Abstract
Background: Sphingosine kinase interacting protein (SKIP) has been shown to be mostly silenced by hypermethylation in AML [1]. SKIP interacts with and regulates the function of sphingosine kinase (SK) enzyme. SK activity results in phosphorylation of sphingosine (SPH) to form sphingosine 1 phosphate (S1P), which promotes cell survival and resistance to apoptosis. On the other hand, S1P precursors ceramide (CER) and SPH mediate antiproliferative and apoptotic responses. SKIP has been reported to negatively regulate SK1 activity in fibroblasts. Therefore, we investigated the consequences of SKIP silencing in primary AML cells. In addition, we studied the effects of SKIP re-expression in leukemic cell lines.
Methods: CTS and K562 cells were transfected with SKIP gene using standard techniques. SKIP is normally silenced in both cell lines. Intracellular and extracellular S1P, SPH and CER were measured by UPLC-MS/MS. In addition, intracellular SK activity was determined based on C17 S1P production from C17 SPH substrate. Chemosensitivity to doxorubicin, Imatinib and Ara-C in transfected cells was also studied.
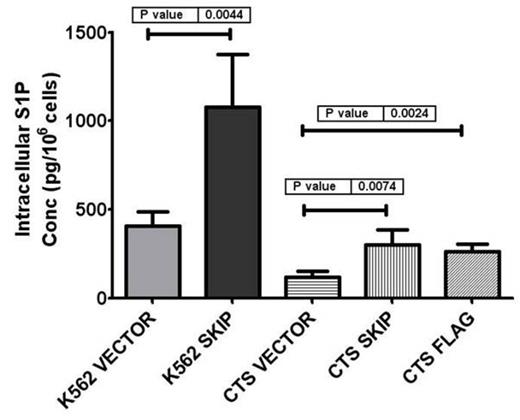
Results: In Primary AML cells, intracellular S1P and CER concentrations were reduced compared to G-CSF-mobilized peripheral blood mononuclear cells. In addition, SK activity was found to be downregulated in AML primary cells. When we transfected leukemic cell lines with SKIP gene, S1P and CER showed at least 2 fold increase in intracellular and extracellular basal levels compared to vector alone control (Figure 1). Further studies confirmed a significant increase in intracellular SK activity in SKIP transfected compared to vector alone cells, based on C17 S1P production (8.8 ± 2.6 vs 1.4 ± 0.4 ng/106 cells respectively after 24 hrs, p< 0.05). This increase in S1P and CER was associated with increasing apoptotic signals as evidenced by Annexin V staining and cleaved PARP expression. Moreover, chemosensitivity to Imatinib and AraC was significantly increased in SKIP transfected cell lines. These experiments confirm the regulation of SK1 function by SKIP.
Conclusion: These data indicate that SKIP is downregulated in AML leading to reduced SK activity, which ultimately inhibits the apoptosis response.
Effect of SKIP transfection on intracellular concentrations of S1P.
1. Saied, M.H., et al., Genome wide analysis of acute myeloid leukemia reveal leukemia specific methylome and subtype specific hypomethylation of repeats. PLoS One, 2012. 7(3): p. e33213.
EAG and PS contributed equally
JG and DT contributed equally
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal