Abstract
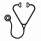
Background: Prognosis for older patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is poor, with lower response rates and shorter survival compared with younger patients. Vosaroxin is a first-in-class anticancer quinolone derivative that is active in AML, is minimally metabolized, evades P glycoprotein receptor-mediated efflux, and has activity independent of p53 status. In the phase 3 VALOR trial, overall survival (OS) was significantly improved with vosaroxin plus cytarabine vs placebo plus cytarabine in a prespecified analysis in patients ≥ 60 years of age (median OS: 7.1 mo vs 5.0 mo, respectively; HR = 0.75 [95% CI: 0.62-0.92]; P = 0.0030). At the time of the primary analysis (September 2014), patients had been followed for a median of 24.4 months (as estimated by the reverse Kaplan-Meier method). Here, after a median follow-up of 39.9 months, we provide updated survival information for patients ≥ 60 years treated in the VALOR trial.
Methods: In VALOR, patients with refractory or first relapsed AML were randomized 1:1 to receive cytarabine (1 g/m2 IV over 2 h, d 1-5) plus either vosaroxin (90 mg/m2 IV over 10 min, d 1, 4; 70 mg/m2 in subsequent cycles) or placebo. Eligible patients had refractory disease (persistent disease after induction, or first complete remission [CR1] lasting < 90 d) or were in first relapse (early relapse: CR1 lasting 90 d to 12 mo; late relapse: CR1 lasting 12 mo to 24 mo). Randomization was stratified by age (< 60, ≥ 60 years), disease status (refractory, early relapse, late relapse), and geographic location (US, non-US). Patients were followed for survival until death. At the time of the primary analysis (September 2014), 63/451 (14%) patients ≥ 60 years were alive and in continued follow-up.
Results:As of Jan 22, 2016, 33/451 patients ≥ 60 years treated in the VALOR trial were alive and in continued follow-up: 23/226 (10.2%) in the vosaroxin/cytarabine arm and 10/225 (4.4%) in the placebo/cytarabine arm. Updated OS data in patients ≥ 60 years of age was consistent with the primary analysis, demonstrating a significant improvement with the addition of vosaroxin (Figure; HR = 0.75 [95% CI: 0.62-0.91]; P = 0.0017). The survival benefit associated with vosaroxin/cytarabine was durable, as demonstrated by the separation of the survival curves through 48 mo. At 24 and 36 mo after randomization, the estimated survival rate was twice as high with vosaroxin/cytarabine as with placebo/cytarabine in patients ≥ 60 years (17.0% vs 8.5% and 12.8% vs 6.0%, respectively). The OS benefit was consistent across various age subgroups in the population ≥ 60 years of age; in patients 60-64 years (n = 124), 65-74 years (n = 293), and 75-84 years (n = 34), vosaroxin/cytarabine treatment increased median survival by 2.9 mo (8.1 vs 5.2 mo; HR = 0.72 [95% CI: 0.49-1.06]), 2.0 mo (7.0 vs 5.0 mo; HR = 0.76 [95% CI: 0.60-0.97]), and 2.2 mo (5.5 vs 3.3 mo; HR = 0.72 [95% CI: 0.36-1.45]) over placebo/cytarabine treatment, respectively. An improvement in OS was observed among patients ≥ 60 years who received post-treatment transplantation (n = 91; 19.9 mo with vosaroxin/cytarabine vs 12.2 mo with placebo/cytarbine; HR = 0.70 [95% CI: 0.43-1.13]) and those who did not (n = 360; 5.3 mo vs 3.8 mo, respectively; HR = 0.75 [95% CI: 0.60-0.92]). When analyzed by disease status, the greatest OS benefit was observed in patients ≥ 60 years with refractory disease (n = 210; 6.7 mo with vosaroxin/cytarabine vs 3.8 mo with placebo/cytarabine; HR = 0.75 [95% CI: 0.57-1.00]) and those with early relapse (n = 154; 6.5 mo vs 3.9 mo, respectively; HR = 0.62 [95% CI: 0.44-0.87]). In patients ≥ 60 years with late relapse (n = 87), median OS was similar in both treatment arms (9.2 mo with vosaroxin/cytarabine vs 9.8 mo with placebo/cytarabine; HR = 1.06 [95% CI: 0.68-1.66]).
Conclusions: After a median of 39.9 months of follow-up in the VALOR trial, the OS observed in patients ≥ 60 years of age treated with vosaroxin/cytarabine remains significantly improved versus placebo/cytarabine, with a separation of the survival curves through 48 months. The OS benefit is consistent among all older patients, even those ≥ 75 years of age, and is seen in patients with and without post-treatment transplantation. The updated survival data from VALOR continue to support the use of vosaroxin/cytarabine as a treatment option in patients ≥ 60 years of age with R/R AML.
Ravandi:BMS: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Ritchie:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria; Arian: Speakers Bureau. Vey:Sunesis: Honoraria. Strickland:Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Ambit: Consultancy; Baxalta: Consultancy; Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy, Research Funding; CTI Biopharma: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Sunesis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma: Research Funding; Celator: Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Research Funding; Karyopharm Therapeutica: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding. Schiller:Incyte Corporation: Research Funding. Jabbour:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy. Erba:Ariad: Consultancy; Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Research Funding; Celator: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Agios: Research Funding; Juno: Research Funding; Gylcomimetics: Other: DSMB; Astellas: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, DSMB, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Sunesis: Consultancy; Jannsen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Pigneux:Agios: Consultancy, Honoraria; Sunesis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Horst:Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, Gilead, Agios: Consultancy; Amgen, Regeneron: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria. Recher:Celgene, Sunesis, Amgen, Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene, Sunesis, Amgen, Novartis, Chugai: Research Funding. Cortes:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squib: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding. Roboz:Agios, Amgen, Amphivena, Astex, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celator, Celgene, Genoptix, Janssen, Juno, MEI Pharma, MedImmune, Novartis, Onconova, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Sunesis, Teva: Consultancy; Cellectis: Research Funding. Craig:Sunesis: Employment, Equity Ownership. Ward:Sunesis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Employment. Smith:Sunesis: Employment, Equity Ownership. Stuart:Agios: Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accomodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Celator: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal