Abstract
Relapsing/refractory (r/r) B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is associated with a poor prognosis in both pediatric and adult patients. Novel therapies targeting CD19 on leukemic blasts, such as anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells (CART19, CTL019) or bi-specific anti-CD19/CD3 antibodies (blinatumomab) induce significant responses in this population. However, CD19-negative relapses have been reported in 5-10% of patients following CART19 or blinatumomab therapies. This is likely due to selective pressure on leukemia sub-clones by these potent anti-CD19 agents. Hence, novel effective immunotherapies are needed in order to treat these patients.
In order to identify potential additional B-ALL antigens, samples from 20 r/r patients (including two that relapsed with CD19-negative disease after treatment with CART19 therapy) were screened using a custom Quantigene RNA panel (Affymetrix) and expression on cell surface was confirmed by multiparametric flow cytometry. The IL-3 receptor α (CD123) was one of the most highly and homogeneously expressed antigens in the blasts of 16/20 r/r ALL patients, and 2/2 CD19-negative relapses. Therefore, we sought to investigate the role of CART targeting CD123 (CART123) against r/r B-ALL, focusing on treating patients with CD19-negative relapses after prior anti-CD19 directed therapy. CART123 was shown to be effective in eradicating acute myeloid leukemia in xenograft mouse models but its role in ALL has not been investigated (Gill et al, Blood, 2014).
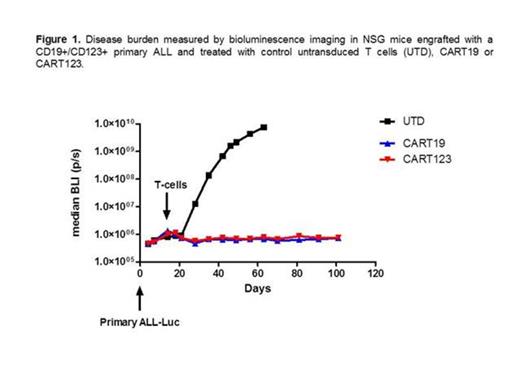
We used a 2nd generation CAR123 construct that comprised a 4-1BB (CD137) co-stimulatory domain. T cells were lentivirally transduced and expanded using anti-CD3/CD28 beads. Head-to-head in vitro comparisons between CART123 and CART19 revealed similar rates of proliferation, CD107a degranulation, cytokine production and cytotoxicity when CART were co-cultured with the CD19+CD123+ B-ALL cell line NALM-6 and with primary B-ALL blasts. For in vivo evaluation, we utilized the primary ALL model that was developed by our group (Barrett et al, Blood, 2011). In this model, primary blasts obtained from ALL patients were passaged in NOD-SCID-γ chain KO (NSG) mice, and transduced with GFP/luciferase. We injected NSG mice with 2 million primary ALL blasts i.v. (CD19+, CD123+) and after engraftment, mice were treated with CART19, CART123 or control untransduced T cells (1 million i.v.). Mice treated with control T cells succumbed quickly to disease, while mice treated with either CART19 or CART123 showed tumor eradication and long term survival (Figure 1).
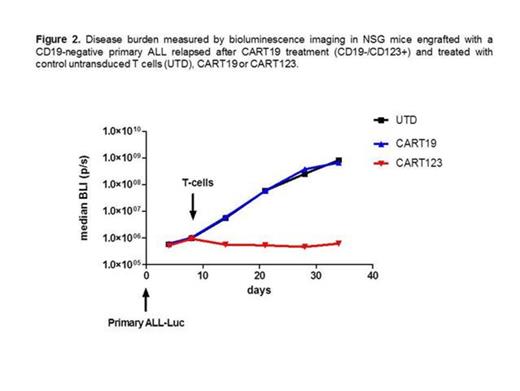
We then evaluated the role of CART123 in the treatment of leukemia obtained from an ALL patient that relapsed with CD19-negative disease after CART19 treatment. Both CART123 and CART19 were incubated with CD19-negative ALL blasts; CART123, but not CART19 resulted in significant degranulation, robust cytokine production, and potent cytotoxicity. To confirm these results in vivo, we established a unique model of CD19-negative B-ALL xenograft. We used primary CD19-negative blasts obtained from a pediatric patient that relapsed after CART19 therapy; CD19-negative blasts were passaged in vivo in NSG mice and stably transduced with GFP/luciferase. Importantly, the blasts retained their CD19-negative phenotype. After engraftment, mice were treated with CART19, CART123 or control T cells. CART19 and control T cells had no anti-tumor activity, while CART123 resulted in a complete eradication of the disease and long term survival in these mice (Figure 2).
In conclusion, CART123 represents an important additional approach to treating B-ALL, in particular due to its activity against CD19-negative relapses. Since we have previously shown that treatment with CART123 can lead to myelosuppression, CART123 should be employed to eradicate disease prior to allogeneic transplantation. Future direction may include combining CART123 with CART19 preemptively in order to avoid CD19 antigen escapes.
Ruella:Novartis: Research Funding. Kenderian:Novartis: Research Funding. Shestova:Novartis: Research Funding. Scholler:Novartis: Research Funding. Lacey:Novartis: Research Funding. Melenhorst:Novartis: Research Funding. Nazimuddin:Novartis: Research Funding. Kalos:Novartis: CTL019 Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Porter:Novartis: Research Funding. June:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Grupp:Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding. Gill:Novartis: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal