Abstract
BACKGROUND
Despite the efficacy of 2nd generation TKIs (dasatinib and nilotinib) used as frontline therapy for CML-CP, some patients experience resistance or intolerance. The outcome of these patients has not been described.
METHODS
A retrospective review of CML-CP patients receiving frontline 2nd generation TKIs on clinical trials at our institution was conducted. Patients were assessed for causes of TKIs discontinuation, subsequent therapies, and outcome after discontinuation of initial therapy. Patients who lost follow up (11 pts for nilotinib and 8 pts for dasatinib) or died were excluded form subsequent analysis.
RESULTS
A total of 54 patients on nilotinib (of 149 treated, 36%) and 44 pts on dasatinib (of 93 treated, 47%) discontinued their initial TKI on a non-elective basis. The median age was 51 yrs (range, 16-86) and 49 yrs. (18 - 82), respectively. The median treatment duration was 34 mos (1-123) and 27 mos (1 - 102), respectively.
In the nilotinib group, reasons for discontinuation were: intolerance in 24 (44%), resistance in 12 (22%), death in 6 (11%), and other in 12 (22%). At discontinuation, among those in CP, 30 (51%) had complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) (20 MR4.5, 6 MMR and 4 no MR), 2 (4%) partial cytogenetic response (PCyR), 11 (20%) no cytogenetic response (CyR). Eleven (20%) pts had transformed to blast phase (BP; n=7) or accelerated phase (n=4).
Dasatinib discontinuation was due to intolerance in 22 (50%), resistance in 8 (18%), other in 12 (27%), and 2 (5%) died on study. At that time, 24 (54%) had CCyR (11 MR4.5, 4 MR4, 4 MMR and 5 no MR), 3 (7%) PCyR, 13 (30%) no CyR; all were in CP.
Mutations were investigated in 22 pts (11 resistant, 10 intolerant, 1 noncompliant) after nilotinib discontinuation and were identified in 6 pts (27%), including E255K (2), Y253H (2), F359I (1), and T315I (1) (all resistant). Of 9 pts assessed for mutations in the dasatinib cohort (6 resistant, 2 intolerant, 1 noncompliant) BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations was identified in 5 (56%), including T315I (2), V299L (1), L271A (1), and F317L (1) (all resistant).
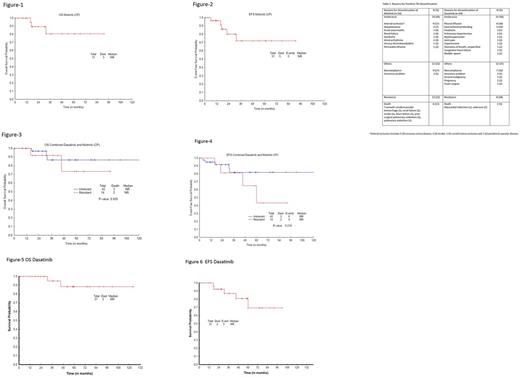
After nilotinib discontinuation, 27 (68%) received other TKI (11 dasatinib, 8 imatinib, 4 nilotinib off protocol, 2 bosutinib, 1 ponatinib, 1 rebastinib), 7 (18%) observation (5 eventually started TKI), 4 (10%) HyperCVAD + TKI, 1 (2%) SCT, and 1 (2%) decitabine + dasatinib. After dasatinib, 27 (87%) received other TKI (12 nilotinib, 8 imatinib, 3 ponatinib, 2 dasatinib off protocol, 1 bosutinib, 1 rebastinib), 3 (10%) observation (1 eventually started dasatinib off protocol after pregnancy), and 1 (3%) SCT. The median duration of post nilotinib therapy was 28 mos (1 - 91) and post dasatinib 42 mos (1 - 124). With a median follow-up of 28 mos (1 - 91) after nilotinib discontinuation, 15 pts (CP) maintained CCyR; 9 of 13 pts in CP not in CCyR at discontinuation achieved CCyR. In addition, 2 pts in AP and 3 in BP at discontinuation achieved CCyR. Thus overall 31 (78%) achieved or maintained CCyR (20 MR4.5, 4 MMR) 1 (2%) PCyR, and 8 (20%) no CyR. Among CP pts 12 maintained MR4.5, 3 achieved MR4.5, 1 achieved MR4, 2 pts achieved MMR and 2 pts maintained MMR. Three of the 6 BP pts and 2 of 3 in AP achieved MR4.5. One AP pt transformed to BP and died. Among pts intolerant to nilotinib, 15 pts maintained CCyR and 4 achieved CCyR. Of those considered resistant to nilotinib, 9 pts achieved CCyR and 1 maintained CCyR (had lost MMR prior to switch). With a median follow-up of 42 mos (1 - 124) after dasatinib discontinuation, 18 of pts with CCyR at discontinuation maintained CCyR and 12 additional pts achieved CCyR with a total of 30 (97%) achieving or maintain CCyR (20 MR4.5, 4 MR4, 5 MMR) and 1 (3%) PCyR. Of pts discontinuing dasatinib for intolerance, 16 maintained and 6 achieved CCyR. Among those discontinuing dasatinib for resistance, 4 pts achieved CCyR and 1 maintained CCyR. The median OS and EFS, post frontline dasatinib discontinuation were not reached (3-year OS and EFS 95% and 87%, respectively). After nilotinib discontinuation, median OS was not reached and median EFS was not reached (3-year, OS and EFS were 81 % and 72 %, respectively). Among patients who received a second TKI after discontinuation, 22 of those initially treated with nilotinib and 18 of those initially treated with dasatinib remain on therapy with their second TKI.
CONCLUSION
The most common reason for discontinuation of frontline 2nd generation TKIs in CML-CP is intolerance. In this setting, outcomes are still favorable with adequate EFS and OS.
Kantarjian: ARIAD: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding. Verstovsek: Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Galena BioPharma: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Galena BioPharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Lilly Oncology: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Lilly Oncology: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding. Daver: Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy; Kiromic: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy; Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.: Consultancy; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Consultancy, Research Funding. Pemmaraju: Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria; Cellectis: Research Funding; Stemline: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; LFB: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Thompson: Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. DiNardo: Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Honoraria, Research Funding. Jabbour: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Cortes: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sun Pharma: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.