Key Points
MOZ-TIF2 AML cells harboring deletion of Ring1A/B lose self-renewal capacity.
Gli-similar 2 promotes differentiation of MOZ-TIF2 AML cells and is derepressed in Ring1A/B-knockout cells.
Abstract
Eradication of chemotherapy-resistant leukemia stem cells is expected to improve treatment outcomes in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). In a mouse model of AML expressing the MOZ-TIF2 fusion, we found that Ring1A and Ring1B, components of Polycomb repressive complex 1, play crucial roles in maintaining AML stem cells. Deletion of Ring1A and Ring1B (Ring1A/B) from MOZ-TIF2 AML cells diminished self-renewal capacity and induced the expression of numerous genes, including Glis2. Overexpression of Glis2 caused MOZ-TIF2 AML cells to differentiate into mature cells, whereas Glis2 knockdown in Ring1A/B-deficient MOZ-TIF2 cells inhibited differentiation. Thus, Ring1A/B regulate and maintain AML stem cells in part by repressing Glis2 expression, which promotes their differentiation. These findings provide new insights into the mechanism of AML stem cell homeostasis and reveal novel targets for cancer stem cell therapy.
Introduction
The maintenance of cancer depends on a small population of self-renewing cells, called cancer stem cells or cancer-initiating cells, which generate a large population of more highly differentiated cells that lack self-renewal capacity.1 The existence of cancer stem cells was revealed by studies of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).2,3 In leukemia, stem cells survive cytotoxic chemotherapy and radiotherapy, often causing relapse.4,5 Accordingly, therapy targeting leukemia stem cells is expected to improve outcomes in patients with AML. A novel recurrent translocation involving CBFA2T3 and GLIS2 was identified in approximately 30% of children with non-Down syndrome acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) and other cytogenetically normal patients with AML.6-8 Because the CBFA2T3–GLIS2 fusion transcript is associated with poor prognosis in pediatric patients with AML,6-8 we hypothesized that Gli-similar 2 (GLIS2) is involved in the regulation of leukemia stem cells.
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins function as transcriptional repressors to regulate expression of genes that determine cell identity.9,10 These proteins form complexes called Polycomb repressive complexes 1 and 2 (PRC1 and PRC2). Histone H3K27 trimethylation is mediated by PRC2, whereas histone H2AK119 monoubiquitylation is mediated by Ring1A and its paralog Ring1B, which are both components of PRC1.11 The PRC1 component Bmi-1 plays a crucial role in the maintenance of normal and leukemic hematopoietic stem cells.12,13 Because Bmi-1 stimulates the ubiquitylation activity of Ring1A and Ring1B (Ring1A/B),14-16 these proteins may play important roles in the regulation of stem cell homeostasis.
Ring1A-deficient mice are fertile and exhibit no overt phenotype.17 By contrast, Ring1B-deficient mouse embryos do not survive, and studies of hematopoiesis suggest that Ring1B is required to restrict the proliferation of immature progenitors and promote the proliferation of maturing committed precursors.18,19 Recent work showed that Ring1A/B is essential for leukemogenesis.20,21 However, the mechanistic role of Ring1A/B in regulation of leukemia stem cells is not fully elucidated.
Retroviral transduction of myeloid progenitors with MOZ-TIF2 confers self-renewal ability and induces AML following transplantation of the transduced cells into irradiated mice.22 In previous work, we identified the AML stem cell population in MOZ-TIF2–transduced AML cells.23 Consistent with previous reports, we showed that the E3 ubiquitin ligase activities of Ring1A/B are reciprocally compensatory15,24 and that deletion of Ring1A or Ring1B does not affect the leukemic potential of MOZ-TIF2– or MLL-AF10–transduced AML cells. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the effect of double deletion of Ring1A/B in MOZ-TIF2 AML stem cells from mice. We investigated the role of GLIS2 in this model of AML to gain insight into the mechanisms underlying regulation of AML stem cells.
Materials and methods
Mice
Ring1A-deficient mice, Ring1B conditionally deficient mice,17,18 Glis2 conditionally deficient mice (European Mouse Mutant Cell Repository, Clone ID:HEPD0539_2B10), Cdkn2a-deficient mice,25 and CreERT2 mice (TaconicArtemis GmbH)26 were maintained on a C57BL/6 genetic background. C57BL/6 mice were purchased from CREA Japan (Tokyo). Mouse experiments were performed in a specific pathogen-free environment at the National Cancer Center animal facility according to institutional guidelines and with the approval of the National Cancer Center Animal Ethics Committee.
Mouse model of AML
We harvested c-Kit+ bone marrow (BM) cells from 8- to 10-week-old Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 mice and transduced them with MSCV-MOZ-TIF2-IRES-GFP or MSCV-MLL-AF10-IRES-GFP expression vectors using a previously described retrovirus system.23 Infected cells were injected into sublethally irradiated (6 Gy) wild-type C57BL/6 recipient mice. These mice developed AML within 2 to 3 months. For secondary transplantation, sublethally irradiated wild-type C57BL/6 mice were injected with 3 × 105 BM cells from primary AML mice. Two weeks after transplantation, secondary recipients were intraperitoneally administered tamoxifen (Sigma-Aldrich) or corn oil (Wako) 3 times per week and monitored for signs of leukemia (facial edema, lymphadenopathy, moribund status, or elevated count of GFP+ cells in peripheral blood).
Cell culture
GFP+ cells sorted from BM cells transduced with MSCV-MOZ-TIF2-ires-GFP were incubated in methylcellulose media (Stem Cell Technologies) supplemented with 10 ng/mL stem cell factor, 10 ng/mL interleukin-3, and 10 ng/mL granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (Peprotech), with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) (Sigma-Aldrich) or ethanol (Wako; vehicle control) at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2. For Glis2 overexpression assays, GFP+ BM cells were transduced with pGCDNsam-IRES/NGFR-Glis2, which was generated by inserting a complementary DNA (cDNA) encoding Glis2 into pGCDNsam-IRES/NGFR (a gift from Masafumi Onodera, National Center for Child Health and Development). Infected cells were cultured in methylcellulose media M3234 supplemented with the cytokines listed previously, and then stained with anti-NGFR (CD271) antigen-presenting cell (APC) (ME20.4, BioLegend). NGFR+ cells were magnetically labeled with anti-APC Microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec) and isolated by magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS). After replating, the cells were collected and analyzed.
Cell morphology
Cells that formed colonies were collected and stained with May-Grünwald dye, and subsequently with Giemsa (Merck Chemicals).
Antibodies and flow cytometric analysis
BM mononuclear cells (MNCs) from mice with AML were treated with immunoglobulin G from rat serum (Sigma-Aldrich) to prevent reactivity with Fc receptors, and then incubated with anti-macrophage colony stimulating factor receptor (MCSFR) (CD115)-phycoerythrin (PE) (AFS98, eBioscience), anti-Mac-1 (CD11b)-PE-Cy7 (M1/70, eBioscience), anti-Gr-1-Bio (RB6-8C5, BioLegend), and anti-c-Kit (CD117)-APC (2B8, eBioscience) antibodies. Biotinylated antibodies were detected with streptavidin-AF780 (eBioscience). For Lin−, Sca1−, c-Kit+, CD34+, and CD16/32+ (L-GMP) cells, BM cells were stained with anti-Sca1-Bio (D7, BioLegend), anti-B220-Bio (RA3-6B2, eBioscience), anti-TER-119-Bio (eBioscience), anti-CD3ε-Bio (145-2C11, BioLegend), anti-interleukin-7Rα (CD127)-Bio (A7R34, BioLegend), anti-Gr-1-Bio, anti-CD16/32-PE-Cy7 (93, eBioscience), anti-CD34-A647 (HM34, BioLegend), and anti-c-Kit-AF780 (2B8, eBioscience) antibodies, followed by streptavidin-PE. For analysis of cell differentiation by Glis2 overexpression, MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells were stained with anti-F4/80-PE (BM8, eBioscience) or anti-CD14-APC (Sa2-8, eBioscience) antibodies. Flow cytometric analyses and cell sorting were performed using a Japan-made sorter, analyzer cell sorter (Bay Bioscience).
Other materials and methods are provided in the supplemental Data, available on the Blood Web site.
Results
Ring1A/B are crucial for immortalization of MOZ-TIF2–induced AML cells
To elucidate the role of Ring1A/B in determining the malignant phenotype of AML cells, we performed colony formation assays using BM cells derived from Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f mice. Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/+ mice and WT mice were used as controls. To induce AML, c-kit+ progenitors isolated from BM cells were transduced with the retroviral MSCV-MOZ-TIF2-IRES-GFP expression vector. Four days later, GFP+ cells were sorted and cultured in methylcellulose-based medium. After the cells were replated twice, Ring1B was conditionally deleted by treating the cells with 4-OHT (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 1A). Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/+ cells formed large, compact colonies similar to those observed in cultures of wild-type cells, whereas Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ cells formed loose colonies composed of loosely dispersed cells and ultimately lost their self-renewal capacity (Figure 1B-C; supplemental Figure 1B-C). May-Giemsa staining of cells derived from these colonies indicated that deletion of Ring1A/B induced differentiation of MOZ-TIF2–transduced progenitors, primarily into macrophages (Figure 1C; supplemental Figure 1C). At the same time, staining with Annexin V revealed that apoptosis was induced in the cells derived from Ring1A/B-deleted loose colonies (Figure 1D). Flow cytometric analysis using Annexin V and 7-AAD also showed that deletion of Ring1A/B induced apoptotic cell death (supplemental Figure 1D). Similarly, BM-derived progenitors transduced with other fusion genes that cause AML, such as AML1-ETO, PML-RARα, and MLL-AF10, failed to form and maintain colonies (supplemental Figure 1E). These results suggest that deletion of Ring1A/B induces differentiation of leukemic progenitors in vitro.
Ring1A/B are crucial for immortalization of MOZ-TIF2–induced AML cells. (A) PCR analysis of genomic Ring1B sequences in Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 BM cells treated with 4-OHT or ethanol (vehicle control). CreERT2 BM cells are shown as controls. (B) Experimental scheme for colony formation assay (left) and bar chart of the serial replating experiments (right). The graph shows colony number per 10 000 plated cells in each round of plating in methylcellulose media in the presence or absence of 4-OHT. CreERT2 BM cells served as controls. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). (C) Representative morphology and May-Grünwald Giemsa staining of MOZ-TIF2 colonies cultured with 4-OHT or ethanol for 7 days. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Apoptosis analysis by Annexin V staining. After incubation with 4-OHT or vehicle for 72 hours, MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells were stained with Annexin V Alexa Fluor 594 and attached to glass slides by cytospin. (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis of tamoxifen or corn oil–treated mice that received a secondary transplant of MOZ-TIF2−transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 BM cells. Two weeks after transplantation, secondary recipients were intraperitoneally administered tamoxifen or corn oil 3 times per week. KO, knockout
Ring1A/B are crucial for immortalization of MOZ-TIF2–induced AML cells. (A) PCR analysis of genomic Ring1B sequences in Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 BM cells treated with 4-OHT or ethanol (vehicle control). CreERT2 BM cells are shown as controls. (B) Experimental scheme for colony formation assay (left) and bar chart of the serial replating experiments (right). The graph shows colony number per 10 000 plated cells in each round of plating in methylcellulose media in the presence or absence of 4-OHT. CreERT2 BM cells served as controls. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). (C) Representative morphology and May-Grünwald Giemsa staining of MOZ-TIF2 colonies cultured with 4-OHT or ethanol for 7 days. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Apoptosis analysis by Annexin V staining. After incubation with 4-OHT or vehicle for 72 hours, MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells were stained with Annexin V Alexa Fluor 594 and attached to glass slides by cytospin. (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis of tamoxifen or corn oil–treated mice that received a secondary transplant of MOZ-TIF2−transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 BM cells. Two weeks after transplantation, secondary recipients were intraperitoneally administered tamoxifen or corn oil 3 times per week. KO, knockout
Sublethally irradiated mice transplanted with Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 BM-derived c-kit+ progenitor cells transduced with the MOZ-TIF2 expression vector developed AML within 2 to 3 months. BM cells were harvested from the recipients and injected into another set of mice. These secondary recipients were treated with tamoxifen to delete Ring1B from the transplanted cells. All control mice treated with vehicle developed AML within 2 months, whereas none of the mice treated with tamoxifen to delete Ring1B developed leukemia (Figure 1E). On the other hand, secondary recipients that received MOZ-TIF2−transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/+;CreERT2 BM cells developed leukemia even after tamoxifen treatment (supplemental Figure 1F).
We also used Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 BM-derived c-kit+ progenitor cells transduced with the MLL-AF10 expression vector in transplantation assays. As in the experiment using the MOZ-TIF2 fusion gene, Ring1A/B-deleted cells transduced with MLL-AF10 did not initiate AML in recipient mice (supplemental Figure 1G). These results suggest that deletion of Ring1A/B leads to ablation of leukemic cells in vivo, consistent with the idea that Ring1A/B play a crucial role in the development of AML.
Ring1A/B are required for the maintenance of AML stem cells
The L-GMP population is enriched for AML stem cells in the MLL-AF9 model.27 To determine whether the L-GMP population contained AML stem cells in the MOZ-TIF2 model, we sorted L-GMP cells from BM of MOZ-TIF2 AML mice and transplanted limited numbers (10 to 1 × 104 cells) into irradiated mice. All mice that received 1 × 102 or more L-GMP cells rapidly developed leukemia (supplemental Figure 2A). Conversely, none of the mice that received 1 × 102 whole BM cells succumbed to AML (supplemental Figure 2B). These results confirm that the L-GMP population is enriched approximately 10-fold for AML stem cells in MOZ-TIF2 AML mice.
To investigate the effect of Ring1A/B deficiency on AML stem cells, we analyzed the frequency of the L-GMP population of BM following conditional deletion of Ring1B. After the proportion of GFP+ cells in MNCs in peripheral blood of MOZ-TIF2 AML mice reached 50%, we administered tamoxifen or corn oil (vehicle) for 5 consecutive days, and then harvested BM cells on the day after the last tamoxifen treatment. The frequency of L-GMP cells in the GFP+ population of BM decreased following deletion of Ring1B (Figure 2A), whereas the frequency of Gr1+ leukemic cells increased (Figure 2B). Heterozygous knockout of Ring1B was insufficient to decrease the frequency of L-GMP cells (supplemental Figure 2C). These results suggest that AML stem cells were eliminated by double deletion of Ring1A/B.
Ring1A/B are required for maintenance of AML stem cells. Secondary recipients of MOZ-TIF2 AML mice that received a secondary transplant of MOZ-TIF2−transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 BM cells were treated with tamoxifen or corn oil (vehicle) for 5 consecutive days when the proportion of GFP+ MNCs in peripheral blood reached 50%. On the day following the last treatment, BM-MNCs were harvested and analyzed for quantification of L-GMP (A), Gr1+ (B), and Mac1− MCSFR+ (C) cells by flow cytometry (mean ± SD, *P < .01, n = 4), or transplanted into sublethally irradiated recipient mice. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve. Tamo, tamoxifen.
Ring1A/B are required for maintenance of AML stem cells. Secondary recipients of MOZ-TIF2 AML mice that received a secondary transplant of MOZ-TIF2−transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 BM cells were treated with tamoxifen or corn oil (vehicle) for 5 consecutive days when the proportion of GFP+ MNCs in peripheral blood reached 50%. On the day following the last treatment, BM-MNCs were harvested and analyzed for quantification of L-GMP (A), Gr1+ (B), and Mac1− MCSFR+ (C) cells by flow cytometry (mean ± SD, *P < .01, n = 4), or transplanted into sublethally irradiated recipient mice. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve. Tamo, tamoxifen.
We previously demonstrated that MOZ-TIF2–induced AML cells expressing high levels of MCSFR have high leukemogenic potential, suggesting that MCSFR expression is a marker of the AML stem cell phenotype.23 Flow cytometric analysis of BM cells from MOZ-TIF2 AML mice revealed that the L-GMP and Mac1− MCSFR+ populations partially overlapped (supplemental Figure 2D). To further assess the role of Ring1A/B in the regulation of AML stem cells, we determined the expression level of MCSFR in Ring1A/B-deleted leukemic cells. MCSFR+ Mac1− cells were ablated upon deletion of Ring1B from MOZ-TIF2–induced leukemic cells but maintained upon heterozygous knockout of Ring1B (Figure 2C; supplemental Figure 2E). These results suggest that Ring1A/B are required for the maintenance of AML stem cells.
Using the transplantation assay, we next investigated the leukemogenic potential of BM cells harvested from recipient mice treated with either vehicle or tamoxifen. To this end, we transplanted vehicle-treated Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f or tamoxifen-treated Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/ΔMOZ-TIF2–induced leukemic cells into sublethally irradiated mice. All recipient mice transplanted with Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/fMOZ-TIF2–induced leukemic cells developed AML, whereas none of the mice transplanted with Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ cells developed leukemia (Figure 2D). Together, these data suggest that Ring1A/B are crucial for the maintenance of AML stem cells.
Inactivation of Ink4a/Arf partially restores self-renewal potential and prevents differentiation of Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/ΔMOZ-TIF2 AML cells
The Ink4a/Arf locus, 1 of the major substrates of PRC1, encodes the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16Ink4a and the tumor suppressor p19Arf, which mediate cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis.28 Self-renewal capacity, which is lost in Bmi1−/− hematopoietic stem cells, is restored by deletion of Ink4a and Arf.25 Because Ring1B is the catalytic subunit of PRC1, we hypothesized that deletion of Ink4a/Arf would restore the self-renewal activity of AML stem cells in Ring1A/B-deleted mice. First, we determined the expression level of p16Ink4a messenger RNA (mRNA) in vehicle-treated Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f and 4-OHT-treated Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/ΔMOZ-TIF2−induced leukemic cells. As expected, deletion of Ring1B along with Ring1A induced derepression of p16Ink4a in MOZ-TIF2–induced leukemic cells (supplemental Figure 3A). Derepression of p16Ink4a in the cells derived from Ring1A/B-deleted loose colonies was also observed by immunofluorescence staining (supplemental Figure 3B).
To determine the effect of Ink4a/Arf on the phenotype of Ring1A−/−Ring1BΔ/ΔMOZ-TIF2–induced leukemic cells, we harvested fetal liver cells from E12.5 Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ink4a/Arf−/− embryos, and transduced them with the MOZ-TIF2 expression vector. Transductants were cultured and evaluated for colony formation in the presence of 4-OHT or vehicle. Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf+/+ cells lost their colony-forming capacity, whereas Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf−/− cells maintained it, suggesting that derepression of Ink4a/Arf impairs the self-renewal activity of leukemic cells (supplemental Figure 3C). May-Giemsa staining revealed that cultured Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf+/+ cells, but not Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf−/− cells, differentiated into mature myeloid cells (supplemental Figure 3D). These results suggest that inactivation of Ink4a/Arf by Ring1A/B contributes to self-renewal potential and prevents differentiation of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells in vitro.
Next, we investigated the stem cell properties of Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Ink4a/Arf−/− and Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf−/− cells by transplanting the GFP+MOZ-TIF2–transfected cells into mice. Although Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf−/− cells restored colony formation in vitro, these cells were incapable of initiating leukemia in mice (supplemental Figure 3E), indicating that deletion of Ink4a/Arf did not restore the stem cell function of Ring1A/B-deleted MOZ-TIF2–expressing leukemic cells. Taken together, these findings indicate that inactivation of Ink4a/Arf did not fully rescue the phenotypes associated with Ring1A/B deficiency, suggesting that other targets of Ring1A/B are involved in regulation of AML stem cells.
Deletion of Ring1A/B induces derepression of Glis2 expression in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells
To identify the novel target genes implicated in the regulation of AML stem cells by PRC1, we performed gene expression profiling in Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f and Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ MOZ-TIF2 cells. We also compared the gene expression profiles of Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Ink4a/Arf+/+, Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf+/+, Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Ink4a/Arf−/−, and Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf−/− fetal liver cells. Consistent with the transcriptional repressor activity of Ring1A/B, most genes exhibiting a more than twofold change in expression levels were upregulated in Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ cells relative to Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f cells (Figure 3A). These changes were not altered by deletion of Ink4a/Arf, and gene expression patterns of Ink4a/Arf wild-type and knockout cells were similar when Ring1B was deleted.
Derepression of Glis2 expression in Ring1A/B-deleted MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells. (A) Hierarchical clustering analysis of gene expression in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells from Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/fBM, Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/ΔBM, Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/fInk4a/Arf+/+ FL, Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf+/+ FL, Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Ink4a/Arf−/− FL, and Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf−/− FL. 1, 2, 4, and 5 refer to results obtained from cells cultured for 48 hours in the presence or absence of 4-OHT; 3 refers to results obtained from cells cultured for 7 days. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Glis2 expression. RNA was extracted from cells incubated with 4-OHT for 48 hours (mean ± SD, *P < .05, n = 3). (C) Western blot analysis of Ring1B, Glis2, and MOZ-TIF2 expression. Cell lysates were obtained after incubation with 4-OHT for 48 hours. (D) Immunofluorescence staining for Glis2 in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells incubated with 4-OHT for 96 hours. Cells were picked from vehicle-treated compact colonies or 4-OHT–treated loose colonies and attached to glass slides by cytospin. Scale bar, 50 μm. FL, fetal liver.
Derepression of Glis2 expression in Ring1A/B-deleted MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells. (A) Hierarchical clustering analysis of gene expression in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells from Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/fBM, Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/ΔBM, Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/fInk4a/Arf+/+ FL, Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf+/+ FL, Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Ink4a/Arf−/− FL, and Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Ink4a/Arf−/− FL. 1, 2, 4, and 5 refer to results obtained from cells cultured for 48 hours in the presence or absence of 4-OHT; 3 refers to results obtained from cells cultured for 7 days. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Glis2 expression. RNA was extracted from cells incubated with 4-OHT for 48 hours (mean ± SD, *P < .05, n = 3). (C) Western blot analysis of Ring1B, Glis2, and MOZ-TIF2 expression. Cell lysates were obtained after incubation with 4-OHT for 48 hours. (D) Immunofluorescence staining for Glis2 in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells incubated with 4-OHT for 96 hours. Cells were picked from vehicle-treated compact colonies or 4-OHT–treated loose colonies and attached to glass slides by cytospin. Scale bar, 50 μm. FL, fetal liver.
Among the subset of genes exhibiting a more than fivefold upregulation in Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ cells relative to Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f cells (Table 1), we focused on Glis2, which encodes a transcription factor associated with neural differentiation and regulation of kidney morphogenesis. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), western blot analyses, and immunofluorescence staining confirmed that Glis2 mRNA and protein expression was derepressed by deletion of Ring1A/B in MOZ-TIF2–induced leukemic cells (Figures 3B-D). Derepression of Glis2 expression by deletion of Ring1A/B was confirmed in AML1-ETO–, PML-RARα–, and MLL-AF10–induced leukemic cells (supplemental Figure 4A).
To determine whether Ring1B is directly involved in silencing of Glis2 in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. MOZ-TIF2–transduced cells were cultured in the presence of either 100 nM 4-OHT or vehicle for 2 days. This condition was sufficient to completely abolish Ring1B expression and global histone H2AK119 monoubiquitylation (H2AUb1) mediated by Ring1A/B (Figures 3C and 4A). Ring1B bound the Glis2 promoter, but no binding was observed when Ring1B was deleted (Figure 4B-C).
Ring1B binds to the Glis2 promoter region and is associated with histone modification of Glis2. (A) Western blotting showing levels of total H2AUb1 in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells cultured for 48 hours in the presence or absence of 4-OHT. (B) Diagram illustrating the Glis2 locus. Each of the regions amplified by the indicated primer sets are indicated by black rectangles. (C-F) Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses of the Glis2 locus in Ring1A- or Ring1A/B-knockout MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells using anti-Ring1B, anti-H2AUb1, anti-H3K4 me3, and anti-H3K27 me3 antibodies. The Myf5 and Ink4a/Arf promoter regions were used as controls. Error bars represent SD (n = 3).
Ring1B binds to the Glis2 promoter region and is associated with histone modification of Glis2. (A) Western blotting showing levels of total H2AUb1 in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells cultured for 48 hours in the presence or absence of 4-OHT. (B) Diagram illustrating the Glis2 locus. Each of the regions amplified by the indicated primer sets are indicated by black rectangles. (C-F) Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses of the Glis2 locus in Ring1A- or Ring1A/B-knockout MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells using anti-Ring1B, anti-H2AUb1, anti-H3K4 me3, and anti-H3K27 me3 antibodies. The Myf5 and Ink4a/Arf promoter regions were used as controls. Error bars represent SD (n = 3).
Methylation of H3K4 (H3K4 me3) or H3K27 (H3K27 me3) acts as an active or a repressive mark, respectively, in chromatin regions that contain functionally opposed histone marks. Such regions, termed bivalent domains, are considered as specialized chromatin structures associated with maintenance of silenced genes in a transcription-ready state.29 Ring1A/B-mediated H2AUb1 is required to maintain stalling of RNA pol II at promoters within bivalent domains of embryonic stem (ES) cells.30 H3K27 me3, which is dependent on PRC2, stabilizes the association of PRC1.31 Many of these bivalent structures are resolved during differentiation of ES cells so that active and silent genes either maintain their H3K4 me3 and H3K27 me3 marks, respectively, or lose both marks.32 The Glis2 promoter contained H3K4 me3 and H3K27 me3, as well as H2AUb1 (Figure 4D-F). When Ring1A/B were deleted, H2AUb1 and H3K27 me3 were lost, whereas H3K4 me3 remained unchanged (Figure 4D-F). These data suggest that Ring1A/B are involved in histone modification of Glis2, and that deletion of Ring1A/B caused the sequential loss of H2AUb1 at the Glis2 promoter and derepression of Glis2 transcription.
Glis2 induces differentiation of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells
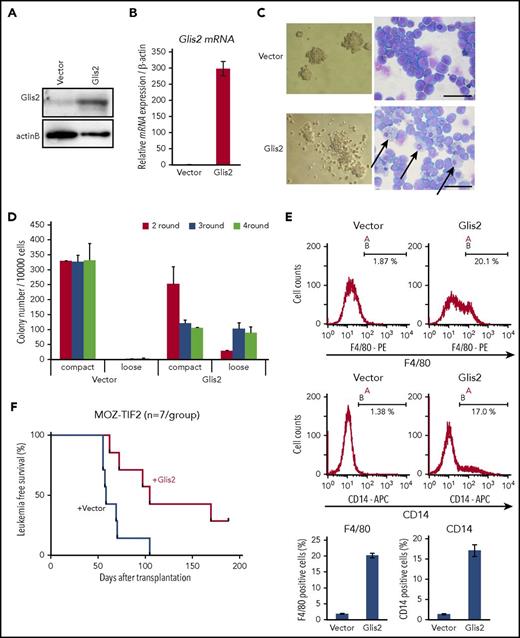
To determine whether derepression of Glis2 caused the loss of stem cell potential of Ring1A/B-deleted MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells, we first investigated the effect of Glis2 expression in MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells. For this purpose, MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells derived from wild-type mouse BM were transduced with Glis2 and subjected to colony-forming assays. In comparison with controls, enforced expression of Glis2 induced differentiation of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells into mature myeloid cells such as macrophages and increased the proportion of loose colonies mainly composed of differentiated cells (Figure 5A-D; supplemental Figure 5A). Flow cytometry analysis showed that enforced expression of Glis2 increased the numbers of F4/80+ and CD14+ cells, indicating that Glis2 stimulated differentiation of AML progenitors into macrophage (Figure 5E); however, the number of colonies did not decrease after the third plating. These data suggest that by promoting differentiation, Glis2 overexpression does not fully abrogate the self-renewal capacity of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells. The differentiation of leukemic cells into macrophage-like myeloid cells, as well as the reduced number of colonies in the second round following Glis2 overexpression, was also observed in MLL-AF10 and AML1-ETO–induced leukemic cells (supplemental Figure 5B-E).
Overexpression of Glis2 induces cell differentiation and suppresses leukemic transformation of cells expressing MOZ-TIF2. (A) Western blot analysis of MOZ-TIF2–expressing leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector. MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells were transfected with GCDNsam-IRES/NGFR-Glis2 or empty vector and then stained with anti-NGFR-APC. NGFR+ cells were magnetically labeled with anti-APC Microbeads and isolated by MACS. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Glis2 expression. Error bars represent SD (n = 4). (C) Representative colony morphology and May-Grünwald Giemsa staining of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Serial replating experiments of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (E) Flow cytometry analysis of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector after staining for F4/80 or CD14. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis of mice that received MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector.
Overexpression of Glis2 induces cell differentiation and suppresses leukemic transformation of cells expressing MOZ-TIF2. (A) Western blot analysis of MOZ-TIF2–expressing leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector. MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells were transfected with GCDNsam-IRES/NGFR-Glis2 or empty vector and then stained with anti-NGFR-APC. NGFR+ cells were magnetically labeled with anti-APC Microbeads and isolated by MACS. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Glis2 expression. Error bars represent SD (n = 4). (C) Representative colony morphology and May-Grünwald Giemsa staining of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Serial replating experiments of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (E) Flow cytometry analysis of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector after staining for F4/80 or CD14. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis of mice that received MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells transduced with Glis2 or empty vector.
We next examined the effect of Glis2 overexpression on development of AML in vivo. For this purpose, we transplanted BM-derived c-kit+ progenitor cells transduced with MOZ-TIF2 into sublethally irradiated mice. Leukemic cells derived from primary recipient mice were transduced with Glis2 expression vector or control vector, and vector-positive cells were isolated by MACS and injected into another set of mice. Overexpression of Glis2 delayed the development of AML in mice relative to controls, suggesting that Glis2 may impair the ability of leukemia stem cells to initiate AML by inducing them to differentiate (Figure 5F).
Glis2 is an important target of Ring1A/B involved in regulation of AML stem cells
To determine the significance of repression of Glis2 by Ring1A/B in leukemic cells, we transduced BM cells harvested from Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f triple-knockout mice with MOZ-TIF2 and subjected them to colony formation assays. Deletion of Glis2 by treatment with 4-OHT was confirmed by genotyping and quantitative real-time PCR (Figure 6A-B). Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ cells were incapable of maintaining colony formation and ultimately lost their self-renewal capacity, whereas Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Glis2Δ/Δ maintained the formation of loose colonies (Figure 6C). We harvested cells from the colonies at the sixth round and confirmed that the deletions of Ring1B and Glis2 were maintained even after replating (supplemental Figure 6A-B). May-Giemsa staining of Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ cells and Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Glis2Δ/Δ cells from colonies cultured with 4-OHT or vehicle for 5 days revealed that deletion of Glis2 interfered with differentiation of leukemic progenitors induced by deletion of Ring1A/B (Figure 6D). These results suggest that derepression of Glis2 expression is crucial for the differentiation of leukemic progenitors into mature myeloid cells induced by Ring1A/B deficiency in vitro.
Deletion of Glis2 interferes with differentiation of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells induced by deletion of Ring1A/B. (A) PCR analysis of genomic Ring1B and Glis2 sequences in MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells in the presence of either 4-OHT or ethanol. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Glis2 expression in Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells transduced with MOZ-TIF2. RNA was extracted from cells incubated with 4-OHT for 48 hours. Error bars represent SD (n = 4). (C) Serial replating experiments of MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells in the presence of either 4-OHT or ethanol. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (D) Representative colony morphology and May-Grünwald Giemsa staining of cells from first-round colonies formed by MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells in the presence of either 4-OHT or ethanol. Scale bar, 50 μm. (E,F) Secondary recipients of AML mice transplanted with MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells were treated with tamoxifen or corn oil (vehicle) for 5 consecutive days when the proportion of GFP+ MNCs in peripheral blood reached 50%. On the day following the last treatment, BM-MNCs were harvested and subjected to (E) flow cytometric analyses and (F) quantitation of L-GMP cells (mean ± SD, *P < .01, n = 6).
Deletion of Glis2 interferes with differentiation of MOZ-TIF2 leukemic cells induced by deletion of Ring1A/B. (A) PCR analysis of genomic Ring1B and Glis2 sequences in MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells in the presence of either 4-OHT or ethanol. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Glis2 expression in Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells transduced with MOZ-TIF2. RNA was extracted from cells incubated with 4-OHT for 48 hours. Error bars represent SD (n = 4). (C) Serial replating experiments of MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells in the presence of either 4-OHT or ethanol. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (D) Representative colony morphology and May-Grünwald Giemsa staining of cells from first-round colonies formed by MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;CreERT2 and Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells in the presence of either 4-OHT or ethanol. Scale bar, 50 μm. (E,F) Secondary recipients of AML mice transplanted with MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2/f/f;CreERT2 BM cells were treated with tamoxifen or corn oil (vehicle) for 5 consecutive days when the proportion of GFP+ MNCs in peripheral blood reached 50%. On the day following the last treatment, BM-MNCs were harvested and subjected to (E) flow cytometric analyses and (F) quantitation of L-GMP cells (mean ± SD, *P < .01, n = 6).
To determine the effect of Glis2 deletion on the phenotype of Ring1A−/−Ring1BΔ/ΔMOZ-TIF2-induced leukemic cells in vivo, we transplanted MOZ-TIF2–transduced Ring1A−/−;Ring1Bf/f;Glis2f/f cells into mice and then transplanted their primary BM cells into the secondary recipient mice. After development of overt AML, secondary recipient mice were treated with tamoxifen or vehicle for 5 consecutive days to delete Ring1B and Glis2; BM cells were then harvested and analyzed to measure the L-GMP fraction. Although the total number of GFP+ leukemic cells in BM was decreased by deletion of Ring1B and Glis2, the number of L-GMP cells was almost unchanged because L-GMP cells were preferentially retained (Figure 6E-F). Because L-GMP cells were eliminated by deletion of Ring1A/B (Figure 2A), additional deletion of Glis2 prevented elimination of L-GMP cells by deletion of Ring1A/B. These results suggest that Glis2 is an important target of Ring1A/B involved in maintenance of undifferentiated state of AML stem cells; however, MCSFR+ Mac1− cells were ablated upon deletion of Ring1B and Glis2 in the same way as deletion of Ring1B (supplemental Figure 6C). Moreover, Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Glis2Δ/Δ cells were incapable of causing leukemia, indicating that deletion of Glis2 is insufficient to restore the impairment of leukemogenic capacity of stem cells resulting from Ring1A/B deficiency (supplemental Figure 6D). The lack of leukemia-initiating activity may be due to the derepression of p16Ink4a mRNA and the induction of apoptosis in Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Glis2Δ/Δ cells (supplemental Figure 6E-F). Taken together, these data suggest that Glis2 is an important target of Ring1A/B, especially in the maintenance of undifferentiated state of AML stem cells, and that Ring1A/B maintain AML stem cells, at least in part, by epigenetically inhibiting expression of Glis2.
Discussion
Epigenetic modifications such as alterations of DNA methylation or the pattern of histone modification play important roles in leukemogenesis.33,34 PcG proteins generate histone modifications that repress gene expression. For example, PRC2 tags target loci within chromatin by methylating lysine 27 of histone H3.35 This H3K27 me3 mark is recognized and bound by the chromodomain of CBX proteins present in PRC1, which mediates transcriptional silencing by binding methylated histones in the vicinity and by ubiquitylating histone H2A.16 Ring1A/B are components of PRC1 and are the major E3 ubiquitin ligases for H2A; their activity maintains stalled RNA pol II at repressed promoters, leading to transcriptional repression.11,36 In this study, we demonstrated that deletion of Ring1A/B abolished leukemogenic capacity in AML stem cells. RING1A is overexpressed in AML stem cells and in myelodysplastic syndrome/AML cells of patients with a poor prognosis,37,38 whereas RING1B is overexpressed in lymphomas as well as in gastric and colon tumors.39 Together, our findings support the oncogenic function of RING1A/B. Upregulation of PcG proteins in cancer cells contributes to proliferation by repressing the transcription of Ink4a/Arf.40,41 Therefore, we analyzed the effect of Ink4a/Arf expression in cells with deletion of Ring1A/B and found that although inactivation of Ink4a/Arf led to immortalization of AML cells in vitro, the stem cell fraction was not maintained.
PcG proteins repress the transcription of a large number of genes. Consistent with this, ∼200 genes were derepressed by the deletion of Ring1A/B (Figure 3A). Among the genes listed in Table 1, SDC1 is a well-known marker of myeloma cells42 and is highly expressed in some cases of AML.43,44 Although a previous study reported that SDC1 is a target of Polycomb regulation,45 we have not determined the impact of this gene because it was upregulated in Ring1A/B-deleted AML cells that had lost leukemic potential. In this study, we focused on Glis2, a member of the Glis subfamily of Kruppel-like zinc finger transcription factors.46 Glis2 is mutated in nephronophthisis, and its product plays an essential role in the maintenance of normal kidney tissue architecture by preventing apoptosis and fibrosis.47 Glis2 is highly expressed in patients with AMKL with the CBFA2T3-GLIS2 fusion gene, and CBFA2T3-GLIS2 expression increases the self-renewal potential of hematopoietic progenitors, contributing to development of AMKL.8 By contrast, our results show that, although colony formation activity was maintained, MOZ-TIF2 AML cells with Glis2 overexpression were incapable of maintaining typical monoblastic morphology and differentiated into mature cells.
Among leukemia cells, GLIS2 expression levels are the highest in CBFA2T3-GLIS2+ AMKL cells, but much lower than those in human solid tumors.48 The CBFA2T3-GLIS2 fusion transcript is present in up to 8.4% of patients with cytogenetically normal AML, of which 50% have non-AMKL leukemias.6 In these cases, GLIS2 may contribute to the maintenance of the ability to self-renew. Forced expression of GLIS2 in leukemic cells expressing a leukemia-initiating chimeric transcript other than CBFA2T3-GLIS2 may be disadvantageous for sustaining self-renewal.
We found that deletion of Ring1A/B from MOZ-TIF2 AML cells caused the upregulation of Glis2 expression and induced differentiation, leading to the loss of leukemogenic activity. Deletion of Glis2 restored the ability of these cells to form colonies containing morphologically immature monoblastic cells, suggesting that Glis2 promotes the differentiation of MOZ-TIF2 cells harboring deletion of Ring1A/B. Moreover, deletion of Glis2 prevented elimination of L-GMP cells induced by deletion of Ring1A/B in vivo. These results indicate that Ring1A/B regulate and maintain AML stem cells by repressing the expression of Glis2, which promotes the differentiation of AML cells. Although the differentiation of MOZ-TIF2 cells was promoted by overexpression of Glis2, the self-renewal capacity of these cells was maintained independently of Glis2 expression, suggesting that other targets of Ring1A/B, such as Ink4a/Arf, regulate self-renewal ability of MOZ-TIF2 AML cells. MOZ is a histone acetyltransferase (HAT), and repression of Ink4a by MOZ-HAT activity is crucial for protection of hematopoietic stem cells.49,50 On the other hand, a recent report suggested that MOZ and BMI1 maintain hematopoietic stem cells in a synergistic manner, although the function of MOZ but not BMI1 may be independent of Ink4a.51 Moreover, the HAT activity of MOZ-TIF2 fusion protein is crucial for repression of Ink4a and prevention of senescence.52 These reports suggest that repression of Ink4a is important for stem cell maintenance in MOZ-TIF2–induced AML cells; therefore, deletion of Glis2 was not sufficient to restore the leukemic potential of Ring1A/B-deleted MOZ-TIF2 cells, possibly because of derepression of Ink4a. Indeed, leukemia-initiating capacity was lost in Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Glis2Δ/Δ cells in which expression of p16Ink4a mRNA was derepressed (supplemental Figure 6E). Inactivation of Glis2, as well as Ink4a/Arf, did not fully rescue the phenotypes associated with Ring1A/B deficiency, suggesting that Glis2 and Ink4a/Arf function redundantly or that Ring1A/B has other downstream targets. Therefore, deletion of Ink4a/Arf or another target in Ring1A−/−;Ring1BΔ/Δ;Glis2Δ/Δ cells may restore their self-renewal capacity, which is impaired by Ring1A/B deficiency. Because numerous genes are derepressed by deletion of Ring1A/B, the mechanism of the regulation of leukemia stem cells by Ring1A/B may be complex. Several other genes listed in Table 1, including Btbd11, Ptprf, and Galnt12, were also analyzed. However, enforced expression of these genes made no difference in mock-transduced control MOZ-TIF2 cells (data not shown). Further study is required to define the mechanism underlying the regulation of self-renewal capacity of AML cells by Ring1A/B and the Ring1A/B–Glis2 pathway.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare; the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology; and the National Cancer Center Research and Development Fund.
Authorship
Contribution: H.S., E.T.-I., K.Y., T.K., S.F., and I.K. designed the experiments; H.S., E.T.-I., M.S., and Y.A. performed the experiments; H.K. provided genetically modified mice; and H.S., E.T.-I., and I.K. analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Issay Kitabayashi, Division of Hematological Malignancy, National Cancer Center Research Institute, 5-1-1 Tsukiji Chuo-ku, Tokyo 104-0045, Japan; e-mail: ikitabay@ncc.go.jp.
References
Author notes
H.S. and E.T.-I. contributed equally to this work.