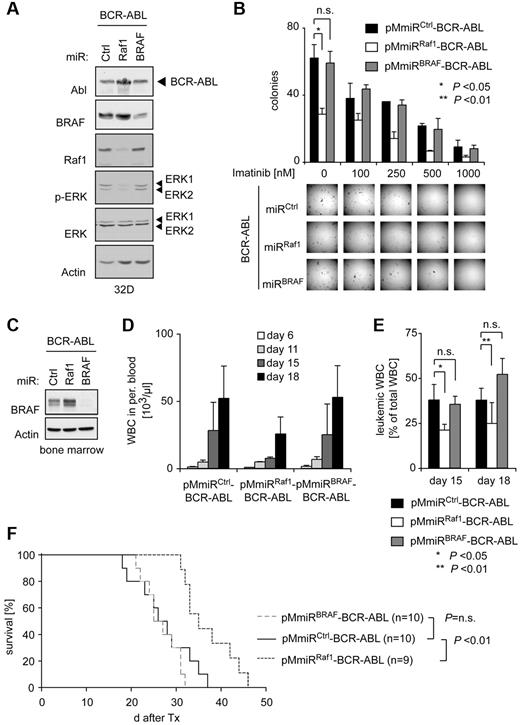
BRAF is dispensable for BCR-ABL–mediated ERK activation and transformation in vitro and in vivo. (A) Verification of the pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL vector. Ba/F3 cells were retrovirally infected with indicated vectors and BCR-ABL, BRAF, Raf1, p-ERK, ERK, and actin levels were determined by Western blot analysis. (B) Results of methylcellulose colony formation assays. Murine BM cells were retrovirally infected with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL, pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL, or pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL and plated in methylcellulose medium without growth factor supplement in the absence or presence of imatinib as indicated. Representative photographs of methylcellulose colonies of pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL, pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL, or pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL–transduced BM cells are shown (top panel) and CFUs were quantified 10 days after plating (bottom panel). Results shown are from 1 of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicates. P values were determined by Student t test. (C) Functional analysis of pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL in murine primary BM. BM of 5-FU–pretreated donor mice was transduced with indicated vectors, sorted by FACS, and analyzed by Western blot. (D) BRAF knockdown has no effect on BCR-ABL–mediated leukocytosis in a BM transplantation model for CML. Mice were transplanted with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL (n = 5), pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL (n = 4), or pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL (n = 5) transduced BM and WBC counts and (E) proportion of leukemic cells in peripheral blood were determined. (F) Kaplan-Meier plot detailing survival times of mice transplanted with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL (n = 10), pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL (n = 9) or pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL (n = 10). Data from 1 of 3 independent experiments are shown.
BRAF is dispensable for BCR-ABL–mediated ERK activation and transformation in vitro and in vivo. (A) Verification of the pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL vector. Ba/F3 cells were retrovirally infected with indicated vectors and BCR-ABL, BRAF, Raf1, p-ERK, ERK, and actin levels were determined by Western blot analysis. (B) Results of methylcellulose colony formation assays. Murine BM cells were retrovirally infected with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL, pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL, or pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL and plated in methylcellulose medium without growth factor supplement in the absence or presence of imatinib as indicated. Representative photographs of methylcellulose colonies of pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL, pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL, or pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL–transduced BM cells are shown (top panel) and CFUs were quantified 10 days after plating (bottom panel). Results shown are from 1 of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicates. P values were determined by Student t test. (C) Functional analysis of pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL in murine primary BM. BM of 5-FU–pretreated donor mice was transduced with indicated vectors, sorted by FACS, and analyzed by Western blot. (D) BRAF knockdown has no effect on BCR-ABL–mediated leukocytosis in a BM transplantation model for CML. Mice were transplanted with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL (n = 5), pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL (n = 4), or pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL (n = 5) transduced BM and WBC counts and (E) proportion of leukemic cells in peripheral blood were determined. (F) Kaplan-Meier plot detailing survival times of mice transplanted with pMmiRCtrl–BCR-ABL (n = 10), pMmiRRaf1–BCR-ABL (n = 9) or pMmiRBRAF–BCR-ABL (n = 10). Data from 1 of 3 independent experiments are shown.
Discussion
In a genetically complex disease like cancer, which is further complicated by the diverse interactions between the tumor cell and the host organism, in vivo genetic loss-of-function studies in the mouse are an invaluable tool to determine functional dependencies within the tumor network. Before the advent of RNAi technology, knockout mice were central for the study of loss-of-function effects. To generate suitable tumor models, usually a tumor-initiating oncogenic line has to be crossed to the knockout mouse line in time-consuming breedings. For hematopoietic malignancies, introduction of an oncogene into HSCs derived from respective knockout mice by retroviral infection and subsequent transplantation into irradiated host animals accelerates the analysis, and is also restricted by the availability of the respective knockout strain as well as the requirement for an immunologically compatible donor mouse strain. These obstacles so far have strongly impacted a more widespread use of genetic loss-of-function studies in the analysis of hematopoietic malignancies. In 2002, Cullen and colleagues discovered that hairpin sequences of the endogenous microRNA (miR) miR30 can be replaced by a target-specific sequence, generating a synthetic, target-specific miR30-based shRNA.21 In contrast to conventional shRNAs, these miR30-based shRNAs can be transcribed by RNA Pol II promoters.21,34-36 This feature of miR30-based shRNAs seemed to increase the efficiency of target knockdown in vivo compared with regular shRNAs expressed from Pol III promoters, as shown in a series of elegant studies.20,35,37 Furthermore, some endogenous microRNAs have been found within introns or 3′ UTRs of other genes,38 suggesting that cotranscription of miRs together with other genes may be feasible. Taking advantage of these characteristics of miR-based shRNAs, we now have developed an RNAi-based system that alleviates most of the problems entailed in the “classic” approach using knockout mice. The system described in this study is designed for simultaneous expression of a miR30-based shRNA and an oncogene from a single transcript. This facilitates stable and durable target knockdown in every oncogene-expressing cell and distinguishes the present vector design from other polycistronic single-vector designs for coexpression of shRNAs and transgenes.39 Because oncogene and miRTOI are derived from the same transcript, transfected cells selecting for expression of the oncogene automatically coselect for the miRTOI. Thus, this vector is suited for the investigation of oncogenic signaling networks, in which down-regulation of crucial signaling targets may lead to a strong negative selection against shRNA-expressing cells. In addition, combined expression of oncogene, miRTOI and EGFP eliminate the need for cell sorting or antibiotic selection. The single-vector design will be particularly beneficial in target cells, which can only be temporarily cultured ex vivo or are only moderately permissive for transduction, such as embryonic or HSCs and also other primary cells. Here the single-vector system allows introduction of both miRTOI and transgene by a single-step transduction. In principle, any target gene of interest for which suitable shRNAs are available can be stably down-regulated in combination with the expression of a positively selected oncogene. In contrast to the approach where the shRNA is transduced into a transgenic animal with an established disease in our model the disease has to establish in the setting of knockdown of potential mediators, which is one potential drawback of the system. Nevertheless, this system is highly flexible and not only limited to studies on oncogenic signaling cascades. It can for example also be used to express a mutant form of a given protein while knocking down the endogenous wildtype protein, thus mimicking gene replacement. We additionally established a cloning strategy to facilitate introduction of the miRTOI cassette into a transgene-encoding vector harnessing sequence and ligation independent cloning22,40 (SLIC; supplemental Figure 3), thereby enabling subcloning of whole miR30-based shRNA libraries.34,41
We analyzed the functionality of this vector system in a BM transduction transplantation model for CML. The gold standardfor CML therapy is the BCR-ABL kinase inhibitor imatinib. The majority of patients with BCR-ABL–positive CML show excellent responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment.42,43 However, the persistence of BCR-ABL–positive cells in imatinib-treated patients indicates that inhibition of the Abl kinase activity alone might not be sufficient to eradicate the leukemia. Combining a BCR-ABL tyrosine inhibitor with inhibitors of its downstream signaling targets may improve CML therapy. Inhibitors that target various stages of the Ras signaling pathway, such as farnesyl transferase, MEK1, PI3K, mTOR, and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), have been shown in vitro to have synergistic or additive effects in preventing BCR-ABL–mediated transformation.44-47 Only a few of the molecules involved in BCR-ABL signaling have so far been directly examined for their role in mediating BCR-ABL–induced transformation in vivo, an important aspect in the validation of potential therapeutic targets.3,44,48,49 Here we show that Raf1 but not BRAF is an important intermediate in the BCR-ABL signaling cascade in vivo, required for the efficient activation of the promitogenic MAPK/ERK pathway. Interestingly, a recent study does also show a role of Raf1 but not BRAF in the pathogenesis of lung cancer.30
Several Raf inhibitors have already entered clinical trials and especially in melanoma with BRAF mutations the clinical results are very encouraging50 However, a series of papers could demonstrate that on BRAF inhibition the MAPK/ERK cascade can get paradoxically activated by various mechanisms which may lead to acceleration of the malignant growth on BRAF inhibition. It is thus important to carefully study the effects of the inhibition of Raf isoforms on malignant growth in every tumor type. According to our results, BRAF inhibitors are predicted to be of limited use in the treatment of CML, whereas inhibition of Raf1 would seem to be more promising. However, Raf1 knockdown alone was not sufficient to prevent leukemia onset in mice. Thus, combinatorial studies of BCR-ABL inhibitors and inhibitors targeting Raf1 may be warranted in Philadelphia chromosome–positive leukemia.
The outlined vector system pMmiRTOI-oncogene represents a very efficient and versatile approach to perform loss-of-function studies in hematologic malignancies. By strongly facilitating the characterization of oncogenic signaling networks, this system should help to establish a hierarchical map of functionally relevant genes in a defined tumor context and supply new targets for drug development.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank M. Schiemann and K. Goetsch for cell sorting, and S. W. Lowe for the gift of p53 miR.
This work was supported by a Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) grant (J.D.).
Authorship
Contribution: C.A. and J.D. conceived and designed the experiments; C.A., A.L.I., and M.T. performed the experiments; C.A. analyzed data; A.L.I. and H.L. contributed to interpretation of experimental data; C.P. discussed experiments; and C.A., C.M., and J.D. wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for C.M. is Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Correspondence: Justus Duyster, Department of Internal Medicine III, Technical University Munich, Ismaningerstrasse 22, 81675 Munich, Germany; e-mail: justus.duyster@lrz.tum.de.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal