Abstract
Background: Based on new genetic classifications, co-mutations in MYD88 and CD79B (C5 and MCD subgroups) are associated with an inferior survival after standard R-CHOP. MYD88 mutations (MYD88MT) constitutively activate both NF-kB and AP1 pathways, promoting B-cell proliferation and survival. Essential to the Myddosome-dependent signaling pathway is the recruitment of IRAK4 which complexes with MYD88 to activate lymphomagenesis. Targeting IRAK4 is therefore a rational therapeutic approach in MYD88MT lymphomas. IRAKIMiDs are novel degraders that simultaneously target IRAK4 as well as Ikaros and Aiolos, to inhibit both the NFkB and IRF4 pathways (Walker et al. ACCR 2020). We have previously demonstrated IRAKIMiDs are more potent than IRAK4 kinase inhibitors and IMiD compounds in MYD88 MT lymphomas (Lue et al. ASH 2020). MYD88 MT DLBCL is characterized by high basal NF-kB activity which is driven by several mechanisms. Increased BCL2 expression and activity has been associated with activation of NF-kB. Potential synergistic drug combinations in conjunction with KTX-582, an IRAKIMiD, were evaluated as a means to simultaneously inhibit several pathways contributing to NF-kB activation and downstream effects in MYD88MT DLBCL. Of those, venetoclax was found to be the most potent in combination. Herein, we describe the activity of KTX-582 in combination with venetoclax across ABC-DLBCLs.
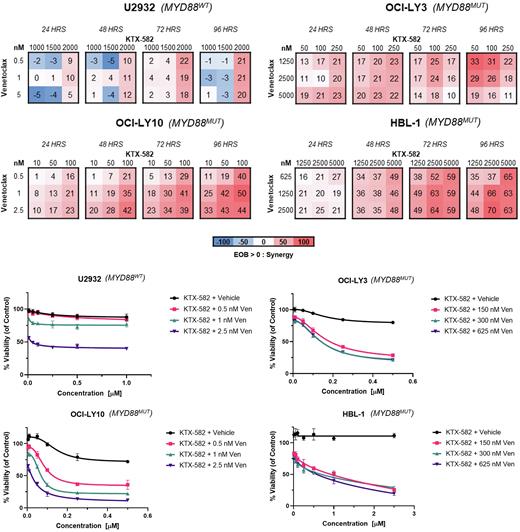
Methods: MYD88MT (n=3) and wild type (n=1) ABC-DLBCL cell lines were exposed to single agent KTX-582 and venetoclax in order to establish the drug concentration/cytotoxicity effect relationship. Cell viability was assessed using Celltiter-Glo assay at 24-hour intervals. IC50 values were computed. MYD88MT DLBCL cells were co-exposed to combinations of KTX-582 in combination with venetoclax at concentrations representing their respective IC10-40 in order to determine synergy using the excess over bliss (EOB) method. Immunoblotting analysis was performed to evaluate the degradation effect on IRAK4, Ikaros, Aiolos, BCL-2 family proteins, and NF-kB targets. Apoptosis was evaluated by western blot analysis and flow cytometry. RT-qPCR was performed to evaluate the transcription levels of NF-kB pathway members as well the transcriptional modulation of BCL-2 family genes in order to characterize bases of apoptosis.
Results: Exposure to KTX-582 led to potent activity across multiple MYD88MT DLBCL cell lines with IC50s in the low nanomolar range, and diminished activity in the MYD88WT DLBCL. Venetoclax showed diverse activity across the DLBCL cell lines regardless of the MYD88 status. Sensitivity to venetoclax was not impacted by BCL2 protein expression. As evaluated by EOB, synergy was observed after exposure to KTX-582 in conjunction with venetoclax (K+V) in MYD88MT DLBCL cell lines, with maximum values peaking at 72-96 hours. Synergy was also observed in MYD88WT ABC-DLBCL but to a lesser effect. After dual drug exposure, the activity of KTX-582 on IRAK4 degradation was not impaired with the addition of venetoclax. Increase apoptosis as evaluated by western blot and by flow cytometry was more pronounced in the K+V combination as compared to either single agent alone, including in the HBL-1 cell line, which showed relative resistance to both single agents. Evaluation of transcript abundance of the BCL2 proteins family is currently underway.
Conclusions: Preclinical studies highlight the potential of IRAKIMiDs as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of MYD88MT DLBCL. KTX-582 demonstrates preferential activity in MYD88MT ABC-DLBCL. Single agent venetoclax demonstrated varying potency in ABC-DLBCL cell lines, irrespective of MYD88 mutational status. At nanomolar concentrations, KTX-582 and venetoclax synergistically suppressed cell growth and increased apoptotic cell death in MYD88MT DLBCL. This data suggests that inhibiting multiple pathways of NF-kB activity is a viable and rational strategy for MYD88MT DLBCL. Evaluating the molecular mechanism underlying the activity of this novel combination is in progress, with the aim of identifying additional biomarkers that can predict for sensitivity to this combination, as well as translation and validation in mouse models. A single agent lead IRAKIMiD compound, KT-413, is currently being evaluated in a Phase 1 trial for the treatment of MYD88MT DLBCL, and our studies support a potential combination with venetoclax in the future.
Disclosures
Klaus:Kymera Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. McDonald:Kymera Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Gollob:Kymera Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Weiss:Kymera Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. O'Connor:TG Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Salles:Roche/Genentech, Janssen, Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Novartis, AbbVie, MorphoSys AG, Amgen, Bayer, Epizyme, Regeneron, Kite, a Gilead Company: Honoraria; AbbVie, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Debiopharm, Epizyme, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Incyte, Kite, a Gilead Company, Miltenyi, MorphoSys, Takeda, and VelosBio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche/Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Celgene, Novartis, MorphoSys AG, Epizyme, Alimera Sciences, Genmab, Debiopharm Group, Velosbio, Bristol-Myers Squibb, BeiGene, Incyte, Miltenyi Biotec, Ipsen, Kite, a Gilead Company, Loxo, Rapt: Consultancy. Lue:Epizyme: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal