Abstract
Background: MPN-AML, MPN-AP, and DIPSS-plus high risk PMF are associated with a poor response to therapy and shortened survival. Several studies have shown clinical activity of hypomethylating agents (DNA methyltransferase inhibitors) in these situations. We reviewed our database to evaluate the clinical outcome of patients (pts) with MPN-AML, MPN-AP and DIPSS-plus high risk PMF who received decitabine (DAC; a hypomethylating agent) in the course of their treatment at our institution.
Methods: Retrospective chart review identified 21 pts with MPN-AML, 13 with MPN-AP and 11 with DIPSS-plus high risk PMF treated with DAC in our center over last 7 years. MPN- AP was defined by 10%-19% blasts in the peripheral blood or bone marrow (BM). DIPSS-plus is a prognostic model for PMF and can be applied at any point during the disease course (Gagnat et al. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29:392-7). Responses in MPN-AML were defined according to published recommendations (Mascarenhas et al. Leuk Res 2012; 36:1500-4). Responses in MPN-AP and DIPSS-plus high risk PMF were defined according to the revised IWG-MRT and ELN consensus report (Tefferi et al. Blood 2013; 122: 1395-8).
Results: MPN-AML pts characteristics: median age 64 yrs (range, 45-82); initial MPN: ET 4 (19%), PV 5 (24%), PMF 10 (48%), and MPN unclassified 2 (10%) pts. The median number (no.) of prior therapies for MPN was 1 (range, 0-4). The median time for transformation from MPN to MPN-AML was 93 mo (range, 1.4-292). Thirteen (39%) pts had unfavorable cytogenetics. DAC was given as first-line therapy in 12 (57%) pts, as second-line therapy in 8 (38%), and as third-line in 1 (5%). The median no. of DAC cycles given was 2 (range, 1-15). MPN-AP pts characteristics: median age 63 yrs (range, 50-81); initial MPN: ET 2 pts (15%), PV 5 (39%), and PMF 6 (46%). The median no. of prior therapies for MPN was 2 (range, 0-5). The median time from diagnosis of MPN to DAC was 65 (0-389) mo. The median no. of DAC cycles given was 2 (range 1-37). PMF with DIPSS-plus high risk pts characteristics: median age 67 yrs (range, 55-77). Seven (64%) pts had a JAK2 mutation. The median hemoglobin (Hb) was 9.2 g/dl (range, 7.7-11.7), median WBC was 41.5 K/uL (range, 2-140), median platelet (plt) count was 69 K/uL (range, 9-860) and bone marrow blast percentage (BM BL %) was 2% (range, 0-9). The median number of DIPSS-plus risk factors was 6 (range, 4-8), and median no. of prior therapies was 1 (range, 0-4). The median time to DAC from diagnosis of PMF was 19 (3-195) mo. The median no. of DAC cycles given was 3 (range 1-8).
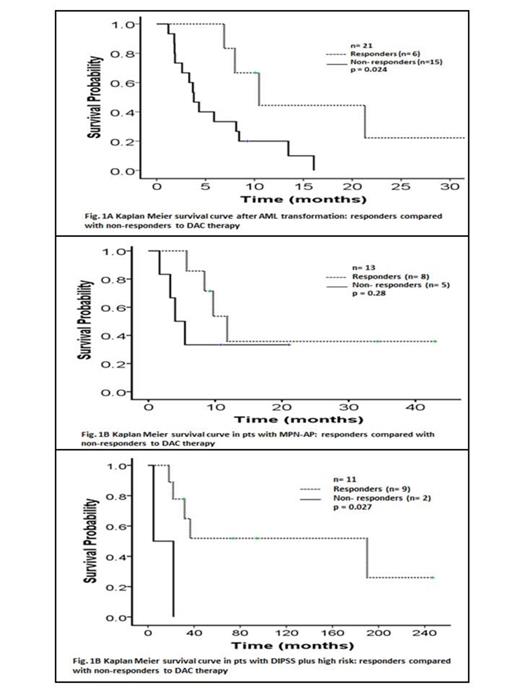
Six (29%) MPN-AML pts responded to DAC: 3 CR, 2 CRi and 1 PR. Two pts who achieved CR, received DAC as second line after falling induction chemotherapy for AML. The median time to response was 2.6 mo (range, 1-13.5). Among non-responders; 10(48%) pts died due to disease progression, 3 (14%) pts died due to sepsis, one is alive with stable disease (SD) on therapy, and one pt died 2 months after bone marrow transplant (BMT). The median response duration (defined as time to next therapy/death/last follow up) was 7 mo (range, 2-24). One patient responding to DAC had BMT after 2 months of maintaining the response. The median OS from the time of post MPN-AML acquisition was 6.9 mo. The OS was 10.5 mo in responders vs 4 mo in non-responders (p= 0.024) (Fig. 1A). Among MPN-AP, 1 pt had clinical improvement (CI) in Hb and plt, and 7 had SD (with improvements in blood count), for overall benefit in 8 (61%) pts. The median benefit duration was 6.5 mo. (1.8-14). Four (31%) pts with SD after improvement in leukocytosis and BM BL % had BMT. The median OS from the time of MPN-AP acquisition was 9.7 mo. The OS in responders was 11.8 mo. vs 4 mo. in non-responders (p=0.28) (Fig.1B). Among non-responders 3 (23%) pts transformed to AML, one pt received next line of therapy and had BMT, one pt died due to disease progression. Nine (82%) pts with DIPSS-plus high risk PMF benefited from DAC: 1 had CI in plt, 1 had CI in spleen, and 7 had SD (with improvements in blood count). Median response duration was 9 mo (1-23). Three (27%) pts had BMT after improvement in leukocytosis and BM BL %. Both pts who did not respond, progressed to AML and died due to infectious complication. The median OS was 36.6 mo: OS in responders was 190 mo vs 4.7 mo in non-responders (p=0.027) (Fig. 1C).
Conclusion: DAC is a viable therapeutic option for pts with MPN-AML, MP-AP and high-risk PMF. Prospective clinical studies combining DAC with other clinically active agents are needed to improve overall outcome.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.