Abstract
Background: Treatment outcomes for patients with CLL have improved with the use of targeted agents, such as ibrutinib, yet complete remissions (CR) are rare, and the outcomes of patients with relapsed CLL still remain suboptimal. T cells from patients with CLL express higher levels of checkpoint inhibitory molecules, such as PD-1, compared to normal T cells (Ramsay et al. Blood 2012). Furthermore, CLL cells express ligands for these molecules, including PD-L1 and PD-L2. We hypothesized that blocking this interaction should enable T cell recognition and reactivity against CLL cells. Ibrutinib, via effect on ITK, is known to modulate immune responses, and has been shown to be synergistic with checkpoint blockade in preclinical models (Sagiv-Barfi et al. PNAS. 2015). Therefore, we designed a clinical trial of combined checkpoint inhibitor mAb with ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) CLL or Richter transformation (RT).
Methods: We designed an investigator-initiated phase II clinical trial combining nivolumab (anti-PD1 monoclonal antibody) with ibrutinib in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL or RT (NCT02420912). The study included two cohorts: Cohort 1 (relapsed/refractory CLL or RT) and cohort 2 (patients with CLL who achieved partial remission after at least 9 months on ibrutinib). In cohort 1, patients received a lead-in window of nivolumab monotherapy for course 1; ibrutinib was added starting with course 2. In cohort 2, patients were already receiving ibrutinib when they entered the study, and continued ibrutinib; nivolumab is added from course 1. Ibrutinib dose was 420 mg once daily. Nivolumab was given 3 mg/kg IV every 2 weeks. Eligibility criteria included age ≥18 years, adequate organ function (total bilirubin ≤1.5 x ULN, ALT and AST ≤3 x ULN, creatinine ≤1.5 x ULN). Prior allogeneic SCT was allowed. Patients with autoimmune diseases were excluded. The primary objective of the trial was CR/CRi rate in cohort 1, and the rate of conversion from PR to CR/CRi in cohort 2. Peripheral blood and bone marrow samples were collected at baseline and serially on treatment to assess for T cell subsets and immune marker expression (Receptors: PD1, CTLA4, LAG3, TIM3, GITR, OX40, 41BB, ICOS; Ligands: PDL1, PDL2, OX40L, Gal-9, 41BBL, B7-1, B7-2). Immune monitoring studies were conducted by the Immunotherapy Platform at M. D. Anderson Cancer Center.
Results: 13 patients have been consented; 12 initiated treatment. We report data on these 12 patients. The median age is 63 years (range, 42-78), 8 were men and 4 women. 9 patients are in cohort 1; 3 patients are in cohort 2.
Five patients with relapsed/refractory CLL were treated on cohort 1. Median number of prior therapies were 1 (range 1-3). Prognostic markers included [(del 13q (n=3), del17p (n=1), FISH negative (n=1)]. Three patients achieved PR; one patient had no response and came off study after course 5; one patient was too early for response assessment.
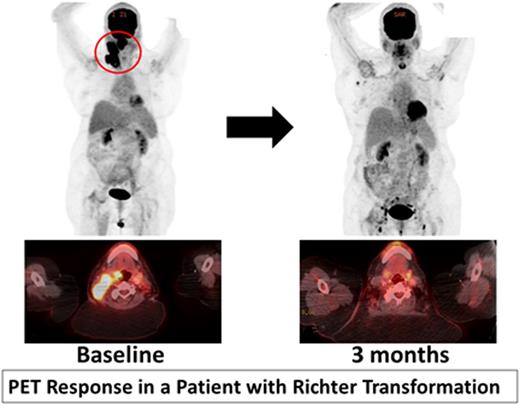
Four patients with previously untreated RT (including one with accelerated CLL) were treated in cohort 1. Median number of prior therapies for CLL were 2 (range 1-3). Two patients had a response and are currently in month 5 and 7 of treatment. Figure 1 shows PET response in a 62 year old with del17p, unmutated IGHV, complex karyotype CLL who developed RT with a large oropharyngeal mass. She had complete resolution of this mass at 3 months. One patient progressed after transient response. One patient is too early for response assessment.
Three patients were enrolled in cohort 2 [(del 17p (n=2), del13q (n=1); unmutated IGHV (n=2); no PCR amplification (n=1)]. Patients were on ibrutinib from 13-32 months prior to study enrollment. All three patients noted decrease in the lymphocytic infiltrate in the marrow. No patient has achieved CR/CRi. All 3 patients are continuing on study with a follow-up from 5-9 months.
One patient in cohort 2 developed thyroiditis. No other immune-related adverse events were noted. One patient had tumor flare. Correlative studies, including flow-cytometry and IHC for PD1 and PDL1 in serial blood and marrow samples are ongoing.
Conclusions: The combination of nivolumab and ibrutinib has activity in patients with relapsed, refractory CLL and RT. The trial continues to enroll patients, and updated results will be presented at the ASH meeting.
Jain:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novimmune: Consultancy, Honoraria. Thompson:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria. Cortes:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding. O'Brien:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics, LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Wierda:Abbvie: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal